Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
1st and 2nd Lec 19 Sep
Caricato da
Waqar AhmadTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1st and 2nd Lec 19 Sep
Caricato da
Waqar AhmadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
Public Policy & its Management
Dr Sabina Imran Durrani
SZABIST
19 September 2014
Contents
Definitions
Ways to use policy
Final definition
Nature of public policy
Theories of public policy
Policy studies/analysis
Policy objectives
Functions of Govt
Reasons for govt involvement
Instruments for policy
implementation
Policy Cycle
Policy agenda
Factors affecting Policy agenda
Steps of Policy Cycle
Policy Appraisal
Policy Formulation
Policy Implementation
Top Down Approach
Bottom Up Approach
Factors responsible for successful
Policy implementation
Policy Evaluation
Course of Action
Good Policy
Managing Policy
Summary
Introduction
To understand what policy is specially in our sociocultural environment
To explore the reasons & importance for introducing
policies, types of policies underpinned by different
circumstances, and the ways in which they are
implemented
Cyclical model of policy will be examined,
underpinned by policy making theory and factors
essential for making good policy
Definition
Pre-determined course of action established by
elected representatives
Anything Govt decide to do
Purposive course of actions followed by all
stakeholders in dealing with an issue
Goal oriented (SMART)
Specific set of actions-inactions/decisions to be
taken by govt over a period of time
Ways to use Policy
Label for specific activity- industrial, environmental policy
Desired activity-provision of healthy environment
Specific proposal- reduce IR by 5% in the next 3 yrs
Policy decision- announced by the parliament
Program- Land reform program
Output-actually delivered (no of subsidies given)
Outcome-actually achieved (better health)
Theory/model- if X done, Y happen (MMR/IMR)
Process- long-term matter, issues, objective-setting, decisionmaking, implementation, evaluation
Final Definition
Interplay of values, interest, resources
Express values, support/restrict interest,
distribute resources
Shape or are shaped by politics
Specific def. Narrow study field
General def. Wide study field, little use
Nature of Public Policy
Everything Govt does is Public Policy & what the
private sector does is not.............Yes/No
Private sector activities-significant public impact e.g
pollution/industrial hazard control
Govt engagement in commercial activities through
govt owned enterprises, more impact on private
Implementation through private sector(PPP)
(Margaret Thatcher, Benazir Bhutto)
Exercise
Govt owned enterprises working in collaboration
with private sector
Transport-PIA/Railways
Health
Postal
PTCL
Scope/Theories of Policy
Theory: Common language, mean to recognize set of
activities & procedures. Can be
Descriptive/Explanatory: what is happening or what has
happened
Normative/Prescriptive: how situations should be
Normative Policy making Model: prescribe the way how
policy making should occur (improve Policy making)
10
Policy Studies/Policy Analysis
Policy Studies: Knowledge of Policy & Process. It includes
Content: description of its origin, intention, operation
Process: actions taken by different actors at each stage
Outputs: statistical analysis/performance indicators
Evaluation: objectives achieved or not?
Policy Analysis: Knowledge in the Policy Process. It includes
Information for policy making
11
Cont....
Process advocacy-analysis of policy
making/changing process (rational or prescriptive
approach)
Policy advocacy-analysis to make argument for a
particular policy
Analyst as Political Actor-e.g consultant or public
servant
Political Actor as Analyst: community member or
politician (prescriptive)
12
Policy Objectives
Govt. responsible for ensuring equity, justice,
accountability for use of public funds
Different choices are made in the expenditure
depending on vested interest
Many functions are performed in a better way by
private sector Western world-privatization, reduction in the size
of public sector since 1980s
13
Why Policies are Developed?
14
Government Functions
Economic Infra-structure: basic institution,
rules/arrangement, system to work e.g property protection
right, enforcement of contract, provision of currency.
Goods/Services-health, education, currency, clean water,
sewerage
Conflict Resolution- resolve disputes b/w individuals /
groups/institutions
15
Cont...
Competition Maintenance-market mech not always
perfect, maximize the operation of competition
Protection of natural resources- protection against
depletion of natural resources, including
environment in general
Provision of access to goods/services-poverty,
malnutrition, un-employment, old age etc
Economy Stabilization- foreign investment
16
Reasons for Govt Involvement
Mostly related to market failure, where govt intervene
Public Goods-beneficial for all, paid or not
(directly/indirectly) e.g public parks, clean air, national def,
bridge tolls tax, (Non-excludable), including merit goods
(education/health)
Externalities- provision of regulation/services to counteract
the effects of market transaction on 3rd party e.g public
transport prevent traffic congestion, street cleaning for air
pollution
17
Cont...
Natural monopoly- WAPDA
Imperfect information- market mechanism not
providing goods or perfect information to
consumer e.g packaging info for consumer
protection, price control
18
Instruments for Policy Implementation
Provision: Services not provided by the private
sector
Allocation: Funds granted to particular prog
Distribution: unemployment/tax benefit to redress
inequalities in wealth
Stabilization: economic improvement through
budgetary policies e.g taxation, control interest rate
19
Cont...
Subsidy: assistance for manufacturing/provision of
private good /specific grant to private sector
Production: good/services to be user charged like
water, electricity, used in combination with subsidy
Regulation: Punishment for non compliance,
prohibition of certain activities
20
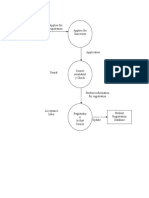
Policy Cycle
Sequential Model of Policy-Making
Policy initiation/agenda setting
Appraisal or assessment
Formulation
Implementation
Evaluation
Policy continuation / termination / reformulation
/succession or progression
New policies or existing ones adjusted
Initiation by Politician, Implementation by public
servant
Importance/limitations of Policy Cycle
21
Policy Agenda
Issues which the govt decides is important need to be
addressed, policies developed/implemented
Agenda items, political influence
Also include those issues which are being pressed by pressure
group, public opinion, media etc
Some are ignored, less/not important, immediate response
Non decision making is a form of decision-power that
suppressed issue to be discussed or heard
Highly influenced by political power
22
Factors Affecting Policy Agenda
Ideology: Political beliefs & values
Pressure Gp: if they can withdraw public attention
to their ideas
Elections/public opinion: determine who wins
power. Certain agendas like education, health care,
employment are given
Crises/disasters: govt must have a prompt response
at all levels.
23
Cont...
Changing conditions: tech development, social events
etc, modify policies e.g in-vitro fertilization, int.
changes lead to the introduction/alteration of
existing policies
Culture/religion:
Inertia: unchanged policies as not reviewed.
Civil servants: can give advice to the politicians.
Issue identification from issue evaluation:
24
Cont...
Particularity: issue achieved particularity,
depicts larger problem e.g acid rain due to
atmospheric pollution, increase in cancer, poor
life style with increasing cost
Emotive aspects: issue with emotive aspect e.g
child labor
25
Cont...
Wide Impact: increase petroleum prices,
affecting financial situation, health care
(dengue)
Power & Legitimacy: Current situation. union
rights, ownership of electricity
Fashion: environmentalism, multi-culturalism,
transparency
26
Steps of policy Cycle
27
Policy Appraisal
Assessment of potential policies is appraisal, determine feasibility of
policy proposal before finalization through rationale approaches
Evaluation is assessment of existing policies, occur after
implementation
Ex ante analysis: future prediction of consequences of various courses of
action based on some model of process involved
Ex post analysis: examine, measure actual consequences of some
prog/policy, to decide whether to maintain, institutionalize, expand or
modify/abandon the program, no future prediction
Steps
28
Policy Formulation Formulation: Decisions are made and the policy
is given a final shape
29
Policy Implementation
Implementation: formulated policy is executed.
Translation of policy into action through public
servants
Two approached
Top-down/forward planning:
Bottom up/backward mapping
30
Top Down Approach
Focus is on why this is so?
Highlight the factors causing implementation gap,
includes
Lack of adequate resources
Fail to get approval (clearance by the public)
Lack of coordination at individual/organizational level
Ambiguous roles & responsibilities
Prioritization of the factors/steps
Change in government
31
Bottom up Approach
Policy making continues from formulation to
implementation stage
Not based on cyclical model
Based on Policy-Action-Continuum, include negotiation,
bargaining, interaction as an ongoing process
Not clear whether policy is influencing action or vice versa
Many actors with changing interest or circumstances over
time
No pre-determined goal
32
Factors Responsible for Successful Policy
Implementation
Policy implemented as per schedule with no variation
SMART objectives to be achieved
Best possible outcome
Not accompanied by unexpected side effects e.g law & order
situation
Cost effective measures
approval of general public
Satisfied recipient or public
33
Policy Evaluation
It leads to policy changes like termination, re
-formulation or progression
Types of Evaluation
Appropriateness evaluation: program to be apposite or
not?
Efficiency evaluation: how efficiently inputs/resources
are used to get desired outputs.
Effectiveness evaluation: objectives achieved or not
Meta evaluation: assess the process of evaluation itself
34
Course of Action
Continuation: as such with no change
Termination: discontinuation
Modification-Reformulation
Problems to end a program
Intellectual reluctance
Lack of political incentives
Institutional permanence
Legal obstacles
High start up cost
Adverse consequences
35
Good Policy
Subjective issue
Analysis of the actual contents & relationship to policy
objectives
How it was implemented and objectives achieved
To ensure effective achievement of objectives & efficient
utilization of resources, evaluation is done
Policy appraisal & evaluation before & after
implementation subsequently, based on the following
criteria:
36
Cont..
Identification of target group- reached or not?
Identification of success standards (Pvt), requires
Comparison over time
Comparison with similar agencies
Comparison with different agencies providing similar
services
Comparison against theoretical framework
Not easy to be measured (read)
37
Managing Policy
Structured policy innovation approach
Systemic application of human initiative & democratic values
Recognition of the role of social conflict
Concerted negotiation, coordination among all
Re-organization of public & private resources
Re-consideration of the values, determining resource
allocation
Policy innovation through institutional set up, need
networking of key social interests
38
Summary
Concept of Public Policy
Definitions, objectives, instruments
Cyclical model
Stages
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Icd-10 CM Step by Step Guide SheetDocumento12 pagineIcd-10 CM Step by Step Guide SheetEdel DurdallerNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Plant Management TafskillsDocumento4 paginePlant Management TafskillsTHEOPHILUS ATO FLETCHERNessuna valutazione finora
- Guillang Vs Bedania and SilvaDocumento2 pagineGuillang Vs Bedania and Silvajdg jdgNessuna valutazione finora
- TIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USDocumento656 pagineTIAPortalOpennessenUS en-USskyttt135Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kumara SwamiyamDocumento21 pagineKumara SwamiyamVijey KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Practice Tests Dumps 2021Documento10 pagineAWS Certified Cloud Practitioner Practice Tests Dumps 2021Aaron Clifton100% (1)
- Ergonomics and Facilities Planning For The Hospitality IndustryDocumento5 pagineErgonomics and Facilities Planning For The Hospitality IndustryJulie Fe de AlcaNessuna valutazione finora
- in The Matter of The Estate of Remigia SaguinsinDocumento3 paginein The Matter of The Estate of Remigia SaguinsinAila AmpieNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Presidential SystemDocumento2 pagine4 Presidential SystemWaqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- New Zealand Model-Wm Presidential System: Sabina Imran Szabist 10 Oct 2014Documento13 pagineNew Zealand Model-Wm Presidential System: Sabina Imran Szabist 10 Oct 2014Waqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 SzilDocumento8 pagine11 Szil8148593856Nessuna valutazione finora
- Public Policy Management SZABISTDocumento5 paginePublic Policy Management SZABISTWaqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Lec PDFDocumento34 pagine1st Lec PDFWaqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3, 3 Oct 2014Documento18 pagineLecture 3, 3 Oct 2014Waqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5Documento14 pagineLecture 5Waqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rule of Law Problems, DR AzamDocumento26 pagineThe Rule of Law Problems, DR AzamSaad AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For MDBsDocumento8 pagineGuidelines For MDBsWaqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT ch07Documento46 paginePPT ch07Waqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed Computing Assignment 2Documento12 pagineDistributed Computing Assignment 2Waqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 DaqDocumento45 pagineLecture 2 DaqWaqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3Documento60 pagineLecture 3Waqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- AnswerDocumento1 paginaAnswerWaqar AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- DLL Sci 10 12-09-2022Documento3 pagineDLL Sci 10 12-09-2022Lovely Shiena Cain AragoncilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Website Banners With Photoshop PDFDocumento18 pagineCreating Website Banners With Photoshop PDFLiza ZakhNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.0 Design Andheri Khola Bridge, 1x25m 8.4m 3 GirderDocumento18 pagine1.0 Design Andheri Khola Bridge, 1x25m 8.4m 3 GirderManoj ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Paper About Charter ChangeDocumento5 pagineResearch Paper About Charter Changegz46ktxrNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbseskilleducation Com Digital Presentation Class 9Documento11 pagineCbseskilleducation Com Digital Presentation Class 9riscomputersirNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008 Almocera vs. OngDocumento11 pagine2008 Almocera vs. OngErika C. DizonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mystique-1 Shark Bay Block Diagram: Project Code: 91.4LY01.001 PCB (Raw Card) : 12298-2Documento80 pagineMystique-1 Shark Bay Block Diagram: Project Code: 91.4LY01.001 PCB (Raw Card) : 12298-2Ion PetruscaNessuna valutazione finora
- Text-Book P3Documento147 pagineText-Book P3Nat SuphattrachaiphisitNessuna valutazione finora
- Intermediate Course Study Material: TaxationDocumento34 pagineIntermediate Course Study Material: TaxationMd IbrarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lapid V CADocumento11 pagineLapid V CAChami YashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesDocumento10 pagineModern Computerized Selection of Human ResourcesCristina AronNessuna valutazione finora
- CHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryDocumento30 pagineCHR Report 2017 IP Nat InquiryLeo Archival ImperialNessuna valutazione finora
- Lua ApiDocumento176 pagineLua Apiyaotl albores tecuautzinNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Free Fonts PDFDocumento61 pagine100 Free Fonts PDFzackiNessuna valutazione finora
- NAGIOS Inspeção Relatório de DadosDocumento2 pagineNAGIOS Inspeção Relatório de DadosRuben QuintNessuna valutazione finora
- CV: LT Col MD Rakibul Hassan, Raqueeb HassanDocumento14 pagineCV: LT Col MD Rakibul Hassan, Raqueeb HassanRakibul Hassan100% (26)
- GX Deloitte 2017 TMT PredictionsDocumento60 pagineGX Deloitte 2017 TMT PredictionsMontevideo PortalNessuna valutazione finora
- Review of Polyurea Coating ResearchesDocumento12 pagineReview of Polyurea Coating ResearchesDineshNessuna valutazione finora
- ''Adhibeo'' in LatinDocumento5 pagine''Adhibeo'' in LatinThriw100% (1)
- TSD OSD Portal Quick Start Guide V1.0Documento5 pagineTSD OSD Portal Quick Start Guide V1.0sijovow282Nessuna valutazione finora
- 14.quality of Life in Patients With Recurrent AphthousDocumento7 pagine14.quality of Life in Patients With Recurrent AphthousCoste Iulia RoxanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Welcome To Our Presentation: Submitted byDocumento30 pagineWelcome To Our Presentation: Submitted byShamim MridhaNessuna valutazione finora