Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Erosional Landforms
Caricato da
api-2588136080 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
95 visualizzazioni11 pagineTitolo originale
erosional landforms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
95 visualizzazioni11 pagineErosional Landforms
Caricato da
api-258813608Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 11
Learning objectives
How do waves operate?
What are sub-aerial processes and why are they
important?
What processes of erosion operate at the coast?
What landforms are created by erosion?
What processes of transport operate at the coast?
What landforms are created by deposition?
1 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Dorset coastline
2 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Landforms of coastal erosion
1) Headlands and Bays
2) Cliffs and Wave Cut Platforms
3) Caves, Arches, Stacks and Stumps
3 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Swanage Bay
An example of headlands and bays on the Dorset coastline.
4 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Headlands and bays
5 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
How are cliffs and wave-cut platforms formed?
6 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Wave-cut platform
The waves attack the base of the cliff through the processes of
abrasion, corrosion, hydraulic action and attrition.
Over time the cliff will be undercut and a wave-cut notch is
formed.
Eventually the cliff becomes unstable and collapses. Further
cliff retreat will form a wave-cut platform.
7 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
How are caves, arches, stacks and stumps formed?
8 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Caves, arches, stacks and stumps
9 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
The formation of caves, arches, stacks and stumps
10 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
If these photos were taken of one headland over time,
which of these landforms would be the first to be formed?
11 of 43
Boardworks Ltd 2005
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Flooding in YorkDocumento24 pagineFlooding in Yorksuejacksonthree100% (26)
- Littoral Cells and Sediment BudgetDocumento18 pagineLittoral Cells and Sediment Budgetmrceejay100% (1)
- IB Geography Oceans Case StudiesDocumento6 pagineIB Geography Oceans Case StudiesMarc Wierzbitzki0% (1)
- Fragile Environments IGCSE RevisionDocumento18 pagineFragile Environments IGCSE Revisionapi-232441790Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geography Internal Assessment About Stream DischargeDocumento40 pagineGeography Internal Assessment About Stream DischargeFirasco94% (35)
- Depositional Landforms - BoardworksDocumento13 pagineDepositional Landforms - Boardworksapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coastal ProcessesDocumento15 pagineCoastal Processesapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coastal Processes and LandformsDocumento43 pagineCoastal Processes and LandformsPoornimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coasts: Earth: Our HomeDocumento32 pagineCoasts: Earth: Our HomeVernon100% (1)
- Landforms in The Upper CourseDocumento26 pagineLandforms in The Upper Courseapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geo Term-2 Denudation 1Documento11 pagineGeo Term-2 Denudation 1Tvisha AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- River Field Work Pack 2019Documento20 pagineRiver Field Work Pack 2019GeoBlogsNessuna valutazione finora
- l7 - Case Study On The River TeesDocumento8 paginel7 - Case Study On The River Teesapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course of A RiverDocumento9 pagineCourse of A Riverapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Theme 1 - Rivers and Coasts Revision NotesDocumento26 pagineTheme 1 - Rivers and Coasts Revision NotesZantaye ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Coasts Key Word Glossary (1) MDocumento5 pagineCoasts Key Word Glossary (1) MRia PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Coral Landforms in East AfricaDocumento5 pagineCoral Landforms in East Africakalule elvisNessuna valutazione finora
- Finishing ProcessesDocumento16 pagineFinishing ProcessesAjay P AntonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Formation of Glaciers NotesDocumento4 pagineFormation of Glaciers NotesBenson LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Passive Voice: Year 7 Sentence StartersDocumento20 pagineThe Passive Voice: Year 7 Sentence StartersMuhammad KholikNessuna valutazione finora
- Drainage PatternsDocumento3 pagineDrainage Patternsapi-298948027Nessuna valutazione finora
- Year 8 Ottoman Research Assignment 2013 Inquiry2Documento4 pagineYear 8 Ottoman Research Assignment 2013 Inquiry2api-263327522100% (1)
- Coasts Revision BookDocumento31 pagineCoasts Revision Bookapi-261914272Nessuna valutazione finora
- GA376 Managed Coastal Retreat North Norfolk Coast - Apr 2007 Series 18 Issue 3Documento4 pagineGA376 Managed Coastal Retreat North Norfolk Coast - Apr 2007 Series 18 Issue 3geoboom12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Holderness CoastlineDocumento1 paginaCase Study Holderness Coastlinebiology111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Geo IGCSEDocumento3 pagineGeo IGCSEZeynep Akı100% (1)
- Igcse Plate Tectonics 2015Documento39 pagineIgcse Plate Tectonics 2015api-261914272100% (3)
- Earth: Our Home: Full GeographyDocumento31 pagineEarth: Our Home: Full GeographyVernonNessuna valutazione finora
- Coasts Field WorkDocumento22 pagineCoasts Field WorkGeoBlogsNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 14 Hard Vs Soft Card Sort CompleteDocumento1 pagina13 14 Hard Vs Soft Card Sort Completeapi-336814146Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guidance and Exemplars For IGCSE Geography Fieldwork OpportunitiesDocumento7 pagineGuidance and Exemplars For IGCSE Geography Fieldwork OpportunitiesSadhana KuriyanNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 1 Topic1RestlessEarthDocumento43 pagineUNIT 1 Topic1RestlessEarthIlayda UludagNessuna valutazione finora
- Hazardous Environments: A Comparison of The Impacts of Tropical Storms, in An LIC and An HICDocumento26 pagineHazardous Environments: A Comparison of The Impacts of Tropical Storms, in An LIC and An HICapi-232441790Nessuna valutazione finora
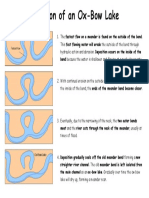
- Ox-Bow Lake Handout 1Documento1 paginaOx-Bow Lake Handout 1api-336814146Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Contour ReadingDocumento12 pagineWireless Contour ReadingAsunaNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 - CoastsDocumento38 pagine06 - CoastsDharam JagroopNessuna valutazione finora
- Geofile Exam Techniques AsDocumento4 pagineGeofile Exam Techniques AsreservoirgeogsNessuna valutazione finora
- KS4 Earth's StructureDocumento25 pagineKS4 Earth's StructurejtNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsDocumento42 pagineIGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsxerxesNessuna valutazione finora
- Save Water Essay 2 (150 Words)Documento2 pagineSave Water Essay 2 (150 Words)saraNessuna valutazione finora
- FA-2 Activity-2 Topic-: Water ResourcesDocumento18 pagineFA-2 Activity-2 Topic-: Water ResourcesBobby SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Supervolcano?Documento4 pagineWhat Is A Supervolcano?api-26229229Nessuna valutazione finora
- Water AssignmentDocumento3 pagineWater Assignmentapi-239344986100% (1)
- Terminology For The Study of RiversDocumento7 pagineTerminology For The Study of Riversrishipatel96Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 15 Limestone EnvironmetDocumento19 pagineChapter - 15 Limestone Environmetgope100% (1)
- Mass WastingDocumento64 pagineMass WastingEkala XuhalxNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrology & Fluvial GeomorphologyDocumento13 pagineHydrology & Fluvial Geomorphologylyana1234100% (1)
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42Documento16 pagineCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/42EffNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Checklist Geography IGCSEDocumento2 pagineRevision Checklist Geography IGCSECarlosLópezNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomes Reading PassagesDocumento12 pagineBiomes Reading Passagesapi-290509627100% (1)
- IB Geography Generic Essay RubricDocumento4 pagineIB Geography Generic Essay Rubricgabr0088Nessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Geography - Worksheet 12.2Documento1 paginaIGCSE Geography - Worksheet 12.2SangkasNessuna valutazione finora
- 04.river LandformsDocumento13 pagine04.river LandformsfujiNessuna valutazione finora
- Urban Model Comparaison Between MEDC and LEDCDocumento7 pagineUrban Model Comparaison Between MEDC and LEDCEmilieMariaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.minerals Physical PropertiesDocumento23 pagine3.minerals Physical Propertiesdarshan chodvadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- SOW Geography Upper Sec 3 YrsDocumento73 pagineSOW Geography Upper Sec 3 YrsYenny TigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sedimentary RocksDocumento6 pagineSedimentary RocksCydrick P DescalzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Coastal Processes and Landforms 1g2xo2kDocumento56 pagineCoastal Processes and Landforms 1g2xo2kWilfred MuiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Beaufort Building Visit - 119477054Documento9 pagineBeaufort Building Visit - 119477054npmyers726Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coastal Protection StructuresDocumento107 pagineCoastal Protection StructuresKhrl K Khrl88% (8)
- The Drainage Basin SystemDocumento29 pagineThe Drainage Basin Systemapi-258813608100% (1)
- l7 - Case Study On The River TeesDocumento8 paginel7 - Case Study On The River Teesapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- V Shaped ValleysDocumento12 pagineV Shaped Valleysapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Middle and Lower Course of A RiverDocumento34 pagineMiddle and Lower Course of A Riverapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Describe The Causes of FloodingDocumento10 pagineDescribe The Causes of Floodingapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson PressiDocumento9 pagineLesson Pressiapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course of A RiverDocumento9 pagineCourse of A Riverapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study - HoldernessDocumento8 pagineCase Study - Holdernessapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- River ProcessessDocumento10 pagineRiver Processessapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Holderness Landforms Case StudyDocumento15 pagineHolderness Landforms Case Studyapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Coasts Under ThreatDocumento9 pagineCoasts Under Threatapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mass Movement MhyDocumento13 pagineMass Movement Mhyapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Causes Climate ChangeDocumento32 pagine1 Causes Climate Changeapi-258813608100% (1)
- Longshore DriftDocumento15 pagineLongshore Driftapi-258813608100% (1)
- Types of WeatheringDocumento24 pagineTypes of Weatheringapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Upland Areas and Rivers in The UkDocumento11 pagineUpland Areas and Rivers in The Ukapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mhs Hurricane Observation LessonDocumento11 pagineMhs Hurricane Observation Lessonapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Reducing and Managing Climate ChangeDocumento14 pagine4 Reducing and Managing Climate Changeapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Hull Floods of 2007Documento4 pagineThe Hull Floods of 2007api-258813608100% (1)
- Design Success CriteriaDocumento2 pagineDesign Success Criteriaapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vulnerability To Tropical StormsDocumento4 pagineVulnerability To Tropical Stormsapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Pressure SystemsDocumento12 pagineWhat Are Pressure Systemsapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment ObjectivesDocumento1 paginaAssessment Objectivesapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric Circulation ModelDocumento24 pagineAtmospheric Circulation Modelapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Location and Formation of Tropical StormsDocumento19 pagine1 Location and Formation of Tropical Stormsapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tectonic Hazards: Predicting and Preventing Volcanoes and EarthquakesDocumento14 pagineTectonic Hazards: Predicting and Preventing Volcanoes and Earthquakesapi-258813608Nessuna valutazione finora