Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Muscular System Overview
Caricato da
Ronald Susanto BudhyTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Muscular System Overview
Caricato da
Ronald Susanto BudhyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
The Muscular System
The Striated Muscle (those responsible
for voluntary movements)
Anatomy - Two types of fibers
Extrafusal Fiber: these fibers do the work of the
muscle.
Intrafusal Fiber or Muscle Spindle: controls muscle
tone and provides important sensory information.
Contraction
Controlled by the nervous system
Muscles only shorten (i.e., only go one direction)
Organized in opposition pairs.
04/18/16
The Stretch Reflex
Neural Input into
the Muscle
Extrafusal fibers are
input by alpha motor
neurons
These neurons are
large and fast.
Intrafusal Fibers are
input by gamma
motor neurons
These neurons are
relatively small and
slow.
They are involved in
the control of muscle
tone.
04/18/16
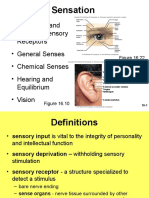
Proprioception: Sensing Muscle
Condition
Limb Position
Sensoryand
Endings
in Muscles
Anulospiral: wraps around muscle spindle,
senses dynamic changes in muscle length.
Flower spray: looks like little flowers,
sense static changes in muscle length,
helps determine position.
04/18/16
Innervation of a Skeletal Muscle
The arm is commanded to a particular position.
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
A weight is applied to the arm.
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
A weight is applied to the arm.
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
This weight pushes down the arm which stretches
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
This stretch is detected by the sensory neurons in
and transferred to the interneron in the spinal cho
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
A command to further contract the muscle is sent
alpha motor neuron.
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
The arm is returned to its commanded position.
sensory neuron
interneuron
motor neuron
04/18/16
The Stretch Reflex and Muscle Tone
The Intruafusal Muscle Fiber or Muscle Spindle
Gamma Motor Neuron
Rubber bands
]
Posts
[
]
Model of the Muscle Spindle and Stretch Detectio
04/18/16
Muscle Tone
Muscle tone is the general state of
contraction of the muscles.
If you have low muscle tone the muscles are
flaccid (relaxed).
If high muscle tone, the muscle is contracted.
Muscle tone changes over time, e.g. during a
step
Muscle tone is low as we pick up our leg
Muscle tone is high on all leg muscles as we
prepare to put it back down and it has to support
our weight
04/18/16
The Spindle and Stretch
The Muscle Spindle
Gamma Motor Neuron
[
]
Model of the Muscle Spindle and Stretch Detectio
04/18/16
The Spindle and Stretch
The Muscle Spindle
The ends of the spindle are pulled out
Gamma Motor Neuron
[
]
Model of the Muscle Spindle and Stretch Detectio
04/18/16
The Spindle and Stretch
What happens when the spindle is
stretched?
Which motor neuron is effected?
04/18/16
Activation of the Motor Neuron
The Muscle Spindle
Gamma Motor Neuron
[
]
Model of the Muscle Spindle and Stretch Detectio
04/18/16
Activation of the Motor Neuron
The Muscle Spindle
The middle is pulled in
Gamma Motor Neuron
[]
Model of the Muscle Spindle and Stretch Detectio
04/18/16
The effects of motor neuron
activation
What happens to the rubber bands in
the model?
Can the sensory endings tell the
difference in the cause of the stretch?
What happens when the spindles are
stretched?
How could this be used in muscle tone?
04/18/16
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Bio Cam Clips PresentationDocumento5 pagineBio Cam Clips Presentationapi-552227798Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular Long ActivityDocumento6 pagineMuscular Long Activity26jmuzychenkoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8Documento44 pagineThe Muscular System Powerpoint 1227697713114530 8ninya puella100% (1)
- Muscles: Skeletal MuscleDocumento12 pagineMuscles: Skeletal MuscleLee Angelo BorbeNessuna valutazione finora
- DR - Irfan - Phisiologi of MuscleDocumento20 pagineDR - Irfan - Phisiologi of MuscleilhamaminsyaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Trainer-E-BookDocumento4 paginePersonal Trainer-E-BooksampradanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System Anatomy GuideDocumento5 pagineMuscular System Anatomy GuideĘđı AzøıcăNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Muscular System ExplainedDocumento14 pagineThe Human Muscular System ExplainedOana Maria FrancNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMDocumento20 pagineModule 5 MUSCULAR SYSTEMMisha WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Body Map - Muscle Types & FunctionsDocumento2 pagineBody Map - Muscle Types & FunctionsFani Try Utami BoedaxRed'waterzzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscylar SystemDocumento31 pagineThe Muscylar SystemXavier Mark BeatingoNessuna valutazione finora
- Negrete, A: Muscle Research 1Documento9 pagineNegrete, A: Muscle Research 1api-286318965Nessuna valutazione finora
- K00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular SystemDocumento14 pagineK00429 - 20180831110050 - Muscular Systemroesil juniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ankles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingDocumento18 pagineAnkles Knees Hip Trunk Elbows Shoulders: Netball Goal ShootingJess Zausa MasulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocumento4 pagineNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ns Elec 4 - Muscular SystemDocumento5 pagineNs Elec 4 - Muscular SystemONGLENGCO WILSON JAKE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Tissue Differences and Contraction TypesDocumento2 pagineMuscle Tissue Differences and Contraction TypesChris CaoagdanNessuna valutazione finora
- VIDEO SCRIPT: The Muscular System Explained in 6 MinutesDocumento2 pagineVIDEO SCRIPT: The Muscular System Explained in 6 MinutesD IngaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Muscular System 4Documento4 pagineSummary of Muscular System 4api-253866502100% (1)
- Muscular System AnatomyDocumento34 pagineMuscular System AnatomyDivya JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento7 pagineMuscular Systemchristianoliver.aceroNessuna valutazione finora
- Human AnatomyDocumento7 pagineHuman AnatomydecastroghislaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Human AnatomyDocumento92 pagineHuman Anatomymohamed.sewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mascular System Hand Out 2Documento2 pagineMascular System Hand Out 2قى قىNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Muscular System 1Documento11 pagineAp Muscular System 1SALAZAR, John Vincent C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System Notes 16 17Documento66 pagineMuscular System Notes 16 17api-305436791100% (3)
- Musculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Documento22 pagineMusculoskelet Al System - Muscles: Year 11 Human Biology ATAR Unit 1 & 2Anonymous vwR8xcIxNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocumento63 pagineMuscle Anatomy and Physiology GuideTeguh SantosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento6 pagineMuscular SystemJules ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch.7 NotesDocumento8 pagineCh.7 NotesMohd ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-6 Muscular SystemDocumento48 pagineUNIT-6 Muscular SystemChandan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Major Muscle Groups ExplainedDocumento4 pagineMajor Muscle Groups ExplainedChris Sevilla BurhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento56 pagineMuscular SystemTrisha BawaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 11Documento58 pagineCH 11Riya PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle ContractionDocumento5 pagineMuscle ContractionYasmeen AlnajjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Strength and Muscle ActionDocumento54 pagineMuscle Strength and Muscle ActionFarrukh Shahzad100% (6)
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM Q&ADocumento11 pagineMUSCULAR SYSTEM Q&ARashini FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 2 PublishedDocumento13 pagineTask 2 Publishednickoh28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocumento14 pagineBiology: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAdrien ChewNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Tone - Spinal RefelxesDocumento17 pagineMuscle Tone - Spinal RefelxesLaw YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle System Kd13Documento46 pagineMuscle System Kd13patriciaperidot12Nessuna valutazione finora
- MusclesDocumento89 pagineMusclesSelena ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System AnatomyDocumento12 pagineMuscular System AnatomyTishonna DouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy & Physiology For Sport Origins & Insertions: Session 10Documento24 pagineAnatomy & Physiology For Sport Origins & Insertions: Session 10Venus Tumampil AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Curs 3 - Generalitati Despre MuschiDocumento60 pagineCurs 3 - Generalitati Despre MuschiJust MariaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The Muscular SystemDocumento2 pagineWhat Is The Muscular SystemJoshua Capa FrondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Bones and Muscles of the Human BodyDocumento6 pagineImportant Bones and Muscles of the Human Bodysunnykhan bwnNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Ligaments & TendonsDocumento5 pagineMuscle Ligaments & TendonsMahnoor JawadNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Muscle StimulationDocumento4 pagineElectrical Muscle Stimulationquickrecaps01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidDocumento7 pagineUnit Four: Muscular System: Cilia Flagellum AmoeboidKath RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading 4 The Muscular SystemDocumento16 pagineReading 4 The Muscular Systemlephuongvy1406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocumento32 pagineMuscular System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum MarieNessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscular SystemDocumento18 pagineThe Muscular SystemAirene Mae Lamputi SupilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Unit Review Guide (Chapter 8) : Notes CoveredDocumento2 pagineMuscle Unit Review Guide (Chapter 8) : Notes Coveredsara_wilhelm6408Nessuna valutazione finora
- Muscles WorksheetDocumento4 pagineMuscles WorksheetAndreea BuicuNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular SystemDocumento24 pagineMuscular SystemRobi SariegoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Muscular System Part 2Documento34 pagineThe Muscular System Part 2ISTORYANessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Six The Muscular SystemDocumento30 pagineChapter Six The Muscular SystemabiyotNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System OverviewDocumento18 pagineMuscular System OverviewRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- AscoDocumento33 pagineAscoRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- SensationDocumento76 pagineSensationRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Newborn ReflexDocumento37 pagineNewborn ReflexRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular System OverviewDocumento18 pagineMuscular System OverviewRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- ReflexesDocumento46 pagineReflexesRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Melena E.C Gastritis Errosive Haemorrhagic-WentyDocumento28 pagineMelena E.C Gastritis Errosive Haemorrhagic-WentyRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Melena E.C Gastritis Errosive Haemorrhagic-WentyDocumento28 pagineMelena E.C Gastritis Errosive Haemorrhagic-WentyRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- Algorithm Lung Massive HemoptysisDocumento1 paginaAlgorithm Lung Massive HemoptysisRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- OperculectomyDocumento4 pagineOperculectomyRonald Susanto BudhyNessuna valutazione finora
- C70Documento3 pagineC70Jorge Luis Arevalo LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Report of Mechanics of Machines 1Documento12 pagineReport of Mechanics of Machines 1muhammaduzairNessuna valutazione finora
- Dubai UAE InformationDocumento28 pagineDubai UAE InformationsefdeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Avl Tree Definition: Avl Trees Are Balanced Anavltreeisa Such That For Every Internal Node V of T, TheDocumento3 pagineAvl Tree Definition: Avl Trees Are Balanced Anavltreeisa Such That For Every Internal Node V of T, TheSumanta DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulp Digester FailuredDocumento93 paginePulp Digester FailuredTim Ku100% (1)
- CEEAMA-TECHNICAL-PAPER-2018 by Sunil VoraDocumento6 pagineCEEAMA-TECHNICAL-PAPER-2018 by Sunil VorasunilgvoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Matrix Analysis of Networks: J. R. LucasDocumento63 pagineMatrix Analysis of Networks: J. R. LucasNethmini SamarawickramaNessuna valutazione finora
- Theories and philosophies that shaped early childhood educationDocumento3 pagineTheories and philosophies that shaped early childhood educationJamille Aira PascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat Marine Engine ProgramDocumento4 pagineCat Marine Engine ProgramRobert BeddingfieldNessuna valutazione finora
- Artists Budget TemplateDocumento9 pagineArtists Budget TemplateMaia CelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Belecobeauty Company ProfileDocumento19 pagineBelecobeauty Company ProfileBisma BrawijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.3 Resource - Allocation - of - Downlink - Heterogeneous - NOMA - Network - Based - On - Multi-User - With - Different - SpeedsDocumento5 pagine5.3 Resource - Allocation - of - Downlink - Heterogeneous - NOMA - Network - Based - On - Multi-User - With - Different - SpeedsmuradNessuna valutazione finora
- Urban green-blue grids: Hammarby SjöstadDocumento5 pagineUrban green-blue grids: Hammarby SjöstadAlejandra SusaNessuna valutazione finora
- R/C Soaring Digest - May 2009Documento80 pagineR/C Soaring Digest - May 2009Aviation/Space History LibraryNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm D 2113-14Documento20 pagineAstm D 2113-14aswathy annie vargheseNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento40 pagineCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- PDF If I Break 15 Portia Moore CompressDocumento61 paginePDF If I Break 15 Portia Moore CompressAlbenis RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- SPE 18184 OPUS: An Expert Advisor For Artificial LiftDocumento8 pagineSPE 18184 OPUS: An Expert Advisor For Artificial Liftlepro brunelNessuna valutazione finora
- Ihp MicroDocumento13 pagineIhp MicroTejas HambirNessuna valutazione finora
- Modelacion UreaDocumento20 pagineModelacion UreaJesus Enrique Alfonzo RiveroNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Tutorial Present Worth AnalysisDocumento4 pagine4 Tutorial Present Worth AnalysisMuhamad SyazwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shortcuts and Quick Tips To Solve CAT MBA Quantitative Questions CAT, Entrance Exams, MBA - iHelpStudyDocumento21 pagineShortcuts and Quick Tips To Solve CAT MBA Quantitative Questions CAT, Entrance Exams, MBA - iHelpStudySofi DinendranNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOpolitics PDFDocumento3 pagineBIOpolitics PDFalpar7377Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Manual-Perfect YORKDocumento19 pagineInstallation Manual-Perfect YORKjesNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Upper Preparation StepsDocumento7 pagineBasic Upper Preparation StepsumidgrtNessuna valutazione finora
- Bagi Exercise Listening and StructureDocumento16 pagineBagi Exercise Listening and StructureDwiva Muna100% (1)
- Volvo A30e2 PDFDocumento28 pagineVolvo A30e2 PDFsafdey100% (1)
- Sample/Pre-Board Paper 14 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 English Language and Literature (Code 184)Documento5 pagineSample/Pre-Board Paper 14 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 English Language and Literature (Code 184)parmila raniNessuna valutazione finora
- Geometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Documento3 pagineGeometry Dba Study Guide 07.07Tyler CosgroveNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Sterile ServiceDocumento75 pagineCentral Sterile ServiceSUBHENDU SIKDAR100% (1)