Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Stages of International Marketing Involvement
Caricato da
Sudipto BoseTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Stages of International Marketing Involvement
Caricato da
Sudipto BoseCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 1
The Scope and Challenge of International Marketing
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
2005 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
Chapter Learning Objectives
1.
1. The
The changing
changing face
face of
of U.S.
U.S. business
business
2.
2. The
The scope
scope of
of the
the international
international marketing
marketing task
task
3.
3. The
The increasing
increasing importance
importance of
of global
global awareness
awareness
4.
4. The
The progression
progression of
of becoming
becoming aa global
global marketer
marketer
5.
5. The
The importance
importance of
of the
the self-reference
self-reference criterion
criterion (SRC)
(SRC) in
in
international
international marketing
marketing
Preface
Never
Never before
before in
inAmerican
American history
history have
have U.S.
U.S. businesses,
businesses, large
large
and
and small,
small, been
been so
so deeply
deeply involved
involved in
in and
and affected
affected by
by
international
international business.
business.A
Aglobal
global economic
economic boom,
boom, unprecedented
unprecedented
in
in modern
modern economic
economic history,
history,has
has been
been under
under way
way as
as the
the drive
drive for
for
efficiency,
efficiency,productivity,
productivity,and
and open,
open, unregulated
unregulated markets
markets sweeps
sweeps
the
the world.
world. Powerful
Powerful economic,
economic, technological,
technological, industrial,
industrial, political,
political,
and
and demographic
demographic forces
forces are
are converging
converging to
to build
build the
the foundation
foundation of
of
aa new
new global
global economic
economic order
order on
on which
which the
the structure
structure of
of aa
one-world
one-world economic
economic and
and market
market system
system will
will be
be built
built
(Cateora
(Cateora and
and Graham)
Graham)
Global Perspective: Recent Events
Information
Information technology
technology boom
boom of
of the
the late
late 1990s
1990s
The
The high-tech
high-tech bust
bust of
of 2001
2001
Enron
Enron and
and WorldCom
WorldCom scandals
scandals
September
September 11th
11th attacks
attacks on
on the
the World
World Trade
Trade Center
Center
and
and Pentagon
Pentagon
Wars
Wars in
in Afghanistan
Afghanistan and
and Iraq
Iraq
Global Perspective: Recent Events
International
International conflict
conflict among
among China,
China,
Taiwan,
Taiwan, and
and the
the United
United States
States
2003
2003 SARS
SARS outbreak
outbreak in
in Asia
Asia
Global
Global terrorism,
terrorism, e.g.,
e.g., Indonesia,
Indonesia, Israel,
Israel,
India,
India, and
and Morocco
Morocco
Transcending
Transcending these
these events,
events, international
international
commerce
commerce continued
continued
Global Business Trends
1.
1. The
The rapid
rapid growth
growth of
of the
the
World
World Trade
Trade Organization
Organization
and
and regional
regional free
free trade
trade
areas,
areas, e.g.,
e.g., NAFTA
NAFTAand
and the
the
European
European Union
Union
2.
2. General
General acceptance
acceptance of
of the
the
free
free market
market system
system among
among
developing
developing countries
countries in
in Latin
Latin
America,
America, Asia,
Asia, and
and Eastern
Eastern
Europe
Europe
3.
3. Impact
Impact of
of the
the Internet
Internet and
and
other
other global
global media
media on
on the
the
dissolution
dissolution of
of national
national
borders,
borders, and
and
4.
4. Managing
Managing global
global
environmental
environmental resources
resources
Internationalization of U.S. Business
Increasing
Increasing globalization
globalization of
of
markets
markets
Many
Many U.S.
U.S. companies
companies are
are
now
now foreign
foreign controlled:
controlled:
Carnation
Carnation (Swiss),
(Swiss),
Daimler-Chrysler
Daimler-Chrysler (German)
(German)
Firms
Firms face
face competition
competition on
on
all
all fronts
fronts
U.S.
U.S. firms
firms seeking
seeking foreign
foreign
markets
markets to
to increase
increase profits
profits
International Marketing: A Definition
International
International marketing
marketing is
is defined
defined as
as the
the
performance
performance of
of business
business activities
activities designed
designed to
to plan,
plan,
price,
price, promote,
promote, and
and direct
direct the
the flow
flow of
of aa companys
companys
goods
goods and
and services
services to
to consumers
consumers or
or users
users in
in more
more
than
than one
one nation
nation for
for aa profit
profit
Marketing
Marketing concepts,
concepts, processes,
processes, and
and principles
principles are
are universally
universally
applicable
applicable all
all over
over the
the world
world
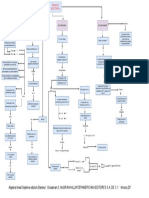
The International Marketing Task
Foreign Environment
(Uncontrollables)
7. Structure of
Distribution
1. Competition
Domestic environment
(Uncontrollables)
Environmental
uncontrollables
country market A
(Controllables) 1. Competition
Price
Product
2. Technology
Target
5. PoliticalEnvironmental
7
Market
Legal
uncontrollables
6. Geography and
country
Promotion Place or 2 .Technology
Infrastructure
market B
Distribution
4.
Culture
Environmental
3. Economy
uncontrollable
5. Political3. Economy
s
Legal
country
market C
4.
Culture
Environmental Adaptation Needed
Differences
Differences are
are in
in the
the uncontrollable
uncontrollable environment
environment of
of international
international
marketing
marketing
Firms
Firms must
must adapt
adapt to
to uncontrollable
uncontrollable environment
environment of
of international
international
marketing
marketing by
by adjusting
adjusting the
the marketing
marketing mix
mix (product,
(product, price,
price,
promotion,
promotion, and
and distribution)
distribution)
Continuum
Adaptation
(of Marketing Mix)
Standardization
(of Marketing Mix)
INFLUENCED BY 7 ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
Self-Reference Criterion (SRC)
and Ethnocentrism:Major Obstacles
SRC is an unconscious reference to ones own cultural
values, experiences, and knowledge as a basis for
decisions
Ethnocentrism refers to the notion that ones own culture
or company knows best how to do things
Both the SRC and ethnocentrism impede the ability to
assess a foreign market in its true light
Reactions to meanings, values, symbols, and behavior
relevant to our own culture are different from those of
foreign
Relying on ones SRC could produce an unsuccessful
marketing program
Avoiding the Self Reference Criterion
To
To avoid
avoid the
the SRC,
SRC, the
the following
following steps
steps are
are suggested:
suggested:
1: Define the business problem or goal in home-country
cultural traits, habits, or norms
2: Define the business problem or goal in foreign-country
cultural traits, habits, or norms. Make no value
judgments
3: Isolate the SRC Influence in the problem and examine it
carefully to see how it complicates the problem
4: Redefine the problem without the SRC influence and
solve for the optimum business goal situation*
Developing a Global Awareness
To
To be
be globally
globally aware
aware is
is to
to have:
have:
1. Tolerant of Cultural Differences, and
2. Knowledgeable of:
(a) Culture, (b) History, (c) World Market Potential,
(d) Global Economic, Social and Political Trends
Stages of International Marketing
Involvement
In
In general,
general, firms
firms go
go through
through five
five different
different phases
phases in
in going
going
international:
international:
No
No Direct
Direct Foreign
Foreign Marketing
Marketing
Infrequent
Infrequent Foreign
Foreign Marketing
Marketing
Regular
Regular Foreign
Foreign Marketing
Marketing
International
International Marketing
Marketing
Global
Global Marketing
Marketing
Strategic Orientation: EPRG Schema
Orientation
EPRG Schema
Domestic Marketing
Extension
(Ethnocentric)
Multi-Domestic
Marketing
(Polycentric)
Global Marketing
(Regio/Geocentric)
Strategic Orientation: EPRG Schema
Generally, four distinctive approaches dominate strategic thinking in
international marketing:
1. Ethnocentric or Domestic Marketing Extension Concept:
Home country marketing practices will succeed elsewhere
without adaptation; however, international marketing is
viewed as secondary to domestic operations
2. Polycentric or Multi-Domestic Marketing Concept:
Opposite of ethnocentrism
Management of these multinational firms place importance
on international operations as a source for profits
Management believes that each country is unique and
allows each to develop own marketing strategies locally
Strategic Orientation: EPRG Schema
Generally, four distinctive approaches dominate strategic thinking in
international marketing:
3. Regiocentric:
Sees the world as one market and develops a standardized
marketing strategy for the entire world
4. Geocentric:
Regiocentric and Geocentric are synonymous with a Global
Marketing Orientation where a uniform, standardized
marketing strategy is used for several countries, countries in
a region, or the entire world
Road Map of the Course
Introduction to International Marketing
Understanding the External Environments
Evaluation of Global Market Opportunities
Developing Global Marketing Strategies
Implementing Global Marketing Strategies
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- International Marketing TotalDocumento88 pagineInternational Marketing TotalAli NadafNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 - Concept of Global Marketing & Global Marketing StrategyDocumento18 pagineModule 2 - Concept of Global Marketing & Global Marketing StrategyAriel Bobis100% (1)
- International MarketingDocumento26 pagineInternational MarketingSikiru Issa NuhuNessuna valutazione finora
- International MarketingDocumento59 pagineInternational MarketingRahul Singh100% (3)
- International MarketingDocumento8 pagineInternational MarketingNisha Solanki100% (1)
- Course Syllabus International Marketing: Vietnam National University - HCMC International University School of BusinessDocumento13 pagineCourse Syllabus International Marketing: Vietnam National University - HCMC International University School of BusinessDao CoNessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing AssignmentDocumento7 pagineInternational Marketing AssignmentNokuphiwa DondaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing (Chapter 1)Documento29 pagineInternational Marketing (Chapter 1)Iftekhar Amin Chowdhury100% (5)
- International MarketingDocumento58 pagineInternational MarketingVeer Jawandha100% (1)
- Strategic Marketing ManagementDocumento7 pagineStrategic Marketing ManagementsruthimbaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing Chapter 3Documento4 pagineInternational Marketing Chapter 3Abviel Yumul100% (1)
- Value Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandValue Chain Management Capability A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 - Product Life Cycle in Theory and PracticeDocumento11 pagineModule 3 - Product Life Cycle in Theory and PracticeRonald Reagan AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing CH1Documento7 pagineInternational Marketing CH1Nour Ali100% (1)
- International MarketingDocumento54 pagineInternational MarketingSimone SegattoNessuna valutazione finora
- International MarketingDocumento76 pagineInternational MarketingAbdallah El Jeddawi Asa100% (1)
- Department Ofmanagement StudiesDocumento10 pagineDepartment Ofmanagement StudiesHarihara PuthiranNessuna valutazione finora
- International MarketingDocumento243 pagineInternational Marketingmdkareem22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Distribution Channel ManagementDocumento9 pagineDistribution Channel ManagementsujeetleopardNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 - Trade PromotionsDocumento20 pagineChapter 9 - Trade PromotionsmziabdNessuna valutazione finora
- International MarketingDocumento440 pagineInternational MarketingHari Krishna67% (3)
- Agricultural MarketingDocumento4 pagineAgricultural Marketingbari TVNessuna valutazione finora
- Contemporary Issues in HRMDocumento9 pagineContemporary Issues in HRMVenky NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management Ime PGDM Iv SemesterDocumento95 pagineStrategic Management Ime PGDM Iv SemesterPankaj JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- New Products Management Merle Crawford & Anthony Di Benedetto 9th EditionDocumento39 pagineNew Products Management Merle Crawford & Anthony Di Benedetto 9th EditionFaizan Babar100% (1)
- Personal Equity and Retirement Account (Pera)Documento12 paginePersonal Equity and Retirement Account (Pera)lorkan19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rural RetailingDocumento18 pagineRural RetailingAmyra Johnson100% (1)
- Rural Marketing EnvironmentDocumento3 pagineRural Marketing EnvironmentMahesh Bhansali0% (2)
- Chapter 03. Analyzing The Marketing EnvironmentDocumento37 pagineChapter 03. Analyzing The Marketing EnvironmentReem AlAssirNessuna valutazione finora
- Ibm Class Notes - 1Documento4 pagineIbm Class Notes - 1standalonemba100% (1)
- International Product PolicyDocumento35 pagineInternational Product PolicyMegha KashyapNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 019Documento34 pagineChap 019ReemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stragic Management AssignmentDocumento37 pagineStragic Management Assignmentayub_balticNessuna valutazione finora
- International MarketingDocumento6 pagineInternational MarketingNafisa AurnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trade PromotionDocumento19 pagineTrade PromotionjunuclassicNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Market Opportunity AsessmentDocumento23 pagineGlobal Market Opportunity Asessmentmentari fazrinniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consumer Behaviour PPT Most FinalDocumento38 pagineConsumer Behaviour PPT Most FinalAbdullah Sheikh100% (1)
- Introduction To Global MarketingDocumento37 pagineIntroduction To Global Marketingpavann231100% (1)
- Uniqlos Marketing Plan To Expand To VietDocumento42 pagineUniqlos Marketing Plan To Expand To Vietkhanh nguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch08 Location StrategiesDocumento13 pagineCh08 Location Strategieslsmklvb100% (1)
- How McCain Responds To Changes in The External EnvironmentDocumento6 pagineHow McCain Responds To Changes in The External EnvironmentIla Mehrotra AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing Notes PDFDocumento262 pagineInternational Marketing Notes PDFmusik loveNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management ModelDocumento22 pagineStrategic Management ModelVeinraxzia Llamar100% (1)
- 13 International Business200910300331Documento13 pagine13 International Business200910300331Tu Hoai NamNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro and Macro EnviromentDocumento23 pagineMicro and Macro EnviromentPranita BhavarNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Areas of ManagementDocumento12 pagineFunctional Areas of Managementrisarn50% (2)
- EPRG FrameworkDocumento3 pagineEPRG FrameworkshalemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapt 1Documento11 pagineChapt 1RajKamNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of International TradeDocumento2 pagineBenefits of International Tradeasifmahmud20diuNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovation Management NotesDocumento4 pagineInnovation Management NotesMohd Izzudin100% (1)
- MarketEntryStrategyDocumento32 pagineMarketEntryStrategyShashankkSharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rural ManagementDocumento168 pagineRural ManagementPrasanjeet Bhattacharjee90% (10)
- Question On Defining Marketing For The 21st CenturyDocumento2 pagineQuestion On Defining Marketing For The 21st CenturyZakaria Haider50% (4)
- International Human Resource Management (IHRM) : Unit 1Documento30 pagineInternational Human Resource Management (IHRM) : Unit 1richa928Nessuna valutazione finora
- International Marketing Chapter 2Documento42 pagineInternational Marketing Chapter 2wubeNessuna valutazione finora
- International MarketingDocumento272 pagineInternational MarketingMuralidharanHarikrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap1 CateoraDocumento20 pagineChap1 CateoraalihubaisNessuna valutazione finora
- IB 311: International Marketing: Fall 2007 The Concept of Global MarketingDocumento22 pagineIB 311: International Marketing: Fall 2007 The Concept of Global MarketingAudreyNessuna valutazione finora
- L1 Scope & Challeges of Intl MKTGDocumento21 pagineL1 Scope & Challeges of Intl MKTGBhavini ModiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap1 (Debbie)Documento21 pagineChap1 (Debbie)Maciel García FuentesNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Activities of Tropical Homes-Ltd. in The Real Estate Sector of BangladeshDocumento36 pagineMarketing Activities of Tropical Homes-Ltd. in The Real Estate Sector of BangladeshSudipto Bose100% (1)
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocumento2 pagineQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- Personal RESUME Making Tips For Job SeekersDocumento30 paginePersonal RESUME Making Tips For Job SeekersSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Category: All Categories: Khulna InternationalDocumento3 pagineCategory: All Categories: Khulna InternationalSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Exceptence LetterDocumento1 paginaExceptence LetterSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Glossary of Human Resources TermsDocumento124 pagineGlossary of Human Resources TermsAJAY KULKARNI100% (1)
- Basics of International Marketing: Mode of Entry, Product, Positioning, Pricing, and PromotionDocumento51 pagineBasics of International Marketing: Mode of Entry, Product, Positioning, Pricing, and PromotionKumayl VirjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Real Estate Companies Profile in BangladeshDocumento8 pagineReal Estate Companies Profile in BangladeshSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- COVER LETTER For Job VacanciesDocumento2 pagineCOVER LETTER For Job VacanciesSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Cards Fees & Charges PDFDocumento1 paginaCards Fees & Charges PDFSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcoholic Beverages in Bangladeshhow Much We Know 2327 4972.1000123 PDFDocumento4 pagineAlcoholic Beverages in Bangladeshhow Much We Know 2327 4972.1000123 PDFSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 18Documento45 pagineChapter 18Navnita JayachandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Global Marketing, R & DDocumento31 pagineGlobal Marketing, R & DJayant KhatwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerging MarketsDocumento23 pagineEmerging MarketsVinod JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Marketing Communications and International AdvertisingDocumento8 pagineIntegrated Marketing Communications and International AdvertisingSudipto BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Ficha Álvaro y Jesús 3Documento8 pagineFicha Álvaro y Jesús 3Alex8mRNessuna valutazione finora
- Apartheid in South AfricaDocumento24 pagineApartheid in South Africaapi-300093410100% (1)
- COSMO NEWS September 1, 2019 EditionDocumento4 pagineCOSMO NEWS September 1, 2019 EditionUnited Church of Christ in the PhilippinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Team 12 Moot CourtDocumento19 pagineTeam 12 Moot CourtShailesh PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Developmental PsychologyDocumento2 pagineDevelopmental PsychologyPatricia Xandra AurelioNessuna valutazione finora
- Phoenix Wright Ace Attorney - Episode 2-2Documento39 paginePhoenix Wright Ace Attorney - Episode 2-2TheKayOneNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple FTP UploadDocumento10 pagineSimple FTP Uploadagamem1Nessuna valutazione finora
- ACA 122-My Academic Plan (MAP) Assignment: InstructionsDocumento5 pagineACA 122-My Academic Plan (MAP) Assignment: Instructionsapi-557842510Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assertiveness FinlandDocumento2 pagineAssertiveness FinlandDivyanshi ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- CHANDRA RAHU Yuti (Moon Rahu Conjunction)Documento3 pagineCHANDRA RAHU Yuti (Moon Rahu Conjunction)Shailendra Shrivastava0% (1)
- Chapter 12 Financial Management and Financial Objectives: Answer 1Documento9 pagineChapter 12 Financial Management and Financial Objectives: Answer 1PmNessuna valutazione finora
- Using JAXB For XML With Java - DZone JavaDocumento20 pagineUsing JAXB For XML With Java - DZone JavajaehooNessuna valutazione finora
- Pr1 m4 Identifying The Inquiry and Stating The ProblemDocumento61 paginePr1 m4 Identifying The Inquiry and Stating The ProblemaachecheutautautaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Documento4 pagineCambridge O Level: Pakistan Studies 2059/02Azfar RashedNessuna valutazione finora
- Before The Hon'Ble High Court of Tapovast: 10 Rgnul National Moot Court Competition, 2022Documento41 pagineBefore The Hon'Ble High Court of Tapovast: 10 Rgnul National Moot Court Competition, 2022sagar jainNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento8 pagineChapter 1Shidan MohdNessuna valutazione finora
- Algebra Lineal Septima Edicion Stanley I. Grossman S. Mcgraw-Hilliinteramericana Editores S.A. de C.V Mexico, DFDocumento1 paginaAlgebra Lineal Septima Edicion Stanley I. Grossman S. Mcgraw-Hilliinteramericana Editores S.A. de C.V Mexico, DFJOSE JULIAN RAMIREZ ROJASNessuna valutazione finora
- Bekic (Ed) - Submerged Heritage 6 Web Final PDFDocumento76 pagineBekic (Ed) - Submerged Heritage 6 Web Final PDFutvrdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Independence of Costa RicaDocumento2 pagineIndependence of Costa Ricaangelica ruizNessuna valutazione finora
- PT3 Liste PDFDocumento2 paginePT3 Liste PDFSiti KamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Conformity Observation Paper 1Documento5 pagineConformity Observation Paper 1api-524267960Nessuna valutazione finora
- Due Date: 29-12-2021: Fall 2021 MTH104: Sets and Logic Assignment No. 1 (Lectures # 16 To 18) Total Marks: 10Documento3 pagineDue Date: 29-12-2021: Fall 2021 MTH104: Sets and Logic Assignment No. 1 (Lectures # 16 To 18) Total Marks: 10manzoor ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Math Country Ranking Alevel 2023Documento225 pagineMath Country Ranking Alevel 2023Lutaaya Paul BamutaliraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Supplier Quality ManagementDocumento71 pagineChapter 8 Supplier Quality ManagementAnh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- PH Scale: Rules of PH ValueDocumento6 paginePH Scale: Rules of PH Valuemadhurirathi111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Faculty of Computer Science and Information TechnologyDocumento4 pagineFaculty of Computer Science and Information TechnologyNurafiqah Sherly Binti ZainiNessuna valutazione finora
- DeathoftheegoDocumento123 pagineDeathoftheegoVictor LadefogedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sjögren's SyndromeDocumento18 pagineSjögren's Syndromezakaria dbanNessuna valutazione finora
- MTE Radionuclear THYROID FK UnandDocumento44 pagineMTE Radionuclear THYROID FK UnandAmriyani OFFICIALNessuna valutazione finora
- Waa Sik Arene & Few Feast Wis (FHT CHT Ste1) - Tifa AieaDocumento62 pagineWaa Sik Arene & Few Feast Wis (FHT CHT Ste1) - Tifa AieaSrujhana RaoNessuna valutazione finora