Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Part 2 Routing Prt3
Caricato da
Marwan Ahmed0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni8 pagineThe document discusses router path determination and packet switching. Routers use path determination to select the best route to a destination by searching their routing tables. During packet switching, routers strip off layer 2 headers, examine the IP header to determine the next hop, re-encapsulate the packet into a new frame, and forward it out the appropriate interface. The source and destination IP addresses remain the same as packets traverse multiple routers, but the MAC addresses change as packets are forwarded from one router to the next.
Descrizione originale:
gr
Titolo originale
-Part 2 Routing Prt3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThe document discusses router path determination and packet switching. Routers use path determination to select the best route to a destination by searching their routing tables. During packet switching, routers strip off layer 2 headers, examine the IP header to determine the next hop, re-encapsulate the packet into a new frame, and forward it out the appropriate interface. The source and destination IP addresses remain the same as packets traverse multiple routers, but the MAC addresses change as packets are forwarded from one router to the next.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
10 visualizzazioni8 paginePart 2 Routing Prt3
Caricato da
Marwan AhmedThe document discusses router path determination and packet switching. Routers use path determination to select the best route to a destination by searching their routing tables. During packet switching, routers strip off layer 2 headers, examine the IP header to determine the next hop, re-encapsulate the packet into a new frame, and forward it out the appropriate interface. The source and destination IP addresses remain the same as packets traverse multiple routers, but the MAC addresses change as packets are forwarded from one router to the next.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 8
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Path determination is a process used by a router to pick the best path
to a destination
One of 3 path determinations results from searching for the best path
Directly connected network
Remote network
No route determined
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Switching Function of Router is the process used by a
router to switch a packet from an incoming interface to
an outgoing interface on the same router.
-A packet received by a router will do the following:
Strips off layer 2 headers.
Examines destination IP address located in Layer 3
header to find best route to destination.
Re-encapsulates layer 3 packet into layer 2 frame.
Forwards frame out exit interface.
Router Paths and Packet Switching
As a packet travels from one networking device to another
-The Source and Destination IP addresses NEVER change
-The Source & Destination MAC addresses CHANGE as
packet is forwarded from one router to the next.
-TTL field decrement by one until a value of zero is reached at
which point router discards packet (prevents packets from
endlessly traversing the network)
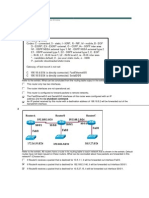
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Path determination and switching function details. PC1
Wants to send something to PC 2 here is part of what
happens
Step 1 - PC1 encapsulates packet into a frame. Frame
contains R1s destination MAC address
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Step 2 - R1 receives Ethernet frame.
R1 sees that destination MAC address matches its own
MAC.
R1 then strips off Ethernet frame.
R1 Examines destination IP.
R1 consults routing table looking for destination IP.
After finding destination IP in routing table, R1 now looks up
next hop IP address.
R1 re-encapsulates IP packet with a new Ethernet frame.
R1 forwards Ethernet packet out Fa0/1 interface.
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Path determination and switching function details. PC1 Wants to
send something to PC 2 here is part of what happens
Step 3 - Packet arrives at R2
R2 receives Ethernet frame
R2 sees that destination MAC address matches its own
MAC
R2 then strips off Ethernet frame
R2 Examines destination IP
R2 consults routing table looking for destination IP
After finding destination IP in routing table, R2 now looks up
next hop IP address
R2 re-encapsulates IP packet with a new data link frame
R2 forwards Ethernet packet out S0/0 interface
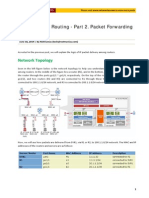
Router Paths and Packet Switching
Path determination and switching function details. PC1 Wants to
send something to PC 2 here is part of what happens
Step 4 - Packet arrives at R3
R3 receives PPP frame
R3 then strips off PPP frame
R3 Examines destination IP
R3 consults routing table looking for destination IP
After finding destination IP in routing table, R3 is directly
connected to destination via its fast Ethernet interface
R3 re-encapsulates IP packet with a new Ethernet frame
R3 forwards Ethernet packet out Fa0/0 interface
Step 5 - IP packet arrives at PC2. Frame is decapsulated &
processed by upper layer protocols.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONDa EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna Fast Track: Week 3 DAYS 1, 2 and 3Documento15 pagineCcna Fast Track: Week 3 DAYS 1, 2 and 3Edgar Giraldo ArdilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Basic Routing FinalDocumento71 pagineCisco Basic Routing Finalsasha zavatinNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet FlowDocumento135 paginePacket Flowprasadpra17Nessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Processing Part 2Documento2 paginePacket Processing Part 2vijay6996Nessuna valutazione finora
- NotaDocumento29 pagineNotaJavier Soto LedezmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 1Documento7 pagineExp 1neha yarrapothuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture9 Routing ConceptsDocumento51 pagineLecture9 Routing Conceptsnguyenquanglinh01121999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Internet Protocol (IP)Documento4 pagineInternet Protocol (IP)Dragan StančevNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 1 v3.1 Module 10 Routing Fundamentals and Subnets: © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocumento52 pagineCCNA 1 v3.1 Module 10 Routing Fundamentals and Subnets: © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedSao SovannarithNessuna valutazione finora
- Cisco Netacad Chapter 5Documento59 pagineCisco Netacad Chapter 5Carlos IzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Packet Processing StepsDocumento3 paginePacket Processing Stepsvijay6996Nessuna valutazione finora
- Details of ARP and PPPDocumento40 pagineDetails of ARP and PPPYogesh Palkar100% (1)
- CN - Unit Iii NotesDocumento45 pagineCN - Unit Iii Notesu25sivakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Routing: Destination AddressDocumento8 pagineIntroduction To Routing: Destination AddressB RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Expo DLLDocumento1 paginaExpo DLLDaniella PoloNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 10 - Routing Fundamentals and SubnetsDocumento6 pagineMODULE 10 - Routing Fundamentals and SubnetsGrecu GianiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 MPLS: 1.1 IP ForwardingDocumento19 pagine1 MPLS: 1.1 IP ForwardingFelix FrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Modules 8 - 10 - EnglishDocumento34 pagineModules 8 - 10 - EnglishChabi HonoratNessuna valutazione finora
- ccna 1 Chapter 5 v5 0 AnswersDocumento8 pagineccna 1 Chapter 5 v5 0 AnswersPriscila Beatriz Cabrera CabralNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 1 v3.1 Module 10 Routing Fundamentals and Subnets: © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedDocumento52 pagineCCNA 1 v3.1 Module 10 Routing Fundamentals and Subnets: © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights ReservedAnonymous ZCrVvMdNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network After Mid-1Documento17 pagineComputer Network After Mid-1Muhammad MubashirNessuna valutazione finora
- 01.introducing To Routing and Packet ForwardingDocumento4 pagine01.introducing To Routing and Packet ForwardingjentriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Case StudyDocumento9 pagineChapter 2 Case Studyd9700380Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Review Ccna2Documento48 pagineTest Review Ccna2saanireNessuna valutazione finora
- RoutingDocumento9 pagineRoutingCosmin StanNessuna valutazione finora
- Week08 RoutingDocumento30 pagineWeek08 RoutingSara El-GendyNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA 2 Ch4 ExamDocumento8 pagineCCNA 2 Ch4 ExamBryant Villarin BaldivicioNessuna valutazione finora
- COMP3250 Assignment 1Documento5 pagineCOMP3250 Assignment 1Anonymous 4qvaR8ZeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cours ReseauDocumento14 pagineCours ReseauNlend IsraëlNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Semester 1: Layer 3 ProtocolsDocumento65 pagineCCNA Semester 1: Layer 3 ProtocolsTung HoangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ccna (Router Configurations)Documento159 pagineCcna (Router Configurations)Sudhir MaherwalNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit-5Documento17 pagineCN Unit-5Chaitra kharviNessuna valutazione finora
- How Packet Flow Between Two Different NetworksDocumento9 pagineHow Packet Flow Between Two Different NetworksMd. Jahid Bin HossainNessuna valutazione finora
- Layer 3 SwitchingDocumento8 pagineLayer 3 SwitchingKaushik DasNessuna valutazione finora
- CCENT Chapter 5 Key TopicsDocumento6 pagineCCENT Chapter 5 Key Topicshoang nguyen baNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 9 - Basic Router Troubleshooting: CCNA 2 Version 3.0Documento30 pagineCh. 9 - Basic Router Troubleshooting: CCNA 2 Version 3.0Anonymous 38uRzxvutbNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - OSI Network LayerDocumento32 pagineChapter 5 - OSI Network Layerhappy girlNessuna valutazione finora
- EntraDocumento4 pagineEntraedwinyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Ipv6 Route::/0 Serial 0/1/1Documento12 pagineIpv6 Route::/0 Serial 0/1/1apdailey0625Nessuna valutazione finora
- Netmanias.2014.06.18.Part 2. Packet Forwarding by IP Router (En)Documento8 pagineNetmanias.2014.06.18.Part 2. Packet Forwarding by IP Router (En)TaroFukusoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Routing: Destination AddressDocumento18 pagineIntroduction To Routing: Destination AddressnsadnanNessuna valutazione finora
- By Default, Router Will Learn The Directly Connected NetworkDocumento3 pagineBy Default, Router Will Learn The Directly Connected Networkamudhu2684Nessuna valutazione finora
- TCP IpDocumento69 pagineTCP IpHein Khant ShaneNessuna valutazione finora
- RIP Protocol Using Cisco Packet TracerDocumento8 pagineRIP Protocol Using Cisco Packet TracerSwarnali NathNessuna valutazione finora
- (Data Communication Lab)Documento13 pagine(Data Communication Lab)Sourav Bin SarwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Part 3Documento76 pagineModule 3 Part 3monikareddy200317Nessuna valutazione finora
- 0.6 IP Routing 01Documento20 pagine0.6 IP Routing 01jack10786Nessuna valutazione finora
- TCP PaperDocumento25 pagineTCP PaperHoD Poly CWNessuna valutazione finora
- S2M09 Basic Router TroubleshootingDocumento46 pagineS2M09 Basic Router TroubleshootingRamesh AlagarsamyNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA2 - Final Exam (Version 2) Ccna2 Final Version 4.0 (97,2%)Documento10 pagineCCNA2 - Final Exam (Version 2) Ccna2 Final Version 4.0 (97,2%)Tanase CristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Static Vs Dynamic Routing in TCP - IP NetworksDocumento9 pagineComparison of Static Vs Dynamic Routing in TCP - IP NetworksSyed Rahmath AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1B Routing ConceptsDocumento35 pagineChapter 1B Routing ConceptsNewton Dannie AbelNessuna valutazione finora
- Capitulo 1Documento8 pagineCapitulo 1Raquel FagundesNessuna valutazione finora
- CS8591 / Computer Networks Department of CSE & IT 2019 - 2020Documento25 pagineCS8591 / Computer Networks Department of CSE & IT 2019 - 2020logesswari srinivasanNessuna valutazione finora
- 22-Egi Wiratama-12 - SIJA A-Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes TerbaruDocumento16 pagine22-Egi Wiratama-12 - SIJA A-Packet Tracer - Investigating Directly Connected Routes TerbaruEgik SamsiahNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Command Guide - (Yinkolatt)Documento147 pagineCCNA Command Guide - (Yinkolatt)AUNG HTOO ZAW100% (1)
- Module 1 CH 5 ExamDocumento6 pagineModule 1 CH 5 ExamŁukasz GołębiowskiNessuna valutazione finora
- Modules 8 and 9Documento4 pagineModules 8 and 9EmmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Acn NotesDocumento79 pagineAcn NotesShubNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions&Notes On Imp TopicsDocumento15 pagineSolutions&Notes On Imp TopicsMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Companies Database 1Documento36 pagineCompanies Database 1Marwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Valeo QsDocumento7 pagineImportant Valeo QsMarwan Ahmed100% (1)
- Optimization of Noc Wrapper Design Under Bandwidth and Test Time ConstraintsDocumento6 pagineOptimization of Noc Wrapper Design Under Bandwidth and Test Time ConstraintsMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Description:: Comm14 Version (I) MicroprocessorDocumento7 pagineProject Description:: Comm14 Version (I) MicroprocessorMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 3 Itroduction To Wan Ch1 Part2Documento22 paginePart 3 Itroduction To Wan Ch1 Part2Marwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Routing: Prof DR Hesham ArafatDocumento26 pagineStatic Routing: Prof DR Hesham ArafatMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Support The Way We Live: Modern Technologies and Trends For Each Give A Brief DiscussionDocumento8 pagineNetwork Support The Way We Live: Modern Technologies and Trends For Each Give A Brief DiscussionMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- TCP and Udp: Connectionless Low Overhead DatagramsDocumento11 pagineTCP and Udp: Connectionless Low Overhead DatagramsMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: IP Addresses and Other Information Can Be ObtainedDocumento8 pagineDHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol: IP Addresses and Other Information Can Be ObtainedMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- OSI Reference Model: ITE PC v4.0 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco PublicDocumento8 pagineOSI Reference Model: ITE PC v4.0 © 2007 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco PublicMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Altera Max Plus TutorialDocumento15 pagineAltera Max Plus TutorialMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- OFDM in VerilogDocumento6 pagineOFDM in VerilogMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Graduation Project Competition 2014: AbstractDocumento1 paginaElectronics Graduation Project Competition 2014: AbstractMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- N Nterconnect Rchitecture FOR Etworking Ystems On Hips: A I A N S CDocumento10 pagineN Nterconnect Rchitecture FOR Etworking Ystems On Hips: A I A N S CMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Compact Yet High-Performance (Cyhp) Library For Short Time-To-Market With New TechnologiesDocumento7 pagineCompact Yet High-Performance (Cyhp) Library For Short Time-To-Market With New TechnologiesMarwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- DEV262 - Evolution of The ABAP Programming Language - Exercise - SolutionDocumento33 pagineDEV262 - Evolution of The ABAP Programming Language - Exercise - SolutionrajaNessuna valutazione finora
- A1sy40 PDFDocumento73 pagineA1sy40 PDFHoang NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematical Cryptography, 4MA423: Assignment 1, 2019Documento2 pagineMathematical Cryptography, 4MA423: Assignment 1, 2019Meriem AbidliNessuna valutazione finora
- FragmentationDocumento3 pagineFragmentationHARISHNessuna valutazione finora
- NUS SoC Module DescDocumento55 pagineNUS SoC Module DescCliff6948Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ccnpv7 Route Lab7-2 BGP As Path InstructorDocumento11 pagineCcnpv7 Route Lab7-2 BGP As Path Instructortaco19933Nessuna valutazione finora
- Olympiad BookDocumento5 pagineOlympiad BookacanubhavNessuna valutazione finora
- L10 Logical & Arithmetic ENE334Documento95 pagineL10 Logical & Arithmetic ENE334Rahmat Ullah KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- PygameDocumento52 paginePygamechinuNessuna valutazione finora
- Procedure To Create The Employee Attendance ProjectDocumento30 pagineProcedure To Create The Employee Attendance ProjectSougata Roy Chowdhury0% (5)
- Manuale Commonstore 8.4Documento380 pagineManuale Commonstore 8.4Federico MaestàNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer ReliabilityDocumento19 pagineComputer ReliabilitytruciousNessuna valutazione finora
- Catatan Belajar CodeigniterDocumento12 pagineCatatan Belajar CodeigniterM. Aji PriyatnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fall-2016Documento4 pagineFall-2016Mirza AlibaigNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Computing U08007: Part A CourseworkDocumento12 pagineBusiness Computing U08007: Part A CourseworkSreeKrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Blender 2.5 Hotkeys Reference SheetDocumento2 pagineBlender 2.5 Hotkeys Reference SheetpedamadoNessuna valutazione finora
- GFG Array Questions ImportantDocumento4 pagineGFG Array Questions Importantakg299Nessuna valutazione finora
- Redline ClearviewDocumento2 pagineRedline ClearviewSaleh Al BlushiNessuna valutazione finora
- CSS COC1 Step and InstructionsDocumento2 pagineCSS COC1 Step and InstructionsJerry100% (1)
- Winrar PasswordDocumento1 paginaWinrar PasswordEdoardo Bighi100% (3)
- 5.1.4.4 Lab - Data Migration in WindowsDocumento26 pagine5.1.4.4 Lab - Data Migration in WindowsMelany SosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Character Recognition Using Artificial Neural NetworksDocumento17 pagineVisual Character Recognition Using Artificial Neural Networksapi-20008301Nessuna valutazione finora
- DSS Pro 2020 DAHUA PeruDocumento66 pagineDSS Pro 2020 DAHUA PeruQaturi MarketplaceNessuna valutazione finora
- 5248 HW 5 SolDocumento3 pagine5248 HW 5 SolHell IshereNessuna valutazione finora
- RevisionsDocumento148 pagineRevisionsDamianNessuna valutazione finora
- SQLDocumento501 pagineSQLCarol MurilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Kernel Adaptive Filtering PDFDocumento124 pagineKernel Adaptive Filtering PDFgeorgez111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Synopsis Of: Algorithm Analysis and Design CSE 408Documento3 pagineSynopsis Of: Algorithm Analysis and Design CSE 408Harjot Singh VirdiNessuna valutazione finora
- ControllerTool Help LIT12011147Documento1.421 pagineControllerTool Help LIT12011147ryanrbosNessuna valutazione finora
- A PC5250 Printer Session On AS400Documento15 pagineA PC5250 Printer Session On AS400Naveen SaharanNessuna valutazione finora