Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2.1 Analysing Linear Motion
Caricato da
Sudhan Nair0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
67 visualizzazioni15 pagineThis chapter discusses key concepts of forces and motion including displacement, velocity, acceleration, Newton's laws of motion, forces, gravity, energy, and Hooke's law. It specifically focuses on analyzing linear motion, defining distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. It provides examples of calculating these values from motion graphs or scenarios. Formulas for linear motion including velocity, displacement, and acceleration are also presented along with sample problems to solve.
Descrizione originale:
F4 Physics Chapter 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis chapter discusses key concepts of forces and motion including displacement, velocity, acceleration, Newton's laws of motion, forces, gravity, energy, and Hooke's law. It specifically focuses on analyzing linear motion, defining distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. It provides examples of calculating these values from motion graphs or scenarios. Formulas for linear motion including velocity, displacement, and acceleration are also presented along with sample problems to solve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
67 visualizzazioni15 pagine2.1 Analysing Linear Motion
Caricato da
Sudhan NairThis chapter discusses key concepts of forces and motion including displacement, velocity, acceleration, Newton's laws of motion, forces, gravity, energy, and Hooke's law. It specifically focuses on analyzing linear motion, defining distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. It provides examples of calculating these values from motion graphs or scenarios. Formulas for linear motion including velocity, displacement, and acceleration are also presented along with sample problems to solve.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 15
CHAPTER 2 Forces and Motion
In this chapter, you will learn about:
Displacement, velocity, acceleration
Motion graphs
Inertia
Newtons Laws 1st, 2nd, 3rd
How forces act on objects
Gravity
Energy
Springs and Hookes Law (most important!)
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Distance and displacement
DISTANCE, d, is how far a body travels during
motion
Distance travelled is a measure of the actual distance covered during
motion.
It does not distinguish between positive and negative direction.
DISPLACEMENT, s = final position initial position
Displacement is the change in position of an object.
It takes into account the starting and finishing points.
The route taken by the object doesnt matter.
Distance is a scalar quantity while displacement is a vector
quantity
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Speed and Velocity
Speed and velocity both indicate how fast
an object is travelling.
Speed = rate of change of distance
Velocity = rate of change of
AVERAGE SPEED, s = distance travelled / time taken = d / t
displacement
AVERAGE VELOCITY, v = displacement / time taken = s / t
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Worked Example 2.1A (Textbook)
Consider Figure 2.1.
(a) What is the distance jogged by
Satish?
(b) What is his average speed?
(c) What is his average velocity?
2.1 Analysing linear motion
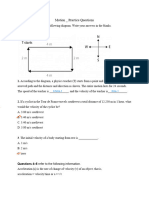
Example 1
The figure shows a car moving round a big roundabout
which has a radius of 70 m. Calculate:
(a) The distance moved by the car
(b)The displacement of the car
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Example 2
A cow moves 3 m to the east and then 4 m to the north.
Find the:
(a) Total distance moved by the cow
(b)Displacement of the cow
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Example 3
A car starts from point O and moved 50 m to the north in
60 seconds. The car then moves 120 m to the west in
40 seconds. Finally it stops. Calculate the:
(a) Total distance moved by the car
(b)Displacement of the car
(c) Velocity of the car
(d)Average speed of the car
(e) Speed of the car when it is moving north
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Acceleration
Acceleration is a measure of how quickly
velocity changes.
POSITIVE acceleration = Increasing velocity
(faster)
NEGATIVE acceleration= Decreasing velocity
(slowing
down) a.k.a deceleration
ACCELERATION is defined as the rate of change of velocity.
Acceleration, a = change in velocity / time = v u / t
where v is final velocity, u is the initial velocity.
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Example 4
A runner runs from the starting line and achieves a
celocity of 18 ms-1 in 3 seconds. Calculate his
acceleration.
Example 5
A car accelerates from 10 ms-1 to 50 ms-1 in 20 seconds.
What is its acceleration?
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Equations for linear motion
There are three equations for linear motion:
1. v = u + at
2. s = ut + at2
3. v2 = u2 + 2as
u = initial velocity
v = final velocity
a = acceleration
t = time taken
s = displacement
2.1 Analysing linear motion
Worked Example 2.1B (Textbook)
A skateboarder in a race is travelling at 10ms-1 as her
crosses the finish line. He then decelerates uniformly
until coming to rest over a distance of 20m.
(a) What is his acceleration as he pulls up?
(b)How long does he take to come to rest?
2.1 Analysing linear motion
2.1 Questions (Textbook)
1. A somewhat confused ant is moving back and forth
along a metre ruler.
(a) A to B
(b)C to B
(c) C to D
(d)C to E and then to D
2.1 Analysing linear motion
2.1 Questions (Textbook)
2. Swee Lee is walking in the park. She walks 300 m north
and then 100 m west, finally turning to walk 300 m
south. It takes her 5 minutes.
a) Calculate the total distance travelled
b) Calculate her average speed (ms-1 )
c) Calculate her displacement
d) Calculate her average velocity
2.1 Analysing linear motion
2.1 Questions (Textbook)
3. A car starts from rest and accelerates uniformly for 8.0
s. It reaches a final speed of 16 ms-1 .
(a) What is the acceleration of the car?
(b)What is the average velocity of the car?
(c) Calculate the distance travelled by the car.
2.1 Analysing linear motion
2.1 Questions (Textbook)
4. A new model Proton can start from rest and travel 400
m in 16 s.
(a) What is its average acceleration during this time?
(b)Calculate the final speed of the car.
(c) How fast is this final speed in km h-1 ?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Forces and MotionDocumento150 pagineForces and MotionAz MYNessuna valutazione finora
- SMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.1 Linear MotionDocumento69 pagineSMK Tat Beng Physics Form 4 2.1 Linear MotionTee Ting QINessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Linear MotionDocumento18 pagineChapter 3 Linear MotionMuhd Faizal MdkNessuna valutazione finora
- Yr 11 Special Notes On FizzDocumento54 pagineYr 11 Special Notes On FizzNayab ShahzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsDocumento54 pagineScience 9 Q4 Intro To KinematicsSire WillNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Motion LessonDocumento6 pagineLinear Motion LessonSalmizam IzamNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in One DimensionDocumento4 pagineMotion in One DimensionmtsilmaroNessuna valutazione finora
- KinematicsDocumento37 pagineKinematicsBrian LuarNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear Motion LectureDocumento42 pagineLinear Motion LectureTheodore Teddy JNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Linear MotionDocumento33 pagineChapter 2 Linear MotionJerome FizzowNessuna valutazione finora
- BB101 Chapter 2 Linear Motion - EditDocumento9 pagineBB101 Chapter 2 Linear Motion - EditAidi AmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Year 11 Prelim NotesDocumento53 paginePhysics Year 11 Prelim NotesZain Al-LoosNessuna valutazione finora
- Description of MotionDocumento8 pagineDescription of MotionSel FortichNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Motion - NotesDocumento7 pagineBasic Motion - NotesparneetNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 S3Documento6 pagineUnit 1 S3cyumadripNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Force and MotionDocumento65 pagineChapter 2 Force and MotionAdsham100% (1)
- Basic Motion - KeyDocumento7 pagineBasic Motion - KeyAli Ali AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Force, Motion and Momentum - 2024Documento29 pagineForce, Motion and Momentum - 2024Widjaya HS TeacherNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematics in One DimensionDocumento20 pagineKinematics in One DimensionEllah Iracielli TevesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap - 02 Textbook Glencoe MotionDocumento30 pagineChap - 02 Textbook Glencoe MotionAnonymous PAZRKwBILGNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Linear MotionDocumento12 pagineChapter 2 Linear MotionFatin AmirNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Linear MotionDocumento10 pagineChapter 2 Linear MotionF1040 AleeyaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 1a Motion - Ticker Timers Notes 2024Documento27 pagineCH 1a Motion - Ticker Timers Notes 2024andilenbNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematice in 1-DDocumento8 pagineKinematice in 1-DTesfu Tadesse TesfishNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionDocumento36 pagineLecture Outline: Physics, 4 EditionRazan AlmuairfiNessuna valutazione finora
- MotionDocumento5 pagineMotionvivek_theeasywaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDocumento73 pagineSpeed Velocity and AccelerationArth LubayNessuna valutazione finora
- MotionDocumento4 pagineMotionHnin NandarNessuna valutazione finora
- Speed VelocityDocumento6 pagineSpeed VelocityJudy Grace ConcordiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Documento17 paginePhysics Form 4 Chapter 2.1Farain RashdiNessuna valutazione finora
- MotionDocumento60 pagineMotionjoshua cerialesNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinametic Intorduction 1Documento26 pagineKinametic Intorduction 1Sec 3 EDUNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Chapter 2 Force and MotionDocumento44 paginePhysics Chapter 2 Force and MotionShatviga VisvalingamNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary - 01 PDFDocumento3 pagineSummary - 01 PDFImran MirzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 7 Lesson 1Documento47 paginePhysics 7 Lesson 1rubyaxxizzi44100% (1)
- Energy, Work and Force: by The End of This Chapter You Will Be Competent To..Documento33 pagineEnergy, Work and Force: by The End of This Chapter You Will Be Competent To..Zah SchlafmützeNessuna valutazione finora
- Vectors vs. Scalars: Scalar QuantitiesDocumento45 pagineVectors vs. Scalars: Scalar Quantitieslala2398Nessuna valutazione finora
- MechanicsDocumento2 pagineMechanicsfroilance100% (2)
- Physics KinematicsDocumento11 paginePhysics KinematicsRichmond CarrilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDocumento28 pagineLesson 1 Dynamics of Rigid BodiesDave Lumas100% (1)
- Motion - 3Documento77 pagineMotion - 3Prudence RwatireraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kin EmeticsDocumento38 pagineKin EmeticsRobin BiswasNessuna valutazione finora
- KinematicsDocumento13 pagineKinematicsiskenderbeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinematicsof Particles - Rectilinear Motion: KinematicsDocumento98 pagineKinematicsof Particles - Rectilinear Motion: KinematicsVinoth RajaguruNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinema TicsDocumento63 pagineKinema TicsTutor JamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Documento27 pagineLakhmir Singh Solutions Class 9 Physics Chapter 1Rekha PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - MotionDocumento8 pagineChapter 2 - MotionDani PrimantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1M2P6Documento17 pagineQ1M2P6Pasend LodiNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ReviewerDocumento21 paginePhysics ReviewerainnahNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Linear MotionDocumento24 pagine4 Linear MotionAbhishek KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MotionDocumento34 pagineMotionKenneth YeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Kinema TicsDocumento32 pagineKinema TicsMatthew Brian UbacNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Linear MotionDocumento8 pagineLesson 1 Linear MotionAbul CepolNessuna valutazione finora
- Fengsc T1 PDFDocumento6 pagineFengsc T1 PDFserufeNessuna valutazione finora
- A Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionDa EverandA Complete Course in Physics (Graphs) - First EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Motion in a Straight Line (Physics) Question BankDa EverandMotion in a Straight Line (Physics) Question BankNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculations for Science Fiction Writers/Circular OrbitsDa EverandCalculations for Science Fiction Writers/Circular OrbitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Definition And Explanation Of Force In PhysicsDa EverandSimple Definition And Explanation Of Force In PhysicsNessuna valutazione finora
- MRSM Pat f4 2012 Phy 2yvDocumento24 pagineMRSM Pat f4 2012 Phy 2yvLelon OngNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Business Studies Test 1Documento6 pagineIGCSE Business Studies Test 1Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Studies Paper 1Documento13 pagineBusiness Studies Paper 1Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcse Bio Food TestsDocumento3 pagineIgcse Bio Food TestsSudhan Nair100% (1)
- IGCSE Math Test 1Documento5 pagineIGCSE Math Test 1Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 - Chemical BondingDocumento6 pagineChapter 5 - Chemical BondingSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry: ST ND RD THDocumento1 paginaChemistry: ST ND RD THSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Studies Paper 1 Cover PageDocumento1 paginaBusiness Studies Paper 1 Cover PageSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Paper 1 Dec 2015Documento11 pagineAccounting Paper 1 Dec 2015Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Evaporates From Land and SeaDocumento8 pagineWater Evaporates From Land and SeaSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounts DecemberDocumento28 pagineAccounts DecemberSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Paper 1 Cover PageDocumento1 paginaAccounting Paper 1 Cover PageSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Paper 2 Dec 2015Documento15 pagineAccounting Paper 2 Dec 2015Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Ozone Is Found in The AtmosphereDocumento4 pagineOzone Is Found in The AtmosphereSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Co-Ordinated Sciences Paper 3Documento13 pagineCo-Ordinated Sciences Paper 3Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Soap Was The First Detergent: Water Dissolves Dirt, However Oily Dirt Will NotDocumento5 pagineSoap Was The First Detergent: Water Dissolves Dirt, However Oily Dirt Will NotSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- A Base Is A Substance That Neutralises An AcidDocumento6 pagineA Base Is A Substance That Neutralises An AcidSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Igcse Listening Answer Key June 20140001Documento5 pagineIgcse Listening Answer Key June 20140001Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Studies Paper 1Documento13 pagineBusiness Studies Paper 1Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- 63 The AirDocumento12 pagine63 The AirSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowDocumento19 pagine2.1 Analysing Electric Fields and Charge FlowSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Co-Ordinated Sciences Paper 1Documento17 pagineCo-Ordinated Sciences Paper 1Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Co-Ordinated Sciences Paper 6Documento4 pagineCo-Ordinated Sciences Paper 6Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Studies Paper 2Documento16 pagineBusiness Studies Paper 2Sudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Form 4 EXPERIMENT: Hooke's Law: © Pusat Tuisyen Minda InspirasiDocumento2 paginePhysics Form 4 EXPERIMENT: Hooke's Law: © Pusat Tuisyen Minda InspirasiSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Charles' Law - ExperimentDocumento2 pagineCharles' Law - ExperimentSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Form 4: © Pure Eloquence SDN BHDDocumento2 paginePhysics Form 4: © Pure Eloquence SDN BHDSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- F5 Chapter 2 - ElectricityDocumento50 pagineF5 Chapter 2 - ElectricitySudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - PressureDocumento3 pagineChapter 3 - PressureSudhan NairNessuna valutazione finora
- ATM BrochuresDocumento5 pagineATM Brochuresगुंजन सिन्हाNessuna valutazione finora
- Intel Corporation Analysis: Strategical Management - Tengiz TaktakishviliDocumento12 pagineIntel Corporation Analysis: Strategical Management - Tengiz TaktakishviliSandro ChanturidzeNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthquake EnggDocumento6 pagineEarthquake EnggAiko VillaluzNessuna valutazione finora
- Treinamento DENSODocumento65 pagineTreinamento DENSOjoao mariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Menu EngineeringDocumento7 pagineMenu EngineeringVijay KumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Competitive Benchmarking Created On 20230208T0816ZDocumento1 paginaCompetitive Benchmarking Created On 20230208T0816ZRrKartika RatnasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One: China Civil Engineering Construction Coorperation (Ccecc) WasDocumento24 pagineChapter One: China Civil Engineering Construction Coorperation (Ccecc) WasMoffat KangombeNessuna valutazione finora
- BBS of Lintel Beam - Bar Bending Schedule of Lintel BeamDocumento5 pagineBBS of Lintel Beam - Bar Bending Schedule of Lintel BeamfelixNessuna valutazione finora
- Build The Tango: by Hank BravoDocumento57 pagineBuild The Tango: by Hank BravoMarceloRossel100% (1)
- X-by-Wire: Fred SeidelDocumento9 pagineX-by-Wire: Fred SeidelHồng TháiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Biology 7th Edition Neil A CampbellDocumento36 pagineTest Bank For Biology 7th Edition Neil A Campbellpoupetonlerneanoiv0ob100% (31)
- Fila 1Documento4 pagineFila 1Karolina Sanchez83% (6)
- Rubrics For Movie AnalysisDocumento1 paginaRubrics For Movie AnalysisJnnYn PrettyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Game Is A Structured Form of PlayDocumento5 pagineA Game Is A Structured Form of PlayNawa AuluddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Presentation (142311004) FinalDocumento60 pagineProject Presentation (142311004) FinalSaad AhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective Sample Questions On The Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (1St Set)Documento51 pagineObjective Sample Questions On The Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 (1St Set)kullsNessuna valutazione finora
- IPASO1000 - Appendix - FW Download To Uncurrent SideDocumento11 pagineIPASO1000 - Appendix - FW Download To Uncurrent SidesaidbitarNessuna valutazione finora
- SPM Bahasa Inggeris PAPER 1 - NOTES 2020Documento11 pagineSPM Bahasa Inggeris PAPER 1 - NOTES 2020MaryNessuna valutazione finora
- LGBT in Malaysia: Social Welfare SystemDocumento24 pagineLGBT in Malaysia: Social Welfare SystemMuhammad Syazwan Ahmad Fauzi100% (1)
- Brand Brand Identity: What Are Brand Elements? 10 Different Types of Brand ElementsDocumento3 pagineBrand Brand Identity: What Are Brand Elements? 10 Different Types of Brand ElementsAŋoop KrīşħŋặNessuna valutazione finora
- The Role of The Board of Directors in Corporate GovernanceDocumento12 pagineThe Role of The Board of Directors in Corporate GovernancedushyantNessuna valutazione finora
- Ks3 English 2009 Reading Answer BookletDocumento12 pagineKs3 English 2009 Reading Answer BookletHossamNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 Fall TSJ s03 The Mystery of The Gospel PT 1 - Stuart GreavesDocumento5 pagine2012 Fall TSJ s03 The Mystery of The Gospel PT 1 - Stuart Greavesapi-164301844Nessuna valutazione finora
- SSD Term 3Documento52 pagineSSD Term 3anne_barltropNessuna valutazione finora
- Serenity Dormitory PresentationDocumento16 pagineSerenity Dormitory PresentationGojo SatoruNessuna valutazione finora
- Gonzales v. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. L-37453, (May 25, 1979), 179 PHIL 149-177)Documento21 pagineGonzales v. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. L-37453, (May 25, 1979), 179 PHIL 149-177)yasuren2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sourabh ResumeDocumento2 pagineSourabh ResumeVijay RajNessuna valutazione finora
- The Constitution Con by Michael TsarionDocumento32 pagineThe Constitution Con by Michael Tsarionsilent_weeper100% (1)
- 2017 Ecatalogue Howtim Exit SignDocumento38 pagine2017 Ecatalogue Howtim Exit SignSatish Phakade-PawarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Prediction of Travel Behaviour Using The Theory of Planned BehaviourDocumento16 pagineThe Prediction of Travel Behaviour Using The Theory of Planned Behaviourhaneena kadeejaNessuna valutazione finora