Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Value Chain
Caricato da
hussainpadrawala07860 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
209 visualizzazioni14 pagineThis document discusses the value chain concept introduced by Michael Porter in 1985. A value chain represents the chain of activities a firm performs to deliver a product or service to customers. It allows alignment with customers to generate quality, focuses on cost management, and provides efficient processes. The value chain model includes primary activities like operations, logistics, marketing, and support activities. Analyzing a value chain identifies value processes, areas for cost improvement, and ways to increase margins through distinctive capabilities or cost advantages.
Descrizione originale:
value chain
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoThis document discusses the value chain concept introduced by Michael Porter in 1985. A value chain represents the chain of activities a firm performs to deliver a product or service to customers. It allows alignment with customers to generate quality, focuses on cost management, and provides efficient processes. The value chain model includes primary activities like operations, logistics, marketing, and support activities. Analyzing a value chain identifies value processes, areas for cost improvement, and ways to increase margins through distinctive capabilities or cost advantages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
209 visualizzazioni14 pagineValue Chain
Caricato da
hussainpadrawala0786This document discusses the value chain concept introduced by Michael Porter in 1985. A value chain represents the chain of activities a firm performs to deliver a product or service to customers. It allows alignment with customers to generate quality, focuses on cost management, and provides efficient processes. The value chain model includes primary activities like operations, logistics, marketing, and support activities. Analyzing a value chain identifies value processes, areas for cost improvement, and ways to increase margins through distinctive capabilities or cost advantages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 14
Value chain
By:- Hussain Padrawala
Urvisha duhlani
Jaydeep jadhav
Gaurang jadhav
Chetan rajput
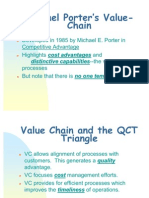
INTRODUCTION
A value chain is a chain of activities that a firm operating in a
specific industry performs in order to deliver a valuable product or
service for the market. The concept comes from business
management and was first described and popularized by Michael
Porter in his 1985 best-seller, Competitive Advantage: Creating and
Sustaining Superior Performance.
VALUE CHAIN AND THE QCT TRIANGLE
VC allows alignment of processes with customers. This
generates a quality advantage.
VC focuses cost management efforts.
VC provides for efficient processes which improves the
timeliness of operations.
VALUE CHAIN MODEL
FROM MICHAEL E. PORTERS COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE
SUPPORT
ACTIVITIES
Firm Infrastructure (General Management)
Human Resource Management
Technology Development
Procurement
Inbound
Logistics
Ops.
Outbound
Logistics
PRIMARY ACTIVITIES
Sales &
Marketing
Service and
Support
VALUE CHAIN ELEMENTS
Customer value added
Margin orientation
Primary activities
Inbound logistics
Operations
Outbound logistics
Sales and marketing
Service and support
Support Activities
Human resources (general and admin.)
Tech. development
Procurement
VALUE CHAIN ANALYSIS
Document the activities
Understand the cost and margins at each step.
Map the value chain to the industry value chain
Use Activity Based Costing
Look for core competencies
Map the cost structure
external values drive cost advantages
VALUE CHAIN BENEFITS
Identifies value processes
Identifies areas for cost improvement
Reduce Delivery Times
Optimize Inventory
Improve Customer Relationships
Enhance Revenue and Profit
GOAL OF VALUE CHAIN
Driven by customer perceptions
Increase margins
Focus on value processes
Distinctive capabilities
Cost advantages
Some examples
Intel Corporation
MacDonald's
VALUE CHAIN AND THE TBC TRIANGLE
Technical:
Increases knowledge of no profit zones
Increases knowledge of forward and/or backward integration
opportunities
Identifies value processes
Identifies win-win alliance opportunities
Behavioral:
Focus shifts to the customer
Focus shifts from conflict to partnering with customers & suppliers
Cultural
Creates externally focused mindset
Generates information sharing environment with respect for
confidentiality
Value Chain Analysis helps you identify the ways in which you
create value for your customers, and then helps you think
through how you can maximize this value: whether through
superb products, great services, or jobs well done.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Value Chain ManagementDocumento59 pagineValue Chain Managementjehangir0000100% (1)
- Porters Value Chain ModelDocumento10 paginePorters Value Chain Modelpradeep110Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Management Worked Assignment: Model Answer SeriesDa EverandMarketing Management Worked Assignment: Model Answer SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Value Chain AnalysisDocumento19 pagineValue Chain Analysisnisha67% (3)
- Road # 3, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad 500 034: For IBS Use Only Class of 2009Documento20 pagineRoad # 3, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad 500 034: For IBS Use Only Class of 2009abcdownload1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Order 153293 Change Management Models AppleDocumento9 pagineOrder 153293 Change Management Models AppleErick KiplimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Value Chain Supply Chain + Demand ChainDocumento29 pagineValue Chain Supply Chain + Demand Chainguru9anand100% (2)
- Lean and Agile Supply ChainDocumento30 pagineLean and Agile Supply ChainboschabdelNessuna valutazione finora
- A Case Study On Tesco Customers' Satisfaction and Loyalty: April 2020Documento95 pagineA Case Study On Tesco Customers' Satisfaction and Loyalty: April 2020Gohan SayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unilever Case StudyDocumento1 paginaUnilever Case StudyVinesh RamNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Strategy Chapter2 PDFDocumento29 pagineOperations Strategy Chapter2 PDFanitasengarphd25% (4)
- Operations Strategy - The Two PerspectivesDocumento6 pagineOperations Strategy - The Two PerspectivesNandkumar KhachaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Impacto de Influencers en La Decisiónde CompraDocumento17 pagineImpacto de Influencers en La Decisiónde CompraYuleisi GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management Revision NotesDocumento16 pagineOperations Management Revision Notescthiruvazhmarban0% (1)
- Operations & Supply Chain Management Across Organization & Corporate StrategyDocumento25 pagineOperations & Supply Chain Management Across Organization & Corporate StrategySuleman TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap001 - Introduction To Operations ManagementDocumento32 pagineChap001 - Introduction To Operations ManagementUmar Saeed100% (1)
- The Strategy Clock, Value Chain and Porter's Five Forces ExplainedDocumento6 pagineThe Strategy Clock, Value Chain and Porter's Five Forces ExplainedChristophe Dormenval100% (1)
- Driving Supply Chain InnovationDocumento36 pagineDriving Supply Chain InnovationanolrivNessuna valutazione finora
- Competitive AdvantageDocumento60 pagineCompetitive AdvantageFibin Haneefa100% (1)
- QuantitativeDocumento36 pagineQuantitativeMadhan MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ansoff MatrixDocumento2 pagineAnsoff Matrixkunal lad83% (6)
- Crafting The Brand Positioning - 11Documento3 pagineCrafting The Brand Positioning - 11skillfullyards100% (1)
- A Critical Literature Review On Talent Management, Competitive Advantage and Organizational Performance: A Research AgendaDocumento8 pagineA Critical Literature Review On Talent Management, Competitive Advantage and Organizational Performance: A Research AgendajweerakkodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Value ChainDocumento4 pagineValue ChainNadeem AnsariNessuna valutazione finora
- IKEA Case Study Read The Following Case Carefully and Answer The Questions at The EndDocumento3 pagineIKEA Case Study Read The Following Case Carefully and Answer The Questions at The EndAbdallah Khraim33% (3)
- Multi Attribute Value AnalysisDocumento75 pagineMulti Attribute Value AnalysispatrickafchainNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations ManagementDocumento13 pagineOperations ManagementUsman AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- GE MatrixDocumento26 pagineGE MatrixFijo JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Lewin's Change Model PDFDocumento3 pagineLewin's Change Model PDFJohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1 SMDocumento4 pagineAssignment 1 SMAnam Shoaib67% (3)
- F Unilever's GCSDocumento6 pagineF Unilever's GCSMehedi HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of New Nature of OrganizationsDocumento3 pagineCharacteristics of New Nature of Organizationsjemblem66Nessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of Management Unit 3Documento24 pagineFunctions of Management Unit 3Sarthak KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - Operations ManagementDocumento26 pagineAssignment - Operations ManagementteenuNessuna valutazione finora
- Task 1 AssignmntDocumento10 pagineTask 1 Assignmnttanveer ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- By Dr. Atri Roy SenguptaDocumento30 pagineBy Dr. Atri Roy SenguptaMegha Banerjee100% (1)
- Porter Generic StrategiesDocumento3 paginePorter Generic StrategiesbravehorseNessuna valutazione finora
- Greening The Supply Chain - FinalDocumento24 pagineGreening The Supply Chain - FinalRahul Agarwal100% (2)
- PGBM16 Global Corporate Strategy Aug 2011Documento5 paginePGBM16 Global Corporate Strategy Aug 2011cnu_neveb4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Porters StrategyDocumento14 paginePorters StrategyDeepshikha Goel100% (1)
- Marketing DissertationDocumento88 pagineMarketing Dissertationyrmail778100% (14)
- Bullwhip Effect in Supply ChainsDocumento20 pagineBullwhip Effect in Supply Chainsshlraja_188100% (1)
- Operations ManagementDocumento10 pagineOperations ManagementKARTHIK145Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Designing and Managing The Supply Chain 3rd Edition by David Simchi LeviDocumento56 pagineSolution Manual For Designing and Managing The Supply Chain 3rd Edition by David Simchi LeviOmnia MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Resource ManagementDocumento121 pagineHuman Resource ManagementPhilemon ZachariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento9 pagineChapter 1Nurfitry HareqhNessuna valutazione finora
- SCM-Supply Chain Management-Paper PresentationDocumento23 pagineSCM-Supply Chain Management-Paper Presentationsb_rameshbabu3283100% (1)
- MSC DissertationDocumento53 pagineMSC DissertationTrajankatsNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer Loyalty ThesisDocumento17 pagineCustomer Loyalty Thesishasanjawad1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business Environment NotesDocumento4 pagineBusiness Environment NotesAbhishek SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Sustainable Supply ChainDocumento4 pagineSustainable Supply ChainDaisy100% (1)
- 6sigma in Reverse LogisticsDocumento12 pagine6sigma in Reverse LogisticsParul Soni50% (2)
- Supply Chain StrategyDocumento30 pagineSupply Chain StrategyPilirani Nyoni NyembaNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM 5Documento17 pagineTQM 5soe sanNessuna valutazione finora
- MBAM619 Strategy ManagementDocumento120 pagineMBAM619 Strategy Managementapi-26073353Nessuna valutazione finora
- Step by Step Guide To Exporting 2011Documento54 pagineStep by Step Guide To Exporting 2011Kathy PrestaNessuna valutazione finora
- Us Auto The Future of The Automotive Value Chain 1 PDFDocumento64 pagineUs Auto The Future of The Automotive Value Chain 1 PDFMadhurimaNessuna valutazione finora
- Burundi EconomyDocumento112 pagineBurundi EconomyMandar RasaikarNessuna valutazione finora
- 19e Section6 LN Chapter04Documento14 pagine19e Section6 LN Chapter04benbenchen100% (3)
- Chapter 4, Evaluating Internal EnvironmentDocumento12 pagineChapter 4, Evaluating Internal EnvironmentStuti SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Coach CaseDocumento184 pagineCoach CaseJitboon Laomanit100% (1)
- Kohinoor Chemicals Company, Mgt480Documento13 pagineKohinoor Chemicals Company, Mgt480shovon1717275450% (2)
- Information Systems StrategiesDocumento18 pagineInformation Systems StrategiesArlyn Pearl PradoNessuna valutazione finora
- Management in WorkplaceDocumento14 pagineManagement in Workplace______.________Nessuna valutazione finora
- Connect and Supply-Broj 07Documento40 pagineConnect and Supply-Broj 07Izdavačka Kuća KoraciNessuna valutazione finora
- StrategicDocumento12 pagineStrategicKd KejdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Development: From Start To ScaleDocumento125 pagineBusiness Development: From Start To ScaleNOMRCY REBELNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of OrganizationDocumento9 pagineIntroduction of Organizationthilini100% (1)
- Contemporary Strategic Management An Australasian Perspective 2nd Edition Grant Test BankDocumento19 pagineContemporary Strategic Management An Australasian Perspective 2nd Edition Grant Test Bankarnoldmelanieip30l100% (32)
- Brochure AVEVA DigitalAccelerationintheDownstreamOandG 02-19Documento8 pagineBrochure AVEVA DigitalAccelerationintheDownstreamOandG 02-19ManmeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Intelligence For Supply Chain Managers PDFDocumento256 pagineFinancial Intelligence For Supply Chain Managers PDFyguga100% (3)
- Developing Marketing Strategies and PlansDocumento25 pagineDeveloping Marketing Strategies and PlansAhsan Sayeed Nabeel DeproNessuna valutazione finora
- MacdonaldsDocumento8 pagineMacdonaldsAhmet BabayevNessuna valutazione finora
- DTI Policy Brief 2017 09 The Philippines in The Cocoa Chocolate Global Value ChainDocumento12 pagineDTI Policy Brief 2017 09 The Philippines in The Cocoa Chocolate Global Value ChainRobert de la SernaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Digital Transformation of Industry: How Important Is It? Who Are The Winners? What Must Be Done Now?Documento52 pagineThe Digital Transformation of Industry: How Important Is It? Who Are The Winners? What Must Be Done Now?Daniel Duane LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Report NewDocumento31 pagineSeminar Report NewAniket GargatteNessuna valutazione finora
- ProjectDocumento56 pagineProjectPramod KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ilovepdf MergedDocumento45 pagineIlovepdf MergedAnirudh ArunkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Value Chain Analysis of Organic Tea Dibrugarh District of AssamDocumento7 pagineValue Chain Analysis of Organic Tea Dibrugarh District of AssamInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Management and Business IntegrationDocumento51 pagineStrategic Management and Business IntegrationLy HoàngNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 1 - Global Marketing in The Firm + IntroDocumento35 pagineCH 1 - Global Marketing in The Firm + IntroAyShaRafiQue100% (1)
- Indian Dairy Vision 2030Documento40 pagineIndian Dairy Vision 2030divanshu saxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic Decision Making For Footwear IndustryDocumento10 pagineStrategic Decision Making For Footwear IndustryRishi DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Transformation in The Automotive IndustryDocumento8 pagineDigital Transformation in The Automotive IndustryKal Gyimesi100% (1)