Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Standard Costing 3
Caricato da
iishahbazCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Standard Costing 3
Caricato da
iishahbazCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Standard Costing
Material Variances
There are two factors;
1. Price difference
2. Quantity of material used in production differ from standard material.
Material Price Variance:
(SP-AP) x QP
Possible reasons:
1. Actual prices may exceed standard prices due to inflation.
2. It is beyond the control of the company.
3. A favorable price variance can be due to the purchase of inferior quality lead to inferior product or
more wastages.
4. An emergency purchase may cause higher price because of additional handling and freight on
especial rush order
Material Usage Variance:
(SQ-AQ) x SP
Compared standard quantity used with the actual quantity used.
Calculated on standard price to remove price effects
Possible reasons:
1. Controllable by the production manager
2. Careless handling of material, use of inferior quality material, change in method of production,
change in quality standards, pilferage etc.
Total Material Variance
SC-AC
Difference between the standard material cost for actual production and the actual cost.
Combination of material price & material usage variance
Labor Variance
Labor cost is determined by the price paid & the quantity of labor used.
Price and quantity variance arise for labor.
Labor Rate Variance:
(SR-AR) x AH
Comparing standard price per labor hour with the actual paid per labor hour.
Labor rate is least subject to control by management.
Labor Efficiency Variance:
(SH-AH) x SR
Difference between the standard labor hours for actual production & the actual
labor hours worked x standard wages rate
Represents quantity variance for direct labor
Similar to the material usage variance.
Normally controllable by the manager production
Arise due to use of inferior quality material, failure of machinery, change in
production process
Incase of poor production planning or change in quality control standards then
manager production is not liable
Variable Overhead Variance
Total Variable Overhead Variance :
Difference between standard variable & the actual variable incur
(SC-AC)
Vary with direct labor or machine hour.
will be due to price variance & quantity variance similar to direct labor
Variable Overhead Expenditure:
Difference between budgeted overheads & the actual cost incurred.
(BVO-AVO)
Possible Causes:
Aggregation of a various individual overhead items such as, indirect labor, indirect material,
power consumption, maintenance and other support services
Can arise because prices have been changed.
Can also be effected by the use of overheads. For example; using more electricity than the
amount which should have been used. This will increase cost of power.
Expenditure variance is not informative and meaningful unless comparison of each
individual item of overhead expenditure with the set standard.
focusing on individual line items & not isolated on total variance.
Variable Overhead Efficiency Variance:
Identical to the labor efficiency variable.
(SH-AH) x SR
Fixed Overhead Expenditure or Spending Variance
(VFO-AFO)
Fixed cost assume to remain unchanged in short term in response to changes in the level of activity.
But may change due to price increase such as changes in salaries of supervisors increase in rent rates, taxes &
utilities etc.
Expenditure variance will arise for both marginal and absorption costing systems
Volume Variance
(AP-BP) x SR
Due to actual production different from budgeted production.
if actual production is greater than the budgeted production then volume variance is favorable & vice versa
Not useful for cost control purpose.
Calculated to meet to meet profit measurement requirements of financial reporting.
For absorption costing volume variance will occur as fixed cost are allocated to product.
Volume variance subdivided into efficiency and capacity variance.
Indicates as to why the actual production is different from budgeted production
Company has failed to utilize the plant capacity
Efficiency variance indicates a failure to utilize capacity efficiently
A failure to achieve the budgeted capacity maybe for a reason. Machine breakdown, material shortages, poor
production schedule, labor disputes, reduction in sales demand.
it is not meaningful to attach fixed cost to the variances since, fixed cost will not be affected by a failure to
utilize capacity
Efficiency Variance:
(SH-AH) x SR
Identical with the labor efficiency variance
Not useful because fixed overhead will not change
Volume Capacity Variance
(AH-BH) x SR
Difference between actual hour of input & the budgeted hour of the input.
Indicates failure to utilize capacity
Reasons include: material shortage, machine breakdown, labor disputes, reduction in sales
demand.
Material Mix and Yield:
Material mix variance =
(Actual quantity used - Actual quantity in standard mix %) x standard price
When the mix of materials used differ from standard mix, if the mixture is varied a
larger than expected of expensive material than unfavorable MM arises.
When combination of two or more materials is used
MM is based on standard price of each material to avoid price effect.
Production manager may change standard mix for economical material mixed
to save cost but without compromise on quality of product.
Input standard be established for each material mix. Studies necessary to
establish material mix.
An adverse MM will result in more expensive materials used in place of cheap
materials.
Material Yield variance:
Material yield variance = (Actual yield - standard yield on actual input of material) x standard
cost unit of output
Difference between the actual output & the actual output for a given level of inputs.
Arise failure to follow standard procedures.
Use of inferior quality materials may result in an adverse yield variance.
For example; An input of 100,000 litres expected an output of 90,000 litres of product
Actual production is 92,700 litres. It means , 2,700 litres is produced in excess. Cost per unit
of output is Rs 6 per unit. A favorable yield variance is Rs 16,200
Material price, mix & yield variances are interrelated and should not be interpreted in
isolation.
Inter dependencies be recognized
Changes in relative input prices of materials will affect the optimum standard mix & yield of
material
Appropriate to those production process where manager has the authority to change the mix
of material & deviate from standard mix
Material Usage Variance :
It consists of mix & yield variance
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- GT Ref Guide 2012Documento40 pagineGT Ref Guide 2012Cayle Pua100% (3)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The22ImmutableLawsOfBranding BIZDocumento16 pagineThe22ImmutableLawsOfBranding BIZRaja Sufyan MinhasNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Dismantling The American Dream: How Multinational Corporations Undermine American ProsperityDocumento33 pagineDismantling The American Dream: How Multinational Corporations Undermine American ProsperityCharlene KronstedtNessuna valutazione finora
- Gold and Silver Club EbookDocumento22 pagineGold and Silver Club Ebookmfaisalidreis100% (1)
- Marketting Plan - Car LeasingDocumento7 pagineMarketting Plan - Car LeasingRavindra DananeNessuna valutazione finora
- Guide To Using Internationa 2Documento321 pagineGuide To Using Internationa 2Friista Aulia LabibaNessuna valutazione finora
- Divisional Performance ManagementDocumento31 pagineDivisional Performance ManagementiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Dolmen Shopping Festival.Documento1 paginaDolmen Shopping Festival.iishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Retail QuestionnaireDocumento2 pagineRetail QuestionnaireiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
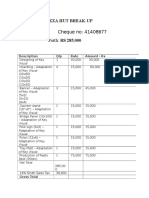
- Cheque No: 41408677 Worth: RS 285,000: Pizza Hut Break-UpDocumento2 pagineCheque No: 41408677 Worth: RS 285,000: Pizza Hut Break-UpiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost ManagementDocumento17 pagineCost ManagementiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Costing 2Documento16 pagineStandard Costing 2iishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Microbial Activity of Garlic 1Documento6 pagineAnti Microbial Activity of Garlic 1iishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Process CostingDocumento7 pagineProcess CostingiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Investment DecisionsDocumento1 paginaCapital Investment DecisionsiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- GD SampleDocumento2 pagineGD SampleiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- The Budgeting ProcessesDocumento9 pagineThe Budgeting ProcessesiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- PLEST Analysis of Global Automotive IndustryDocumento2 paginePLEST Analysis of Global Automotive IndustryiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Photobooth PropsDocumento14 paginePhotobooth PropsiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rapid Advancement in Technology Coupled With The Increasing Awareness On Health IssuesDocumento2 pagineThe Rapid Advancement in Technology Coupled With The Increasing Awareness On Health IssuesiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Sheet For Teaching AssistantDocumento1 paginaTime Sheet For Teaching AssistantiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Analysis of MitchellsDocumento17 pagineFinancial Analysis of MitchellsiishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Accounting I Assignment # 4: (Type Text)Documento2 paginePrinciples of Accounting I Assignment # 4: (Type Text)iishahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- Equity Options Strategy: Naked PutDocumento2 pagineEquity Options Strategy: Naked PutpkkothariNessuna valutazione finora
- Summer Training Project TopicDocumento24 pagineSummer Training Project Topichoneygoel13Nessuna valutazione finora
- USW1 DDBA 8161 Week03 RivalryStrategyToolDocumento1 paginaUSW1 DDBA 8161 Week03 RivalryStrategyToolfiercelemon1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Titan Case StudyDocumento5 pagineTitan Case StudyKeerthivasa TNessuna valutazione finora
- Microeconomics II Chapter on MonopolyDocumento16 pagineMicroeconomics II Chapter on Monopolyvillaarbaminch0% (1)
- Ch15 SG BLTS 8eDocumento31 pagineCh15 SG BLTS 8eHolli Boyd-White100% (1)
- Hemh108 PDFDocumento20 pagineHemh108 PDFhoneygarg1986Nessuna valutazione finora
- Order Details - Carter'sDocumento4 pagineOrder Details - Carter'sSura SeyidovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions 1 The Short Run Supply Curve of ADocumento2 pagineMultiple Choice Questions 1 The Short Run Supply Curve of Atrilocksp SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix - 15 (R) University of MadrasDocumento255 pagineAppendix - 15 (R) University of MadrasMonica KshirsagarNessuna valutazione finora
- My Trading StrategyDocumento10 pagineMy Trading StrategyYiunam LeungNessuna valutazione finora
- LP Batch 2 Business MathDocumento22 pagineLP Batch 2 Business MathSEAN ANDREI TORRESNessuna valutazione finora
- Name: E-Mail: Cell Phone Number:: Balance Sheet Initial 1st MonthDocumento3 pagineName: E-Mail: Cell Phone Number:: Balance Sheet Initial 1st MonthEmiliano Mancilla SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Consolidated SOFP of Sing and DanceDocumento36 pagineConsolidated SOFP of Sing and DanceVicky Fan67% (3)
- Tetra Pak: Defining Markets and Competitive AdvantageDocumento11 pagineTetra Pak: Defining Markets and Competitive Advantagemazzaw12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Spon's Civil Engineering and Highway Works Price B... - (PART 2 On Costs and Profit)Documento6 pagineSpon's Civil Engineering and Highway Works Price B... - (PART 2 On Costs and Profit)mohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Gashub - 2018Documento23 pagineGashub - 2018Ricky PrasetyaNessuna valutazione finora
- NFCPAR-Auditing Problems: Description Machinery Others NotesDocumento1 paginaNFCPAR-Auditing Problems: Description Machinery Others NotesSano ManjiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Rural MarketDocumento38 pagineProject On Rural MarketSmita Keluskar100% (1)
- Homework Solution - Week 10 - Relevant Costing - GarrisonDocumento6 pagineHomework Solution - Week 10 - Relevant Costing - GarrisonGloria WongNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - The Investment SettingDocumento48 pagine1 - The Investment SettingYash Raj SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Productivity CompressDocumento10 pagineProductivity CompresstayerNessuna valutazione finora
- Graeber Summary Chapter 11Documento5 pagineGraeber Summary Chapter 11api-291732914Nessuna valutazione finora
- MaterialDocumento5 pagineMaterialQuestionscastle FriendNessuna valutazione finora
- NH-24 Tenders - ExtractsDocumento4 pagineNH-24 Tenders - Extractsshravan38Nessuna valutazione finora