Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Employee Safety and Health
Caricato da
Asma ChaudhryCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Employee Safety and Health
Caricato da
Asma ChaudhryCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Employee Safety and Health
Lecture Outline
Why Safety is Important
Occupational Safety Laws in Pakistan
Responsibilities and Rights of Employers and
Employees
Top Managements Role in Safety
What Causes Accidents?
Unsafe conditions and other work related factors
What causes unsafe acts?
How to prevent accidents?
Reducing unsafe conditions
Lecture Outline
Reducing unsafe acts by emphasizing safety
Reducing unsafe acts through
selection and placement
Training
motivation
Conduct safety and health audits
Workplace health hazards
Workplace substance abuse
Infectious diseases
Stress burnout and depression
Lecture Outline
Computer related health problems
Workplace smoking
Violence at work
What Accidents Must
Be Reported
Figure 162
Importance of Safety Policy
Pakistani Federal Bureau of Statistics, the
percentage of occupational accidents and injuries
sustained during the 2010 2011 fiscal year was
around 3.5% (1:30) of the labor force whereas
the percentage in rural areas is 70% while in
urban areas is 30%.
Agriculture (49.8%)
manufacturing (15.8%)
construction (13.0%)
wholesale & retail trade (10.3%)
transport/storage & communication (7.1%)
Implications: law suits, medical insurance
claims, loss of employees and wastage of time.
Health and Safety Laws in Pakistan
Factories Act 1934
The applicability of Factories Act 1934 is eminent
to all types of organizations as it acts as a baseline
for the government and the organization to ensure
compliance. The legal framework of Pakistan
Factories Act 1934 consists of 39 essential clauses
in Chapter (III) of the act that ensures the safety
and health compliance.
Safety and Health at Workplace:
Duties and Rights
Employers responsibilities
Provide a safe and healthy workplace.
Set and familiarize with safety and health standards.
Ensure workplace conditions conform to safety
standards.
Employers rights
Seek advice from government agencies.
Receive advice on safety and health regulations.
Safety and Health at Workplace
Employees responsibilities
Follow all employer safety and health rules and
regulations.
Report hazardous conditions to the supervisor.
Employees rights
Demand safety and health on the job without fear of
punishment.
Management Commitment
Accidents can be prevented by reducing accident-
causing conditions and accident-causing acts.
Safety starts with management commitment.
Management to be personally involved in safety
activities.
Give safety matters high priority.
Provide safety training to all workers.
Safety policy
Analyze accidents and take corrective / preventive
actions.
Dealing with Employee Resistance
The employer is liable for any penalties that
result from employees noncompliance with
health standards.
Ways to gain compliance
Bargain with the union for the right to discharge or
discipline an employee who disobeys safety standard.
Use positive reinforcement and training for gaining
employee compliance.
What Causes Accidents?
Unsafe conditions
Improperly guarded equipment
Defective equipment
Hazardous procedures in, on, or around machines
or equipment
Unsafe storagecongestion, overloading
Improper illuminationglare, insufficient light
Improper ventilationinsufficient air change,
impure air source
What Causes Accidents?
Checklist of Mechanical or Physical
Accident-Causing Conditions
Figure 166
Source: Courtesy of the American Insurance Association. From A Safety Committee Mans Guide, p. 164.
How to Prevent Accidents
Remedy unsafe conditions
Emphasize safety
Select safety-minded employees
Provide safety training
Use posters, incentive programs, and positive
reinforcement to motivate employees
Use behavior-based safety
Use employee participation
Conduct safety and health audits and inspections
Cut-Resistant Gloves Ad
Figure 168
Employee Safety Responsibilities Checklist
Figure 169
Source: Reprinted with permission of the publisher,
HRNext.com, Copyright HRNext.com, 2003.
Unsafe acts
Unsafe acts on the part of the employees
Smoking near inflammable Material
Processing at unsafe speed( too fast or too
slow)
Tampering Machinery and Equipment
Using unsafe procedures
Bypassing Safety instructions
Throwing material (supplies, chemical)
Abusing, quarreling, fighting, teasing other
employees etc
Reducing
Unsafe
Conditions
and Acts:
A Summary
Table 161
Reduce Unsafe Conditions
Identify and eliminate unsafe conditions.
Use administrative means, such as job rotation.
Use personal protective equipment.
Reduce Unsafe Acts
Emphasize top management commitment.
Emphasize safety.
Establish a safety policy.
Reduce unsafe acts through selection.
Provide safety training.
Use posters and other propaganda.
Use positive reinforcement.
Use behavior-based safety programs.
Encourage worker participation.
Conduct safety and health inspections regularly.
How to Prevent Accidents
2b. Reducing unsafe acts through selection
Screening through recruitment and selection stage to
isolate traits that may predict accidents on the job
2c. Reducing unsafe acts through training
2d. Reducing unsafe acts through motivation
Safety posters serve as constant reminders but not a
substitute for a comprehensive safety program
Incentive scheme reinforce positive attitude toward
safety
How to Prevent Accidents
Behavior-Based Safety
Identifying the worker behaviors that contribute to
accidents and then training workers to avoid these
behaviors
Use employee participation
2 reasons to get employees involved in designing safety
program:
People doing the actual job knows best
Easier to get employees to accept safety program
Appointing employees as members of safety teams
Routine inspection on all premises for safety and health
problems
Controlling Workers Compensation Costs
Before the accident
Communicate written safety and substance abuse
policies to workers and then strictly enforce those
policies.
After the accident
Be proactive in providing first aid, and make sure
the worker gets quick medical attention.
Make it clear that you are interested in the injured
worker and his or her fears and questions.
Document the accident; file required accident
reports.
Encourage a speedy return to work.
Workplace Health Hazards: Remedies
The Basic Industrial Hygiene Program
Recognition: identification of a possible hazard
Evaluation: assessing the severity of the hazard
Control: elimination or reduction of the hazard
Workplace hazards
Infectious Diseases
Alcoholism and Substance Abuse
Workplace Exposure Hazards
Chemicals and other hazardous materials.
Excessive noise and vibrations.
Temperature extremes.
Slippery floors and blocked passageways.
Dealing with Workplace Drug Abuse
If an employee appears to be under the
influence of drugs or alcohol:
Ask how the employee feels and look for signs of
impairment such as slurred speech.
Send an employee judged unfit for duty home.
Make a written record of your observations and
follow up each incident.
Inform workers of the number of warnings the
company will tolerate before requiring termination.
Refer troubled employees to the companys
employee assistance program.
Workplace Substance Abuse and the Law
Types of drug tests
Pre-employment tests
Random tests
Post-accident
Reasonable suspicion
Return-to-duty testing
Reducing Job Stress: Personal
Build rewarding, pleasant, cooperative relationships
Dont bite off more than you can chew.
Build an effective and supportive relationship with your boss.
Negotiate with your boss for realistic deadlines on projects.
Learn as much as you can about upcoming events and get as
much lead time as you can to prepare for them.
Find time every day for detachment and relaxation.
Take a walk to keep your body refreshed and alert.
Find ways to reduce unnecessary noise.
Reduce trivia in your job; delegate routine work.
Limit interruptions.
Dont put off dealing with distasteful problems.
Make a worry list that includes solutions for each problem.
Reducing Job Stress: Organizational
Provide supportive supervisors
Ensure fair treatment for all employees
Reduce personal conflicts on the job.
Have open communication between management and
employees.
Support employees efforts, for instance, by regularly asking
how they are doing.
Ensure effective jobperson fit, since a mistake can trigger
stress.
Give employees more control over their jobs.
Provide employee assistance programs including professional
counseling.
Burnout
Burnout
The total depletion of physical and mental
resources caused by excessive striving to reach an
unrealistic work-related goal.
Recovering from burnout:
Break the usual patterns to achieve a more well-
rounded life.
Get away from it all periodically to think alone.
Reassess goals in terms of their intrinsic worth
and attainability.
Think about work: could the job be done without
being so intense.
Other Workplace Safety and Health
Issues
Computer-Related Health Problems
Workplace Smoking
Violence at Workplace
Overly defensive, obsessive and paranoid
employee
Overly confrontational or anti-social behavior
Sexually aggressive behavior
Isolationist
Insubordinate behavior
Tendency to overreact
Violence at Work
Steps to reduce workplace violence:
Institute heightened security measures
Improve employee screening
Provide workplace violence training
Provide organizational justice
Pay enhanced attention to employee
retention/dismissal
Take care when dismissing violent employees
Promptly dealing with angry employees
Understand the legal constraints on reducing
workplace violence
Dealing with Angry
Employees
Make eye contact
Pay full attention to the employee
Be calm
Be honest and modest
Listen to the employee
Request for examples
Delicately and diplomatically define the
problem
Inquire about the situation and feelings
Thank You
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Sales-Management Solved MCQsDocumento69 pagineSales-Management Solved MCQskrishna100% (3)
- Busi Environment MCQDocumento15 pagineBusi Environment MCQAnonymous WtjVcZCg57% (7)
- Principle Mining Economics01Documento56 paginePrinciple Mining Economics01Teddy Dkk100% (3)
- Admin Law ReviewerDocumento5 pagineAdmin Law ReviewerNirvana Time Sulivan Estiva100% (1)
- Iraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Documento29 pagineIraq-A New Dawn: Mena Oil Research - July 2021Beatriz RosenburgNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkyl Benzene Sulphonic AcidDocumento17 pagineAlkyl Benzene Sulphonic AcidZiauddeen Noor100% (1)
- Theodore L. Sendak, Etc. v. Clyde Nihiser, Dba Movieland Drive-In Theater, 423 U.S. 976 (1975)Documento4 pagineTheodore L. Sendak, Etc. v. Clyde Nihiser, Dba Movieland Drive-In Theater, 423 U.S. 976 (1975)Scribd Government DocsNessuna valutazione finora
- RBI ResearchDocumento8 pagineRBI ResearchShubhani MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- CTC VoucherDocumento56 pagineCTC VoucherJames Hydoe ElanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Product and Service CostingDocumento28 pagineFundamentals of Product and Service CostingPetronella AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- PotwierdzenieDocumento4 paginePotwierdzenieAmina BerghoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Etik Koas BaruDocumento125 pagineTugas Etik Koas Baruriska suandiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Democratic EducationDocumento11 pagineDemocratic Educationpluto zalatimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Authors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020Documento8 pagineAuthors & Abstract Guideline V-ASMIUA 2020tiopanNessuna valutazione finora
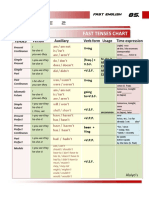
- Table 2: Fast Tenses ChartDocumento5 pagineTable 2: Fast Tenses ChartAngel Julian HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Natural JusticeDocumento20 paginePrinciples of Natural JusticeHeracles PegasusNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento3 pagineAssignment 1Bahle DlaminiNessuna valutazione finora
- 13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDocumento1 pagina13th Format SEX Format-1-1: Share This DocumentDove LogahNessuna valutazione finora
- Satisfaction On Localized Services: A Basis of The Citizen-Driven Priority Action PlanDocumento9 pagineSatisfaction On Localized Services: A Basis of The Citizen-Driven Priority Action PlanMary Rose Bragais OgayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment MS-28 Course Code: MS - 28 Course Title: Labour Laws Assignment Code: MS-28/TMA/SEM - II /2012 Coverage: All BlocksDocumento27 pagineAssignment MS-28 Course Code: MS - 28 Course Title: Labour Laws Assignment Code: MS-28/TMA/SEM - II /2012 Coverage: All BlocksAnjnaKandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Yellow CartoonDocumento1 paginaSimple Yellow CartoonIdeza SabadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lord Chief Justice Speech On Jury TrialsDocumento10 pagineLord Chief Justice Speech On Jury TrialsThe GuardianNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposed Food Truck LawDocumento4 pagineProposed Food Truck LawAlan BedenkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Flipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Documento4 pagineFlipkart Labels 23 Apr 2024 10 18Giri KanyakumariNessuna valutazione finora
- Deed OfAdjudication Cresencio Abuluyan BasilioDocumento4 pagineDeed OfAdjudication Cresencio Abuluyan BasilioJose BonifacioNessuna valutazione finora
- 26candao Vs People of The Philipines, 664 SCRA 769, G.R. No. 186659-710, February 1, 2012Documento5 pagine26candao Vs People of The Philipines, 664 SCRA 769, G.R. No. 186659-710, February 1, 2012Gi NoNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation ADocumento7 pagine10 Grammar, Vocabulary, and Pronunciation ANico FalzoneNessuna valutazione finora
- Gouri MohammadDocumento3 pagineGouri MohammadMizana KabeerNessuna valutazione finora
- ANA A. CHUA and MARCELINA HSIA, Complainants, vs. ATTY. SIMEON M. MESINA, JR., RespondentDocumento7 pagineANA A. CHUA and MARCELINA HSIA, Complainants, vs. ATTY. SIMEON M. MESINA, JR., Respondentroyel arabejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grameenphone Integrates Key Technology: Group 1 Software Enhances Flexible Invoice Generation SystemDocumento2 pagineGrameenphone Integrates Key Technology: Group 1 Software Enhances Flexible Invoice Generation SystemRashedul Islam RanaNessuna valutazione finora