Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
WCDMA System Structure and Principle2
Caricato da
Tariq MuhammadCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
WCDMA System Structure and Principle2
Caricato da
Tariq MuhammadCopyright:
Formati disponibili
WCDMA System Overview
Course Contents
Chapter 1 WCDMA System
Chapter 2 WCDMA Services
Chapter 3 WCDMA System Structure
Chapter 4 WCDMA RAN Interface & Procedure
Chapter 5 WCDMA Basic Signaling Flow
WCDMA SYSTEM
We have 3 generations:
1
st
G analog cellular mobile communication, ex: AMPS
(advanced mobile phone system) uses 800MHZ north&
south America &TACS( Total access communication
system) uses 900MHZ Britain.
Disadvantages: no high speed services, limited types of
services etc..
To Solve this disadvantages 2
nd
G was developed.
2
nd
G ex: DAMPS or IS-54 of USA using 800MHZ &
the IS-95 (CDMA mode) European using 800 or
1900MHZ.
2
nd
G designed as the TDMA support 64kbps, the GSM
system uses FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) &TDMA
modes and each carriers 8 channels 200KHZ B.W.
Advantages: transmission of voice& low speed data
service.
2.5G address the medium rate data transmission
includes GPRS.
3
rd
G system can provide multiple kinds of high quality
multimedia service and implement global roaming and
CDMA has a very large capacity which is 10 times
than analog.
3
rd
G has 2 standardization: 3GPP(3
rd
G partner project)
&3GPP2.
3GPP: it adopts the WCDMA technologies to
construct a new RAN and a core switching network.
3GPP2:its adopts the cdma2000 is applied for radio
access.
3
rd
G consist of a family concept: network part &radio
interface part.
The comparison between the three major
technical systems:
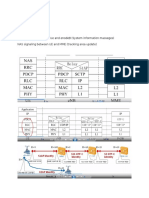
System: WCDMA cdma2000 TD-SCDMA
Chip rate: 3.84Mcps Nx1.2288Mcps 1.28Mcps
Signal bandwidth:5MHZ Nx1.25MHZ 1.6MHZ
Inheritance from: GSM narrowband CDMA GSM
Air interface: WCDMA IS-95 WCDMA
Core network: GSM MAP ANSI-41 GSM MAP
(Mobile Application Part)
Using countries: Europe &Japan USA& Korea China
NOTE: ( N= 1, 3, 6, 9, 12)
Course Contents
Chapter 1 WCDMA System
Chapter 2 WCDMA Services
Chapter 3 WCDMA System Structure
Chapter 4 WCDMA RAN Interface & Procedure
Chapter 5 WCDMA Basic Signaling Flow
WCDMA SERVICES
There are many features of 3G services such as:
Compatible backward with all the services provided
by GSM.
The concept of multimedia service introduced.
The real time service such as voice generally have
the QoS requirement.
The typical service of 3G are CAMEL phase3
intelligent service needs to implement in UMTS
&phase 2 needs to implement in providing the prepaid
service &support services such as forwarding calls
etc
In 3G improvement of location &application of the
system structure, LCS is very attractive, types of
LCS:
Public security service (ex: emergency calls)
Location based charging (ex: some LAs set as
discount area)
Enhanced call routing (ex:enables to the nearest
service point, gas station)
Location based information service (ex: deliver
msg. to user advertisements in to attract
customers)
Mobile yellow page (ex: same as ECR)
Network enhancing services (ex: roaming user
that can use 3G system from other mobile
network).
In 3G multimedia service is the first to be developed
with a little bandwidth, voice service is the first to
be developed with the use of high compression ratio
MP3, types of services:
Circuit real time multimedia service: The
implementation of multimedia service in the circuit
domain.
Packet real time multimedia service: Multimedia
service in the packet domain is mainly implemented
via the SIP (Session Initiation protocol).
Non real time multimedia message service: This
service is called MMS (Multimedia Message Service),
a natural development of SMS.
UMTS Traffic Class
Conversational
Streaming
Interactive
Background
UMTS Traffic Class
Traffic class Conversational class Streaming class Interactive class Background
- Preserve time
relation (variation)
between information
entities of the stream
- Request
response pattern
- Destination is not
expecting the data
within a certain time
Conversational
pattern (stringent and
low delay )
- Preserve payload
content
- Preserve payload
content
Example of the
application
- voice,
videotelephone
VOD, Web broadcast - Web browsing,
network games
- background
download of emails
Fundamental
characteristics
- Preserve time
relation (variation)
between information
entities of the stream
Course Contents
Chapter 1 WCDMA System
Chapter 2 WCDMA Services
Chapter 3 WCDMA System Structure
Chapter 4 WCDMA RAN Interface & Procedure
Chapter 5 WCDMA Basic Signaling Flow
UMTS Architecture
Uu lu
USIM
ME
Cu
Node B
Node B
Node B
Node B
RNC
RNC
lub lur
MSC/
VLR
GMSC
SGSN GGSN
HLR
PLMN PSTN
ISDN,etc
INTERNET
External Networks
CN
UTRAN
UE
UMTS Network Elements Structure
WCDMA System Architecture
Iu
UTRAN
UE
Uu
UTRAN UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network
CN Core Network
UE User Equipment
CN
UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System)
is the 3
rd
G mobile telecommunication system by using
the WCDMA air interface technology, including RAN
&CN. UMTS system consist of UTRAN( UMTS
Terrestrial Radio Access Network), CN &UE.
RAN used to process all radio related functions.
CN used to process all voice calls and data
connections &implement the function of external
network switching &routing, CN is divided into CS
which covers MSC,VLR,IWF &GMSC, &PS which
provides packet data services for subscriber including
the SGSN &GGSN.
UTRAN System Architecture
RNS
RNC
RNS
RNC
Core Network
Node B
Node B
Node B Node B
Iu Iu
Iur
Iub
Iub
Iub Iub
UTRAN is divided into RNC (radio network controller)
it implements connection establishment
modulation/demodulation and Node B is the base
station of WCDMA system.
UE is divided into ME &USIM (UMTS subscriber
module).
R99 network structure has considered the 2G/3G
compatibility so as to support the smooth transition
of GSM/GPRS/3G, its main function includes
MSC,VLR,HLR,AUC,EIR,GMSC,SGSN,GGSN.
R4 the function entities (SGSN &GGSN) of the PS
domain remain unchanged. But have MSC server,
GMSC server, CS-MGW( Circuit switched media
gateway) &T-SGW( Transport signaling Gateway).
RAN I nterfaces
VMSC/VLR
Iu-CS
Gs
SGSN
GMSC
GGSN
BSS RNC
BTS BTS NODE B NODE B
Iu-PS
A
Gb
Abis Iub
Um Uu
Common Protocol Model of UTRAN Interfaces
Application
Protocol
Data
Stream(s)
ALCAP(s)
Transport
Network
Layer
Physical Layer
Signalling
Bearer(s)
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Control Plane User Plane
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Transport Network
Control Plane
Radio
Network
Layer
Signalling
Bearer(s)
Data
Bearer(s)
The principle of interface protocol architecture is the logical mutual-independence
between layers and planes. Protocol layers of a specified protocol version, or even all
layers in a plane can be modified if required in the future.
Basic Notions
UE Working Mode and State
Serving RNCDrift RNC and Control RNC
Source RNC and Target RNC
UE states
CELL_DCH CELL_FACH
CELL_PCH URA_PCH
IDLE
DEAD - Scanning networks (PLMN)
- Camp on cell
- Monitor paging channel
- cell re-selection
- Dedicated Channel
- Radio bearers Transmission Services
- upper layer Signaling
trigger (CN)
- Reduce actionDTXand save power
RRC connection
SRNC/DRNC
In WCDMA system notion of SRNC/DRNC is introduced
because the existence of Iur Interface
In brief, the RNC directly connected to CN and controlling all
the UEs resources is called SRNC(serving RNC) of this UE
The RNC with no connection to CN but only providing
resources for UE is called DRNC(Drift RNC) of this UE
A UE in connection state has at least and only one SRNC, but
can has 0 or multiple DRNCs
CN
SRNC DRNC
Iu
Iur
Source RNC/Target RNC
SRNC Relocation is the process of switching the SRNC of a
specific UE.
Source RNC is the SRNC before SRNC Relocation and Target
RNC is the SRNC after SRNC Relocation
Source RNC and Target RNC refer to different RNCs during a
SRNC Relocation process
CN CN
Source
RNC
Target
RNC
Serving
RNC
Iu Iu
Iur
RNC
UTRAN Interface Protocols and Functions
Iu Interface
Iur Interface
Iub Interface
Uu Interface
I u I nterface System Structure
Core Network (CN) UTRAN
Node B
Node B
Node B
Node B
RNC
Iu Interface
Iu-CS
CS
Domain
PS
Domain
Iu-PS
RNC
I u-CS I nterface Protocol Stack Structure
Q.2150.1
Q.2630.1
RANAP
Iu UP Protocol
Layer
Transport
Network
Layer
Physical Layer
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Control Plane User Plane
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Transport Network
Control Plane
Radio
Network
Layer
ATM
SSCOP
AAL5
SSCOP
SSCF-NNI
AAL2 AAL5
MTP3b MTP3b
SCCP
SSCF-NNI
I u-PS I nterface Protocol Stack Structure
SSCF-NNI
SSCOP
AAL5
IP
SCTP
SCCP
SSCF-NNI
MTP3-B
M3UA
RANAP
Iu UP Protocol
Layer
Transport
Network
Layer
Physical Layer
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Control Plane User Plane
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Transport Network
Control Plane
Radio
Network
Layer
ATM
AAL5
IP
UDP
GTP-U
Physical Layer
ATM
I u I nterface Functions(1)
Mobility Management
Location Area Report
SRNS Relocation
Hard handover between RNCs and inter-system
handover
Radio Access BearerRABManagement
Establishment, Modification and Release of RAB
Iu data transmission
normal data transmission
abnormal data transmission
Transparent transmission of UE-CN connection
information
Iu Interface Functions(2)
Paging
Iu Release
Security Mode Control
Overload Control
Common UE IDIMSIManagement
Iu Signaling Trace Management
Iu Interface Abnormality Management
UTRAN Interfaces Protocols and Functions
Iu Interface
Iur Interface
Iub Interface
Uu Interface
I ur I nterface Protocol Stack Structure
SSCF-NNI
SSCOP
MTP3-B
AAL5
IP
SCTP
SCCP
AAL5
SSCF-NNI
STC (Q.2150.1)
RNSAP
Iur Data
Stream(s)
Transport
Network
Layer
Physical Layer
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Control Plane User Plane
Transport
User
Network
Plane
Transport Network
Control Plane
Radio
Network
Layer
ATM
ALCAP(Q.2630.1)
AAL2
SSCF-NNI
SSCOP
MTP3-B
IP
SCTP
SSCF-NNI
M3UA M3UA
Iur Interface Functions(1)
Support Basic Mobility Functions between RNCs
Support SRNC relocation
Cell Update and URA Update between RNCs
Paging between RNCs
Protocol Error Report
Channel Functions
Establish, Modify or Release Dedicated Channels in
DRNC during handover
Transmission of DCH TB(Transmission Block) on Iur
Management of RL(Radio Link) in DRNS by Dedicated
Measurement Procedure and Filter Control
RL ManagementCompressed Mode Management
UTRAN I nterfaces Protocols and Functions
Iu Interface
Iur Interface
Iub Interface
Uu Interface
Iub Interface Protocol Stack
Node B
Application Part
(NBAP)
AAL Type 2
ALCAP
Transport
Layer
Physical Layer
Radio
Network
Layer
Radio Network
Control Plane
Transport
Network
Control Plane
D
C
H
F
P
R
A
C
H
F
P
ATM
D
S
C
H
F
P
AAL Type 5
User Plane
SSCF-UNI
SSCOP
AAL Type 5
SSCF-UNI
SSCOP
Q.2630.1
Q.2150.2
F
A
C
H
F
P
P
C
H
F
P
U
S
C
H
F
P
C
P
C
H
F
P
Iub Interface Functions(1)
Common Functions
Common Transport Channel Management
Iub Common Channel Data Transmission
Logical O&M of Node Bmaintenance functions such
as cell configuration ManagementFault Management
Block Management, etc.
System Information Management
Common Measurement
Resource Verification
Abnormality Management
Timing and Synchronization Management
Iub Interface Functions(2)
Dedicated Functions
Dedicated Transport Channel Management
Radio Link(RL) Monitoring
Dedicated Measurement Management
Timing and Synchronization Management
Up-link outer loop Power Control
Iub Dedicated Data transmission
Balance on down-link power drifting
Compressed Mode Control
UTRAN I nterfaces Protocols and Functions
Iu Interface
Iur Interface
Iub Interface
Uu Interface
Uu I nterface Protocol Stack Structure
L3
c
o
n
t
r
o
l
c
o
n
t
r
o
l
c
o
n
t
r
o
l
c
o
n
t
r
o
l
Logical
Channels
Transport
Channels
C-plane signalling
U-plane information
PHY
L2/MAC
L1
RLC
DC
Nt
GC
L2/RLC
MAC
RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
RLC
Duplication avoidance
UuS boundary
BMC
L2/BMC
RRC
control
PDCP
PDCP L2/PDCP
DC
Nt
GC
Uu I nterface
Channel Structure
Physical Channel
Transport Channel
Logical Channel
Physical Channel Structure
Dedicated Physical Channel
DPDCH: Dedicated Physical Data Channel
DPCCH: Dedicated Physical Control Channel
Common Physical Channel
Uplink:
PRACH: Physical Random Access Channel
PCPCH: Physical Common Packet Channel
Downlink:
CCPCH: Common Control Physical Channel
SCH: Synchronization Packet Channel
PDSCH: Physical Downlink Shared Channel
PICH: Paging Indicator Channel
CPICH: Common Pilot Channel
Transport Channel Structure
Dedicated Transport Channel
DCH
Common Transport Channel
BCH: Broadcast Channel(Downlink)
PCH: Paging Channel(Downlink)
FACH: Forward Access Channel(Downlink)
RACH: Random Access Channel(Uplink)
CPCH: Common Packet Channel(Uplink, Optional)
DSCH: Downlink Shared Channel(Downlink, Optional)
Transport/Physical Channel Mapping
Transport Channels
DCH
RACH
CPCH
BCH
FACH
PCH
DSCH
Physical Channels
Dedicated Physical Data Channel (DPDCH)
Dedicated Physical Control Channel (DPCCH)
Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH)
Physical Common Packet Channel (PCPCH)
Common Pilot Channel (CPICH)
Primary Common Control Physical Channel (P-CCPCH)
Secondary Common Control Physical Channel (S-CCPCH)
Synchronisation Channel (SCH)
Physical Downlink Shared Channel (PDSCH)
Acquisition Indicator Channel (AICH)
Access Preamble Acquisition Indicator Channel (AP-AICH)
Paging Indicator Channel (PICH)
CPCH Status Indicator Channel (CSICH)
Collision-Detection/Channel-Assignment Indicator
Channel (CD/CA-ICH)
Logical Channel Structure
Control Channels
BCCH: Broadcast Control Channel
PCCH: Paging Control Channel(Downlink)
DCCH: Dedicated Control Channel(bi-directional)
Traffic Channels
CCCH: Common Control Channel(bi-directional)
DTCH: Dedicated Traffic Channel(bi-directional)
CTCH: Common Traffic Channel(Downlink)
Logical/Transport Channel Mapping
BCH
PCH
DSCH FACH RACH DCH
BCCH-
SAP
DCCH-
SAP
CCCH-
SAP
PCCH-
SAP
DTCH-
SAP
Transport
Channels
MAC SAPs
FAUSCH USCH
(TDD only)
CPCH
(FDD only)
CTCH-
SAP
SHCCH-
SAP
(TDD only)
Uu I nterface Protocol
L3: Network Layer
RRC: Radio Resource Control
L2: Data Link Layer
PDCP: Packet Data Convergence Protocol
RLC: Radio Link Control Protocol
MAC: Medium Access Control Protocol
BMC: Broadcast/Multicast Control
L1: Physical Layer
Uu Interface L1 Functions(1)
Multiplexing of transport channels and de-multiplexing
of encoded composite channels
Mapping of encoded composite transport channels on
physical channels
Macro-diversity distribution/combining and soft
handover execution
Error detection on transport channels and indication to
higher layers
FEC encoding/decoding and interleaving/de-interleaving
of transport channels
Rate matching of coded transport channels to physical
channels
Uu I nterface L1 Functions(2)
closed-loop power control
open-loop power control
Modulation and spreading/demodulation and de-spreading
of physical channels
Synchronization between frequency and time (chip, bit,
slot, frame)
Radio characters measurements (FER, SIR, Interference
power) and indication to higher layers
Compressed mode support
Diversity of Transmission/Receiving
Course Contents
Chapter 1 WCDMA System
Chapter 2 WCDMA Services
Chapter 3 WCDMA System Structure
Chapter 4 WCDMA RAN Interface & Procedure
Chapter 5 WCDMA Basic Signaling Flow
BASIC SIGNALING PROCEDURES
We have two stratum signaling procedures:
Access stratum: such as RRC( radio resource control)
&RANAP( radio access network application protocol)
layers refer to the procedures of which radio access
stratum equipment such as RNC &NodeB.
Non-access stratum: refer to the procedure in which
only UE &CN participate. The UE may operates in
one or two modes: Idle mode & Connected mode.
After being switched on the UE operates in Idle
mode and is identified as non-access stratum such as
IMSI, TMSI or P-TMSI. UTRAN doesnt save the
information of the UE in this mode.
After establishing an RRC connection the UE shifts
from the idle mode to the connected mode,
UMTS Architecture
Uu lu
USIM
ME
Cu
Node B
Node B
Node B
Node B
RNC
RNC
lub lur
MSC/
VLR
GMSC
SGSN GGSN
HLR
PLMN PSTN
ISDN,etc
INTERNET
External Networks
CN
UTRAN
UE
UMTS Network Elements Structure
Radio resource management procedures:
RRC connection setup procedure: each UE has
one RRC connection only. When the non
access layer of the UE requests to establish
a signaling connection in the idle mode the UE
will initiate the RRC connection.
Signaling setup procedure: after the RRC
connection between the UE and the UTRAN
is successfully setup the UE sets up signaling
connection with the CN via the RNC .
RAB establishment: Radio Access Bearer refers to
the user plane bearer that is used to transfer voice,
data &multimedia services between UE &CN.
Call release procedure: is a procedure that the RRC
connection release procedure it falls into two types:
UE initiated release &CN initiated release. The
difference between the two release types lies in who
sends the call release request message of the upper
layer first, though the final resource release is
initiated by the CN.
Hand over procedure: when the cell or the mode
(TDD/FDD) used by the UE changes.
SRNS (serving radio network subsystem): the RNC
relocation refers to that the SRNC of the UE
changes from one RNC to another RNC, it is divided
into two cases based on UE location at the time of
relocation: static relocation (UE not involved) &
associated relocation (UE involved).
Call overall Procedures
Network side Start
1Initialize equipment
2Process system
broadcast
Step 1
Handset Power on
1cell reselection
2Location registration
3Waiting for call
Step 2
Paging UE
Step 3
RRC connection
Establish
Step 4
NAS signaling
connection establish
Step 5
RAB set up
1synchronous set up
2asynchronous set up
Step 6
RAB/RB modification
Step 6
Transport channel
reconfiguration
Step 6
Physical channel
reconfiguration
Step 6
Soft/hard handover
Step 6
URA update
Step 6
Cell update
Step 6
Handover with GSM
Step 7
RRC connection
release
Step 8
Waiting for call again
1cell selection
2wait for call
Originating Call Procedure (1)
Downlink Synchronisation
UE
Node B
Serving RNS
Serving
RNC
DCH-FP
DCH-FP
RRC RRC
CCCH: RRC Connection Request
NBAP
Radio Link Setup Response
NBAP
NBAP
Radio Link Setup Request
CCCH: RRC Connection Setup
Start RX
Start TX
RRC
RLC
RRC
DCCH : RRC Connection Setup Complete
DCH-FP DCH-FP
Uplink Synchronisation
NBAP
Q.AAL2 Q.AAL2
Q.AAL2
Establish Request
Establish Confirm
Inital Direct Transfer
CN
DCCH:
RRC
RLC
RRC
RRC
RRC
Q.AAL2
DCCH : RRC Connection Setup Complete ack
Inital Direct Transfer
Originating Call Procedure (2)
Inital Direct Transfer
RRC
RANAP RANAP
UE
Node B
Serving RNS
Serving
RNC CN
Initial UE Message
RANAP RANAP
DCCH
Direct Transfer
RANAP
RANAP
Direct Transfer
:
Direct Transfer DCCH
::
Direct Transfer DCCH ::
RRC
Downlink
RRC
RRC
Uplink
RRC
RRC
RRC
(CM Service Request)
(CM Service Accept)
(Setup)
DCCH
:
DCCH
:
Downlink
Uplink
Direct Transfer
Direct Transfer
RRC RRC
RRC
RRC
RRC
RANAP
RANAP
Direct Transfer
(Call Proceeding)
Inital Direct Transfer
Originating Call Procedure (3)
UE
Node B
Serving RNS
Serving
RNC CN
DCCH
:
DCCH
:
Downlink
Uplink
Direct Transfer
Direct Transfer
RRC RRC
RRC
RRC
RRC
RAB Assignment Request
RANAP
RANAP
Establishment (
)
Q.AAL2 Q.AAL2
Q.AAL2
Establish Request
Establish Confirm
Q.AAL2
NBAP
Prepare
NBAP
Radio Link Reconfiguration
NBAP
Radio Link Reconfiguration
NBAP
Ready
Originating Call Procedure (4)
UE
Node B
Serving RNS
Serving
RNC
CN
DCCH : Radio Bearer Setup
DCCH : Radio Bearer Setup Complete
Q.AAL2 Q.AAL2
Q.AAL2
Establish Request
Establish Confirm
Q.AAL2
Downlink Synchronisation
Uplink Synchronisation
Radio Link Reconfiguration
NBAP
NBAP
NBAP
NBAP
NBAP
NBAP
Apply new transport format set
RRC
RRC
RRC
RRC
RAB Assignment Response
RANAP
RANAP
Establishment ( )
Commi t
DCCH : Radio Bearer Setup Complete ack
RLC
RLC
Originating Call Procedure (5)
UE
Node B
Serving RNS
Serving
RNC
CN
RRC
RANAP
RANAP
Direct Transfer
RRC
RANAP
RANAP
Direct Transfer
(Alerting)
(Connect)
RRC
RRC
RANAP
RANAP
Direct Transfer
(Connect Acknowledge)
RRC
RANAP
RANAP
Direct Transfer
(Rlease Complete)
RANAP
RANAP Direct Transfer
(Release)
RANAP RANAP
Direct Transfer
(Disconnect)
RRC
DCCH::
DCCH ::
Downlink
Uplink
Direct Transfer
Direct Transfer
RRC
RRC
DCCH
::
Downlink
DCCH::
Downlink
Direct Transfer
RRC
DCCH :: Uplink
RRC
Direct Transfer
Direct Transfer
RRC
DCCH :: Uplink
Direct Transfer
RRC
Originating Call Procedure (6)
UE
Node B
Serving RNS
Serving
RNC
CN
RANAP RANAP
RANAP RANAP
Iu Release Command
Iu Release Complete
Q.AAL2 Q.AAL2
Q.AAL2 Q.AAL2
Release Request
Release Complete
Q.AAL2
Q.AAL2
Q.AAL2 Q.AAL2
Release Request
Release Complete
DCCH : RRC Connection
DCCH : RRC Connection
Release
ReleaseComplete
NBAP
Radio Link Deletion
NBAP
Radio LinkDeletion
NBAP
NBAP
Complete
Soft Handover Illustration (Intra RNC)
Before Soft Handover
After Soft Handover
CN
SRNC
NodeB NodeB
CN
SRNC
NodeB NodeB
CN
SRNC
NodeB NodeB
During Soft Handover
Soft Handover Flow (I ntra RNC add branch)
Decision to setup
new RL
7. DCCH : Active Set Update Complete
6.DCCH: Active Set Update Command
UE Node B(new) SRNC
NBAP
1. Radio Link Setup Request
NBAP
NBAP
2. Radio Link Setup Response
NBAP
3 ALCAP Iub Data Transport Bearer Setup
Start RX description
DCH-FP
4. Downlink Synchronization
DCH-FP
DCH-FP
5.Uplink Synchronization
DCH-FP
Start RX description
RRC
RRC
RRC
RRC
Soft Handover Flow (I ntra-RNC delete branch)
Decision to delete
a RL
2. DCCH : Active Set Update Complete
1.DCCH: Active Set Update Command
UE Node B(old) SRNC
NBAP
3. Radio Link Deletion Request
NBAP
NBAP
4. Radio Link Deletion Response
NBAP
RRC
RRC
RRC
RRC
Stop RX and Tx
5 ALCAP Iub Transport Bearer release
Soft Handover I llustration (I nter-RNC)
Before Soft Handover
After Soft Handover
Radio Link(RL) is added and deleted simultaneously
CN
SRNC
RNC
NodeB
NodeB NodeB
CN
SRNC
RNC
NodeB
NodeB NodeB
Soft Handover Flow (I nter-RNC)
7. Uplink Synchronization
RNSAP RNSAP
1. Radio Link Setup Request
Start TX description
RNSAP RNSAP
4. Radio Link Setup
Response
NBAP
NBAP
2. Radio Link Setup Request
NBAP NBAP
3. Radio Link Setup Response
Start RX description
Decision to setup
new RL and
release old RL
NBAP
10. Radio Link Deletion Request
NBAP
NBAP
11. Radio Link Release Response
Stop RX and TX
12. ALCAP Iub Data Transport Bearer Release
RRC RRC
9. DCCH : Active Set Update Complete
RRC RRC
8. DCCH: Active Set Update Command
[Radio Link Addition & Deletion]
NBAP
UE
Node B
Drift RNS
Node B
Serving RNS
Drift RNC Serving RNC
ALCAP Iur Bearer Setup 5. ALCAP Iub Data Transport Bearer Setup
DCH-FP
DCH-FP
DCH-FP
DCH-FP
6. Downlink Synchronization
THANK YOU
Done By: UAE TSD Department
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Residential Tenancy Agreement (RTB - 1)Documento6 pagineResidential Tenancy Agreement (RTB - 1)masudrana7300Nessuna valutazione finora
- LTE SignalingDocumento2 pagineLTE SignalingTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cover Letter SamplesDocumento4 pagineCover Letter Samplescarval21Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple PDFDocumento2 pagineA Simple PDFJaheer MakalNessuna valutazione finora
- PPC TimDocumento1 paginaPPC TimTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- English SentencesDocumento1 paginaEnglish SentencesTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Select Type From Where Order BY: 'September 14,1994'Documento1 paginaSelect Type From Where Order BY: 'September 14,1994'Tariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Residential Tenancy Agreement (RTB - 1)Documento6 pagineResidential Tenancy Agreement (RTB - 1)masudrana7300Nessuna valutazione finora
- Places To VisitDocumento1 paginaPlaces To VisitTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical LayerDocumento1 paginaPhysical LayerTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- MataDocumento1 paginaMataTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- UL ChannelsDocumento1 paginaUL ChannelsTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Initiating, - Planning, - Executing, - Monitoring and Controlling, and - ClosingDocumento1 paginaInitiating, - Planning, - Executing, - Monitoring and Controlling, and - ClosingTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- English SentencesDocumento1 paginaEnglish SentencesTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Enodeb Starts Another Timer ToDocumento1 paginaThe Enodeb Starts Another Timer ToTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- PPC TimDocumento1 paginaPPC TimTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Tranmission and ReceptionDocumento2 pagineData Tranmission and ReceptionTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Signaling Type As Signaling Is Between Ue and Enodeb (System Information Masseges) Nas Signaling Between Ue and Mme (Tracking Area Update)Documento2 pagineSignaling Type As Signaling Is Between Ue and Enodeb (System Information Masseges) Nas Signaling Between Ue and Mme (Tracking Area Update)Tariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1coverage Kpis: 1.1 Class B - Ul Interference Cell RatioDocumento46 pagine1coverage Kpis: 1.1 Class B - Ul Interference Cell RatioTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 Class A - Radio Access Success Ratio: Associated Counters NotesDocumento44 pagine1.1 Class A - Radio Access Success Ratio: Associated Counters NotesTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical LayerDocumento1 paginaPhysical LayerTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- RrcConnStateTimer.T302 and related timersDocumento1 paginaRrcConnStateTimer.T302 and related timersTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE SignalingDocumento2 pagineLTE SignalingTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1coverage Kpis: 1.1 Class B - Ul Interference Cell RatioDocumento46 pagine1coverage Kpis: 1.1 Class B - Ul Interference Cell RatioTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- I DT There Are Many OptionDocumento1 paginaI DT There Are Many OptionTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Redirretcion 2Documento1 paginaRedirretcion 2Tariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- 11222Documento248 pagine11222Tariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- In Soft HandoverDocumento1 paginaIn Soft HandoverTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- I DT There Are Many Option To UseDocumento1 paginaI DT There Are Many Option To UseTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- I DT There Are Many Option To UseDocumento1 paginaI DT There Are Many Option To UseTariq MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)