Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Cogeneration Plant
Caricato da
Krushnasamy SuramaniyanDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cogeneration Plant
Caricato da
Krushnasamy SuramaniyanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Cogeneration
INTRODUCTION:
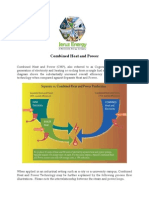
Cogeneration, also known as Combined Heat
and Power, or CHP, is the production of
electricity and heat in one single process for
dual output streams.
Cogeneration also helps save energy costs,
improves energy security of supply, and
creates jobs. It is the most efficient way to
use fuel.
Key points
The heat produced by cogeneration can be delivered
through various mediums, including warm water (e.g., for
space heating and hot water systems), steam or hot air
(e.g., for commercial and industrial uses).
It is also possible to do trigeneration, the production of
electricity, heat and cooling
(through an absorption chiller) in one single process.
Trigeneration:
Trigeneration is an attractive
option in situations where all
three needs exist, such as in
production processes with
cooling requirements.
Scope of Co generation:
In recent years cogeneration has become an attractive and
practical proposition for a wide range of applications.
These include the process industries
pharmaceuticals,
Paper and board,
brewing,
ceramics, brick, cement, food, textile, minerals etc.),
Commercial sector
Commercial and public sector buildings
Hotel
Hospitals,
Leisure centers ,
Swimming pools,
Universities,
Airports,
Offices,
Barracks, etc.
and district heating schemes.
COGENERATION TYPES
Topping System
Electricity is produced first and
the thermal
energy exhausted is captured for
further use
in the process
Bottoming System
Usable thermal energy is extracted from a
waste stream (after it has been used in a
process) to produce power, usually for
driving a turbine to generate electricity
Bottoming System
In a bottoming cycle, the primary fuel
produces high temperature thermal
energy and the heat rejected from the
process is used to generate power
through a recovery boiler and a turbine
generator
`
To evaluate cogeneration
For an economical evaluation of co gen.
plant some thermodynamically related
quantities are required
Net power output
Heat load
Net electrical efficiency
Fuel utilization
Net power output
The net power output is the
amount of power that can be
delivered from power plant.
This quantity is equal to
difference between total
generated power and plant
internal consumption of power
Heat load
The heat load is the amount of net useful
heat extracted to an external process from
the plant which is
Q =m (H out-H in )
H out =Energy of steam supplied to external process
H in =Enthalpy of return steam or condensate from
external process
Net Electrical efficiency
The ratio between the net
power output and fuel
energy input both for gas
turbine and supplementary
burner based on the lower
heating value
Fuel Utilization
Ratio between total useful energy output
from plant and total energy input based
on lower heating value it can be denoted
as combined heat and power (CHP)
Efficiencies of Generation
Cycles
Type of Generation Efficiency
Thermal Plants (Coal Based) 30 to 40%
Thermal Plants (Gas Turbine) 25 to 30%
Combined Cycle 55 to 60%
Co Generation 60 to 70%
Advantages of Co-gen in the present
Power Sector Scenario
Act as a Booster station
Self reliance
It can maintain grid stability
Pollution reduction & Environnemental
friendly
Helps to meet the national target of 10%
of power
It offers cheap power in the long term
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- TRIGENERATIONDocumento21 pagineTRIGENERATIONShreyas Saumitra100% (1)
- Combined Heat and PowerDocumento8 pagineCombined Heat and Powerawhk2006Nessuna valutazione finora
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP)Documento2 pagineCombined Heat and Power (CHP)الحمد لله100% (1)
- A Case Study On Thermodynamic Analysis of Cogeneration Power Plant (IRJET-V2I9163)Documento5 pagineA Case Study On Thermodynamic Analysis of Cogeneration Power Plant (IRJET-V2I9163)luis hyungNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermodynamicsDocumento26 pagineThermodynamicsManikanta Reddy100% (1)
- Micro Gas Turbine TechnologyDocumento69 pagineMicro Gas Turbine TechnologyJayaAmirthavarshini100% (1)
- Powr PlantDocumento10 paginePowr PlantSajjad Ibraheem100% (1)
- Gas Turbine Power PlantDocumento48 pagineGas Turbine Power PlantArif Ahmed100% (1)
- Economic Dispatch Power SystemDocumento36 pagineEconomic Dispatch Power SystemBanan Al BarghouthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Adiabatic Flame TemperatureDocumento5 pagineAdiabatic Flame TemperatureRaghav SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Turbine Tutorial Part 1: Brayton Cycle AnalysisDocumento4 pagineGas Turbine Tutorial Part 1: Brayton Cycle AnalysisGulain MayomboNessuna valutazione finora
- Grand Composite Curve (GCC) - Heat PumpDocumento4 pagineGrand Composite Curve (GCC) - Heat PumpMuhammad IqmalNessuna valutazione finora
- Cogeneration ApplicationsDocumento46 pagineCogeneration ApplicationsEngSafwanQadousNessuna valutazione finora
- Power StationDocumento10 paginePower Stationletter_ashish4444Nessuna valutazione finora
- CCHP Presentation AnalysisDocumento35 pagineCCHP Presentation AnalysisAmit BharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Plant EfficiencyDocumento5 paginePower Plant EfficiencyMadhu BNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Cycle, Oil, Coal and Natural Gas Introduction To The Rankine Steam Cycle and Carnot EfficiencyDocumento69 paginePower Cycle, Oil, Coal and Natural Gas Introduction To The Rankine Steam Cycle and Carnot EfficiencyLenin PaudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Turbine Thermal Power PlantDocumento7 pagineGas Turbine Thermal Power PlantAkshay ManzaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHP Feasibility Software PackagesDocumento7 pagineCHP Feasibility Software PackagessunatrutgersNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion Engines GuideDocumento16 pagineInternal Combustion Engines GuideAshton SelokaNessuna valutazione finora
- MEC551 Assignment - Design September 2015Documento7 pagineMEC551 Assignment - Design September 2015SyafiqAsyrafNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.1.prob - Sheet Gas Power CyclesDocumento3 pagine7.1.prob - Sheet Gas Power CyclesAnonymous mXicTi8hB0% (1)
- Biaya PembangkitanDocumento28 pagineBiaya PembangkitanblackzenyNessuna valutazione finora
- Psoc 0Documento60 paginePsoc 0Santosh ThapaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE2451 EEGUC Hand WrittenDocumento256 pagineEE2451 EEGUC Hand Writtensrivaas131985100% (1)
- Joule Brayton CycleDocumento12 pagineJoule Brayton CyclecaptfoleyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 210 Midterm Exam SolutionsDocumento11 pagineCHE 210 Midterm Exam SolutionsJaspreet SandhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimal Rotor Tip Speed RatioDocumento10 pagineOptimal Rotor Tip Speed RatioHaposan YogaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Concept of Exergy and Energy Quality - Truls GundersenDocumento26 pagineThe Concept of Exergy and Energy Quality - Truls Gundersenuser_account100% (1)
- Unit Commitment ProblemDocumento13 pagineUnit Commitment ProblemTanishqNessuna valutazione finora
- Formulas BoilerDocumento0 pagineFormulas BoilerJopha S Deva100% (1)
- 08 Laminar Forced Convection Over A Heated Flat PlateDocumento27 pagine08 Laminar Forced Convection Over A Heated Flat PlatecesariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar: Fuel Cell (Working, Principle, Types & Application)Documento16 pagineSeminar: Fuel Cell (Working, Principle, Types & Application)vishnu chaudhary100% (1)
- TP CFB 12 03Documento16 pagineTP CFB 12 03Harish MechNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Internal Combustion Engines 1Documento8 pagineAdvanced Internal Combustion Engines 1Veera Pratap ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel CellsDocumento6 pagineFuel CellsJayan PillaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost Rate CurvesDocumento27 pagineCost Rate CurvesThiện VươngNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Steam and Combined CyclesDocumento84 pagineGas Steam and Combined CyclesJane SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Introduction To PPE: A) Power GenerationDocumento55 pagineUnit 1: Introduction To PPE: A) Power GenerationArun PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal Combustion Engine TypesDocumento35 pagineInternal Combustion Engine TypesMuhammad FaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Vapor Power CyclesDocumento8 pagineVapor Power CyclesGürel ÖzeşmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ideal Regenerative Rankine Cycle - Closed Feedwater Heaters: Thermodynamics - IIDocumento10 pagineIdeal Regenerative Rankine Cycle - Closed Feedwater Heaters: Thermodynamics - IIsamhameed2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 28 Modeling of GTDocumento59 pagineLecture 28 Modeling of GTCindy CarvalhoNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Review of Thermodynamics, Fluid Flow and Heat TransferDocumento7 pagineME 5129 - Principles of Thermal Energy Conversion: Review of Thermodynamics, Fluid Flow and Heat TransferAnandNessuna valutazione finora
- The ENER-G Quality CHP Plan How To Calculate Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Economic Feasibility With Load Profiling PDFDocumento23 pagineThe ENER-G Quality CHP Plan How To Calculate Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Economic Feasibility With Load Profiling PDF3238NDNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Power PlantDocumento139 pagineThermal Power PlantSadiq AntuNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITDocumento47 pagineGas Power Cycles Sivakumar.E VITmohan govindasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimum Pressure Ratio Gas Turbine CycleDocumento12 pagineOptimum Pressure Ratio Gas Turbine CycleJoseph Samir FaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Thermodynamics - Problems and Solutions, Chapter-9Documento20 pagineEngineering Thermodynamics - Problems and Solutions, Chapter-9ZelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 Exergy Analysis of Cogeneration and District Energy Systems 2013 Exergy Second EditionDocumento15 pagineChapter 13 Exergy Analysis of Cogeneration and District Energy Systems 2013 Exergy Second EditionAnonymous dUXvWL61Nessuna valutazione finora
- Concepts of ThermodynamicsDocumento41 pagineConcepts of ThermodynamicsMichael ElliottNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 Report ThermodynamicsDocumento9 pagineLab 2 Report ThermodynamicsOse Colix Jr.100% (1)
- To Improve Thermal Efficiency of 27mw CoDocumento24 pagineTo Improve Thermal Efficiency of 27mw Codixie0630Nessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No.:-3 TITLE: Study of Co-Generation Power Plant AIM: Study of Co-Generation Power Plant TheoryDocumento10 pagineExperiment No.:-3 TITLE: Study of Co-Generation Power Plant AIM: Study of Co-Generation Power Plant Theory9527530909100% (1)
- 7 Lecture (Heat Rate, Cogeneration)Documento12 pagine7 Lecture (Heat Rate, Cogeneration)Ali Haider RizviNessuna valutazione finora
- Reliable Systems and Combined Heat and Power: BstractDocumento6 pagineReliable Systems and Combined Heat and Power: BstractLuis Felipe ZuñigaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment No 4: Power PlantDocumento5 pagineAssignment No 4: Power PlantusamaNessuna valutazione finora
- CogenerationDocumento53 pagineCogenerationSri Ch.V.Krishna Reddy Assistant Professor (Sr,)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jenbacher Gasm BHKW enDocumento28 pagineJenbacher Gasm BHKW ensaniterm100% (1)
- A. 2730 B. 1650 C. 3099 D. 3730 Answer: A. 2730: Solution: Codeword (Vin X 4095) / Vref (2.2 X 4095) /3.3 2730Documento2 pagineA. 2730 B. 1650 C. 3099 D. 3730 Answer: A. 2730: Solution: Codeword (Vin X 4095) / Vref (2.2 X 4095) /3.3 2730Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design For Iot: NOTES - Week 6Documento18 pagineDesign For Iot: NOTES - Week 6Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH 233 - Linear Algebra I Lecture Notes: Cesar O. AguilarDocumento206 pagineMATH 233 - Linear Algebra I Lecture Notes: Cesar O. AguilarKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Robot End Effectors: DR V S KrushnasamyDocumento48 pagineRobot End Effectors: DR V S KrushnasamyKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes - 5Documento133 pagineLecture Notes - 5Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- 18ei7deran-Cie2 Answer KeyDocumento4 pagine18ei7deran-Cie2 Answer KeyKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Linear AlgebraDocumento395 pagineLinear AlgebraAbhisek Datta67% (3)
- C. ISO/IEC 15693Documento2 pagineC. ISO/IEC 15693Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1 AnswersDocumento2 pagineWeek 1 AnswersKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes in Linear Algebra: Dr. Abdullah Al-AzemiDocumento149 pagineLecture Notes in Linear Algebra: Dr. Abdullah Al-AzemiKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Microelectronic Fabrication: DiffusionDocumento47 pagineIntroduction To Microelectronic Fabrication: DiffusionKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- (NPTEL Course) Applied Linear Algebra Assignment 1Documento6 pagine(NPTEL Course) Applied Linear Algebra Assignment 1Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- USN Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering Robotics and Automation Answer KeyDocumento8 pagineUSN Dayananda Sagar College of Engineering Robotics and Automation Answer KeyKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering Continuous Internal Evaluation - 1Documento2 pagineDepartment of Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering Continuous Internal Evaluation - 1Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key - CIE1Documento10 pagineAnswer Key - CIE1Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key - CIE2Documento8 pagineAnswer Key - CIE2Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- (An Autonomous Institute Affiliated To Vtu, Belagavi) : Shavigemalleshwara Hills, Kumaraswamy Layout, Bengaluru-560078Documento3 pagine(An Autonomous Institute Affiliated To Vtu, Belagavi) : Shavigemalleshwara Hills, Kumaraswamy Layout, Bengaluru-560078Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- QP - Control System Assignment 2021-22Documento3 pagineQP - Control System Assignment 2021-22Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Response Analysis ModuleDocumento69 pagineTime Response Analysis ModuleKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Root Locus Technique Hand Written - Basic IdeaDocumento10 pagineRoot Locus Technique Hand Written - Basic IdeaKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- NEP Final For Circulation PDFDocumento60 pagineNEP Final For Circulation PDFNaren SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Root Locus Technique - Module IIIDocumento72 pagineRoot Locus Technique - Module IIIKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Himanshu Shekhar ProfileDocumento1 paginaHimanshu Shekhar ProfileKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Frequency Response Analysis - 1Documento33 pagineModule 4 Frequency Response Analysis - 1Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- New Education Policy 2020 PPT AarohanDocumento17 pagineNew Education Policy 2020 PPT AarohanKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Robot Programming - PART2Documento49 pagineRobot Programming - PART2Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 4 Frequency Response Analysis - 2Documento16 pagineModule 4 Frequency Response Analysis - 2Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Career OptionsDocumento31 pagineSeminar Career OptionsKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Instrumentation in Water Industries - VipulDocumento28 pagineApplication of Instrumentation in Water Industries - VipulKrushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Robot Programming - PART1Documento48 pagineRobot Programming - PART1Krushnasamy SuramaniyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials I: Lecture Course 5 Phase Diagrams. Fe-C Diagram. Crystallisation of Alloys in Fe - Fe C SystemDocumento24 pagineMaterials I: Lecture Course 5 Phase Diagrams. Fe-C Diagram. Crystallisation of Alloys in Fe - Fe C SystemTiger ClaudiuNessuna valutazione finora
- CAD/CAM Geometric Modelling RepresentationsDocumento34 pagineCAD/CAM Geometric Modelling Representationsshantikiran shantikiranNessuna valutazione finora
- cO2CH4 Permselective GassensorDocumento5 paginecO2CH4 Permselective GassensorKartik RamasubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- DPP-1 QuantizationDocumento1 paginaDPP-1 QuantizationVikasNessuna valutazione finora
- ES 15 Lec 9 Dimensional Analysis and SimilitudeDocumento28 pagineES 15 Lec 9 Dimensional Analysis and SimilitudeAngela Mae LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Jaulas de Agujas PDFDocumento52 pagine02 Jaulas de Agujas PDFRodrigo Schaider Dos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- E-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)Documento3 pagineE-CAPS-28 - For CoE (XI) - Chemistry - (Que. - Answer Key)darling deanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of the Pickett Plot: Recognizing Reservoir PatternsDocumento9 pagineFundamentals of the Pickett Plot: Recognizing Reservoir PatternsAngelMeso100% (1)
- Measuring Elastic Modulus of Beams Using Deflection MethodDocumento14 pagineMeasuring Elastic Modulus of Beams Using Deflection MethodHaziq PazliNessuna valutazione finora
- Phased Array Probes and Wedges: Probe CatalogDocumento3 paginePhased Array Probes and Wedges: Probe CatalogDavidMontillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Weather in Kuttiadi - Google SearchDocumento1 paginaWeather in Kuttiadi - Google Searchsorry Its My StyleNessuna valutazione finora
- HotelSolution: Induction Units VS Fan-Coil SolutionDocumento1 paginaHotelSolution: Induction Units VS Fan-Coil SolutionMoriyasu NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Fourier Transform and Its Medical ApplicationDocumento55 pagineFourier Transform and Its Medical Applicationadriveros100% (1)
- Lab 3 - Intro To DynamicDocumento36 pagineLab 3 - Intro To DynamicRacheal KirbyNessuna valutazione finora
- CHY382-01 Ester Hydrolysis Lab ReportDocumento5 pagineCHY382-01 Ester Hydrolysis Lab ReportJoshua AunNessuna valutazione finora
- TCL Air Conditioner Service ManualDocumento138 pagineTCL Air Conditioner Service ManualFabian EtcheniqueNessuna valutazione finora
- HW1Documento8 pagineHW1Anonymous fXSlye100% (1)
- WISDM-dataset-description 2Documento5 pagineWISDM-dataset-description 2yuliasihkripsianditaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Second Term Exam of EnglishDocumento2 pagineThe Second Term Exam of Englishsof chimiste100% (1)
- Laws of Motion All DerivationsDocumento13 pagineLaws of Motion All DerivationsYashwanthiNessuna valutazione finora
- McCabe-Thiele Diagrams For Binary DistillationDocumento8 pagineMcCabe-Thiele Diagrams For Binary DistillationwetcoNessuna valutazione finora
- AP PHYSICS B 1988 MC + AnswersDocumento17 pagineAP PHYSICS B 1988 MC + AnswersbastardNessuna valutazione finora
- DWC ElecConduit Is 16205 P24 2018Documento11 pagineDWC ElecConduit Is 16205 P24 2018Vamsi Manoj60% (5)
- Rocket PropulsionDocumento41 pagineRocket PropulsionV DhinakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- GEAS 1 - Chemistry - 2Documento4 pagineGEAS 1 - Chemistry - 2Leoneil Angelo AbreuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonnewtonian and Newtonian Blood Flow in Human Aorta A Transient AnalysisDocumento10 pagineNonnewtonian and Newtonian Blood Flow in Human Aorta A Transient AnalysisDivyaVatsNessuna valutazione finora
- Vector CalculusDocumento62 pagineVector CalculuswaleedNessuna valutazione finora
- 2oo3plus - A New Design of Electro-Hydraulic Safety Controls For Critical ApplicationsDocumento6 pagine2oo3plus - A New Design of Electro-Hydraulic Safety Controls For Critical Applicationsultrasonic81Nessuna valutazione finora
- Background Glass - Part-2 - Plate CalculationDocumento16 pagineBackground Glass - Part-2 - Plate CalculationusonNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm F1717-21Documento11 pagineAstm F1717-21wenhsiaochuanNessuna valutazione finora