Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
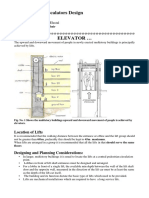
Elevators: Kinds, Functions, Mechanisms
Caricato da
Trehmani0010 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
68 visualizzazioni26 pagineElevators: Kinds, Functions, Mechanisms!
Note: Most of the pictures and data is taken from educational websites. If you are planning on to use these pictures and data, please cite it properly, and give credit to the websites and people who have designed it. I should have cited it as well, but I did not as I compiled it last year only for self learning purposes. I am making it available solely for the learning purpose. No Copyrights issues!
For animations: Please see how stuff works for elevators!
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoElevators: Kinds, Functions, Mechanisms!
Note: Most of the pictures and data is taken from educational websites. If you are planning on to use these pictures and data, please cite it properly, and give credit to the websites and people who have designed it. I should have cited it as well, but I did not as I compiled it last year only for self learning purposes. I am making it available solely for the learning purpose. No Copyrights issues!
For animations: Please see how stuff works for elevators!
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
68 visualizzazioni26 pagineElevators: Kinds, Functions, Mechanisms
Caricato da
Trehmani001Elevators: Kinds, Functions, Mechanisms!
Note: Most of the pictures and data is taken from educational websites. If you are planning on to use these pictures and data, please cite it properly, and give credit to the websites and people who have designed it. I should have cited it as well, but I did not as I compiled it last year only for self learning purposes. I am making it available solely for the learning purpose. No Copyrights issues!
For animations: Please see how stuff works for elevators!
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPTX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 26
Elevators
Functions & Mechanisms
Outline
Definition
Major Elevator Designs
Hydraulic Elevator System
Roped Elevator System
MRL
Definition
Compartment attached to a rope
Modern Passenger & Freight Elevators are more complex
Mechanical Systems
Control Mechanism
Safety Devices
Major Elevator Designs
Three Major designs are:
Hydraulic Elevator
Traction (Roped) Elevators
Machine room less
Hydraulic Elevator System
Lift car using a Hydraulic ram
The system has three main parts:
Tank (fluid reservoir)
Rotary Pump (powered by Electric Motor)
Valve (Between Cylinder & Tank)
Direct acting plunger or roped
Hydraulic Elevator System: Operations
Hydraulic Elevator System: Operations
Car Approached Floor:
Control System (CS) sends signal to Electric Motor (EM) To
gradually shut the pump
Pump off: No more fluid to cylinder
The fluid already in the cylinder can not escape as Valve is still
closed
Piston rests on fluid and stays where it is
To Lower Car:
CS sends signal to Valve
Fluid can flow to tank
Weight of car & cargo pushes down on piston: car descends
To stop car at any floor, CS closes the valve
Hydraulic Elevator System: Pros &
Cons
Pros
Easily multiply the relatively weak force of the pump to
generate stronger force needed to lift the car
Cons
Size of Equipment
Dig Deeper: 10 story building, dig at least 9 stories deep
Fairly inefficient: Takes lots of energy and do not reserve it, so
one have to regenerate energy on every turn
Rope Elevator System
Car is raised and lowered by Cable System
Main System Components
Control System
Electric Motor
Sheave
Traction steel ropes
Counterweight
Guide Rails
Cushion back
Rope Elevator System: Operations
Rope Elevator System: Operations
Traction steel ropes are attached to car and looped around sheave
The other end of rope is connected to a counterweight
Why CW?
To conserve energy: PE levels shift
To act as a see-saw
Sheave is connected to electric motor and it raises/descends the elevator according to
the motion of motor
Gearless Elevators: Motor rotates the sheave directly
Geared Elevators: Motor turns a gear train to rotate the sheave
Car and CW rides on guide rails along the sides of elevator shaft. No swaying back and
forth
Rope Elevator System: Gearless
Rope Elevator System: Geared
Rope Elevator System: Pros & Cons
Pros
Versatile
Efficient
More safety systems
Cons
Machine rooms must be air conditioned
Energy cost
Rope Elevator System: Comparison
Rise Limitations
300 feet (G)
Unlimited (GL)
Cost
150,000 200,000 (G)
200,000 + (GL)
Speeds
350-500 fpm (G)
500 1800+ (GL)
Safety Systems
Hollywood?
Line of Defenses
Rope System
Several length of steel material is used in each rope
Multiple ropes (between 4 & 8)
Powerful enough to deal with the weight of car and
counterweight
Safeties
Built in braking systems that can grab rail
It is activated by a governor if elevator moves too fast
Safeties: Governor System
Governor rope looped around a governor sheave
Connected to the car and another weighted sheave at
the bottom of the shaft
As car speed up so does the governor
Safeties: Governor Sheave
Mechanism
Outfitted with two hooked flyweights that pivot on pin
Flyweights can move freely back and forth & kept in
position by high tension spring
As car speed up .. Rotary movement of governor ..
Centrifugal forces moves the flyweight outwards (to the
outer edges of governor) against the spring
Flyweight hooked ends catch hold of ratchets mounted
to stationary cylinder sheave
Safeties: Governor Sheave
Mechanism
Safeties: Governor Sheave Break
Mechanism
Animation
Safeties: More Backups
Electromagnetic brakes (open position): Engages when
car stops
Automatic breaking system: Stop the car if it moves too
far, located the top and bottom
Shock Absorber System: piston mounted in oil filled
cylinder and acts as a giant cushion
Load sensors
Making Rounds?
Computer control
Buttons in car and floor
Vertical holes along the shaft (magnetic or light)
Building with many floor
Avoid reversing the elevator direction
Passenger traffic in specific times
Computer directs to the fastest elevator to desired floor
Compass (OTIS Vs. Schindler)
Automatic Doors
Machine Room Less
Reference
How stuff works?
Otis Elevators Mechanisms
Note: Most of the pictures and data is taken from
educational websites. If you are planning on to use these
pictures and data, please cite it properly, and give credit to
the websites and people who have designed it. I should
have cited it as well, but I did not as I compiled it last year
only for self learning purposes. I am making it available
solely for the learning purpose. No Copyrights issues!
Thanks!
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- How Elevators Work: Mechanisms and Major DesignsDocumento26 pagineHow Elevators Work: Mechanisms and Major DesignsTrehmani001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical Transportation SystemDocumento59 pagineVertical Transportation SystemShraddha AdhikariNessuna valutazione finora
- How Elevators Work - FinalDocumento7 pagineHow Elevators Work - Finalhitokiri_knivesNessuna valutazione finora
- So How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkDocumento12 pagineSo How Do Elevators or Lifts WorkAyesha MAhmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Week_10_Tutorial_1 - CopyDocumento12 pagineWeek_10_Tutorial_1 - CopysonukumarmarchadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cable System: Electric MotorDocumento4 pagineThe Cable System: Electric Motorgajendrabanshiwal8905Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Elevators WorkDocumento9 pagineHow Elevators WorkVishal Kumar ShawNessuna valutazione finora
- How Elevators WorkDocumento6 pagineHow Elevators WorkalvinhamNessuna valutazione finora
- How lifts work: components and systemsDocumento4 pagineHow lifts work: components and systemsmikko intalNessuna valutazione finora
- HTTP Science - Howstuffworks.com Elevator - HTM PrintableDocumento12 pagineHTTP Science - Howstuffworks.com Elevator - HTM PrintableAkhil DasariNessuna valutazione finora
- ElevatorsDocumento11 pagineElevatorsDalia M-aNessuna valutazione finora
- Lift System & EscalatorDocumento18 pagineLift System & EscalatorJamal DinNessuna valutazione finora
- High Rise Building Transportation Guide: Lifts, Escalators, ConveyorsDocumento40 pagineHigh Rise Building Transportation Guide: Lifts, Escalators, Conveyorsروسيده بت محمد سعد100% (1)
- PLC Based Elevator Model Collage Project 2006Documento4 paginePLC Based Elevator Model Collage Project 2006Pawan D BarondeNessuna valutazione finora
- ElevatorsDocumento12 pagineElevatorsAbhishek RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulic ElevatorsDocumento4 pagineHydraulic ElevatorsAshish DeotaleNessuna valutazione finora
- How The Elevator Works: by Joseph Mackay Plaxco The University of The South Sewanee, TN 37383Documento15 pagineHow The Elevator Works: by Joseph Mackay Plaxco The University of The South Sewanee, TN 37383Bharath KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- LIFTDocumento15 pagineLIFTRishabhNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical Transportation SystemDocumento14 pagineVertical Transportation Systempassionpropel100% (3)
- Vehicle AssemblyDocumento16 pagineVehicle Assemblyashishkhurana93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Gear TransmissionDocumento11 pagineAutomatic Gear TransmissionIntruder 47100% (1)
- 0709kone Article PDFDocumento8 pagine0709kone Article PDFfury7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Honda Jazz Fit 2007 To 2014 Workshop Manual PDFDocumento4.178 pagineHonda Jazz Fit 2007 To 2014 Workshop Manual PDFmyrmidon164% (11)
- Transportation System in The High Rise BuildingsDocumento24 pagineTransportation System in The High Rise Buildingsshada aidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hospital Stretcher Lift FunctionsDocumento15 pagineHospital Stretcher Lift FunctionsCharchil SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Design ELEVDocumento30 pagineDesign ELEVShiella Barroga LorenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Project ElevatorDocumento45 pagineProject ElevatorTun TunNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study KliaDocumento54 pagineCase Study KliaamirulhaziqmohamadyazidNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevators and Escalators DesignDocumento10 pagineElevators and Escalators DesignNiong DavidNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation EscalatorDocumento48 paginePresentation EscalatorFaried Putra SandiantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Assign 1Documento15 pagineAssign 1Aakarshit JainNessuna valutazione finora
- EscalatorDocumento38 pagineEscalatorDazuky UkyNessuna valutazione finora
- How Is An Elevator MadeDocumento7 pagineHow Is An Elevator MadeHyderabadReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevators and Escalators Design PDFDocumento13 pagineElevators and Escalators Design PDFAmble LamNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevators and Escalators Design PDFDocumento10 pagineElevators and Escalators Design PDFdanokrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Elevators and Escalators Design PDFDocumento10 pagineElevators and Escalators Design PDFdanokrayNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional Requirements of 8 Transportation Systems in A Building.Documento40 pagineFunctional Requirements of 8 Transportation Systems in A Building.Umar Faruq AfokeNessuna valutazione finora
- Automatic Transmission: Presented by Shiv Raj Khoja Mechanical Iv YearDocumento28 pagineAutomatic Transmission: Presented by Shiv Raj Khoja Mechanical Iv YearShiv Raj Khoja100% (1)
- AUTO TRANSMISSION SYSTEMDocumento35 pagineAUTO TRANSMISSION SYSTEMAalekh PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lift22 PDFDocumento21 pagineLift22 PDFSejal MengajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Escalator drive systems and components explainedDocumento24 pagineEscalator drive systems and components explainedWawan AriessandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Steering Mechanism Using Cut Piece Model: Supervisor: M.R Soran Saleem Student: Shkar Hussain HamadDocumento7 paginePower Steering Mechanism Using Cut Piece Model: Supervisor: M.R Soran Saleem Student: Shkar Hussain HamadShkar GalalyNessuna valutazione finora
- Main Components of A CarDocumento17 pagineMain Components of A CarSujan BanikNessuna valutazione finora
- 无机房用维护(2016 8 9)Documento33 pagine无机房用维护(2016 8 9)iyed dadaNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEVATORSDocumento24 pagineELEVATORSAyesha SiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- How The Elevator WorksDocumento15 pagineHow The Elevator WorksPandaGendutNessuna valutazione finora
- Lift System EscalatorDocumento18 pagineLift System EscalatorolomizanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Escalators ExplainedDocumento32 pagineDesign of Escalators ExplainedRonalyn CalleleroNessuna valutazione finora
- ECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.5 Lift and ElevatorDocumento5 pagineECM 216 BUILDING SERVICES Bab 2.5 Lift and ElevatorAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZINessuna valutazione finora
- Selection of Drives and Control Systems For LiftsDocumento4 pagineSelection of Drives and Control Systems For LiftsSaikat ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertical TransportationDocumento8 pagineVertical TransportationNupur BhadraNessuna valutazione finora
- LIFTDocumento28 pagineLIFTBirla RajasekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Escalators Basic ComponentsDocumento37 pagineEscalators Basic Componentsnoedita100% (3)
- Unit-5-Industrial Electrical Systems-IIDocumento12 pagineUnit-5-Industrial Electrical Systems-IIvikram patilNessuna valutazione finora
- Uromac T-Rail MV - BrochureDocumento2 pagineUromac T-Rail MV - BrochureCristiano RonaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionDa EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume Iv: Performancing the EvolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Construction and Manufacture of AutomobilesDa EverandConstruction and Manufacture of AutomobilesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- 13 Things Mentally Strong People Dont Do (Telugu) by Amy MorinDocumento256 pagine13 Things Mentally Strong People Dont Do (Telugu) by Amy MorinPala Pala Mohankishore100% (2)
- Maintenance Instruction for WS 4519 MachineDocumento134 pagineMaintenance Instruction for WS 4519 Machinerknaidu100% (3)
- Mumbai Metro OneDocumento27 pagineMumbai Metro OneAnkita Balotia100% (1)
- Steam Traps Heat Railcars Faster for Asphalt TerminalsDocumento2 pagineSteam Traps Heat Railcars Faster for Asphalt TerminalsAnonymous v5uipHNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Paris Metro MapDocumento1 paginaCircular Paris Metro MapAna VillaramaNessuna valutazione finora
- 14000Documento85 pagine14000Haitham MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Abb Special Report 11 - 03Documento68 pagineAbb Special Report 11 - 03detroit44Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lawang Sewu - Iconic Art Deco Architecture in SemarangDocumento1 paginaLawang Sewu - Iconic Art Deco Architecture in SemarangMuhamad rizqi mawalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Omega Seals: Trelleborg Ridderkerk BVDocumento17 pagineOmega Seals: Trelleborg Ridderkerk BVlee_cur_van4883Nessuna valutazione finora
- Orlando Tampa Intercity Rail Alignment Cost ComparisonDocumento7 pagineOrlando Tampa Intercity Rail Alignment Cost ComparisonCharles FrazierNessuna valutazione finora
- Route Descriptions Useful Information: This Timetable Covers Bus Services LinkingDocumento6 pagineRoute Descriptions Useful Information: This Timetable Covers Bus Services LinkingBobby ChippingNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Design Plan For Fort Greene Park RenovationDocumento49 pagineFinal Design Plan For Fort Greene Park RenovationDNAinfoNewYorkNessuna valutazione finora
- The Iloilo Ice and Cold Storage Company v. Public Utility BoardDocumento6 pagineThe Iloilo Ice and Cold Storage Company v. Public Utility BoardElephantNessuna valutazione finora
- English Stage 4 Sample Paper 1 Insert - tcm142-594884Documento4 pagineEnglish Stage 4 Sample Paper 1 Insert - tcm142-594884gordon50% (2)
- Electrical Interview Question PDFDocumento22 pagineElectrical Interview Question PDFGopi Srikanth VegiNessuna valutazione finora
- Design/Build Replacement of Beaufort & Morehead Railroad Trestle Over Newport River, Morehead City, N.CDocumento25 pagineDesign/Build Replacement of Beaufort & Morehead Railroad Trestle Over Newport River, Morehead City, N.CFebry ChristoperNessuna valutazione finora
- Ways of TransportDocumento11 pagineWays of TransportKaren FragosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Suga DevDocumento6 pagineSuga DevSuga DevNessuna valutazione finora
- French National Railways Apply Thermography For Maintenance and Use A FLIR Systems ThermoVision A40-M To Inspect Overhead Catenaries at A Speed of 120 KM/HDocumento2 pagineFrench National Railways Apply Thermography For Maintenance and Use A FLIR Systems ThermoVision A40-M To Inspect Overhead Catenaries at A Speed of 120 KM/H熙槃Nessuna valutazione finora
- 765kV - Bornagar SS DetailsDocumento24 pagine765kV - Bornagar SS DetailsRagavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Timetable: Book CGDocumento10 pagineWorking Timetable: Book CGLewis BellNessuna valutazione finora
- Iec61375 1 TCNDocumento54 pagineIec61375 1 TCNreza11998868Nessuna valutazione finora
- HK G3 Hensoldt Scopes ©mg-42Documento11 pagineHK G3 Hensoldt Scopes ©mg-42tzimistigrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Coduri Defectiuni Auto EngDocumento15 pagineCoduri Defectiuni Auto EngNicu TerciuNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian Railways Loconotives Training Project Report Loco ShedDocumento83 pagineIndian Railways Loconotives Training Project Report Loco Shedjohn powerNessuna valutazione finora
- Travel by Jaitik Group: TR IPDocumento7 pagineTravel by Jaitik Group: TR IPYash SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice 2Documento37 pagineMultiple Choice 2Dave SalvadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Perhitungan Struktur TangkiDocumento2 paginePerhitungan Struktur TangkiRizal GahtanNessuna valutazione finora
- Downee Sliding Track CatalogueDocumento7 pagineDownee Sliding Track CatalogueQUOC HANessuna valutazione finora
- Water Mist Spec Mdts 46352Documento4 pagineWater Mist Spec Mdts 46352Abhey DograNessuna valutazione finora