Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
SDLC
Caricato da
Rohit Thakur0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
77 visualizzazioni18 pagineSystem Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Six Phases of the SDLC Preliminary Investigation Assesses feasibility and practicality of system System Analysis Study old system and identify new requirements System Design Design new / alternative system Defines system from technical view System Operation and Maintenance Daily operation Periodic evaluation and updating.
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoSystem Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Six Phases of the SDLC Preliminary Investigation Assesses feasibility and practicality of system System Analysis Study old system and identify new requirements System Design Design new / alternative system Defines system from technical view System Operation and Maintenance Daily operation Periodic evaluation and updating.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
77 visualizzazioni18 pagineSDLC
Caricato da
Rohit ThakurSystem Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Six Phases of the SDLC Preliminary Investigation Assesses feasibility and practicality of system System Analysis Study old system and identify new requirements System Design Design new / alternative system Defines system from technical view System Operation and Maintenance Daily operation Periodic evaluation and updating.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 18
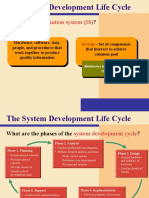
System Development
Life Cycle (SDLC)
Six Phases of the System
Development Life Cycle
Preliminary Investigation
Assesses feasibility and practicality of
system
System Analysis
Study old system and identify new
requirements
Defines system from user's view
System Design
Design new/alternative system
Defines system from technical view
Six Phases of the System
Development Life Cycle
System Development
New hardware and software is acquired,
developed, and tested
System Implementation
System installation and training
System Operation & Maintenance
Daily operation
Periodic evaluation and updating
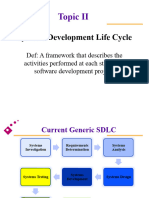
SDLC Phases
Preliminary
Investigation
System Operation
& Maintenance
System
Analysis
System
Implementation n
System
Design
System
D evelopment
Phase 1:
Preliminary Investigation
Determine if a new system is needed
Three primary tasks:
Define the problem
By observation and interview, determine what
information is needed by whom, when, where and
why
Suggest alternative solutions
Prepare a short report
In depth study of the existing system to
determine what the new system should do.
Expand on data gathered in Phase 1
In addition to observation and interviews,
examine:
Formal lines of authority (org chart)
Standard operating procedures
How information flows
Reasons for any inefficiencies
Phase 2:
System Analysis
Phase 2: System Analysis
Tools Used
Checklists - list of questions
Top-down analysis - start with top level
components, break down into smaller parts
through each successive level
Grid charts - to show relationship between
inputs and outputs
System flowcharts - charts flow of input data,
processing, and output which show system
elements and interactions
Phase 2: System Analysis
Documentation Produced
Complete description of current system and its
problems
Requirements for for new system including:
Subject
Scope
Objectives
Benefits
Possible development schedule
Phase 3:
System Design
Uses specifications from the systems analysis to
design alternative systems
Evaluate alternatives based upon:
Economic feasibility - Do benefits justify costs?
Technical feasibility - Is reliable technology and
training available?
Operational feasibility - Will the managers and
users support it?
Phase 3: System Design
Tools Used
Computer-Aided Software Engineering
(CASE) tools are software-based products
designed to help automate the production of
information systems.
Examples:
Diagramming Tools
Data Repositories
Prototyping Tools
Test Data Generators
Documentation Tools
Project Management Tools
Phase 3: System Design
Documentation Produced
System Design Report
Describe Alternatives including:
Inputs/Outputs
Processing
Storage and Backup
Recommend Top Alternative based upon:
System Fit into the Organization
Flexibility for the future
Costs vs. benefits
Phase 4:
System Development
Build the system to the design specifications
Develop the software
Purchase off-the-shelf software OR
Write custom software
Acquire the hardware
Test the new system
Module (unit) test - tests each part of system
Integration testing - tests system as one unit
Create manuals for users and operators
Phase 5:
System Implementation
Convert from old system to new system
Train users
Compile final documentation
Evaluate the new system
Phase 5: System Implementation
Types of Conversion
Direct/plunge/crash approach entire new
system completely replaces entire old system, in one
step
Parallel approach - both systems are operated side
by side until the new system proves itself
Pilot approach - launched new system for only one
group within the business -- once new system is
operating smoothly, implementation goes company-
wide
Phased/incremental approach - individual parts of
new system are gradually phased-in over time, using
either crash or parallel for each piece.
Phase 5: System Implementation
User Training
Ease into system, make them comfortable,
and gain their support
Most commonly overlooked
Can be commenced before equipment
delivery
Outside trainers sometimes used
Phase 6: Operations &
Maintenance
Types of changes:
Physical repair of the system
Correction of new bugs found (corrective)
System adjustments to environmental
changes
Adjustments for users changing needs
(adaptive)
Changes to user better techniques when they
become available (perfective)
Phase 6: Operations &
Maintenance
Evaluation Methods
Systems audit - performance compared to
original specifications
Periodic evaluation - checkups from time
to time, modifications if necessary
Deliverables of the SDLC
Begin building
new system
System converted
Users trained
Coded and
Tested System
Design Specifications
Preliminary
Investigation
System
Analysis
System
Design
System
Implementation
System
Development
System
Maintenance
Approved Feasibility
Study
Operational System
Documentation completed
Abort Project
Goto next phase
Goto Previous phase
Problem
Specifications
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Documento17 pagineSystem Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Suman JyotiNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life CycleDocumento22 pagineSystem Development Life Cyclejai doiNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) : Asma SajidDocumento20 pagineSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC) : Asma SajidIsrar ulhaqNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Documento18 pagineSystem Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Sandz SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- JSD SDLCDocumento22 pagineJSD SDLCjsdtrainerNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Internal System Analysis and Design AssignmentDocumento22 pagine3rd Internal System Analysis and Design Assignmentdivyanshir650Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture On SDLC 20210531160229Documento22 pagineLecture On SDLC 20210531160229mainakmondal24Nessuna valutazione finora
- Janu Jaiswal's MISDocumento33 pagineJanu Jaiswal's MISFikir CaNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Documento19 pagineSystem Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Usman JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Documento14 pagineSoftware Development Life Cycle (SDLC)Rahul LokeshNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life Cycle Implementation of MisDocumento17 pagineSystem Development Life Cycle Implementation of Misatul211988Nessuna valutazione finora
- FCT10010 Lec 9 Systems Analysis DesignDocumento21 pagineFCT10010 Lec 9 Systems Analysis DesignJaniceNessuna valutazione finora
- MBA Marketing IV Sem SDLC Project SubmissionDocumento17 pagineMBA Marketing IV Sem SDLC Project SubmissionRakesh MaheshwariNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLC: Software Development Life Cycle OverviewDocumento20 pagineSDLC: Software Development Life Cycle OverviewBilal IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems Overview SDLCDocumento72 pagineSystems Overview SDLCIsha BhattaNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life Cycle: Internship TopicDocumento17 pagineSystem Development Life Cycle: Internship TopicRohit GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLC: Software Development ProcessDocumento4 pagineSDLC: Software Development ProcessSana ShafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 SDLC Systems Development Life CycleDocumento105 pagine5 SDLC Systems Development Life CycleRae Anne Abrasado100% (2)
- Unit2 FlipclassDocumento25 pagineUnit2 FlipclassAakrit NagariNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLC PDFDocumento14 pagineSDLC PDFDalia JoseNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLC Eddited - 2017Documento9 pagineSDLC Eddited - 2017ano mlamboNessuna valutazione finora
- Sadcw 6e Chapter13 131120095717 Phpapp01Documento39 pagineSadcw 6e Chapter13 131120095717 Phpapp01John MwaipopoNessuna valutazione finora
- The System Development Life Cycle PhasesDocumento29 pagineThe System Development Life Cycle Phasesneropalma88Nessuna valutazione finora
- SYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Unit 2Documento6 pagineSYSTEM ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Unit 2Md HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life CycleDocumento7 pagineSystem Development Life Cyclevictory IsaacNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Process ModelDocumento14 pagineSoftware Process Modeladitya keshariNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1Documento47 pagineTopic 1DIVYA SRINessuna valutazione finora
- Making The System Operational: Systems Analysis and Design in A Changing World 6 Ed Satzinger, Jackson & BurdDocumento35 pagineMaking The System Operational: Systems Analysis and Design in A Changing World 6 Ed Satzinger, Jackson & BurdRussel LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento29 pagineChapter 2behailuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2: System Development MethodologyDocumento6 pagineLesson 2: System Development Methodologysambal2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Phase in SDLCDocumento6 paginePhase in SDLCNurul Syuhada ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- SDLCDocumento14 pagineSDLCTulika KabirajNessuna valutazione finora
- System Analysis and Development and Models ClassDocumento92 pagineSystem Analysis and Development and Models ClassLakskmi Priya M CNessuna valutazione finora
- Application DevelopmentDocumento2 pagineApplication DevelopmentYamunaNessuna valutazione finora
- SAAD Lecture II - SDLCDocumento100 pagineSAAD Lecture II - SDLCKisyenene JamusiNessuna valutazione finora
- Input/output of Requirements Engineering ProcessDocumento7 pagineInput/output of Requirements Engineering Processer_sushilkumargNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life CycleDocumento44 pagineSystem Development Life CycleShan AgharrNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design: of E-Commerce Systems 10Documento36 pagineAnalysis and Design: of E-Commerce Systems 10hamedskyNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems OverviewDocumento29 pagineSystems OverviewMac BadmashNessuna valutazione finora
- 2MIS - Foundation of Information System - Part IIIDocumento18 pagine2MIS - Foundation of Information System - Part IIIPravakar GhimireNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development & SDLCDocumento9 pagineSystem Development & SDLCproshanto salmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 SDLC ControlsDocumento33 pagine5 SDLC ControlsDennis IsananNessuna valutazione finora
- HRIMS Development SystemDocumento20 pagineHRIMS Development SystemBagambe BarnarbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture-2 - Software Development Life CycleDocumento25 pagineLecture-2 - Software Development Life Cycless3351086Nessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Software Development Life CycleDocumento12 pagineReport On Software Development Life CycleShailu SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Software Process Model SPM NotesDocumento17 pagineComputer Software Process Model SPM Notesdjjshshd hdjdjdkdjNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 SadDocumento13 pagineChapter 2 SadR CNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Life CycleDocumento3 pagineSystem Development Life Cycleraajpout.343Nessuna valutazione finora
- SDLC Testing and Deployment StrategiesDocumento25 pagineSDLC Testing and Deployment StrategiesJesseSpero75% (4)
- Developing an E-Business System Using the Systems Development ProcessDocumento26 pagineDeveloping an E-Business System Using the Systems Development Processismahan mukhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Seven Major ActivitiesDocumento36 pagineSeven Major ActivitiesComedy TvNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5-Systems Implementation and MaintenanceDocumento50 pagineChapter 5-Systems Implementation and Maintenancekassahun addissNessuna valutazione finora
- Defining A SAADDocumento5 pagineDefining A SAADRoy ArsenalNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - Systems DevelopmentDocumento43 pagineLecture 3 - Systems Developmentdemmm demmmNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 3 - Systems DevelopmentDocumento43 pagineLecture 3 - Systems Developmentdemmm demmmNessuna valutazione finora
- System Development Models PDFDocumento25 pagineSystem Development Models PDFNancy Dhanuka100% (1)
- Miserp - Unit Iv PNRDocumento95 pagineMiserp - Unit Iv PNRDr. Potu NarayanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit1. Software ProcessesDocumento42 pagineUnit1. Software ProcessesKaran PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing the Testing Process: Practical Tools and Techniques for Managing Hardware and Software TestingDa EverandManaging the Testing Process: Practical Tools and Techniques for Managing Hardware and Software TestingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (8)
- CISA Exam-Testing Concept-Testing in SDLC (Domain-3)Da EverandCISA Exam-Testing Concept-Testing in SDLC (Domain-3)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Distributed Data Storage Systems - From RAID To BlockchainsDocumento6 pagineDistributed Data Storage Systems - From RAID To BlockchainsanevelkoskaNessuna valutazione finora
- U.C. Berkeley Engages FireEye For Advanced Malware ProtectionDocumento2 pagineU.C. Berkeley Engages FireEye For Advanced Malware ProtectionFireEyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Filtering Unwanted Packets On Atm Network: ISSN: 0975-766XDocumento9 pagineFiltering Unwanted Packets On Atm Network: ISSN: 0975-766XAsadullah HesamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Python: After Reading This Chapter, The Reader Will Be Able ToDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To Python: After Reading This Chapter, The Reader Will Be Able ToRayJay BilgeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Gus Dimitrelos Deleted Files Report REDACTED - 1Documento26 pagineGus Dimitrelos Deleted Files Report REDACTED - 1David SivakNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study 19: STUXNET and the Changing Face of CyberwarfareDocumento8 pagineCase Study 19: STUXNET and the Changing Face of CyberwarfarelevinazemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cyber CrimeDocumento24 pagineCyber CrimeJ QatarNessuna valutazione finora
- IoT IntroductionDocumento34 pagineIoT IntroductionsubhampandaNessuna valutazione finora
- A10 DG Microsoft Exchange 2013Documento19 pagineA10 DG Microsoft Exchange 2013Marcos SachiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nmu Siemens Course Detail Guide 2021Documento24 pagineNmu Siemens Course Detail Guide 2021Industrial ItNessuna valutazione finora
- ConfigDocumento89 pagineConfigramitNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Console System 9500: The Next Generation TETRA Dispatch SolutionDocumento2 pagineRadio Console System 9500: The Next Generation TETRA Dispatch SolutionSe ZeNessuna valutazione finora
- Automotive Virtual Platform Using VIRTIO ALS 2019 1Documento24 pagineAutomotive Virtual Platform Using VIRTIO ALS 2019 1Baoan DuNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Ticket Machine: E-Ticketing 1Documento63 pagineElectronic Ticket Machine: E-Ticketing 1Samaya Sanjeevi Kumaran KathiresanNessuna valutazione finora
- Meraki MX Firewalls and Sophos UTM Buyer's Guide and Reviews January 2020Documento19 pagineMeraki MX Firewalls and Sophos UTM Buyer's Guide and Reviews January 2020Erik RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Setting up your DevNet Developer EnvironmentDocumento18 pagineSetting up your DevNet Developer EnvironmentpacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Virus Best Practices PDFDocumento8 pagineAnti Virus Best Practices PDFkprasad_mlNessuna valutazione finora
- Pro Active Directory Certificate Services Creating and ManagingDocumento462 paginePro Active Directory Certificate Services Creating and ManagingGhino CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Pega Certified System Architect PCSA CerDocumento9 paginePega Certified System Architect PCSA CerSanthiya MurugesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Getting Started With Anypoint Platform (Mule 4) : Development: Fundamentals Course, Which Includes This Content and MoreDocumento3 pagineGetting Started With Anypoint Platform (Mule 4) : Development: Fundamentals Course, Which Includes This Content and Moreur munnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Performance of SISO, SIMO, MISO & MIMO Wireless SystemsDocumento6 pagineStudy Performance of SISO, SIMO, MISO & MIMO Wireless SystemsDr. M. Muntasir RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- EY CertifyPoint - Google AdsAnalytics Scope Expansion Certificate 2016 - ISO27001Documento2 pagineEY CertifyPoint - Google AdsAnalytics Scope Expansion Certificate 2016 - ISO27001Stan DanilinNessuna valutazione finora
- Five Malware Types and ExamplesDocumento3 pagineFive Malware Types and ExamplesGela SiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Information AgeDocumento13 pagineInformation AgeCubillas Jane DorothyNessuna valutazione finora
- Netwrix Sbpam: Leave No Chance For Compromise or Misuse of Privileged AccountsDocumento2 pagineNetwrix Sbpam: Leave No Chance For Compromise or Misuse of Privileged AccountsAbdul Rahaman GaffarNessuna valutazione finora
- Apple Inc.Documento4 pagineApple Inc.Weldon KeneiNessuna valutazione finora
- Eucalyptus Cloud Computing PDFDocumento2 pagineEucalyptus Cloud Computing PDFBradNessuna valutazione finora
- Riverbed Xirrus Wi-Fi Designer: Product Release NotesDocumento3 pagineRiverbed Xirrus Wi-Fi Designer: Product Release NotesLuchoNandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mi603 - Micro Service ArchitectureDocumento7 pagineMi603 - Micro Service ArchitectureShubham AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet 1100 Acme Packet Oracle SBCDocumento5 pagineDatasheet 1100 Acme Packet Oracle SBCJose AndresNessuna valutazione finora