Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Total Qualit
Caricato da
Sushil KumarCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Total Qualit
Caricato da
Sushil KumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Key Factors
Globalization of markets.
Advances in IT.
Growth of trans- national business.
Establishment of WTO.
Interpenetration of Economics.
European single market.
- Intensified competition.
- Improving competitiveness
Total Quality Management(TQM)
Definitions
TQM can be seen as a process, used to manage the
change in environment that will ensure that
company reaches the goal of TCI
Total - involves everybody in the organization
Continuous- for ever
Improvement- elimination of waste
- reduction of variations
- innovation
Contd
TQM is a management approach of an
organization, centered on the participation
of all its members and aiming at long term
success through customer satisfaction and
benefits to the members of organization
and society
ISO 8402/IS 13999
Total Quality Management(TQM)
Definitions
Contd
TQM is an approach for continuously improving the
quality of goods/ services delivered through the
participation of all levels & functions of organization .
JOHN PIGGOTT
TQM is an integrated organization approach in
delighting customers (internal & external) by meeting
their expectations on a continuous basis through
everyone involved on a continuous basis for
improvement in all product/ processes along with
proper problem solving methodology.
Dr.M. ZAIRI
Total Quality Management(TQM)
Definitions
TQM is an organization- wide quality focused
culture. It is a journey to achieve excellence in all
aspects of the organization's activity.It involves all
members of the organization at all levels of
operation.
TQM is a management philosophy rather than a
quality- technology. Ironically, TQM began in
Japan based on the quality philosophy of
Dr. W. Edwards Deming.
The major phases of TQM are:
Statistical-quality-control,
Total-quality-control
Totalquality-management
TQM PRINCIPLES
Customer orientation.
Management-by-Fact.
Employee involvement.
Continuous improvement.
1. BETTER QUALITY REQUIRES HIGHER COST.
2. QUALITY IS INNATELY PERCEIVED AS
SEPARATING GOOD FROM BAD.
3. INCREASED QUALITY CAN BE ACHIEVED
THROUGH INVESTMENT IN TECHNOLOGY.
4. QUALITY IS CONFINED TO THE PRODUCT AND
THEREFORE MANUFACTURING PROCESS.
5. QUALITY IS RESPONSIBILITY OF QUALITY
MANAGER AND HIS DEPARTMENT.
Quality: Misconceptions
Quality concepts
Continuous improvement
Customer orientation
Employee involvement
Management by facts
Process control
Transparency
Quality
Management
concepts
Contd
Award systems
Benchmarking
Co-marking
Complaints handling
Customer surveys
Empowerment
Just in time management
Quality circles
Quality awards
Quality audits
Quality function deployment
Quality policy deployment
Reward systems
Top management commitment
Quality concepts
Quality
Management
Instruments
And
Organizational
Arrangements
Contd
Design of Experiments
Reliability Techniques
The 7- Management
and Planning Tools
The 7-SPC Tools
Quality concepts
Quality
Management
techniques
Customer orientation
Human resource
excellence
Product/ process
leadership
Management
leadership
Total
Quality
Require-
ments
Customer Orientation
Participa- Develop- motivation
tion ment
Products/ Processes/ Information Suppliers
Services procedures
Culture Planning Communication Accountability
CONDITIONS OF EXCELLENCE
THE McKINSEY TQM
MODEL
TOTAL QUALITY
DESIGN
PROCESS
PROCESS
QUALITY
COMPANY
QUALITY
PRODUCT
QUALITY
PROCESS
CAPABILITY
SERVICE
QUALITY
LOGISTICS
QUALITY
FIVE GURUS
-Process orientation
-Use of statistics
-Drive out fear
-Reduction of variation
Deming
-Management involvement
-Quality planning
-Quality control
-Quality improvement
Juran
-Total quality system
- Design quality In
-Customer orientation
Feigenbaum
-Use of statistics
-Quality circles
-Involvement of employees
Ishikawa
-Zero defects
-Cost of quality
-Hidden factory
-Slogans
Crosby
MAINTAIN AT ALL TIMES
FOCUSES ON OBJECTIVE:
TO SATISFY CUSTOMERS
BETTER THAN
COMPETTIORS DO
TURN EMPLOYEES FROM SKILL
HOLDERS TO DISEMINATORS
CREATE LEARNING,
ENABLING MANAGERS WHO
DEVELOP, NOT FILTER PEOPLE
EMPHASIS PROCEESS
MORE THAN PRODUCT
GET PEOPLE TO
PERFORM MUNDANE
ACTIVITIES WITH FULL
QUALITY FOCUS
USE TECHONOLGY
EFFICIENTLY
MEASURE KEY PARAMETERS
OF ALL ACTIVITIES
BUILD IN CONTINOUS
LEARNING & IMPROVEMENT
PROCESSES
COMPENSATE FOR WEAKNESS
INHERENT IN CULTURE
USE FACILITATION
MEDIATE STRUCTURE TO
BRING IN CHANGE
BENCHMARK AGAINST
BEST OF BREED
COMPANIES & COPY
THEIR BEST PRACTICES
USE SCIENTIFIC METHODS
NOT OPINION OR GUT
FEEL
DEPLOY THE
WORKFORCE
USE SINCERITY AND TRUST
AS BASIS FOR ALL
DEALINGS SAYINGS DOING
USE CROSS
FUNCTIONAL TEAMS
USE CUSTOMER AND
COMPETITORS TO
DRIVE ALL DECISIONS
GET WORK-FORCE TO
MANAGE ITSELF
Different approaches are Possible.:-
The best way to implement
TQM?
Soft - hard
Rhetoric - Concrete actions
Total organization - Pilot project
General - Specific
Bottom up - Top down
In practice interaction between the different
approaches is needed
Seven Steps of TQM
Select a theme.
Grasp the present system.
Analyze the present situation.
Set countermeasures into motion.
Determine the effectiveness of the counter-
measures.
Use a standard operating procedures.
Plan for future action.
THE SEVEN STEP TQM MODEL
STEP-1: MANAGEMENT
ESTABLISH A TQM ENVIRONMENT
VISION/MISSION
COMMITMENT
EMPLOYEE INVOLVEMENT
CUSTOMER FOCUS
SUPPORT SYSTEM
DISCIPLINED METHODOLOGY
KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS
STEP-2: MISSION
ESTABLISH SUPPLIER / CUSTOMER/MANAGEMENT: MISSION,
NEEDS, AND REQUIREMENTS
STEP 3: PROCESSES
ESTABLISH PROCESS:
REQUIREMENTS, DEALS, PRIORITIES
STEP 4: PROJECTS
CHECK/ ENSURE PROJECTS:
IMPLEMENTATION, MEASUREMENT, ASSESSMENT,
PERFORMANCE
STEP 5: CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
ESTABLISH: IMPROVEMENT OPPORTUNITIES, STRATEGIC
INITIATIVES
STEP 6: EVALUATION
ESTABLISH: AUDIT/ EVALUATION PROCEDURES
STEP 7: REVIEW REVISION
REPEAT CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
CYCLE
THANKS!!!
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- EOS Traction Library SamplerDocumento152 pagineEOS Traction Library SamplerNafis Ayan100% (3)
- Pmbok 4Th Edition DocumentsDocumento1 paginaPmbok 4Th Edition DocumentsgrzewoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceoguidetotalentmanagement BK Ddi PDFDocumento57 pagineCeoguidetotalentmanagement BK Ddi PDFVikram TanwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Balanced Scorecard BBSDocumento15 pagineBusiness Balanced Scorecard BBSOgangwu BenjaminNessuna valutazione finora
- Crew Resource Management (CRM) EvolutionDocumento9 pagineCrew Resource Management (CRM) EvolutionAlfonso RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento54 pagineTotal Quality ManagementKaushika Rajapaksha PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento229 pagineTotal Quality ManagementbejumohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento15 pagineTotal Quality ManagementAtul SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management Unit I GE2022Documento52 pagineTotal Quality Management Unit I GE2022standalonembaNessuna valutazione finora
- PPT3-Managing QualityDocumento29 paginePPT3-Managing QualityIka FitriNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Total QualityDocumento47 pagine7 Total QualityTejas BhavsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento14 pagineTotal Quality ManagementNishant Jain60% (10)
- Total Quality Management: P. M. SagareDocumento32 pagineTotal Quality Management: P. M. SagareDeep UmradiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Proceeding 2Documento102 pagineProceeding 2userscribd2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Time ManagementDocumento21 pagineTime Managementagnasmaria100% (1)
- TQM Productivity and Quality Management Question BankDocumento87 pagineTQM Productivity and Quality Management Question BankMinal ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Leadership: "A Leader Lives in Each of Us"Documento41 pagineLeadership: "A Leader Lives in Each of Us"mariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management Explained in 40 CharactersDocumento70 pagineTotal Quality Management Explained in 40 CharactersAnjali GirishNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM AND PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT COURSEDocumento67 pagineTQM AND PRODUCTION MANAGEMENT COURSEanreddyharishNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento175 pagineTotal Quality Managementimad83% (6)
- 1 TQMDocumento24 pagine1 TQMLakky ViswanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM Principles and EvolutionDocumento60 pagineTQM Principles and EvolutionAshlay BaichooNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Public Organizations GuideDocumento110 pagineUnderstanding Public Organizations GuidejupdiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management: Lecture # 1Documento23 pagineTotal Quality Management: Lecture # 1Awan NadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocumento36 pagineTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsRathnakrajaNessuna valutazione finora
- The SEWA Project Management ModelDocumento147 pagineThe SEWA Project Management ModelAhmed Latif100% (1)
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento17 pagineTotal Quality Managementleni shara100% (1)
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento19 pagineTotal Quality ManagementVishal MeenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Quality Quality For Sustainability T R ParasuramanDocumento26 pagineBuilding Quality Quality For Sustainability T R ParasuramanSudhagar PNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Total Quality Management An Overview: DefinitionDocumento8 pagineChapter 1 - Total Quality Management An Overview: Definitionnanocid100% (1)
- MGT 6650 - Lecture 2 - Total Quality Management - 12022014v1Documento21 pagineMGT 6650 - Lecture 2 - Total Quality Management - 12022014v1Muhammad Faiz HarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Skill Enhancement TechniquesDocumento17 pagineSkill Enhancement TechniquesYogesh GurnuleNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 14tqmDocumento24 pagineLecture 14tqmapi-3754041Nessuna valutazione finora
- TQM_1712197365Documento103 pagineTQM_1712197365Rogério Andrade Dos SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 Total Quality ManagementDocumento88 pagineTopic 1 Total Quality ManagementncubemellonNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods of Quality Management: College of Nursing Meng Qinghui 2007-4Documento31 pagineMethods of Quality Management: College of Nursing Meng Qinghui 2007-4s_jithsreeNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM INTRO QUALITY EVOLUTIONDocumento6 pagineTQM INTRO QUALITY EVOLUTIONYogita NarangNessuna valutazione finora
- Revisi PPT3-Managing QualityDocumento28 pagineRevisi PPT3-Managing QualityAbdul GhoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Mce 6221 Total Quality ManagementDocumento26 pagineMce 6221 Total Quality ManagementMohammad Muhtasim Mashfy, 170011054Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1tqmDocumento16 pagineLecture 1tqmapi-3754041Nessuna valutazione finora
- Session 5 TQMDocumento12 pagineSession 5 TQMALINessuna valutazione finora
- GE 8077 - TQM Principles and ToolsDocumento36 pagineGE 8077 - TQM Principles and ToolsmenakadevieceNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocumento17 pagineTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsAnkeshNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM: Total Quality ManagementDocumento30 pagineTQM: Total Quality ManagementMd. Mizanur RahamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus TQMDocumento56 pagineSyllabus TQMAnand RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento10 pagineTotal Quality ManagementJamel torresNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management Unit-I: DefinitionDocumento86 pagineTotal Quality Management Unit-I: DefinitionRaj DharodNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM S9-12 21-24.07.2020 PDFDocumento27 pagineTQM S9-12 21-24.07.2020 PDFAllu SaitejaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-3 complete notes.Documento44 pagineUnit-3 complete notes.apakkiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 TotalQualityManagementDocumento59 pagine3 TotalQualityManagementPrateek HosamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management System: NotesDocumento17 pagineQuality Management System: NotesJenine BatiancilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management: By: Zaipul Anwar Manager, R & D Dept. Business & Advanced Technology Centre UTMDocumento14 pagineTotal Quality Management: By: Zaipul Anwar Manager, R & D Dept. Business & Advanced Technology Centre UTMविशाल छुगानीNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM - HandoutDocumento11 pagineTQM - Handoutrdx216Nessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management TQM Course No. 622: Dr. Mustafa HyderDocumento25 pagineTotal Quality Management TQM Course No. 622: Dr. Mustafa Hydermuhammad bilal baigNessuna valutazione finora
- TQM by Group 1Documento69 pagineTQM by Group 1Anjali GirishNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsDocumento36 pagineTotal Quality Management: TQM: Origins, Evolution & Key ElementsMuhannad AbdulRaoufNessuna valutazione finora
- Philosophies of Quality ManagementDocumento10 paginePhilosophies of Quality ManagementTanmay ParikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Productivity Improvement Through Total Quality ManagementDocumento14 pagineProductivity Improvement Through Total Quality ManagementgokulNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManangementDocumento9 pagineTotal Quality ManangementRakhesh MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento106 pagineTotal Quality ManagementJohanna GutiérrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality Control: Presented By:-Aakash D. Bhongade 132130015 (M. Tech 1 Year)Documento33 pagineTotal Quality Control: Presented By:-Aakash D. Bhongade 132130015 (M. Tech 1 Year)Jitendra PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous Improvement Strategy T Q M: Definition, Concept & Pillars of TQM Breakthrough Improvement Strategy Business Process Reengineering (BPR)Documento25 pagineContinuous Improvement Strategy T Q M: Definition, Concept & Pillars of TQM Breakthrough Improvement Strategy Business Process Reengineering (BPR)Sam DreamNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation1 TQMDocumento70 paginePresentation1 TQMrochelle regenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operation Management: Topic: Total Quality Management-TQMDocumento20 pagineOperation Management: Topic: Total Quality Management-TQM버니 모지코Nessuna valutazione finora
- QualityDocumento25 pagineQualitygsidhu156276Nessuna valutazione finora
- Otal Quality ManagementDocumento53 pagineOtal Quality ManagementdrrajputNessuna valutazione finora
- Component Used in That Projects PricesDocumento1 paginaComponent Used in That Projects PricesSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 39 Non Conventional MachiningDocumento15 pagine39 Non Conventional MachiningPRASAD326100% (2)
- Qspear Debarred ListDocumento4 pagineQspear Debarred ListSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Futuristic CarmmmmmDocumento41 pagineFuturistic CarmmmmmSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- REMOTE CONTROLLED MOTORIZED HYDRAULIC JACKDocumento72 pagineREMOTE CONTROLLED MOTORIZED HYDRAULIC JACKSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PlanDocumento23 paginePlanSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- To Describe Your Skills The Following Adjectives Are UsefulDocumento1 paginaTo Describe Your Skills The Following Adjectives Are UsefulSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MotivationDocumento3 pagineMotivationSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhel ReportDocumento49 pagineBhel ReportSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 8. Introduction To CNC Milling: Manual NC Programming: Objectives of The LabDocumento1 paginaLab 8. Introduction To CNC Milling: Manual NC Programming: Objectives of The LabSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
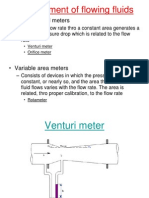
- Measrement of FlowDocumento12 pagineMeasrement of FlowSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhel ReportDocumento49 pagineBhel ReportSushil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Operations Management 1 - BeaDocumento27 pagineOperations Management 1 - BeaBea Renela Gabinete ConcepcionNessuna valutazione finora
- Nicole Scheppers: 14552 W. White Hawk Ct. Boise, ID 83713 Phone: 818-312-7497 ObjectiveDocumento5 pagineNicole Scheppers: 14552 W. White Hawk Ct. Boise, ID 83713 Phone: 818-312-7497 Objectiveapi-238872194Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ted ScriptDocumento3 pagineTed ScriptVietNamtrongToiNessuna valutazione finora
- Youth Dream Scholarship Application FormsDocumento3 pagineYouth Dream Scholarship Application FormsAnthony HarrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Leader 3Documento65 pagineLeader 3Aklilu100% (1)
- A Construction Safety Competency Framework (AU Construction) PDFDocumento36 pagineA Construction Safety Competency Framework (AU Construction) PDFMalappareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Aboriginal Cultural Standards FrameworkDocumento16 pagineAboriginal Cultural Standards Frameworkapi-377468075Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business Case AssignmentDocumento2 pagineBusiness Case AssignmentgalakNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 21500 and Pmbok GuideDocumento10 pagineIso 21500 and Pmbok GuideALVARO CHAMONessuna valutazione finora
- The Napoleonic CodeDocumento3 pagineThe Napoleonic CodeAshleyCyriacNessuna valutazione finora
- Strategic FitDocumento7 pagineStrategic FitLuchoNessuna valutazione finora
- Teacher and Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocumento17 pagineTeacher and Community, School Culture and Organizational LeadershipAirish Mae BelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Assessment of Teacher Leader QualitiesDocumento4 pagineSelf-Assessment of Teacher Leader Qualitiesapi-621936548Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ielts SpeakingDocumento20 pagineIelts SpeakingDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- New Hire Evolution PreDocumento21 pagineNew Hire Evolution PreYoussef DaoudNessuna valutazione finora
- SHRM Mod 3 Part 1Documento25 pagineSHRM Mod 3 Part 1Vishal Singh JaswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Letter New ZealandDocumento7 pagineReference Letter New Zealandnew0nikazuw3100% (1)
- Ethical Levels: - Definition of Law - Historical Development of The Law - The Different Between Law and EthicsDocumento11 pagineEthical Levels: - Definition of Law - Historical Development of The Law - The Different Between Law and EthicsAlia Al ZghoulNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelsey E. Peck: Objective EducationDocumento1 paginaKelsey E. Peck: Objective Educationapi-272740785Nessuna valutazione finora
- Increasing The Impact of Thought Leadership in Crisis CommunicationDocumento20 pagineIncreasing The Impact of Thought Leadership in Crisis CommunicationGeorge BekatorosNessuna valutazione finora