Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
POLYMER MICROSTRUCTURES AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
Caricato da
Brain Choirul IchsanDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
POLYMER MICROSTRUCTURES AND MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
Caricato da
Brain Choirul IchsanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 14/15-
ISSUES TO ADDRESS...
What are the basic microstructural features?
1
How do these features dictate room T tensile
response?
Hardening, anisotropy, and annealing in polymers.
How does elevated temperature mechanical
response compare to ceramics and metals?
CHAPTERS 14/15:
POLYMER STRUCTURES,
APPLICATIONS, & PROCESSING
Chapter 14/15- 2
Polymer = many mers
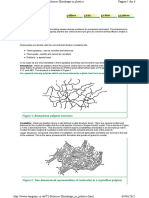
Covalent chain configurations and strength:
Direction of increasing strength
Adapted from Fig. 14.2, Callister 6e.
Adapted from Fig. 14.7, Callister 6e.
POLMER MICROSTRUCTURE
Chapter 14/15-
Molecular weight, Mw: Mass of a mole of chains.
3
Tensile strength (TS):
--often increases with Mw.
--Why? Longer chains are entangled (anchored) better.
% Crystallinity: % of material that is crystalline.
--TS and E often increase
with % crystallinity.
--Annealing causes
crystalline regions
to grow. % crystallinity
increases.
crystalline
region
amorphous
region
Adapted from Fig. 14.11, Callister 6e.
(Fig. 14.11 is from H.W. Hayden, W.G. Moffatt,
and J. Wulff, The Structure and Properties of
Materials, Vol. III, Mechanical Behavior, John Wiley
and Sons, Inc., 1965.)
MOLECULAR WEIGHT & CRYSTALLINITY
Chapter 14/15- 4
Stress-strain curves adapted from Fig. 15.1, Callister 6e. Inset figures along plastic response curve (purple)
adapted from Fig. 15.12, Callister 6e. (Fig. 15.12 is from J.M. Schultz, Polymer Materials Science, Prentice-Hall,
Inc., 1974, pp. 500-501.)
TENSILE RESPONSE: BRITTLE & PLASTIC
Chapter 14/15- 5
Drawing...
--stretches the polymer prior to use
--aligns chains to the stretching direction
Results of drawing:
--increases the elastic modulus (E) in the
stretching dir.
--increases the tensile strength (TS) in the
stretching dir.
--decreases ductility (%EL)
Annealing after drawing...
--decreases alignment
--reverses effects of drawing.
Compare to cold working in metals!
Adapted from Fig. 15.12, Callister
6e. (Fig. 15.12 is from J.M.
Schultz, Polymer Materials
Science, Prentice-Hall, Inc.,
1974, pp. 500-501.)
PREDEFORMATION BY DRAWING
Chapter 14/15- 6
Compare to responses of other polymers:
--brittle response (aligned, cross linked & networked case)
--plastic response (semi-crystalline case)
Stress-strain curves
adapted from Fig. 15.1,
Callister 6e. Inset
figures along elastomer
curve (green) adapted
from Fig. 15.14, Callister
6e. (Fig. 15.14 is from
Z.D. Jastrzebski, The
Nature and Properties of
Engineering Materials,
3rd ed., John Wiley and
Sons, 1987.)
TENSILE RESPONSE: ELASTOMER CASE
Chapter 14/15- 7
Thermoplastics:
--little cross linking
--ductile
--soften w/heating
--polyethylene (#2)
polypropylene (#5)
polycarbonate
polystyrene (#6)
Thermosets:
--large cross linking
(10 to 50% of mers)
--hard and brittle
--do NOT soften w/heating
--vulcanized rubber, epoxies,
polyester resin, phenolic resin
Callister,
Fig. 16.9
T
Molecular weight
T
g
T
m
mobile
liquid
viscous
liquid
rubber
tough
plastic
partially
crystalline
solid
crystalline
solid
Adapted from Fig. 15.18, Callister 6e. (Fig. 15.18 is from F.W. Billmeyer,
Jr., Textbook of Polymer Science, 3rd ed., John Wiley and Sons, Inc.,
1984.)
THERMOPLASTICS VS THERMOSETS
Chapter 14/15- 8
Decreasing T...
--increases E
--increases TS
--decreases %EL
Increasing
strain rate...
--same effects
as decreasing T.
Adapted from Fig. 15.3, Callister 6e. (Fig. 15.3 is from T.S. Carswell and
J.K. Nason, 'Effect of Environmental Conditions on the Mechanical
Properties of Organic Plastics", Symposium on Plastics, American Society
for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1944.)
T AND STRAIN RATE: THERMOPLASTICS
Chapter 14/15- 9
Stress relaxation test:
E
r
(t )
(t )
o
--strain to o and hold.
--observe decrease in
stress with time.
Relaxation modulus:
Data: Large drop in Er
for T > Tg.
(amorphous
polystyrene)
Sample Tg(C) values:
PE (low Mw)
PE (high Mw)
PVC
PS
PC
-110
- 90
+ 87
+100
+150
Adapted from Fig.
15.7, Callister 6e.
(Fig. 15.7 is from
A.V. Tobolsky,
Properties and
Structures of
Polymers, John
Wiley and Sons, Inc.,
1960.)
Selected values from
Table 15.2, Callister
6e.
TIME DEPENDENT DEFORMATION
Chapter 14/15- 10
General drawbacks to polymers:
-- E,
y
, K
c
, T
application
are generally small.
-- Deformation is often T and time dependent.
-- Result: polymers benefit from composite reinforcement.
Thermoplastics (PE, PS, PP, PC):
-- Smaller E,
y
, T
application
-- Larger K
c
-- Easier to form and recycle
Elastomers (rubber):
-- Large reversible strains!
Thermosets (epoxies, polyesters):
-- Larger E,
y
, T
application
-- Smaller K
c
Table 15.3 Callister 6e:
Good overview
of applications
and trade names
of polymers.
SUMMARY
Chapter 14/15-
Reading:
Core Problems:
Self-help Problems:
0
ANNOUNCEMENTS
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 14 15 PolymerDocumento11 pagineChapter 14 15 PolymerKholisa Intan RokhmanaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 15-Characteristics, Applications and Processing of PolymersDocumento28 pagineCH 15-Characteristics, Applications and Processing of PolymersVicces P. Estrada100% (1)
- Polymers PDFDocumento39 paginePolymers PDFSabith MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Issues To Address... : Chapter 14/15-1Documento11 pagineIssues To Address... : Chapter 14/15-1Alex Nico JhoentaxsNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Processing-3Documento25 paginePolymer Processing-3andrijanto12350% (2)
- Polymer Structures: Issues To Address..Documento4 paginePolymer Structures: Issues To Address..Oliver MacaraegNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Studies: Microstructure, Properties & ProcessingDocumento52 paginePolymer Studies: Microstructure, Properties & ProcessingPieter Karunia DeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch07 Mechanical PropertiesDocumento15 pagineCh07 Mechanical Propertiesyahay1412Nessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer ProcessingDocumento28 paginePolymer ProcessingMousom SomNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro - Mechanical PropertiesDocumento40 pagineIntro - Mechanical PropertiesFitra WahyudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of Materials Testing WorkshopDocumento19 pagineMechanical Properties of Materials Testing WorkshopAndy PhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite MaterialsDocumento38 pagineComposite MaterialsjoyboyjayanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 3 Materials CorrosionDocumento21 pagineHandout 3 Materials CorrosionSimon Tin Hann PyngNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties: Issues To Address..Documento29 pagineMechanical Properties: Issues To Address..luisNessuna valutazione finora
- CompositeDocumento11 pagineCompositeAbhishek PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Material ScienceDocumento42 pagineChapter 6 Material Science9al6oonNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Mechanical Behaviour of MaterialsDocumento44 pagine6 Mechanical Behaviour of MaterialsArjun MahendraNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 16-Composite MaterialsDocumento23 pagineCH 16-Composite MaterialsNamer NoNessuna valutazione finora
- Topik PolimerDocumento43 pagineTopik PolimerZindarud Muhammad HaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Procesos de Conformado de Plasticos1Documento176 pagineProcesos de Conformado de Plasticos1ZarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch06 Mechanical PropertiesDocumento49 pagineCh06 Mechanical PropertiesEva NovitaliaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 16: Composite Materials: Issues To Address..Documento21 pagineChapter 16: Composite Materials: Issues To Address..AlfredjeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch15 CompositesDocumento8 pagineCh15 CompositesJuan RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- Strain in OtrsionDocumento45 pagineStrain in OtrsionrenebbNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Testing: Dr. Mohammad Dalour Hossen Beg Fkksa, UmpDocumento29 paginePolymer Testing: Dr. Mohammad Dalour Hossen Beg Fkksa, UmpmirazieyNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers Homework1 1Documento4 paginePolymers Homework1 1mike100% (1)
- Day 29: Mechanical Behavior of PolymersDocumento24 pagineDay 29: Mechanical Behavior of Polymersmailnewaz9677Nessuna valutazione finora
- Composites: Many Engineering Components Are CompositesDocumento30 pagineComposites: Many Engineering Components Are CompositesRahman HakimNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatigue in Polymers: By: Ido GalDocumento24 pagineFatigue in Polymers: By: Ido GalidogalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Introduction To PolymerDocumento11 pagineChapter 11 Introduction To Polymersyed izzuddin alhadyNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Strain Stress CurveDocumento15 paginePolymer Strain Stress CurvearelanopNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6: Mechanical Properties Elastic Deformation: Stress Strain Elastic Plastic ReversibleDocumento6 pagineChapter 6: Mechanical Properties Elastic Deformation: Stress Strain Elastic Plastic Reversiblesqaiba_gNessuna valutazione finora
- TI-Polymer-Shrinkage in PlasticsDocumento6 pagineTI-Polymer-Shrinkage in PlasticsRadu Sorin MarinescuNessuna valutazione finora
- MSE 3300-Lecture Note 01-Chapter 01 IntroductionDocumento28 pagineMSE 3300-Lecture Note 01-Chapter 01 IntroductionChuongNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite MaterialsDocumento41 pagineComposite MaterialsDinuk Sakoon BogahawatteNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Science: Prof. Satish V. KailasDocumento27 pagineMaterial Science: Prof. Satish V. KailasAsif KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimensional Molding ShrinkagesDocumento18 pagineDimensional Molding Shrinkagessanthosh5242Nessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics and Application of PolymersDocumento25 pagineCharacteristics and Application of PolymersAbdul RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Materials: R. Lindeke ENGR 2110Documento41 pagineComposite Materials: R. Lindeke ENGR 2110muthupecmec4908Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture No (1) .07 of Polymer EngineeringDocumento11 pagineLecture No (1) .07 of Polymer Engineeringmm11_nedNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Polymers CompositesDocumento35 pagine12 Polymers CompositesMatheus SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Polymers: Molecular Weight Crystallinity CrosslinkingDocumento13 pagineTypes of Polymers: Molecular Weight Crystallinity CrosslinkingspallocNessuna valutazione finora
- 470F Th-Mech Tutorial PDFDocumento5 pagine470F Th-Mech Tutorial PDFschmidtsteve7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Failure AnalysisDocumento6 pagineMechanical Failure Analysismilad66tehNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer - ApplicationsDocumento25 paginePolymer - ApplicationsarghmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Structures: Issues To Address..Documento35 paginePolymer Structures: Issues To Address..Miguel A. GraneroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento24 pagineChapter 7Jennifer MaamaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Reporting in MaterialsDocumento28 pagineReporting in MaterialsAichi SendouNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Deisgn With PolymersDocumento39 pagineEngineering Deisgn With Polymerschristopher_kephart1100% (1)
- Tribology of Polymers and Their Composites - Environmental EffectsDocumento45 pagineTribology of Polymers and Their Composites - Environmental EffectsJigar M. UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- 09C Polymer Structure and Properties (2.5 MB)Documento22 pagine09C Polymer Structure and Properties (2.5 MB)FâtïMâ ZâhřæNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of PolymerDocumento36 pagineProperties of PolymerhedayatinluvNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-1 History Physical Chemistry HdpeDocumento18 pagineChapter-1 History Physical Chemistry HdpeUSUIENessuna valutazione finora
- HDPEDocumento179 pagineHDPEnazar750100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Polymers Thermoplastics and AdditivesDocumento23 pagineChapter 3 Polymers Thermoplastics and AdditivesRusydi JamainNessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento9 pagineIntroductionLeonardo FurlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dynamic Damage and FragmentationDa EverandDynamic Damage and FragmentationDavid Edward LambertNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysDa EverandMaterials Data for Cyclic Loading: Aluminium and Titanium AlloysValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Mechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural MaterialsDa EverandMechanics of Materials 2: The Mechanics of Elastic and Plastic Deformation of Solids and Structural MaterialsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (14)
- Intro to G-Code ProgrammingDocumento55 pagineIntro to G-Code ProgrammingJusuf Kunic100% (1)
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-4Documento1 paginaHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-4Sung LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureDocumento1 paginaHeat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureHuma MaqsoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals - of - Heat - and - Mass - Transfer-Incropera-6th-solutions sm1 - 03Documento1 paginaFundamentals - of - Heat - and - Mass - Transfer-Incropera-6th-solutions sm1 - 03aegis414100% (1)
- sm2 7 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 7 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm1 05Documento1 paginasm1 05awoods12835Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals - of - Heat - and - Mass - Transfer-Incropera-6th-solutions sm1 - 03Documento1 paginaFundamentals - of - Heat - and - Mass - Transfer-Incropera-6th-solutions sm1 - 03aegis414100% (1)
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-4Documento1 paginaHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-4Sung LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- sm1 06Documento1 paginasm1 06awoods12835Nessuna valutazione finora
- sm1 05Documento1 paginasm1 05awoods12835Nessuna valutazione finora
- sm1 06Documento1 paginasm1 06awoods12835Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureDocumento1 paginaHeat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureHuma MaqsoodNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 51 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 51 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental of Heat Transfer Chapter 2 Problem 9 Answer KeyDocumento1 paginaFundamental of Heat Transfer Chapter 2 Problem 9 Answer KeyShubham AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 1Documento1 paginasm2 1Penny RogersNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 17 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 17 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
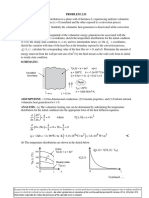
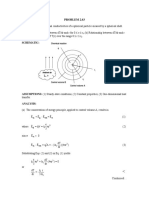
- Problem 2.8: Any Other Reproduction or Translation of This Work Beyond That Permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of The 1976Documento1 paginaProblem 2.8: Any Other Reproduction or Translation of This Work Beyond That Permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of The 1976Brain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 063 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 063 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- PROBLEM 2.27: G - Ax 0 L 0 LDocumento1 paginaPROBLEM 2.27: G - Ax 0 L 0 LLuis BarboNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental of Heat Transfer Chapter 2 Problem 5 Answer KeyDocumento1 paginaFundamental of Heat Transfer Chapter 2 Problem 5 Answer KeyShubham AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 6 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 6 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 061 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 061 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 52 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 52 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 21 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 21 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 53 PDFDocumento3 paginesm2 53 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature Distribution Heat Equation SolutionDocumento1 paginaTemperature Distribution Heat Equation SolutionBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 068 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 068 PDFNilton MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 19 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 19 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 16 PDFDocumento1 paginasm2 16 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- sm2 18 PDFDocumento2 paginesm2 18 PDFBrain Choirul IchsanNessuna valutazione finora
- 11,416 Project Quote for VIBOL's VillaDocumento15 pagine11,416 Project Quote for VIBOL's VillaSothea Born100% (1)
- Foundation DesignDocumento254 pagineFoundation DesignOeng Bunhak100% (2)
- ANSI - ASHRAE Standard 55-2017-11Documento1 paginaANSI - ASHRAE Standard 55-2017-11Mira MaeraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Auto Home Client Information WorksheetDocumento5 pagineAuto Home Client Information WorksheetJulia SharneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Design For Thermal Comfort During Summer & Psychometry Tool For Human ComfortDocumento8 pagineDesign For Thermal Comfort During Summer & Psychometry Tool For Human ComfortSwapan Kumar SarkerNessuna valutazione finora
- ACI Guide TumialanDocumento19 pagineACI Guide TumialanleoNessuna valutazione finora
- GCC Building CodeDocumento8 pagineGCC Building CodeNoorul AmeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Arch Culvert CalculationDocumento52 pagineArch Culvert CalculationJurie_sk36080% (1)
- Construction Techniques and Equipment and Practice - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocumento5 pagineConstruction Techniques and Equipment and Practice - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Analysis Report of Mrs. Pramila Shrestha Residential Building at Kavrepalanchowk, NepalDocumento106 pagineStructural Analysis Report of Mrs. Pramila Shrestha Residential Building at Kavrepalanchowk, NepalSopan GochheNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 M Span CulvertDocumento7 pagine6 M Span Culvertrkpragadeesh85% (13)
- Lecture#2-Introduction of Air Conditioning System - Part IIDocumento36 pagineLecture#2-Introduction of Air Conditioning System - Part IIHhhh GehrhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Eaves & Soffits Technical Specification - Jan 2012 LRDocumento28 pagineEaves & Soffits Technical Specification - Jan 2012 LRec yvia0% (1)
- NormeDocumento33 pagineNormeAndreea Anca BordeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Recirculation of Lab AirDocumento1 paginaRecirculation of Lab AirAhmed LabibNessuna valutazione finora
- Methods For Effective Room Air Distribution, Part 1Documento6 pagineMethods For Effective Room Air Distribution, Part 1anescuveronicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plaster Assemblies Chapter 02 Plaster Substrates LathDocumento26 paginePlaster Assemblies Chapter 02 Plaster Substrates LathFare NienteNessuna valutazione finora
- Deck SlabDocumento12 pagineDeck SlabAhsan SattarNessuna valutazione finora
- New York City Department of Buildings: The New NYC Building Code Chapter 9 Fire ProtectionDocumento39 pagineNew York City Department of Buildings: The New NYC Building Code Chapter 9 Fire ProtectionAfioOoNa100% (5)
- Architecture Is A Creative Process (Edited)Documento27 pagineArchitecture Is A Creative Process (Edited)Abbygail AntiqueraNessuna valutazione finora
- Contents of HvacDocumento2 pagineContents of Hvaclijo johnNessuna valutazione finora
- Bill of Quantities: Name of work:RAA Training Centre Sub Title:Gynasium (1 No.)Documento9 pagineBill of Quantities: Name of work:RAA Training Centre Sub Title:Gynasium (1 No.)Nasir UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- Building & Yard SESP11919Documento55 pagineBuilding & Yard SESP11919Pageduesca Rouel100% (1)
- 8-Bolted Stiffened End Plate DesignDocumento6 pagine8-Bolted Stiffened End Plate DesignlucianduNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of Curtain Wall System For High Rise BuildingsDocumento6 pagineAnalysis and Design of Curtain Wall System For High Rise Buildingsy2kareinNessuna valutazione finora
- Landform to ConstructionDocumento5 pagineLandform to ConstructionKareenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ruukki 41323 Accesorii Panou Termoizolant Sp2e PuDocumento24 pagineRuukki 41323 Accesorii Panou Termoizolant Sp2e PuMunteanu DanNessuna valutazione finora
- GE Product Data Condensing Units, Coils & Air HandlersDocumento16 pagineGE Product Data Condensing Units, Coils & Air HandlersRichard B. LoucksNessuna valutazione finora
- Bricklaying: Brick Laying Types and BondsDocumento6 pagineBricklaying: Brick Laying Types and BondsKate CaranguianNessuna valutazione finora
- Itp For Formworks (Ringlock System)Documento3 pagineItp For Formworks (Ringlock System)damianNessuna valutazione finora