Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sun and The Design Process
Caricato da
Jireh GraceTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sun and The Design Process
Caricato da
Jireh GraceCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SUN AND THE
DESIGN PROCESS
In the design of buildings that makes use of the principles of
passive cooling, one essential consideration is to understand
SOLAR GEOMETRY because the suns rays upon hitting the
earth vary with time and latitudes.
SOLAR GEOMETRY - describes the relationship between the
sun and earth or more importantly the relationship of solar
radiation, the product of the sun with any location on the
earth.
In concept, a specific site is made static and the sun allowed to
move from east to west across the sky. This is technically
called CELESTIAL SPHERE.
Sun Control
Warm Climates excessive solar gain result in
high cooling energy consumption.
Cold Climates south facing windows contribute
to passive solar heating.
RELATIONSHIP OF THE SUN
AND EARTH
SUN Main source of light and
heat . It is the closest star
to earth
Core- 15M degrees Celsius
Distance to Earth = 150M Kms.
- Apparently moves across the
sky at a rate of
15.04 deg/hr.
EARTH
The earth revolves in an
orbit around the sun. It
takes 365.25 days to
complete one revolution
around the sun.
Rotates about its polar
axis at 360.99 degrees
per day as it revolves
around the sun.
The period of rotation of
the earth in its axis is 23
hours 56 minutes and 4
seconds.
The Earths polar axis is
inclined at 23deg 47 from a
vertical to the earths orbital
plane
Inclination causes seasonal
changes on earth.
SOLSTICE - either of the two points on the ecliptic at which the sun
is overhead at the tropic of Cancer or Capricorn at the
summer and winter solstices.
(Astronomy) either the shortest day of the year (winter
solstice) or the longest day of the year (summer solstice)
SUMMER SOLSTICE - lies on the Tropic of Cancer at 2327 north latitude.
WINTER SOLSTICE - lies on the Tropic of Capricorn at 2327 south latitude.
EQUINOX - means "equal day and night
-occurs twice a year, when the tilt of the earths axis is inclined
neither away from nor towards the sun the center of the Sun being in
the same plane as the Earth's equator
-At an equinox, the Sun is at one of two opposite points on the
Celestial sphere where the celestial equator (i.e. declination 0)
and ecliptic intersect. These points of intersection are
called equinoctial points: classically, the vernal point and the autumnal
point.
Note : The inclination of the polar axis reaches its maximum on June 21
during the summer solstice where the sun would be at its farthest
northern position. Therefore, June 21
st
is considered longest day.
During the winter solstice, the inclination draws towards the sun
on December 21. The sun is at its nearest northern position.
It is on this day where we experience the shortest day.
As equinox means equal, on March 21 and September 21, both
northern and southern hemisphere experience equal amount of
solar radiation. During this period the sun rises and sets directly
to the position of east to west, respectively.
THE SUN PATH
The position of the sun is determined by two angles:
SOLAR ALTITUDE ANGLE
SOLAR AZIMUTH ANGLE
SOLAR ALTITUDE
Solar Altitude is the angular
height of the sun measured from
the Horizon. Above the horizon is
positive, below is negative. The
sun directly in the centre of the
sky has a Solar Altitude of 90
degrees.
SOLAR AZIMUTH
Solar Azimuth is the angular
position of the sun measured
around the Horizon with North
being 0 degrees, East 90 degrees,
South 180 degrees and West 270
degrees.
LATITUDES
FACTORS THAT DETERMINE THE AMOUNT
OF SOLAR RADIATION ON EARTH
The position of the sun according to time and
day
The position of the sun according to the
season
Clouds and atmospheric obstructions
The angle of slope of the station
The height of the station
The situation of the station with regards to
its surroundings
THE SOLAR CHARTS
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Henry Irwin and the Indo Saracenic Movement ReconsideredDa EverandHenry Irwin and the Indo Saracenic Movement ReconsideredNessuna valutazione finora
- CONTOURSDocumento12 pagineCONTOURSsoumyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tubular Steel Monitor Roof Truss - Large Span Constructions - Civil Engineering ProjectsDocumento3 pagineTubular Steel Monitor Roof Truss - Large Span Constructions - Civil Engineering ProjectsKranthi Kumar Chowdary ManamNessuna valutazione finora
- Humayun's TombDocumento17 pagineHumayun's TombShivamNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of Tombs in IndiaDocumento25 pagineEvolution of Tombs in IndiaSumit Sharma100% (1)
- ADSSDocumento7 pagineADSSAr tejophaniNessuna valutazione finora
- KhyahDocumento74 pagineKhyahShashi Kant SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Site AnalysisDocumento3 pagineSite Analysisbhargavi100% (1)
- Habib RahmanDocumento23 pagineHabib RahmanAkshay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- CLIMATOLOGY Study For Building Design.: Dayanand Sagar Acadamy of Technology&Management. Udayapura, Bangalore 560 082Documento34 pagineCLIMATOLOGY Study For Building Design.: Dayanand Sagar Acadamy of Technology&Management. Udayapura, Bangalore 560 082arunNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Bye LawsDocumento14 pagineBuilding Bye LawsAlshifa IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Adalaj StepwellDocumento19 pagineAdalaj Stepwell024Gawde SoniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Services: Unit - 2 Electonic SystemsDocumento49 pagineAdvance Services: Unit - 2 Electonic SystemsPratima Mahesh100% (1)
- ARCUATED Literature Study and Site Study PDFDocumento68 pagineARCUATED Literature Study and Site Study PDFAnika SethiNessuna valutazione finora
- Video 3.6: Golconde Dormitory, Pondicherry - A Case Study of Bio-Climatic Architecture in The Warm-Humid TropicsDocumento2 pagineVideo 3.6: Golconde Dormitory, Pondicherry - A Case Study of Bio-Climatic Architecture in The Warm-Humid TropicsAissatou Inna YayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Specific Constructions: Technical SupportDocumento5 pagineSpecific Constructions: Technical SupportEnginerdouglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Conscious Design-Abhilasha FoglaDocumento32 pagineClimate Conscious Design-Abhilasha FoglapallaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Le CorbusierDocumento10 pagineLe CorbusierPruthvi Varma100% (1)
- General Hospital GhansoliDocumento20 pagineGeneral Hospital GhansoliPrianca JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Solar ArchitectureDocumento19 pagineSolar ArchitectureZ43O100% (1)
- 03 Acoustical DefectsDocumento25 pagine03 Acoustical DefectsParth Gupta0% (1)
- Mill Owners Association - PresentationDocumento22 pagineMill Owners Association - PresentationGargi KoulNessuna valutazione finora
- Oakwood, Ub CityDocumento18 pagineOakwood, Ub CityAfreen BandayNessuna valutazione finora
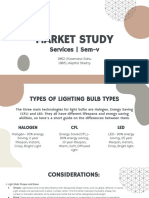
- Lights-Market SurveyDocumento29 pagineLights-Market Survey1965 Aliptha ShettyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cold and Sunny EVSDocumento26 pagineCold and Sunny EVSShubham DabholkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nawabi Kothies and Shekhawati Havelis: Comparative Study of Deserted Architectural MarvelsDocumento7 pagineNawabi Kothies and Shekhawati Havelis: Comparative Study of Deserted Architectural MarvelsKamran 123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cams (ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF GEODESIC STRUCTURES)Documento3 pagineCams (ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF GEODESIC STRUCTURES)maddy laneNessuna valutazione finora
- Audi Case StudyDocumento8 pagineAudi Case Studydhanaraj100% (1)
- Literature Study: Architectural Design V - Play SchoolDocumento21 pagineLiterature Study: Architectural Design V - Play SchoolPunniya100% (1)
- Site Analysis: Krishnapriya 19AR04Documento31 pagineSite Analysis: Krishnapriya 19AR04Mushthaq MahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Adani Vidya Mandir: Architect: Apurva Amin Architects Location: Ahmedabad, Gujrat, IndiaDocumento9 pagineAdani Vidya Mandir: Architect: Apurva Amin Architects Location: Ahmedabad, Gujrat, IndiaRUSHALI SRIVASTAVANessuna valutazione finora
- Literature Study ParkbrowDocumento6 pagineLiterature Study Parkbrowrashi1717Nessuna valutazione finora
- Highway Transit Facility CenterDocumento9 pagineHighway Transit Facility Centersymbiosis architectureNessuna valutazione finora
- Agra Fort: Architectural ConservationDocumento26 pagineAgra Fort: Architectural ConservationRaj DarwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Independence Architecture in India Development of Secular Architecture From The End of The 18th Century To The Middle of The 20th CenturyDocumento59 paginePre-Independence Architecture in India Development of Secular Architecture From The End of The 18th Century To The Middle of The 20th Centuryyashaswini100% (1)
- Site ClimateDocumento8 pagineSite ClimateNidhi MehtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro Climate Analysis of Bhopal ThroughDocumento5 pagineMicro Climate Analysis of Bhopal ThroughDrishti AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ad6 Spa DelhiDocumento25 pagineAd6 Spa DelhimadhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Low Energy Traditional Architecture of LucknowDocumento7 pagineLow Energy Traditional Architecture of LucknowRus NaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study - MetroDocumento12 pagineCase Study - MetroJnanaprakash MdNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Systems: Lamella DomesDocumento19 pagineStructural Systems: Lamella DomesMohammad KHNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate and Built Form-1Documento29 pagineClimate and Built Form-1Deepa Rani RNessuna valutazione finora
- Twa Structural AnalysisDocumento24 pagineTwa Structural Analysisvishnu kapadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laurie Baker PresentedDocumento33 pagineLaurie Baker PresentedArnav DasaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Triveni Kala Sangam India International Center Case StudyDocumento1 paginaTriveni Kala Sangam India International Center Case StudyHimanshu SainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Le - CorbusierDocumento34 pagineLe - CorbusierPavani KajaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oscar Newman: (30TH SEP 1935-14 APRIL 2004)Documento25 pagineOscar Newman: (30TH SEP 1935-14 APRIL 2004)Nayab Khan100% (1)
- Site Analysis: A. About PuneDocumento13 pagineSite Analysis: A. About PuneArchana MahaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Highway Restaurant Case Study: EL CAMIONDocumento11 pagineHighway Restaurant Case Study: EL CAMIONAkshitha Nomula100% (1)
- Artist's ResidenceDocumento23 pagineArtist's ResidenceSahitya H MNessuna valutazione finora
- GRIHADocumento26 pagineGRIHAkumar SpkNessuna valutazione finora
- Trombe Wall and Soalrium: Submitted By: Ibli Nehal Nidhi Ubaid ShrutiDocumento12 pagineTrombe Wall and Soalrium: Submitted By: Ibli Nehal Nidhi Ubaid ShrutiShruti SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Building Design Case Studies: Asia Shabbir 1-2-BAR-005-14Documento6 pagineGreen Building Design Case Studies: Asia Shabbir 1-2-BAR-005-14nikita singhalNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-4 (Dulal Mukherjee, Chandavarkar, Thacker Et Al)Documento21 pagineUnit-4 (Dulal Mukherjee, Chandavarkar, Thacker Et Al)Ankit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- PneumaticDocumento45 paginePneumaticTanuj BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Anant Damodar Raje: - Born: - 1954: - 1957-1960Documento43 pagineAnant Damodar Raje: - Born: - 1954: - 1957-1960prasannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate ConsultantDocumento186 pagineClimate ConsultantAkila KarthikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Buoyant Foundation: Neha Das Sem 5 Roll No.07 Architectural Building Construction & MaterialsDocumento16 pagineBuoyant Foundation: Neha Das Sem 5 Roll No.07 Architectural Building Construction & MaterialsNeha DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Somnath Temple DevelopmentDocumento18 pagineSomnath Temple DevelopmentshubhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Earth and Sun Relationships PDFDocumento9 pagineEarth and Sun Relationships PDFAparajita MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1Documento15 pagineChap 1asfefeNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Service and Electrical CircuitsDocumento20 pagineElectrical Service and Electrical CircuitsJireh Grace100% (3)
- Intro Methods RTPDocumento179 pagineIntro Methods RTPSuresh MgNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To StatsDocumento43 pagineIntro To StatsaziclubNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Descriptive StatisticsDocumento156 pagineIntroduction To Descriptive StatisticsJireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics: For Higher Secondary To First Year CollegeDocumento267 pagineStatistics: For Higher Secondary To First Year CollegeJireh Grace100% (1)
- Surveying and MeasurementDocumento51 pagineSurveying and MeasurementJireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Basic Statistical MethodsDocumento2 pagineIntroduction To Basic Statistical MethodsJireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical TermsDocumento11 pagineStatistical TermsSanath NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Structural ReviewerDocumento17 pagineStructural ReviewerJireh Grace100% (4)
- 2010 MethodsDocumento42 pagine2010 MethodsSaurabh PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Architects National CodeDocumento14 pagineArchitects National CodeGallardo NixonNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To StatisticsDocumento28 pagineIntroduction To StatisticsJireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Graphic Scales (Metric)Documento2 pagineGraphic Scales (Metric)Jireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Good Building Handbook PhilippinesDocumento85 pagineGood Building Handbook Philippines61cmNessuna valutazione finora
- Professional Practice Notes CombinedDocumento32 pagineProfessional Practice Notes CombinedJireh Grace86% (14)
- UAP Documents Review and Practice ExamsDocumento87 pagineUAP Documents Review and Practice ExamsJireh Grace92% (12)
- M Ch11 Slope StabilizationDocumento12 pagineM Ch11 Slope StabilizationSulekha NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Zoning Ordinance For The City of Baguio 2012Documento31 pagineComprehensive Zoning Ordinance For The City of Baguio 2012Jireh Grace91% (22)
- Residential Landscape: Design Process For The Private ResidenceDocumento41 pagineResidential Landscape: Design Process For The Private ResidenceJireh Grace100% (1)
- Literature Study: Sports ComplexDocumento54 pagineLiterature Study: Sports ComplexJireh Grace92% (89)
- Introduction To ElectricityDocumento20 pagineIntroduction To ElectricityJireh Grace100% (1)
- Mixed ReviewerDocumento10 pagineMixed ReviewerAlecsisRoeEstañolFrascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Architecture CompilationDocumento18 pagineModern Architecture CompilationJireh Grace100% (5)
- Site Investigation, Soil Types and Foundation Design in Relation To Ground MovementDocumento63 pagineSite Investigation, Soil Types and Foundation Design in Relation To Ground MovementJireh Grace100% (3)
- Building Permit ProcessDocumento1 paginaBuilding Permit ProcessJireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Logbook GuideDocumento8 pagineLogbook GuideJireh Grace100% (2)
- Sample Problems in Acoustics HandoutDocumento27 pagineSample Problems in Acoustics HandoutJireh GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Owner-Architect Agreement SPP UAP DocumentDocumento10 pagineOwner-Architect Agreement SPP UAP DocumentJireh Grace100% (7)
- Drawing in StyleDocumento54 pagineDrawing in Stylenave101100% (1)
- Physical Law As Alien IntelligenceDocumento5 paginePhysical Law As Alien Intelligencerla97623Nessuna valutazione finora
- Date:: Horoscope Generated by Free Android App "Jyotishapp - Astrology Jyotish". (App Id Com - Vishdroid.Jyotisha)Documento14 pagineDate:: Horoscope Generated by Free Android App "Jyotishapp - Astrology Jyotish". (App Id Com - Vishdroid.Jyotisha)Mandla narendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Astrological Research SuicideDocumento413 pagineAstrological Research Suicidelinchi100% (4)
- Chapter 10Documento2 pagineChapter 10Sha Ismail100% (1)
- Chapter 2. Orbits and Launching MethodsDocumento10 pagineChapter 2. Orbits and Launching MethodsMMhammed AlrowailyNessuna valutazione finora
- Telescope: Reflecting Telescope Mount Wilson Observatory Optical InstrumentsDocumento42 pagineTelescope: Reflecting Telescope Mount Wilson Observatory Optical InstrumentsVicky SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ngang Grin Hkra Gawde Da Sai Amyu Sha Shanglawt Rawt Malan Lam Hpe Ngang Kang Hkra Hkrang Shale Shanglawm Na LamDocumento5 pagineNgang Grin Hkra Gawde Da Sai Amyu Sha Shanglawt Rawt Malan Lam Hpe Ngang Kang Hkra Hkrang Shale Shanglawm Na LamHG KachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ayanamsa &zodiacDocumento2 pagineAyanamsa &zodiacRamanasarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Cycle of A StarDocumento5 pagineLife Cycle of A StarJhuly-an Silva VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Astrology AnalysisDocumento6 pagineAstrology AnalysisNayana SunilNessuna valutazione finora
- 00 Venus Cycle Outline Plus Info PDFDocumento10 pagine00 Venus Cycle Outline Plus Info PDFori-oNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmic Ray Array ReconstructionDocumento15 pagineCosmic Ray Array Reconstructionpriyansh143678Nessuna valutazione finora
- NASA Facts John F. Kennedy Space CenterDocumento8 pagineNASA Facts John F. Kennedy Space CenterBob AndrepontNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Blackboard Background Bordeaux VariantDocumento50 pagineSimple Blackboard Background Bordeaux VariantSilNessuna valutazione finora
- Satellite Motion 9 Sputnik SolnDocumento4 pagineSatellite Motion 9 Sputnik SolnJoey BryanNessuna valutazione finora
- Used SCT Buyers GuideDocumento22 pagineUsed SCT Buyers GuideRuggero RamponeNessuna valutazione finora
- For The Sidereal Zodiac - Kenneth BowserDocumento3 pagineFor The Sidereal Zodiac - Kenneth BowserGuilherme Alves PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Secret KeyDocumento83 pagineSecret KeyMelisa Pizzolato100% (1)
- Aminoacido No Esencial: CisteinaDocumento38 pagineAminoacido No Esencial: CisteinaAdrian tirado lugoNessuna valutazione finora
- BÀI TẬP SO SÁNH HƠN VÀ HƠN NHẤT LỚP 6Documento4 pagineBÀI TẬP SO SÁNH HƠN VÀ HƠN NHẤT LỚP 6Ngọc TạNessuna valutazione finora
- Waffle Charts Powerpoint Template: Edit Here Edit Here Edit Here Edit HereDocumento8 pagineWaffle Charts Powerpoint Template: Edit Here Edit Here Edit Here Edit Herefarhan1675Nessuna valutazione finora
- Messenger, Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging A Mission To Orbit and Explore The Planet MercuryDocumento366 pagineMessenger, Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging A Mission To Orbit and Explore The Planet MercuryBob AndrepontNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Nearest Stars and Brown DwarfsDocumento15 pagineList of Nearest Stars and Brown Dwarfssteffany3442Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eclipse: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocumento10 pagineEclipse: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDexterNessuna valutazione finora
- Transformation GuideDocumento15 pagineTransformation GuideSilvana Bo100% (1)
- The Messenger: No. 127 - March 2007Documento80 pagineThe Messenger: No. 127 - March 2007European Southern ObservatoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Planet JupiterDocumento16 paginePlanet JupiterVaibhav SamantNessuna valutazione finora
- Book - 1919 - Neville Spearman - Everyman's AstrologyDocumento201 pagineBook - 1919 - Neville Spearman - Everyman's AstrologyHij100% (1)
- ASTRONOMICAL DEFINITIONS and CalculationsDocumento9 pagineASTRONOMICAL DEFINITIONS and CalculationsKo Ko AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Ancient Greek Models of The UniverseDocumento5 pagineAncient Greek Models of The UniverseAr Anne Ugot83% (6)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDa EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (392)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDa EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (42)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDa EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDa EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Da EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (378)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsDa EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (722)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceDa EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDa EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (51)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDa EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (137)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDa EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (58)
- From Darkness to Sight: A Journey from Hardship to HealingDa EverandFrom Darkness to Sight: A Journey from Hardship to HealingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (3)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonDa EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (103)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseDa EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (69)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesDa EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2193)
- The Egoscue Method of Health Through Motion: A Revolutionary Program That Lets You Rediscover the Body's Power to Protect and Rejuvenate ItselfDa EverandThe Egoscue Method of Health Through Motion: A Revolutionary Program That Lets You Rediscover the Body's Power to Protect and Rejuvenate ItselfValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (8)
- Lessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Da EverandLessons for Survival: Mothering Against “the Apocalypse”Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisDa EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceDa EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (18)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessDa EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingDa EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingDa EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (5)
- Crooked: Outwitting the Back Pain Industry and Getting on the Road to RecoveryDa EverandCrooked: Outwitting the Back Pain Industry and Getting on the Road to RecoveryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (9)