Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Susanka Presentation @sierra (Repaired)
Caricato da
Susanka SanjeewaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Susanka Presentation @sierra (Repaired)
Caricato da
Susanka SanjeewaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MOBILE COMMUNICATION-Driving
Test
Basic concepts
Prepared By
SUSANKA
SANJEEWA
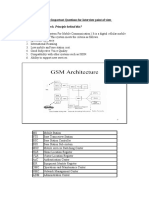
GSM Frequency Allocation
FDMA & TDMA Combination
FDMA & TDMA Cntd..
Uplink frequencies: Fu(n) = 890 + 0.2
n (1 <= n <= 124)
Downlink frequencies: Fd(n) = Fu(n) +
45
Physical & Logical Channel
Logical Channels
Logical Channel Cntd..
Frequency Correction Channel(FCCH)
Find the TRX among the several TRXs
The mobile scans for this signal after it has been
switched on, since it has no information as to
which frequency to use
Synchronization Channel(SCH)
Contains BSIC
Frame synchronizing
Broadcast Channel(BCCH)
Contains detailed network and cell specific
information
Frequency of particular cell and neighboring cells
Paging group
Information about surrounding cells
Logical Channel cntd..
Logical Channel cntd..
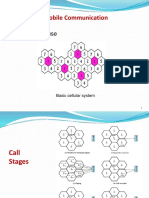
Cell Structure
Frequency Re-use
F=1
F=2
F=3
F=4,8
F=5,9
F=6,10
F=7
F=1
F=2
F=3
F=4,8
F=5,9
F=6,10
F=7
F=1
F=2
F=3
F=4,8
F=5,9
F=6,10
F=7
F= 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10
Clusters
Co-Channel ( Re-use ) Cells
GSM uses concept of cells
One cell covers small part of network
Network has many cells
Frequency used in one cell can be used
in another cells
This is known as Frequency Re-use
Network diagram
PSTN MSC
EIR AuC
HLR VLR
BSC
BSC
Base Station Subsystem
Network Switching Subsystem
Mobile Station
BTS
BTS
Network Components
Mobile Station (MS)
Subscriber Identity module (SIM)
Mobile Equipment (ME)
Base Station System (BSS)
The Base Transceiver Station /BTS
RF components/ antenna
communicates with the MS
The Base Station Controller /BSC
control single or multiple BTSs
communicates with the MSC
The Transcoder XCDR
compact the signals
efficiently sent over the terrestrial interfaces.
often located closer to the MSC.
Network Components Cntd..
Network Switching System
main switching functions of the GSM
databases required for subscriber data and
mobility management.
manage communications between the GSM
network and other telecommunications
networks
The components of the Network Switching
System
Mobile Services Switching Centre MSC
Home Location Register HLR
Visitor Location Register VLR
Equipment Identity Register EIR
Authentication Centre AUC
Network Components Cntd..
MSC
Call Processing
Includes control of data/voice call setup
inter-BSS and inter-MSC handovers
control of mobility management
(subscriber validation and location).
Operations and Maintenance Support
Includes database management
traffic metering and measurement
Interworking
Manages the interface between the
GSM network and the PSTN.
Billing
Collects call billing data.
Network Components Cntd..
Home Location Register (HLR)
Consist of
Reference database for subscriber
parameters.
Subscriber ID(IMSI & MSISDN)
Current VLR
Supplementary services
Supplementary services
Information
Subscriber status
Authentication key & AUC functionality
Mobile subscriber roaming number
Network Components Cntd..
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
Contains a copy of most of
the data stored at the HLR.
Temporary data which exists
for only as long as the subscriber
is active in the particular area
covered by the VLR.
Additional data stored in the VLR
Mobile status (busy/free/no answer etc.).
Location Area Identity (LAI).
Temporary Mobile
Subscriber Identity (TMSI).
Mobile Station
Roaming Number (MSRN).
Network Components Cntd..
Equipment Identity Register (EIR)
Database for validating the International
Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI).
Concerned solely with MS equipment and not
with the subscriber
Authentication Centre (AUC)
perform the authentication
take place each time the
subscriber initializes
on the system.
Multipath Propagation
To reduce it
Equalization
Signal dispersion caused by multipath signals
(Burst distortion)
Training Sequence is sent(set sequence of bits which is
known by both the transmitter and receiver)
Equalizer measures and mimics the distortion
The equalizer then compares the received data with the
distorted possible transmitted sequences and chooses
the most likely one.
Channel coding & Interleaving
Channel coding
User data is encoded using standard algorithms
For error correction and detection
Extra information added to user data
Interleaving
Spreading coded
data in to many burst
If one burst is lost
recovery is possible
Diversity
Diversity cntd..
Modulation
Handovers
HANDOVER - INTRA BSC
BSC
BSC
BSC
BSC
BTS 1
MSC /
VLR
MSC /
VLR
MSC /
VLR
PSTN
HANDOVER - INTRA BSC
BSC
BSC
BSC
BSC
BTS 1
BTS 2
MSC /
VLR
MSC /
VLR
MSC /
VLR
PSTN
HANDOVER - INTER BSC
BTS 2
BTS 1
MSC /
VLR
MSC /
VLR
MSC /
VLR
PSTN BSC 1
BSC 2
BSC
BSC
HANDOVER - INTER MSC
BTS 2
BTS 1
MSC /
VLR1
MSC /
VLR2
MSC /
VLR
PSTN BSC
BSC 1
BSC 2
BSC
Power Control
Purposes of Power control
Reduce power outputs to reduce interference
Limit unnecessary power emissions to increase the
longevity of battery-power equipments
To adjust cell coverage by adjusting BTS output
power.
GSM power control methods
Adaptive Power Control
This automatically adjusts power outputs to meet
the prescribed service quality level
Discontinuous Transmission (DTX)
Transmissions are only made when information is
to be passed.
Discontinuous Reception (DRX)
Only listening out on specific control channels
increase MS battery life
Power Control Cntd..
Obstacles between antennas
called shadowing(Log normal
fading)
Causes to attenuate the signal
Solution is adaptive power
control
Based on quality and strength of
the received signal Base Station
informs the MS to increase or
decrease the power as required
Information sent through the
SACCH
Power Control Cntd..
The VAD detects speech & initiates transmission at
13kbps.
When no speech is detected, data rate is reduced
500bps
Sufficient to provide comfort noise
When switch on the phone
Synchronization information broadcast by network &
analyze by the mobile
Channel Allocation
Paging
In case of mobile terminated call ,the subscriber has to be
paged
During the conversation ,MS measure the signal strength
of adjacent carriers and send measurement report to BSC
Paging cntd..
Mobile Originated Call:
Coach enters the numbers
on his phone and pushes
send...
1 866 567 1234
SEND
Mobile Originated Call:
The mobile then sends a channel request to the network
This is done as an up-link request on the RACH.
Mobile Originated Call:
The network responds to the mobile with an
Immediate Assignment
This is done as a down-link response on the AGCH.
The mobile is given:
Channel Type (SDCCH)
Timeslot number assigned
Training Sequence Number (TSC)
Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number (AFRCN)
Mobile Allocation Number (MAIO)
Hopping Sequence Number (HSN)
The Reference Request that was sent from the BTS
Timing Advance, ( the access delay calculated by the BTS)
Mobile Originated Call:
The Mobile then moves to the assigned
channel (SDCCH) and then sends a
Service Request.
This is a request on the SDCCH to tell
the network what kind of service the
mobile needs.
Mobile Originated call
SMS
Data Call
Mobile Originated Call:
The Network then sends the Mobile an
Authentication Request on the same SDCCH
This is a request for the mobile to process
the RAND sent from the AC via the VLR.
The RAND is included in this message
and the mobile then must process this
RAND number and its own Ki number
with an A3 algorithm stored on its SIM.
This produces a number called SRES. This is the
same SRES number that should be in VLR for this
subscriber.
Mobile Originated Call:
The Mobile then sends a Authentication
Response on the same assigned SDCCH
timeslot.
This will be the SRES number from
the mobiles calculation with the
RAND number just sent.
This SRES number will be sent to the VLR for comparison.
If all is well and there is a match at the VLR the subscriber is
given access.
Mobile Originated Call:
The Network then send the mobile
the Ciphering Mode Setting on the
same SDCCH timeslot.
This sets up the encryption for the
phones further transaction on the air
interface.
Mobile Originated Call:
The mobile responds with a Cipher
Mode Complete command on the
SDCCH.
This tells the network the mobile
received the cipher command and
is ready.
Mobile Originated Call:
The mobile then sends setup
message which is the phone
numbers to call. (On the SDCCH).
This tells the network what number
to route the call to.
Mobile Originated Call:
The network responds with a Call
Proceeding message on the SDCCH
timeslot.
This lets the phone know that the
network got the numbers and is
proceeding to route the call.
Mobile Originated Call:
If the call is routed and the network
gets a connection to the phone then
an Assignment Command is send to
the phone on the SDCCH
This tells mobile to move to a TCH
timeslot and gives the phone its
new timeslot allocation.
Mobile Originated Call:
The mobile responds with a
Assignment Complete Command on
the SDCCH.
This lets the network know the
mobile got its new TCH assignment
and is moving to it.
Mobile Originated Call:
The Network then sends the mobile
an ALERT command letting it know
the call is about to be connected.
This is a FACCH
This is somewhat like the final warning
that the call is about to be connected.
This happened on the physical TCH
timeslot that was just assigned to the
mobile but the network changes the
timeslot to a logical FACCH for this
alert.
Mobile Originated Call:
The Network then sends the connect
command to the phone telling it to
connect onto the TCH for the call.
This also happens on the TCH but
again is a logical FACCH.
This is the connect message to the
phone telling it to go active on the
assigned TCH for the call.
Mobile Originated Call:
The mobile responds to this
message with a Connect
Acknowledge response. This is also
on the TCH assigned but as a
FACCH.
This lets the network know the
mobile has attached to the TCH
timeslot and is ready for the calls
connection.
Mobile Originated Call:
The Call now takes place and Coach
is talking to his dialed party. This is
the TCH.
Routing a call
Routing a call
Routing a call
Routing a call
Routing a call
Mobile Terminated Call:
1 866 567 1234
Mrs.. Coach picks up
here home phone and
calls Coachs mobile
number.
Mobile Terminated Call:
That call is routed to the GSM networks MSC
from the landlines local telco switch.
The MSC contacts the VLR for
information on where Coachs mobile is
located within the network.
The VLR tells the MSC where to find
Coachs mobile.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The VLR then sends a Paging Request to
the LAC Coachs mobile was last updated
in.
This is done as a down-link PCH.
Basically the network is looking for Coachs mobile.
Coachs mobile should be constantly monitoring the
BCH timeslot for PCH, (paging) messages.
The mobile then sends a channel request to the network
This is done as an up-link request on the RACH.
Mobile Terminated Call:
Mobile Terminated Call:
The network responds to the mobile with an
Immediate Assignment
This is done as a down-link response on the AGCH.
The mobile is given:
Channel Type (SDCCH)
Timeslot number assigned
Training Sequence Number (TSC)
Absolute Radio Frequency Channel Number (AFRCN)
Mobile Allocation Number (MAIO)
Hopping Sequence Number (HSN)
The Reference Request that was sent from the BTS
Timing Advance, ( the access delay calculated by the BTS)
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile then moves to the assigned
channel (SDCCH) and then sends a
Paging Response.
This is a reply on the SDCCH in
response to the paging request earlier.
Much like the Service Request the
phone is responding to the network as
to what services it needs setup to
according to the paging request
information.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Network then sends the Mobile an
Authentication Request on the same SDCCH
This is a request for the mobile to process
the RAND sent from the AC via the VLR.
The RAND is included in this message
and the mobile then must process this
RAND number and its own Ki number
with an A3 algorithm stored on its SIM.
This produces a number called SRES. This is the same
SRES number that should be in VLR for this subscriber.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile then sends a Authentication
Response on the same assigned SDCCH
timeslot.
This will be the SRES number from
the mobiles calculation with the
RAND number just sent.
This SRES number will be sent to the VLR for comparison.
If all is well and there is a match at the VLR
the subscriber is given access.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Network then send the mobile
the Ciphering Mode Setting on the
same SDCCH timeslot.
This sets up the encryption for the
Mobiles further transaction on the
air interface.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile responds with a Cipher
Mode Complete command on the
SDCCH.
This tells the Network the mobile
received the cipher command and
is ready.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Network then sends Setup
Message to the mobile. (On the
SDCCH).
This tells the Mobile to being
ringing.
ring
ring
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile responds with a Call
Confirmation message on the
SDCCH timeslot.
This lets the Network know that the
mobile is ready to accept the call.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Network responds with the
Assignment Command on the
SDCCH
This tells the Mobile to move to a
TCH timeslot and gives the phone
its new timeslot allocation.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile responds with a
Assignment Complete Command on
the SDCCH.
This lets the Network know the
mobile got its new TCH assignment
and is moving to it.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile then sends the network
the Alert Command on the FACCH
(TCH).
This is the phones response when
Coach pushes the talk button to
accept the call.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Mobile then sends the connect
command to the Network telling it to
connect onto the TCH for the call.
This also happens on the TCH but
again is a logical FACCH.
This is the connect message to the
Network telling it to go active on
the assigned TCH for the call.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Network responds to this
message with a Connect
Acknowledge response. This is also
on the TCH assigned but as a
FACCH.
This lets the Mobile know the
Network has attached to the TCH
timeslot and is ready for the calls
connection.
Mobile Terminated Call:
The Call now takes place and Coach
is talking to his dialed party. This is
the TCH.
CHAN REQ (RACH)
Mobile
Network
IMM ASSIGN (AGCH)
CM SERVICE REQ (SDCCH)
AUTH REQ (SDCCH)
AUTH RESP (SDCCH)
CIPH MOD CMD (SDCCH)
CIPH MOD COM (SDCCH)
SETUP (SDCCH)
CALL PROC (SDCCH)
ASSIGN CMD (SDCCH)
ASSIGN COM (SDCCH)
ALERT (FACCH/TCH)
CONNECT (FACCH/TCH)
CONECT ACK (FACCH/TCH)
CALL IN PLACE TCH
Mobile Originated...
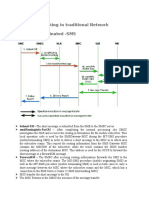
CHAN REQ (RACH)
Mobile
Network
IMM ASSIGN (AGCH)
PAGE RESP (SDCCH)
AUTH REQ (SDCCH)
AUTH RESP (SDCCH)
CIPH MOD CMD (SDCCH)
CIPH MOD COM (SDCCH)
SETUP (SDCCH)
CALL CONF (SDCCH)
ASSIGN CMD (SDCCH)
ASSIGN COM (SDCCH)
ALERT (FACCH/TCH)
CONNECT (FACCH/TCH)
CONECT ACK (FACCH/TCH)
CALL IN PLACE TCH
Mobile Terminated...
PAGE REQ (PCH)
Evolution of GSM to UMTS
UMTS Air Interface
UMTS Air Interface
WCDMA FDD
DL Centre Frequency = DL UARFCN 5
DL Frequency Band = DL Centre Frequency 2.5MHz
UL Frequency Band = DL Frequency Band - 190MHz
UL UARFCN = UL Centre Frequency * 5
WCDMA FDD Technology
Multiple Access
Technologies
WCDMA Technology
UMTS Air Interface
Spreading Codes
Channelization Codes
Spreading means increasing the signal bandwidth.
Spreading includes two operations:
Channelization (increases signal bandwidth) - using orthogonal
codes
Scrambling (does not affect the signal bandwidth) - using pseudo-
noise codes
Scrambling Codes
DL Spreading &
Multiplexing
UMTS Power Control
3G Parameters
1.Recived Signal Code Power(RSCP)-Measure of power received from
antenna
2.Ec/No-Measure of interference from other sites
3.Serving PSC-To identify serving cell
4.Missing neighbors(not configuring HO),Blocked Calls, Dropped Calls
5.Download/Upload through put
2G Parameters
1.Recieve Level-Measure of power receive from antenna
2.Rx Quality Measure of interference
3.Serving ARFCN- to identify serving cell
4.Blocked Calls, Dropped Calls, Hand over Failures
Drive Test Process
Identifying Customer Requirement
Eg: Band Locking, PSC Locking, BCCH Locking
Gathering site details(Latitude, Longitude, Azimuth, BCCH,PSC)
Selecting phone modes accordingly
Making Command Sequence
Updating Cell File
Making TEMS Workspace
Connecting phones, dongle, GPS
Executing Command Sequence
How to identify a swap
How to remove a swap
Notifying parameters
2G
Receive Level(Idle/Dedicated)
Receive Quality/Speech Quality Index
Stationary Test(MMS/SMS/Inter Cell HO/Downloading)
Events(Blocked Call/Dropped Call/Handover Failures/Ping pong
HO)
Serving BCCH
3G
RSCP(Idle/Dedicated)
Speech Quality Index
Missing Neighbors/Stationary Test(SMS/MMS/Downloading)
Serving Primary scrambling Codes
How to identify a Sector Swap
Sector Azimuth BCCH
1 40 997
2 280 987
3 340 989
Corrected Sector Swap
Sector Azimuth BCCH
1 40 997
2 280 987
3 340 989
Ping-Pong Handovers
Ping-Pong Handovers
Ping-Pong Handovers
Example Reports/Materials
1. Cell File
2. Example Mobitel report
3. Example Airtel report
Software Installation
1.TEMS installation
Setup installation/ Copying required additional files
2.Actix installation
Setup installation/ Copying required additional files
3.Mapinfo Installation
Setup installation/ Copying required additional files
Report Making-Using MapInfo
1. How to create a MIPT in Mapinfo to insert Cells in the report
MIPT Tool
2.
3.Setting Symbol size and Icon
Report Making-Using MapInfo
Report Making-Using MapInfo
4.Symbol Icon=Mapinfo Symbal, Symbal Size=6-12
5.
Report Making-Using MapInfo
6.
7.Creating Thematic
Report Making-Using MapInfo
8.
9.
10.
11.
Report Making-Using MapInfo
12.
13
Report Making-Using MapInfo
14.
15
Report Making-Using MapInfo
Report Making-Using Actix
Report Making-Using Actix
Report Making-Using Actix
Report Making-Using Actix
Report Making-Using Actix
Super Streaming
Report Making-Using Actix
Super Streaming
Report Making-Using Actix
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationDa EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- GSM RF Quick Reference GuideDocumento5 pagineGSM RF Quick Reference Guidesantoshkumar2711Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Overview UpdatedDocumento131 pagineGSM Overview UpdatedSandip DasNessuna valutazione finora
- DT DocumentsDocumento10 pagineDT DocumentsSobaan ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1Documento11 pagine1.12 Questions (GSM) : Answers For Chapter 1 Answer - 1edwinNessuna valutazione finora
- GSMDocumento130 pagineGSMhelpbgpNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM SMS and Call FlowDocumento21 pagineGSM SMS and Call FlowLendry NormanNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 GSM Traffic ManagementDocumento58 pagine3 GSM Traffic ManagementEldine100% (1)
- Call FlowDocumento14 pagineCall FlowNitesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Telecom Interview Questions & AnswersDocumento8 pagineTelecom Interview Questions & AnswersMd Saidur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM GPRS EdgeDocumento94 pagineGSM GPRS Edgecoofka JrNessuna valutazione finora
- ProjectDocumento37 pagineProjectSurina KondillyaNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM SystraDocumento67 pagineGSM SystraHi_Lev100% (1)
- SigleRAN Abbreviations V1.0 (With Description)Documento20 pagineSigleRAN Abbreviations V1.0 (With Description)Francesco TrebbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Some Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1Documento23 pagineSome Important Questions For Interview Point of View-1nileshNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM System OverviewDocumento79 pagineGSM System OverviewChee Leong100% (1)
- Network Access Technology Security FinDocumento140 pagineNetwork Access Technology Security FinPARASPKKATHURIANessuna valutazione finora
- 01 CDMA ConceptDocumento53 pagine01 CDMA ConceptSiraj SidhikNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Network Planning: Charotar Institute of Technology, ChangaDocumento34 pagineGSM Network Planning: Charotar Institute of Technology, ChangaPawan PatidarNessuna valutazione finora
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDocumento66 pagineGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM - Lecture (Chapter 3)Documento92 pagineGSM - Lecture (Chapter 3)mkbreaktherulesNessuna valutazione finora
- MC Module 1Documento42 pagineMC Module 1Abhirami SNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Architecture and InterfacesDocumento25 pagineGSM Architecture and InterfacesTelebeansNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Architecture: Project ReportDocumento40 pagineGSM Architecture: Project ReportaadafullNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM and Lte NotesDocumento6 pagineGSM and Lte NotesSubhransu patraNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Concepts & RF Optimization: Presented By: Anjnay SharmaDocumento32 pagineGSM Concepts & RF Optimization: Presented By: Anjnay SharmaAnjnay SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- GsmOverview Qasim, ShahzebDocumento94 pagineGsmOverview Qasim, ShahzebQasimBajwaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.GSM Intro&ArchDocumento6 pagine1.GSM Intro&ArchJ Vijay Suresh BabhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer 2Documento11 pagineAnswer 2Anisa SuloNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Communication CSDocumento31 pagineMobile Communication CSLuvish MahajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Call Processing in GSMDocumento9 pagineCall Processing in GSMjb1929835Nessuna valutazione finora
- GB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-01Documento40 pagineGB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-01JaneYinNessuna valutazione finora
- Global System For MobileDocumento26 pagineGlobal System For MobileAditi AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Part TwoDocumento14 pagineGSM Part TwosaraNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Network Architecture: Mobile StationDocumento6 pagineGSM Network Architecture: Mobile StationGurcan KavogluNessuna valutazione finora
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA)Documento15 pagineTime Division Multiple Access (TDMA)Swapnarekha NarravulaNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM System TheoryDocumento83 pagineGSM System TheoryMuhammad Saqib JadoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : 1 Summer Internship ReportDocumento51 pagineGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : 1 Summer Internship ReportAvay SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- OVERVIEWDocumento79 pagineOVERVIEWseth_awuah100% (1)
- TRG MotorolaDocumento110 pagineTRG MotorolaphaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Wireless Networks And: Mobile Internet Protocol & Wireless Application ProtocolDocumento48 pagineCellular Wireless Networks And: Mobile Internet Protocol & Wireless Application ProtocolSabai SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF GSMDocumento6 paginePDF GSMMahabub AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocumento53 pagineGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationJahan ZaibNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Station Subsystem (BSS)Documento4 pagineBase Station Subsystem (BSS)mailto_gggggNessuna valutazione finora
- The Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Documento32 pagineThe Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)devajeet_nerist2840Nessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Network ComponentsDocumento23 pagineGSM Network ComponentsShakeel AminNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgeDocumento11 pagineGSM General Questions and Answers & Some Practical KnowledgealonindNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Call ProcessingDocumento8 pagineCellular Call ProcessingSaibal RayNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Processing in GSMDocumento46 pagineSignal Processing in GSMMuti Ul BariNessuna valutazione finora
- Drive Test With TEMSDocumento33 pagineDrive Test With TEMSMuhammad Bilal JunaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Drive Test ProcedureDocumento7 pagineDrive Test ProcedureNaveed ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- GSM Architecture PDFDocumento3 pagineGSM Architecture PDFNirmal AnilkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To GSM 2Documento12 pagineIntroduction To GSM 2mba_1604Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento37 pagineUnit 3Vaibhav HolkarNessuna valutazione finora
- NOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Documento10 pagineNOKIA BTS Questions and Answers Post Training Ver1Ramesh MattaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandDa EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNessuna valutazione finora
- Academic Press Library in Biomedical Applications of Mobile and Wireless Communications: Wireless UWB Body Area Networks: Using the IEEE802.15.4-2011Da EverandAcademic Press Library in Biomedical Applications of Mobile and Wireless Communications: Wireless UWB Body Area Networks: Using the IEEE802.15.4-2011Nessuna valutazione finora
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesDa EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Management Decision: Article InformationDocumento20 pagineManagement Decision: Article InformationSusanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Co 17-01-08 TMT Stop The PressesDocumento20 pagineCo 17-01-08 TMT Stop The PressesSusanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Book To Come FacctorsDocumento7 pagineThe Book To Come FacctorsSusanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- News Channels: Emerging Threat For Newspapers: 2. Technological Advancements and Their EffectsDocumento5 pagineNews Channels: Emerging Threat For Newspapers: 2. Technological Advancements and Their EffectsSusanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Planning 2Documento35 pagineCell Planning 2Susanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Interference Optimization: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocumento20 pagineRadio Interference Optimization: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleSusanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mimo and Smart Antennas For 3g and 4g Wireless Systems May 2010 FinalDocumento135 pagineMimo and Smart Antennas For 3g and 4g Wireless Systems May 2010 FinalRizwan BhawraNessuna valutazione finora
- 739636Documento2 pagine739636Katsaras SteliosNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Module For 3 G (WCDMA) : Day:1 - Day:2Documento68 pagineTraining Module For 3 G (WCDMA) : Day:1 - Day:2Susanka SanjeewaNessuna valutazione finora
- 3G W-CDMA (UMTS) Questions & Answers - Sanfoundry PDFDocumento8 pagine3G W-CDMA (UMTS) Questions & Answers - Sanfoundry PDFGayle LokeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Script - RNCDocumento9 pagineScript - RNCBehemothzNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaddx GSM NX 7002n User ManualDocumento8 pagineGaddx GSM NX 7002n User Manualakoyl1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSDocumento7 pagine1.SMS Interworking in Traditional Network 1.1.mobile Originated - SMSdilipsharma04Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lock Sites Script (With 4g Now) HuaweiDocumento13 pagineLock Sites Script (With 4g Now) HuaweiRicardoJorgeRodriguesRochaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Synchronization and System Information Acquisition: eNB UEDocumento22 pagineCell Synchronization and System Information Acquisition: eNB UEclick2klicNessuna valutazione finora
- Etisalat UAE - Prepaid Mobile Data PlansDocumento8 pagineEtisalat UAE - Prepaid Mobile Data PlansMcDaryl MateoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2n Easygate Umts UsbDocumento6 pagine2n Easygate Umts UsbantsouNessuna valutazione finora
- Huawei-4G-Router-B310 Datasheet: Check Its PriceDocumento2 pagineHuawei-4G-Router-B310 Datasheet: Check Its PriceMatheus LeiteNessuna valutazione finora
- Bts Module Alarm and VSWR - Sedayu - Gombong - JAW-JT-KBM-0704Documento53 pagineBts Module Alarm and VSWR - Sedayu - Gombong - JAW-JT-KBM-0704Yudha BloomsNessuna valutazione finora
- 3g Handover Detailed DocumentDocumento434 pagine3g Handover Detailed Documentadam_imam100% (1)
- FAQ's On BSNL Wings ServiceDocumento3 pagineFAQ's On BSNL Wings ServicePraveen Kumar ArjalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smartfren LTE Rollout Project Quick SSV Report: City: Site Name: SF Site Id: Zte Site Id: TechnologyDocumento5 pagineSmartfren LTE Rollout Project Quick SSV Report: City: Site Name: SF Site Id: Zte Site Id: TechnologyZMG FILENessuna valutazione finora
- Network SharingDocumento3 pagineNetwork Sharingdiefenbaker13Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nokia TestDocumento4 pagineNokia TestTcang TanabeNessuna valutazione finora
- Samsung Android Device MessagingDocumento18 pagineSamsung Android Device Messagingparabin.3528101Nessuna valutazione finora
- RF - ZE554KL Trouble Shooting Guide - DiscreteDocumento41 pagineRF - ZE554KL Trouble Shooting Guide - DiscreteVinicius TeixeiraNessuna valutazione finora
- UMTS Interview Questions and AnswerDocumento24 pagineUMTS Interview Questions and AnswervikydilseNessuna valutazione finora
- 3GPP TS 24.008Documento660 pagine3GPP TS 24.008Ahmad NaumanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mobile Economy - Latin America and The Caribbean 2017Documento56 pagineThe Mobile Economy - Latin America and The Caribbean 2017Patricio J. VásconesNessuna valutazione finora
- Traffic Cases in GSMDocumento18 pagineTraffic Cases in GSMkamal100% (1)
- VIV:vivo-iQOO-7-5G-Phone DatasheetDocumento2 pagineVIV:vivo-iQOO-7-5G-Phone Datasheetvishnu csNessuna valutazione finora
- Gprs TelecomDocumento126 pagineGprs Telecomemm11111111Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2G Top Ten High Traffic SitesDocumento16 pagine2G Top Ten High Traffic SitesLake GebrekidanNessuna valutazione finora
- ZXIN10 CDMA Wireless Intelligent Network PPC User Guide - V2.05.01Documento435 pagineZXIN10 CDMA Wireless Intelligent Network PPC User Guide - V2.05.01Raed Saleh MokbelNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobilink Pre Swap DT Report For Cluster 2Documento22 pagineMobilink Pre Swap DT Report For Cluster 2Gill AngNessuna valutazione finora
- New Xiaomi Redmi Note 7-4-64 Tam Barusan Datang Murah Saja IDzHeajDocumento1 paginaNew Xiaomi Redmi Note 7-4-64 Tam Barusan Datang Murah Saja IDzHeajPaket NusveyNessuna valutazione finora
- LTE Phase 3 PDFDocumento14 pagineLTE Phase 3 PDFNavi NaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobilis - VAS ApplicationsDocumento9 pagineMobilis - VAS ApplicationsRupesh TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Layer 3 Messages GSMDocumento15 pagineLayer 3 Messages GSMzeggarinabil100% (2)