Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Flexible Manufacturing Final
Caricato da
ashok_abclDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Flexible Manufacturing Final
Caricato da
ashok_abclCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1
FLEXIBLE
MANUFACTURING
SYSTEM
BY
B. GANDHI
13N71D0403
2
What is Flexible Manufacturing
System?
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is
a form of flexible automation in which
several machine tools are linked together
by a material-handling system, and all
aspects of the system are controlled by a
central computer.
3
What are The Features of FMS?
An FMS is distinguished from an automated
production line by its ability to process more than
one product style simultaneously.
At any moment, each machine in the system
may be processing a different part type.
FMS can let us make changes in production
schedule in order to meet the demands on
different products.
4
New product styles can be introduced into
production with an FMS, so long as they
are to be used on the products that the
system can process.
This kind of system is, therefore, ideal
when there are likely to be changes in
demands.
5
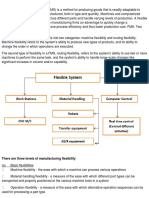
Equipment of FMS
Primary equipment
work centers
Universal machining centers (prismatic FMSs)
Turning centers (rotational FMSs)
Grinding machines
Nibbling machines
Process centers
Wash machines
Coordinate measuring machines
Robotic work stations
Manual workstations
Secondary equipment
Support stations
Pallet/fixture load/unload stations
Tool commissioning/setting area
Support equipment
Robots
Pallet/fixture/stillage stores
Pallet buffer stations
Tools stores
Raw material stores
Transport system(AGVs,RGVs,robots)
Transport units(pallets/stillages)
6
7
There are three levels of
manufacturing flexibility.
1-Basic Flexibilities
Machine flexibility - the ease with which a machine can
process various operations
Material handling flexibility -a measure of the ease with
which different part types can be transported and properly
positioned at the various machine tools in a system
Operation flexibility - a measure of the ease with which
alternative operation sequences can be used for processing a part
type
8
2-System flexibilities:
Volume flexibility
Expansion flexibility
Routing flexibility
Process flexibility
Product flexibility
9
3-Aggregate flexibilities
Program Flexibility
Production Flexibility
Market Flexibility
Objective of FMS
Decreased Lead Times
Increased machine utilization
Improved Due Date Reliability
Decreased Store Inventors levels
Decreased Work in Progress
Increased Quality
10
Types of FMS
Sequential FMS
Random FMS
Dedicated FMS
Engineered FMS
Modular FMS
11
Application of FMS
Metal-cutting machining
Metal forming
Assembly
Joining-welding (arc , spot), glueing
Surface treatment
Inspection
Testing
12
13
Benefits of FMS
FMS systems are intended to solve the
following problems:
Reduced work in process
Increased machine utilization
Better management control
Reduced direct and indirect labor
Reduced manufacturing lead-time
Consistent and better quality
Reduced inventory
14
The Disadvantages of FMS
Expensive, costing millions of dollars
Substantial pre-planning activity
Sophisticated manufacturing systems
Limited ability to adapt to changes in product
Technological problems of exact component
positioning and precise timing necessary to
process a component
Components of Flexible
Manufacturing Systems
NC
CNC
DNC
Robotics
AGV
ASRS
Automated Inspection
Cells and Centers
15
Making FMS Work
By implementing the components of robotics,
manufacturing technology and computer
integrated manufacturing in a correct order one
can achieve a successful Flexible Manufacturing
System
16
Manufacturing Technology
This part of FMS uses:
NC Numerically Controlled Machine
CNC Computer Controlled Machine
DNC Direct Numerical Controlled
17
Computer Integrated
Manufacturing
CIM: The Integration of the total manufacturing enterprise
through the use of integrated systems and data
communications coupled with new managerial
philosophies that improve organizational and personnel
efficiency.
Components of CIM
CAD Computer Aided Design
CAM Computer Aided Manufacturing
CAE Computer Aided Engineering
18
Robots
19
Robots: Programmable Manipulators
Can tolerate hostile environments
Can work much longer hours than humans
Can perform redundant jobs more
consistently
20
21
Future Benefits of FMS
Technology will make 100% inspection feasible
Computer diagnosis will improve estimation of machine
failure, and guide work crews repairing failures
The use of robots that have vision, and tactile sensing
Minimum human labor in manufacturing systems
More sophisticated tools with increased computing
power
Better management software, hardware, and fixturing
techniques
Developed standards that will let us install new machines
easily
22
Future Benefits of FMS
Reduced marketing of products
Custom orders for customers will be made
immediately with exact specifications
Improved network systems between
manufacturers and suppliers
THANK YOU
23
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS)Documento19 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System (FMS)purushothamkr100% (1)
- The CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0Da EverandThe CNC Handbook: Digital Manufacturing and Automation from CNC to Industry 4.0Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento16 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systemm_er100Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer-Managed Maintenance Systems: A Step-by-Step Guide to Effective Management of Maintenance, Labor, and InventoryDa EverandComputer-Managed Maintenance Systems: A Step-by-Step Guide to Effective Management of Maintenance, Labor, and InventoryValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (1)
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento19 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systemtamilselvan nNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento16 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemManish JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing System: Click To Add TextDocumento46 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System: Click To Add Textpranav sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento19 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemAmir FauziNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocumento33 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systemsmhnkumar_375188Nessuna valutazione finora
- FLEXIBLE - MANUFACTURING SYS - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Documento25 pagineFLEXIBLE - MANUFACTURING SYS - PPT (Compatibility Mode)Ramees KpNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocumento33 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemsAshish kaushalNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocumento40 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemsHanoz Patel100% (1)
- CH 1 - Introduction To FMS-MNFGDocumento47 pagineCH 1 - Introduction To FMS-MNFGAshenafi DressNessuna valutazione finora
- Cim PDFDocumento32 pagineCim PDFVarshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible: Manufacturing SystemsDocumento26 pagineFlexible: Manufacturing SystemsSarthakNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento11 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemSapari VelNessuna valutazione finora
- The FMS: Md. WasifDocumento15 pagineThe FMS: Md. WasifKumar ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Project On Automatedprocesses-Fms: Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento12 pagineProject On Automatedprocesses-Fms: Flexible Manufacturing SystemMOHD.ARISHNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Documento24 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)IndriiNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Information Systems: ITEC-3119Documento12 pagineManagement Information Systems: ITEC-3119Shahid IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Documento24 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Padmavathi Putra LokeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Documento26 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Anupama YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages: 1.3 Basic Components of FmsDocumento4 pagineAdvantages: 1.3 Basic Components of FmsBoy LiverpoolNessuna valutazione finora
- FQ Flexible Manufacturing Systems FMSDocumento30 pagineFQ Flexible Manufacturing Systems FMSSasiKumar PetchiappanNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Documento30 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)waqasalitunio100% (2)
- Unit VDocumento30 pagineUnit VSai Syam RallabhandiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Closer LookDocumento49 pagineA Closer LookCương Phạm NgọcNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 Introduction To FMSDocumento30 pagineChapter 1 Introduction To FMSDo Thi My LeNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: Chithralekha R S4 Mba CETDocumento45 pagineSubmitted By: Chithralekha R S4 Mba CETAnish VijayNessuna valutazione finora
- FMS & CimsDocumento9 pagineFMS & Cimsmanjeet_virkNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Integrated Manufactu Ring: Unit 1 Gaurish M SamantDocumento19 pagineComputer Integrated Manufactu Ring: Unit 1 Gaurish M SamantGaurish M SamantNessuna valutazione finora
- FMS Case StudyDocumento41 pagineFMS Case StudyAdhavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Documento28 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Anand Kumar100% (1)
- Experiment No. - 6Documento11 pagineExperiment No. - 6jay_v9Nessuna valutazione finora
- FMS (Flexible Manufacturing System) - Rev1.0Documento21 pagineFMS (Flexible Manufacturing System) - Rev1.0suffianosNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing System A Modern Approach To Manufacturing TechnologyDocumento8 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System A Modern Approach To Manufacturing TechnologySid BramhankarNessuna valutazione finora
- FMSDocumento6 pagineFMS21UME003 TUSHAR DEBNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)Documento4 pagineFlexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS)BHAGYESH JHANWARNessuna valutazione finora
- ZA Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento68 pagineZA Flexible Manufacturing SystemSasiKumar PetchiappanNessuna valutazione finora
- FMS (Flexible Manufacturing System)Documento30 pagineFMS (Flexible Manufacturing System)suffianosNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Manufacturing SystemsDocumento21 pagineAdvanced Manufacturing SystemsV. SudharsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 19 Summary SIMDocumento7 pagineChapter 19 Summary SIMHumberto Dávila GonzálezNessuna valutazione finora
- Fms - Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocumento47 pagineFms - Flexible Manufacturing SystemsYashwanth ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocumento7 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemsUsama AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento10 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemVivek PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Acknowledgement: Mrs - Maneet Kaur, LimDocumento21 pagineAcknowledgement: Mrs - Maneet Kaur, LimKhalid ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS)Documento96 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System (FMS)Jignesh RohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemsDocumento3 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemsDeysi J. Barrera MariscalNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing System and Industrial AutomationDocumento32 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System and Industrial AutomationBizuayehu TadesseNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento5 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemanurajNessuna valutazione finora
- PSM 6 FMSDocumento22 paginePSM 6 FMSAlyssa Jayne Milla NovitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing System Seminar ReportDocumento18 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System Seminar ReportPranav Pandey0% (1)
- CNC Lecture Notes - The Future of CNCDocumento28 pagineCNC Lecture Notes - The Future of CNCgokek29494Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes On Flexible Manufacturing System (ETMT-428)Documento40 pagineLecture Notes On Flexible Manufacturing System (ETMT-428)Deepak Kumar100% (1)
- Ready in 2003Documento7 pagineReady in 2003vaibhav dhandeNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 - 15. Modul 11 Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento68 pagine14 - 15. Modul 11 Flexible Manufacturing SystemFakhar Windratama100% (1)
- Flexible Manufacturing: Reference For BusinessDocumento5 pagineFlexible Manufacturing: Reference For BusinessSREYA HAZRANessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing SystemDocumento10 pagineFlexible Manufacturing SystemShanky JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Flexible Manufacturing System (FMS) 1Documento30 pagineFlexible Manufacturing System (FMS) 1Akatew Haile MebrahtuNessuna valutazione finora
- SmileMakers Canada - PRD - W2 - Report - 2023-07-15 - 17-25-36Documento3 pagineSmileMakers Canada - PRD - W2 - Report - 2023-07-15 - 17-25-36ashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- 305 Prep AzureDocumento118 pagine305 Prep Azureashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Pall-UAT Aug W2 Report 2023-08-11 10-57-48Documento2 paginePall-UAT Aug W2 Report 2023-08-11 10-57-48ashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Sae Technical Paper Series: Timothy P. GardnerDocumento18 pagineSae Technical Paper Series: Timothy P. Gardnerashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Design Improvement of Intake Ma PDFDocumento9 pagineStudy of Design Improvement of Intake Ma PDFashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- ICEF2011-60134: Determination of Optimal Engine Parameters For Exhaust Emissions Reduction Using The Taguchi MethodDocumento11 pagineICEF2011-60134: Determination of Optimal Engine Parameters For Exhaust Emissions Reduction Using The Taguchi Methodashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines: Government of IndiaDocumento6 pagineGuidelines: Government of Indiaashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- The Design and Need For Jigs and Fixtures in Manufacturing: August 2015Documento8 pagineThe Design and Need For Jigs and Fixtures in Manufacturing: August 2015ashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Mckeen2014 PDFDocumento28 pagineMckeen2014 PDFashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- SecuGenHamsterPro20 PDFDocumento2 pagineSecuGenHamsterPro20 PDFashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- 9788189866662Documento2 pagine9788189866662ashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW Livehistoryindia Com Amazing India 2017-07-10 The Secrets of The Gobindgarh FortDocumento17 pagineWWW Livehistoryindia Com Amazing India 2017-07-10 The Secrets of The Gobindgarh Fortashok_abcl100% (1)
- History of Ten Sikh GurusDocumento3 pagineHistory of Ten Sikh Gurusashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Notification ArSRLM 34 Cluster Coordinator BMM Other Posts1Documento10 pagineNotification ArSRLM 34 Cluster Coordinator BMM Other Posts1ashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Invigilation Duties On 01-12-2016 FNDocumento1 paginaInvigilation Duties On 01-12-2016 FNashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Jawaharlal Nehru Technological University HyderabadDocumento2 pagineJawaharlal Nehru Technological University Hyderabadashok_abclNessuna valutazione finora
- Air To Water Heat Pump: Over A Century of InnovationDocumento2 pagineAir To Water Heat Pump: Over A Century of InnovationAshish ModiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Cleaning HRSGDocumento7 pagineChemical Cleaning HRSGAulia NafarinNessuna valutazione finora
- DSR 2018 PDFDocumento505 pagineDSR 2018 PDFVivek Gaur100% (1)
- Wood Dust Sawmills CompilationDocumento395 pagineWood Dust Sawmills CompilationMurray PeartNessuna valutazione finora
- O2FLO1 Product Brochure-UpdateDocumento3 pagineO2FLO1 Product Brochure-UpdateAli UnitedHospitalNessuna valutazione finora
- Instruction API 650 RadioDocumento3 pagineInstruction API 650 RadioAli Clubist100% (1)
- Mechanical EquipmentDocumento17 pagineMechanical EquipmentAnonymous zd5HPB5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ferro ElectricDocumento33 pagineFerro ElectricKarthik RajendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Confi Dence: Bond Bond BondDocumento16 pagineConfi Dence: Bond Bond Bonderickcastillo1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sch3u Synthesis & DecompositionDocumento32 pagineSch3u Synthesis & Decompositionben0706Nessuna valutazione finora
- BAE OPzS Cell en 2011.04-SEDocumento2 pagineBAE OPzS Cell en 2011.04-SEAmir EskandariNessuna valutazione finora
- Fasco Draft Inducer Cross Reference GuideDocumento16 pagineFasco Draft Inducer Cross Reference GuideRobNessuna valutazione finora
- SPE 85-203 - Feb 2014Documento8 pagineSPE 85-203 - Feb 2014Tejash NayakNessuna valutazione finora
- Determining The Young's Modulus REAL ISA CASE STUDY NEWDocumento5 pagineDetermining The Young's Modulus REAL ISA CASE STUDY NEWSerish HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- #Operating Manual r1Documento274 pagine#Operating Manual r1tri arwindaNessuna valutazione finora
- CTS HandbookDocumento882 pagineCTS HandbookFlores Brayan100% (5)
- Aspen Exchanger Design and Rating Air Cooled V11Documento1 paginaAspen Exchanger Design and Rating Air Cooled V11HafidzAliyufaNessuna valutazione finora
- DPA-4.1 e 20071016 v4Documento97 pagineDPA-4.1 e 20071016 v4Williams Medina100% (1)
- Merv 13: High Capacity Commercial Grade PleatsDocumento4 pagineMerv 13: High Capacity Commercial Grade PleatsJomyJoseNessuna valutazione finora
- InterteckDocumento7 pagineInterteckAyman SebaeiNessuna valutazione finora
- BDM Section 14 - 20180101 - Joint and BearingsDocumento10 pagineBDM Section 14 - 20180101 - Joint and BearingsSantosoNessuna valutazione finora
- MGT 445 - Chapter 1 - NotesDocumento9 pagineMGT 445 - Chapter 1 - NotesKatie WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Guiding Formulation: For The Non-Leafing Aluminium Pigment Series PCU in A Powder Clear Coat (App. RAL 9006) (Outdoor)Documento2 pagineGuiding Formulation: For The Non-Leafing Aluminium Pigment Series PCU in A Powder Clear Coat (App. RAL 9006) (Outdoor)podolsky-1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fishfarming LowresDocumento56 pagineFishfarming LowresNomNessuna valutazione finora
- INSEE Knowledge Sharing Session #2 - High Performance Concrete in Construction V3Documento10 pagineINSEE Knowledge Sharing Session #2 - High Performance Concrete in Construction V3KalindaMadusankaDasanayakaNessuna valutazione finora
- San Ace 60A25 E PDFDocumento3 pagineSan Ace 60A25 E PDFThi NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Indesit Manual Wil - 62 PDFDocumento16 pagineIndesit Manual Wil - 62 PDFFranceskoNessuna valutazione finora
- Euxyl K 100 PDFDocumento2 pagineEuxyl K 100 PDFPeterNessuna valutazione finora
- Ice Breaker Refrigerant Numbering System ExplainedDocumento3 pagineIce Breaker Refrigerant Numbering System ExplainedChristine ManongdoNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation of The Corrosion Durability of Steel Systems For Automobile Fuel TanksDocumento90 pagineEvaluation of The Corrosion Durability of Steel Systems For Automobile Fuel TanksĐình Khoa PhanNessuna valutazione finora