Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture2 PPEandTools
Caricato da
biotech_vidhyaTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture2 PPEandTools
Caricato da
biotech_vidhyaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 1
Personal Protective
Equipment and Tool
Safety
Joe Nail
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 2
Introduction to PPE
Employees must be protected from harm.
Common methods for doing this are
Engineering Controls, Work Practices,
Administrative Controls and, Personal
Protective Equipment (PPE). Sometimes
one or more of the above is used and at
times all are used to provide adequate
protection. When only PPE is used, the
PPE is the only thing protecting the
employee from the danger. This unit
discusses basic types of PPE and the
employer requirements.
What is personal protective
equipment?
Personal protective equipment, or PPE, is
designed to protect employees from serious
workplace injuries or illnesses resulting from
contact with chemical, radiological, physical,
electrical, mechanical, or other workplace hazards.
Besides face shields, safety glasses, hard hats, and
safety shoes, PPE includes a
variety of devices and garments such as goggles,
coveralls, gloves, vests, earplugs, and respirators.
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two
3
Employers Responsibilities
(OSHA Subpart I:1910.132-140)
What Kind of PPE Approved PPE
Maintained PPE Training to use PPE
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 4
OSHAs primary PPE standards are in Title 29 of the Code of Federal
Regulations (CFR), Part 1910 Subpart I, and equivalent regulations in states
with OSHA-approved state plans, but you can find PPE requirements
elsewhere in the General Industry Standards. For example, 29 CFR 1910.156,
OSHAs Fire Brigades Standard, has requirements for firefighting gear. In
addition, 29 CFR 1926.95-106 covers the construction industry. OSHAs
general PPE requirements mandate that employers conduct a hazard
assessment of their workplaces to determine what hazards are present that
require the use of PPE, provide workers with appropriate PPE, and require
them to use and maintain it in sanitary and reliable condition. As an employer,
you must assess your workplace to determine if hazards are present
that require the use of PPE.
1910.132(d) Hazard Assessment
(2)The employer shall verify that the required workplace
hazard assessment has been performed through a written
certification that identifies:
The workplace evaluated;
The person certifying that the evaluation has been
performed;
The date(s) of the hazard assessment; and,
Which identifies the document as a certification of hazard
assessment
New Employee Orientation
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 6
Employers Responsibilities
If such hazards are present, you must select PPE and require employees to
use it, communicate your PPE selection decisions to your employees, and
select PPE that properly fits your workers. You must also train employees
who are required to wear PPE on how do the following:
Use PPE properly,
Be aware of when PPE is necessary,
Know what kind of PPE is necessary,
Understand the limitations of PPE in
protecting employees from injury,
Don, adjust, wear, and care for PPE, and
Maintain PPE properly.
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 7
1910.132(f) Training
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 8
Employees Responsibilities
Inspect Maintain Report Defects
Employees should look at their equipment on a daily basis to
make sure it is good working order. This is the responsibility of
each employee.
PPE, especially eye wear and face masks, should be cleaned
daily by the person who wears it.
The employee must reports any problems with PPE, as well as
other protective equipment, as soon as it is detected.
1910.132(f) Training
(2)Workers must demonstrate an
understanding of the training and the ability to
use PPE properly, before being allowed to
perform work requiring the use of PPE:
(4)Verify that each employee has received and
understood the required training through a written
certification that contains:
The name of each employee trained,
The date(s) of training, and that
Identifies the subject of the certification
1910.138(a) General requirements
Employers shall select and require employees
to use appropriate hand protection when
employees' hands are exposed to hazards such
as those from:
Skin absorption of harmful substances;
Severe cuts or lacerations;
Severe abrasions;
Punctures;
Chemical burns;
Thermal burns; and
Harmful temperature extremes
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 11
Introduction to PPE
Hand Protection
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 12
Introduction to PPE
Head
Protection
Webbing: 1 inch
clearance
Early Hard Hats were made
of metal
1910.135(a) General requirements
(1)Ensure that each
employee wears a protective
helmet when working in areas
where there is a potential for
injury to the head from falling
objects
Classes and types of Hard hats
Type I hard hats - intended
to reduce the force of
impact resulting from a
blow to the top of the head
Type II hard hats -
designed to provide
protection against both side
impact (lateral) and blows
to the top of the head
Classes
G (old A)
General
2,200 volts
E (old B)
Electrical
20,000 volts
C (same)
Conductive
1910.135(b) Criteria for protective
helmets
(1)Protective
helmets purchased
after July 5, 1994
shall comply with
ANSI Z89.1-1986
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 16
Introduction to PPE
Care of a Hard Hat
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 17
Introduction to PPE
Eye Protection
Glasses
Goggles
Z 87.1-1989
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 18
Introduction to PPE
Face Protection
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 19
PPE 1910.95
Protection against the effects of noise exposure shall be
provided when the sound levels exceed those shown in
Table G-16.
Hearing Protection: Reusable and Disposable
Ear Muffs
Reusable Ear Plugs
Ear Protection and
Communication
Table G-16
Exposure Hours per Day Sound Level in dBA
8 90
6 92
4 95
3 97
2 100
1 1/2 102
1 105
1/2 110
or less 115
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 20
Ensure that each affected
employee uses protective
footwear when working
in areas where there is:
A danger of foot injuries due to
falling or rolling objects, or
Objects piercing the sole, and
Where such employee's feet are
exposed to electrical hazards
1910.136(a) General requirements
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 22
Introduction to PPE
Foot Protection
1910.136(b) Criteria for protective footwear
(1)Protective footwear purchased after July 5,
1994 shall comply with ANSI Z41-1991,
"American National Standard for Personal
Protection-Protective Footwear,"
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 24
Introduction to PPE
Foot Protection(continued)
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 25
Introduction to PPE
Foot Protection(continued)
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 26
Safety Harness
Limits a fall to only a feet
Must be supplied by employer
Employee MUST be trained on how to use
Requires a written program
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 27
Introduction to PPE
Respiratory Protection
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 28
Respiratory Protection
Filter Respirators
Air-Purifying-particles and gases
Particulate-dusts and mists
Atmosphere-Supplying-Respirators
Supplied Air
Self Contained
1910.134(c)(1) Respiratory
protection program
Where respirators are required you need:
Written program
Worksite-specific procedures
Required elements:
Training
Fit testing
Medical evaluations
Care and maintenance
Procedures for respirator selection
Procedures for routine & emergency use
1910.134(c)(2) Where respirator use is not
required:
(i)If voluntary respirator use is permissible, provide
the respirator users with the information contained
in Appendix D and,
(ii)Establish and implement those elements of a
written respiratory protection program* necessary to
ensure that any employee using a respirator
voluntarily is medically able to use that respirator
(ii)That the respirator is cleaned, stored, and
maintained so that its use does not present a health
hazard to the user
*Written program not required for voluntary use of dust masks
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 31
Introduction to PPE
Atmosphere Supplying
Respirators
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 32
SCBA
Self Contained Breathing Apparatus
Used in Low Oxygen Environments like
Confined Spaces as defined by OSHA
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 33
Part Two-Hand Tools
Defective Tools
Wrong Tool for the Job
Improperly Maintained Tool
Tool in the Wrong Place
Incorrect Body Positioning
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 34
Hand Tools
Defective Tools
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 35
Hand Tools
Wrong Tool for the Job
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 36
Hand Tools
Incorrect Use
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 37
Hand Tools
Wrong Place (storage practices)
Wrong Body Positioning
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 38
Hand Tools
Screwdrivers
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 39
Hand Tools
Wrenches
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 40
Hand Tools
Pliers
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 41
Hand Tools
Hammers and Mallets
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 42
Hand Tools
Chisels and Punches
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 43
Hand Tools
Knives
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 44
Hand Tools
Electric Tools and Electrical Safety
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 45
Hand Tools
Pneumatic Tools
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 46
Hand Tools
Gasoline Powered Tools and
Equipment
General Safety Precautions
Keep all tools in good condition
with regular maintenance
Use the right tool for the right job
Inspect each tool for damage
before use
Operate according to the
manufacturers instructions
Provide and use proper personal
protective equipment
47
General Safety Precautions
Responsibility of the employer
PPE provision and monitoring
Safe work procedures
Safe condition of tools including
personal tools
48
Hand Tools
Non powered
Largest hazard
Misuse
Improper maintenance
Safe use
Direction of knives and blades
Sharp knives and blades
Safe working surfaces
49
Power Tools
Classification by power source
Electric
Pneumatic
Liquid Fuel
Hydraulic
Powder Actuated
50
Power Tools (cont.)
1926.304(d)
Upper blade guard
Lower blade guard
Automatically returns to
starting position
51
Power Tools (cont.)
1926.300(d)(2)
Equipped with a momentary
contact on-off control and
may have a lock-on control
provided.
However, that turnoff must be
accomplished by a single
motion of the same finger or
fingers that turn it on.
52
Power Tools (cont.)
Momentary Contact on/off switch
Drills
Tappers
Fasteners
Drivers
Grinders Greater than 2 in dia.
Disc and Belt Sanders
Reciprocating Saws
53
Power Tools (cont.)
Positive on/off controls
Disc Sanders w/ discs 2 in dia. Or less
Routers
Trimmers
Shears
Jig Saws w/ blade wide or less
54
Power Tools (cont.)
ON POSITION
OFF POSITION
55
Power Tools (cont.)
Never carry tools by cords
Never pull cords to disconnect
Disconnect tools when not in use
or during maintenance
Secure work with vice or clamp
Allows two hands for working
Follow users manual instructions
56
Power Tools (cont.)
Proper apparel
NO loose clothing, hair, or jewelry
Tag all damaged tools Out of Service or discard them
Keep blades and knives sharpened
57
Electric Tools (cont.)
58
Electric Tools (cont.)
Double-Insulated Marking
59
Powered Abrasive Wheels
Flying fragments
Wear proper PPE
Ring test 1926.303(c)(7)
Mounting
Follow manufacturers instructions
60
Abrasive Wheels (cont.)
Maximum RPM
61
Abrasive Wheels (cont.)
180 deg
62
Powder Actuated Tools
1926.302(e)
Meet ANSI A10.3 1970
PPE
Eye Protection
Head and face depending on conditions
Proper training required
63
Powder Actuated Tools (cont.)
1926.302(e)
Fasteners used in tool
specifically designed
for that tool
Designed for the
material that is being
driven into
Concret
e
Concrete/wo
od
Wood
Specific size = Specific operation
64
65
Charges used in
powder actuated tools
Right size charge with right size fastener
Powder Actuated Tools (cont.)
Tools must be inspected before use
Defective tools taken out of service immediately
Tools not loaded until just before intended firing
Loaded or empty tools are never to be pointed at anyone
66
Powder Actuated Tools (cont.)
1926.302(e)(7) Fasteners not driven into:
Very hard or brittle materials
Cast iron
Glazed tile
Surface-hardened steel
Glass block
Live rock
Face brick
Hollow tile
67
Powder Actuated Tools (cont)
Inspection:
Make sure its clean
All parts must operate freely
The barrel is free from obstructions
68
Powder Actuated Tools (cont)
Firing
Keep hands clear of the barrel
5 pounds of force against working material
Misfires
Wait 30 seconds
Try firing again
Wait another 30 sec.
Remove the cartridge
Place in water
69
Powder Actuated Tools (cont)
Defects
Tag do not operate
Remove from service
70
FATAL FACT
Employee killed when struck in head by a nail fired from a powder
actuated tool. Tool operator was attempting to anchor a plywood form
in preparation for pouring a concrete wall.
71
FATAL FACT
Employees performing remodeling operations building a wall.
Operator was attempting to anchor plywood to a 2x 4 stud. The
nail penetrated the stud and struck the victim. One worker killed
when struck by a nail from a powder-actuated tool.
72
Pneumatic Tools
Appropriate PPE
Eye Protection
Hearing Protection
Other Employees
73
74
HOSE CLAMP
UNACCEPTABLE
ACCEPTABLE
Pneumatic Tool
Connections
8/1/2014 Industrial Safety Lecture Two 75
REVIEW
1. What must your employer provide in addition to the appropriate PPE?
2. What is the employees responsibility before using PPE?
3. What is the greatest danger when wearing loose fitting clothing on the job?
4. How long should you shower if you come into contact with a dangerous chemical?
5. How much clearance should a hard hat webbing provide between your head and the top
of the shell?
6. Give the type of eye protection that protects from debris approaching from multiple
angles?
7. What units are used to measure noise?
8. In what areas should disposable ear plugs NOT be used?
9. Before entering a confined space, the workers safety harness is attached to a
__________.
10. What kind of respirator is worn in areas that contain little or no oxygen?
11. What is the first thing to do before using any tool?
12. Which of the jaws is the strongest on the crescent wrench?
13. What is the name given to the wrench that IS meant to be struck with a hammer?
14. What do you call the condition of wear that refers to a badly worn striking surface?
15. When should you use a mallet in place of a hammer?
16. What is the difference between a regular knife and a safety knife?
17. What is the most important feature of an electrical power tool?
18. What is the greatest hazard with electrical tools?
19. State the purpose of a dead man switch.
20. When using compressed air for removing dirt, what should the maximum pressure be?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- BT 2019Documento13 pagineBT 2019biotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting SDS-PAGE 1Documento3 pagineTroubleshooting SDS-PAGE 1biotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
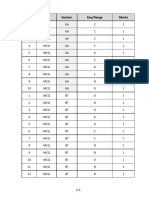
- Q.No. Type Section Key/Range MarksDocumento3 pagineQ.No. Type Section Key/Range Marksbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)Documento3 paginePolymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)biotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Buffer Preparation PDFDocumento6 pagineBuffer Preparation PDFbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Whole Cell ExtractDocumento1 paginaWhole Cell Extractbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear ExtractsDocumento2 pagineNuclear Extractsbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 TolerancesDocumento1 pagina1 Tolerancesbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- TNPSC Group 1 Prelim Book List PDFDocumento2 pagineTNPSC Group 1 Prelim Book List PDFbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ies 17 Set A Me Q ADocumento67 pagineIes 17 Set A Me Q Abiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Engineering Code No. 14: Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2010Documento20 pagineMechanical Engineering Code No. 14: Combined Competitive (Preliminary) Examination, 2010biotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Befcv List PDFDocumento22 pagineBefcv List PDFbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important DatesDocumento13 pagineTeachers Recruitment Board: 1. Important Datesbiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec09 Three PhaseDocumento84 pagineLec09 Three Phasebiotech_vidhyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Isa BusDocumento30 pagineIsa Busbiotech_vidhya100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Seko MSA Data SheetDocumento2 pagineSeko MSA Data SheetdadangNessuna valutazione finora
- No Touch Exit Sensor k1-1 / k1-2: Installation Sensing RangeDocumento1 paginaNo Touch Exit Sensor k1-1 / k1-2: Installation Sensing RangeDWVIZCARRANessuna valutazione finora
- Doosan Product RangeDocumento2 pagineDoosan Product Rangejose luis juarezNessuna valutazione finora
- G. S. Mandal's: Maharashtra Institute of Technology, AurangabadDocumento16 pagineG. S. Mandal's: Maharashtra Institute of Technology, AurangabadShivaji deshmukhNessuna valutazione finora
- EX-9 Hydraulic Pressure Setting and Accumulation Pressure Testing of BoilerDocumento2 pagineEX-9 Hydraulic Pressure Setting and Accumulation Pressure Testing of BoilerAayush AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- FactSheet CellD DPS 2900B 48 5 - enDocumento2 pagineFactSheet CellD DPS 2900B 48 5 - enManuel Torrón FerreiroNessuna valutazione finora
- Model 1266 A/R Sepex: Separately Excited Electronic Motor Speed ControllerDocumento4 pagineModel 1266 A/R Sepex: Separately Excited Electronic Motor Speed ControllermbgprsmsNessuna valutazione finora
- Perkins Hydraulic Lifter Garbage Containers 6291568Documento31 paginePerkins Hydraulic Lifter Garbage Containers 6291568Troy DormoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ball Valves and Cylindrical Valves: Compact One PieceDocumento12 pagineBall Valves and Cylindrical Valves: Compact One PieceershanquneriNessuna valutazione finora
- COM100A: Smart Communication BoxDocumento1 paginaCOM100A: Smart Communication BoxThắng CòiNessuna valutazione finora
- Detector de Gas - TGas-1031Documento6 pagineDetector de Gas - TGas-1031Fernando BonillaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Day Without TechnologyDocumento3 pagineA Day Without TechnologyJohn Joseph AddoNessuna valutazione finora
- 793-P-1C Relay Data SheetDocumento6 pagine793-P-1C Relay Data SheetsendmebooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Final 655N00595 SPDH Frame Repair HingeDocumento2 pagineFinal 655N00595 SPDH Frame Repair HingeKerlos100% (1)
- Manual EVR PDDocumento4 pagineManual EVR PDAnonymous dH3DIEtzNessuna valutazione finora
- Eur 221 enDocumento186 pagineEur 221 enapi-3852468Nessuna valutazione finora
- Easy UPS 3S Parallel Maintenance Bypass Panel: InstallationDocumento24 pagineEasy UPS 3S Parallel Maintenance Bypass Panel: InstallationVicthor CondorNessuna valutazione finora
- IPL, Husqvarna, 541 RB,, BRUSHCUTTERS - CLEARING SAWS PDFDocumento51 pagineIPL, Husqvarna, 541 RB,, BRUSHCUTTERS - CLEARING SAWS PDFJaime AmarizNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts Guide Manual: Bizhub 36/bizhub 42 A3EwDocumento94 pagineParts Guide Manual: Bizhub 36/bizhub 42 A3EwMarian IonutNessuna valutazione finora
- 1014 VS-142 Dome Cam Lift P3719 Data Sheet Y2636 230811Documento4 pagine1014 VS-142 Dome Cam Lift P3719 Data Sheet Y2636 230811Steven RuiterNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Projector Panasonic DT 5700Documento72 pagineManual Projector Panasonic DT 5700Diego C. FigueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Osbl-Etp Instrument List: SL No Location QTY Tag NoDocumento28 pagineOsbl-Etp Instrument List: SL No Location QTY Tag NoINDRAJIT SAONessuna valutazione finora
- Shunt Trip WiringDocumento1 paginaShunt Trip WiringPT INDORAD MEGA BINTANGNessuna valutazione finora
- Mustang PBDocumento2 pagineMustang PBBob ScharfNessuna valutazione finora
- DN-170090 Manual en English 20181015Documento45 pagineDN-170090 Manual en English 20181015DRAGOTA ALEXIANessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Cable Lugs CatalogDocumento36 pagine2 - Cable Lugs CatalogSanjay GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Is VR1404Documento3 pagineIs VR1404dayshift5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Controls, Operation, and TroubleshootingDocumento44 pagineControls, Operation, and TroubleshootingBruno ManestarNessuna valutazione finora
- Arduino KitDocumento9 pagineArduino KitGhulam UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- SH210 5Documento1 paginaSH210 5lionkinghd94% (36)