Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Renal Diseases: Pathology Department University Surakarta For Medical Sciences
Caricato da
Katou Jeffrey ShigehitoTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Renal Diseases: Pathology Department University Surakarta For Medical Sciences
Caricato da
Katou Jeffrey ShigehitoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
RENAL DISEASES
Pathology Department
University Surakarta for Medical Sciences
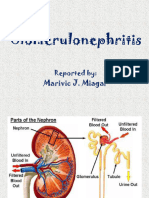
The Nephron
Consists of the glomerulus and its attached
tubules.
The functional unit of the kidney.
Major Renal Syndromes
Acute Nephritic Syndrome
The Nephrotic Syndrome
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
Asymptomatic Hematuria or Proteinuria
Major Renal Syndromes (cont)
Acute Renal Failure
Urinary Tract Infection
Nephrolithiasis
Acute Nephritic Syndrome
Sudden onset of hematuria with RBC casts and
renal failure (days - weeks)
Proteinuria (mild to moderate but NOT Nephrotic
Range)
Hypertension
Hallmark Disease: Post Streptococcal
Glomerulonephritis
What is an
RBC cast?
The Nephrotic Syndrome
Proteinuria (>3.5gm/day)
Hypoalbuminemia
Edema
Hyperlipidema
Lipiduria
Rapidly Progressive
Glomerulonephritis
Nephronal hematuria
Renal failure developing over weeks to months
Diffuse glomerular crescent formation.
Asymptomatic Hematuria or
Proteinuria
Hematuria with or without RBC casts and/or
Proteinuria usually <2.0gm/day
NO RENAL FAILURE
NO NEPHROTIC SYNDROME
Acute Renal Failure
Oliguria (<400ml/day)
Rarely anuria
Recent Onset of Azotemia (hours/days)
Post-Renal Causes
Pre-Renal Causes
RENAL CAUSES
RPGN
Acute Neprhitic Syndrome
Chronic Renal Failure
Uremia
Final Common Path of All Chronic Renal
Diseases
Urinary Tract Infection
Bacteriuria and Pyuria
Dysuria, Frequency, Urgency
Pyelonephritis or Cystitis
WBC casts = Pyelonephritis
Fever
Nephrolithiasis
Renal stones
Renal colic - OOOUUUCCCHHH!!
Severe, Crampy Pain in the flank area
Hematuria (Not RBC casts!)
Glomerular Diseases
An important cause of chronic renal failure
Renal Syndromes related to Glomerular Diseases
Acute Nephritic Syndrome
Nephrotic Syndrome
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
Asymptomatic Hematuria or Proteinuria
Glomerulus
Endothelial cells
Glomerular basement membrane (GBM)
Podocytes - Visceral Epithelial Cell
Mesangial cells and matrix
Parietal epithelium
Bowmans Capsule
Normal Glomerulus PAS
Normal Glomerulus Silver Stain
Normal Glomerulus EM
GBM
Mesangium
Glomerular Basement Membrane
Capillary Space
Endothelium
Urinary Space
GBM
Podocyte
Glomerular Basement Membrane
Podocytes
Glomerular Function
Glomerular filtration
barrier
charge
Pathogenesis of Glomerular Diseases
Immune mechanisms
Non-immune mechanisms
Immune Mechanisms of Glomerular
Disease
Antigen antibody reaction
Antigen - antibody complex deposition
Antibodies reacting in-situ within the glomerulus
Cell mediated immune mechanisms
Circulating Immune Complex Nephritis
Glomerulus is innocent bystander
Antigen is either endogenous or exogenous
Antigen - antibody complexes trapped in
glomeruli.
Role of complement
Circulating Immune Complex Nephritis:
Histologic Manifestations
LM - Cellular proliferation and leukocyte
infiltration
EM - Electron dense deposits
IF - Granular deposits
Immune Complex Nephritis
In-Situ
Antiglomerular basement membrane disease
Antibodies against fixed antigens in the GBM
LM - crescents
IF - linear deposits
Antiglomerular Basement Membrane
Antibodies
Board Hint:
Basement membrane antigen in Good Pastures -
Alpha 3 chain of collagen type 4
Heymanns Nephritis - Membranous
GN
Antigen - Megalin associated with receptor
associated protein
Discontinuous distribution
Granular IF
Immune Complex Nephritis - Planted
Non-glomerular Antigens
Including: Cationic molecules; DNA; Bacterial
products; etc..
IF - granular pattern
Cell Mediated Immune
Glomerulonephritis
Sensitized T-cells are thought to cause glomerular
injury
May account for GN without immune deposits
Mediators of Immune Injury
Glomerular damage - loss of glomerular barrier
function
Manifested by proteinuria and sometimes by
reduced GFR
Complement - Leukocyte Mediated
Mechanism
One Well-Established Pathway!!!
Activation of complement initiates:
Chemotaxis (C5a)
Neutrophil and monocyte infiltration
Neutrophil Activity
Proteases
Reactive oxygen metabolites
Arachidonic acid metabolites
Other Mediators
Cytotoxic antibodies
Macrophages
Platelets
Resident glomerular cells
Fibrin related products
Other Mechanisms of Glomerular
Injury
Epithelial cell injury
X - factors
resulting in epithelial cell detachment
proteinuria
Renal ablation glomerulopathy
fall in GFR
leads to end stage renal failure
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Proteinuria &Documento38 pagineProteinuria &Agustinus BethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerular Disorders: CATALUÑA, Hanz Nikko GDocumento15 pagineGlomerular Disorders: CATALUÑA, Hanz Nikko GHanz Nikko CatalunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento39 pagineUrinary SystemAsna FasilNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 UrineDocumento25 pagine11 UrineMuhammad Shahzad ChandiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulonephritis: Marivic J. MiagarDocumento28 pagineGlomerulonephritis: Marivic J. MiagarMarivic DianoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary System: Dr. Khan, MD, MCPS, DTCD PA 5402 T/W/RDocumento35 pagineThe Urinary System: Dr. Khan, MD, MCPS, DTCD PA 5402 T/W/RCrystal Lynn Keener SciariniNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Pathology EACDocumento115 pagineRenal Pathology EACPavan chowdaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulonephritis: Dr. Isbandiyah, SPPDDocumento21 pagineGlomerulonephritis: Dr. Isbandiyah, SPPDMohammad SutamiNessuna valutazione finora
- GlomerulonephritisDocumento28 pagineGlomerulonephritisqayyum consultantfpscNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerular Syndromes PKDocumento33 pagineGlomerular Syndromes PKamalasywaq2771Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4. Pathology Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento53 pagineLecture 4. Pathology Anatomy of Urinary SystemkrisnadewirahadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Histopathology of Kidney: Krisna MurtiDocumento58 pagineHistopathology of Kidney: Krisna MurtiYUFFANessuna valutazione finora
- Glo Me Rulo NefritisDocumento58 pagineGlo Me Rulo NefritisFany SholehaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerular Disorders - GlomerulonephrtisDocumento56 pagineGlomerular Disorders - GlomerulonephrtisValerie Suge-MichiekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Lectures 2022Documento145 pagineRenal Lectures 2022kastodaniel4971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Microscopy ReviewerDocumento31 pagineClinical Microscopy ReviewerbokbokbokNessuna valutazione finora
- WSU Renal ReviewDocumento100 pagineWSU Renal ReviewLeticia BornsteinNessuna valutazione finora
- Paediatric Glomerolonephritis and NephroticDocumento11 paginePaediatric Glomerolonephritis and NephroticTiong NeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology of Common Glomerular Syndromes: DR Purushotham KrishnappaDocumento34 paginePathology of Common Glomerular Syndromes: DR Purushotham KrishnappaTarin IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerular DiseasesDocumento16 pagineGlomerular DiseasesSamuel kuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephritic Syndrome: Pyuza, MDDocumento41 pagineNephritic Syndrome: Pyuza, MDawadh mbaroukNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System and Male Genital: Fajar L. Gultom Departemen Patologi Anatomik FK UKI December 2017Documento50 pagineUrinary System and Male Genital: Fajar L. Gultom Departemen Patologi Anatomik FK UKI December 2017Sona SiburianNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento35 pagineNephrotic SyndromesudhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento26 pagineNephrotic Syndromeamalfayiz84Nessuna valutazione finora
- NephrologyDocumento54 pagineNephrologyAndarge ImperialNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomdis - GanlinDocumento118 pagineGlomdis - GanlinMEDS easyNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulonephritis: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK Tim Ginjal Hipertensi Unhas 2019Documento68 pagineGlomerulonephritis: Prof DR DR Haerani Rasyid, Mkes, SPPD, KGH, SPGK Tim Ginjal Hipertensi Unhas 2019uzan100% (1)
- Glomerulonephritis TutorialDocumento47 pagineGlomerulonephritis TutorialRocio Ore SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Diseases of Liver1Documento54 pagineSurgical Diseases of Liver1DR MOHAMED HEALTH CHANNELNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of Glomerulus: Chronic Glomerulonephritis (CGN)Documento7 pagineDiseases of Glomerulus: Chronic Glomerulonephritis (CGN)mnr hmcNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseases of Glomerulus: Dr.K.Sathish Kumar, MD (Hom) .Documento15 pagineDiseases of Glomerulus: Dr.K.Sathish Kumar, MD (Hom) .mnr hmcNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Papillary NecrosisDocumento13 pagineRenal Papillary NecrosisMahesh RathnayakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal DisordersDocumento66 pagineRenal Disorderskiemdinhit7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerulopathy: Acute Nephritic SyndromeDocumento109 pagineGlomerulopathy: Acute Nephritic SyndromekamalNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal PathologyDocumento108 pagineRenal PathologyKedir jemalNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento40 pagineNephrotic SyndromesangheetaNessuna valutazione finora
- NephritisDocumento21 pagineNephritisruchikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningDocumento15 pagineQuality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningAnya IgnacioNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal 2Documento82 pagineRenal 2Sherry Kapur KhannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathology of Urology SystemDocumento130 paginePathology of Urology SystemAmirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Sindroma Nefrotik Vs NefritikDocumento22 pagineSindroma Nefrotik Vs NefritikAyueka EkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Between Diseases of Platelets/Vessel Wall or of Coagulation FactorsDocumento10 pagineDifferences Between Diseases of Platelets/Vessel Wall or of Coagulation FactorsIlyasHasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomer Ds TadDocumento190 pagineGlomer Ds TadHaileprince MekonnenNessuna valutazione finora
- Gangguan Darah & Sistem Reproduksi: Dr. Akhmad JufanDocumento49 pagineGangguan Darah & Sistem Reproduksi: Dr. Akhmad JufanSintia EPNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Failure en 2Documento103 pagineRenal Failure en 2ezz sharabyNessuna valutazione finora
- Patology Kidney: Dr. Delyuzar SP - PADocumento71 paginePatology Kidney: Dr. Delyuzar SP - PAJefry SNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome: BY Dr. Clive Bowman: Dip. Rad Mbbs M.Med (Paediatrics)Documento55 pagineNephrotic Syndrome: BY Dr. Clive Bowman: Dip. Rad Mbbs M.Med (Paediatrics)Pavi MuruganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Glomerular Diseases-Part 1Documento68 pagineGlomerular Diseases-Part 1hrg79qzwc2Nessuna valutazione finora
- UTI Dan Glomerular DiseaseDocumento58 pagineUTI Dan Glomerular DiseaseLiana Ika SuwandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Myelodysplasia (Definition/Incidence)Documento10 pagineMyelodysplasia (Definition/Incidence)IlyasHasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Spleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementDocumento53 pagineSpleenomegaly & Hypersplenism Etiology Pathogenesis and Surgical ManagementMuhammad SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- C5. Renal Disorders (Nephrotic S. - Renal F.)Documento44 pagineC5. Renal Disorders (Nephrotic S. - Renal F.)coco brillqnteNessuna valutazione finora
- PATHO Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial DiseaseDocumento43 paginePATHO Glomerular and Tubulointerstitial DiseaseHananya ManroeNessuna valutazione finora
- Aubf RenaallllllllDocumento7 pagineAubf RenaallllllllMarienel PingolNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Procedure For Thrombocyte Disorders: Angelic Trina I. Escoto, RMTDocumento57 pagineDiagnostic Procedure For Thrombocyte Disorders: Angelic Trina I. Escoto, RMTDayledaniel SorvetoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Kidney: Dr. I Made Naris Pujawan, M.Biomed, SP - PADocumento18 pagineThe Kidney: Dr. I Made Naris Pujawan, M.Biomed, SP - PAIda AyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal DisordersDocumento28 pagineRenal DisordersChristine CalumaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephrotic Syndrome: By: Yeni Ayu Prihastuti Moderator: DR. Dr. Hani Susianti, SP - PK (K)Documento42 pagineNephrotic Syndrome: By: Yeni Ayu Prihastuti Moderator: DR. Dr. Hani Susianti, SP - PK (K)yeniNessuna valutazione finora
- Sindroma Nefrotik Vs NefritikDocumento23 pagineSindroma Nefrotik Vs NefritikBetha456100% (1)
- Retro Digi Instruction ManualDocumento5 pagineRetro Digi Instruction ManualKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sindroma CushingDocumento8 pagineSindroma CushingKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- VG Playbook Web PDFDocumento23 pagineVG Playbook Web PDFKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Urothelial Tumor: Sub Bagian Urologi Bagian/Smf Bedah FK Uns/Rsud Dr. Moewardi SurakartaDocumento8 pagineUrothelial Tumor: Sub Bagian Urologi Bagian/Smf Bedah FK Uns/Rsud Dr. Moewardi SurakartaKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke RehabilitationDocumento16 pagineStroke RehabilitationKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Failure - AhaDocumento73 pagineHeart Failure - AhaKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- GINJAL DR - KiyatnoDocumento83 pagineGINJAL DR - KiyatnoKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Responsi KardioDocumento37 pagineResponsi KardioAnonymous 2LcGdsRNessuna valutazione finora
- BCLL ActivationDocumento37 pagineBCLL ActivationKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gene Structure and MutationDocumento25 pagineGene Structure and MutationKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- 610 CarcinogenesisDocumento76 pagine610 CarcinogenesisKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxins WEBDocumento50 pagineToxins WEBKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patologi Sistem Saraf - EditDocumento200 paginePatologi Sistem Saraf - EditKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aktivasi Sel T LimfositDocumento36 pagineAktivasi Sel T LimfositKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.exam Mammae2Documento14 pagine4.exam Mammae2Katou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.anatomi MammaeDocumento15 pagine1.anatomi MammaeKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Penyakit Tubulus Dan Interstitium - ADocumento87 pagine3 Penyakit Tubulus Dan Interstitium - AKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Patologi Sistem Retikulo EndhotelialDocumento35 paginePatologi Sistem Retikulo EndhotelialKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Parathyroids: Controlled by Level of Ionized Ca Ca CaDocumento31 pagineParathyroids: Controlled by Level of Ionized Ca Ca CaKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.anatomy of The Thoracic WallDocumento25 pagine3.anatomy of The Thoracic WallKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Inhibitor Sintesis DINDING SelDocumento59 pagineInhibitor Sintesis DINDING SelKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathogensis - at Risk Populations - Prof Bhisma MurtiDocumento21 paginePathogensis - at Risk Populations - Prof Bhisma MurtiKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermoregulation 2Documento10 pagineThermoregulation 2Fernando Feliz ChristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Viral Hepatitis KBKDocumento36 pagineViral Hepatitis KBKKatou Jeffrey ShigehitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Madan No Ou To Vanadis - 03Documento320 pagineMadan No Ou To Vanadis - 03Katou Jeffrey Shigehito100% (2)
- Thermoregulation 2Documento10 pagineThermoregulation 2Fernando Feliz ChristianNessuna valutazione finora
- Madan No Ou To Vanadis - 04Documento289 pagineMadan No Ou To Vanadis - 04Katou Jeffrey Shigehito100% (2)
- Madan No Ou To Vanadis - 02Documento288 pagineMadan No Ou To Vanadis - 02Katou Jeffrey Shigehito100% (2)
- Madan No Ou To Vanadis - 01Documento289 pagineMadan No Ou To Vanadis - 01Katou Jeffrey Shigehito100% (2)
- CatheterizationDocumento13 pagineCatheterizationsharon ocharaNessuna valutazione finora
- Labstrip U11 Plus PDFDocumento1 paginaLabstrip U11 Plus PDFNukiAdelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kidney Stones - K.S. GopiDocumento4 pagineKidney Stones - K.S. GopiMahmood MuftiNessuna valutazione finora
- NUrsing Care PreschoolerDocumento15 pagineNUrsing Care PreschoolerShamie ColozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal Failure: Presented by Peter Fumo, MD, FACPDocumento20 pagineAcute Renal Failure: Presented by Peter Fumo, MD, FACPlagathurcNessuna valutazione finora
- BBM - 978 3 319 23458 8/1 PDFDocumento22 pagineBBM - 978 3 319 23458 8/1 PDFmedicalNessuna valutazione finora
- GGK PKMRS PugerDocumento12 pagineGGK PKMRS Pugersyamsul arifinNessuna valutazione finora
- Jadwal IbsDocumento41 pagineJadwal Ibsazuma91Nessuna valutazione finora
- HTP UretentionDocumento3 pagineHTP UretentionKM TopacioNessuna valutazione finora
- PhysioEx Exercise 9 Activity 4Documento3 paginePhysioEx Exercise 9 Activity 4t4gjzhpfjcNessuna valutazione finora
- URL in A Case of AdultNeglected Case of Bladder ExstrophyDocumento2 pagineURL in A Case of AdultNeglected Case of Bladder ExstrophyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Lab Act Clinical Pathology-GUS-2021 FOR STUDENT 2122Documento9 pagineManual Lab Act Clinical Pathology-GUS-2021 FOR STUDENT 2122EgieAprianNessuna valutazione finora
- International Consultation On Incontinence Questionnaire Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (ICIQ-MLUTS) Confidential Iciq-Mluts Today's DateDocumento4 pagineInternational Consultation On Incontinence Questionnaire Male Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms (ICIQ-MLUTS) Confidential Iciq-Mluts Today's DatewanggaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14Documento5 pagineGen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14KatsumiJ Aki100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheetDocumento10 pagineUrinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheettoobaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For HematuriaDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan For HematuriaTee Wood63% (8)
- NephrolithiasisDocumento3 pagineNephrolithiasisVince GagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Symptomatology Clinical Manifestations Actual Ideal Significance Basis FeverDocumento5 pagineSymptomatology Clinical Manifestations Actual Ideal Significance Basis FeveropxNessuna valutazione finora
- Biopharm Module Unit-7Documento14 pagineBiopharm Module Unit-7Mitz Evan TabaranzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative Oliguria and ATNDocumento22 paginePerioperative Oliguria and ATNmhelmykhafagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Tubular NecrosisDocumento60 pagineAcute Tubular NecrosisYedesney C. LinaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinalysis in The Diagnosis of Kidney DiseaseDocumento94 pagineUrinalysis in The Diagnosis of Kidney DiseasegibreilNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedDocumento34 pagineOverview of RENAL: Dr. Wilson Arthur Zein, M. BiomedAnnisNessuna valutazione finora
- AUBFDocumento32 pagineAUBFAndrei Tumarong AngoluanNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 9-2Documento4 pagineActivity 9-2Hasya HafiyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Blyden: Urinary Tract Infection (Uti)Documento24 pagineDr. Blyden: Urinary Tract Infection (Uti)Blyden NoahNessuna valutazione finora
- Genitourinary SystemDocumento23 pagineGenitourinary SystemRisma ZulfianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Andersons Caring For Older Adults Holistically 6th EditionDocumento32 pagineTest Bank For Andersons Caring For Older Adults Holistically 6th EditionJohn Rodriguez100% (36)
- Proses Berkemih: Moganasivan S 1301-1211-3074Documento10 pagineProses Berkemih: Moganasivan S 1301-1211-3074Nuansa Chalid AwaluddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cystocentesis K4Documento24 pagineCystocentesis K4Sze KhayNessuna valutazione finora
- The Voice of God: Experience A Life Changing Relationship with the LordDa EverandThe Voice of God: Experience A Life Changing Relationship with the LordNessuna valutazione finora
- Confinement (Book #1 in the Love and Madness series)Da EverandConfinement (Book #1 in the Love and Madness series)Nessuna valutazione finora
- From Raindrops to an Ocean: An Indian-American Oncologist Discovers Faith's Power From A PatientDa EverandFrom Raindrops to an Ocean: An Indian-American Oncologist Discovers Faith's Power From A PatientValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Locked Away (Book #2 in the Love and Madness series)Da EverandLocked Away (Book #2 in the Love and Madness series)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cadet Willie McBride - Operation CrocodileDa EverandCadet Willie McBride - Operation CrocodileNessuna valutazione finora