Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
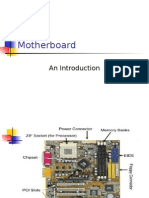
Lectute4 Motherboard Bus-1
Caricato da
Nazmul DwipCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lectute4 Motherboard Bus-1
Caricato da
Nazmul DwipCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CIM101 : Lecture 04
Organization of a computer
Power Supply Microprocessor
Memory
-DRAM
- Cache
- ROM BIOS
Keyboard/
Mouse
Adapter
Port
Printer
Port
Adapter
Display
Port
Adapter
Hard Disk
Drive
Adapter
Floppy Disk
Drive
Adapter
Port
Port
Port
Port
System
Bus
Expansion Bus
Slots
Cards are installed
here
Adapters
7/11/2014 2
The major components of the PC
Processor
I/O devices
Memory
Bus
Adapters
Port
Expansion slot
Storage device
Display
Keyboard
Printer
7/11/2014 3
The major components of the
PC (Cont.)
Mouse
Power supply
Cooling
FDD
HDD
CD-ROM drives
Bus
They connect CPU to each of the memory and I/O
devices.
A collection of wires that act as paths between
the components of a computer.
Example
To read/write data from/to memory, a bus is needed.
Types of buses
Three buses:
Address bus
Data bus
Control bus
Address bus
Collection of parallel wires.
Unidirectional, information flows over it only in one direction.
The number of wires indicate the maximum number of memory
addresses. E.g. 20 wires mean 2^20 = 1MB memory.
CPU uses this to address memory and other I/O devices.
Before accessing a particular location in memory or a particular I/O
device, the CPU places the address of that in the address bus.
The address is decoded to select the particular location or device.
Data bus
Bidirectional.
Used for read/write.
Can be either input or output depending on whether the CPU perform
a READ or WRITE operation.
The number of wires determines the speed at which data can be
read/written.
To read, 1
st
address is sent using the address bus to enable the desired
memory location or I/O device and then memory or the I/O device
places the data on the data bus which is read by the CPU.
To write, 1
st
address is sent using the address bus to enable the
desired memory location or I/O device and CPU places data on the
data bus which is received by the selected memory or I/O device.
Control bus
A set of signals that is used to control the activities of different
components of the computer in a smooth way.
Some are sent by CPU to other components to tell them the
type of operation in progress.
Also I/O device sends control signal to CPU to indicate its
status.
Example
Read/Write, Reset, Interrupt etc.
Figure of Microprocessor Local Buses
Microprocessor
(CPU)
Address Bus
Data Bus
Control Bus
System bus
The 3 buses together are called the system bus
and are guided in parallel to the bus slots.
Several bus architectures used in microcomputers
are:
AT, ISA, EISA, IBM etc.
The PCI BUS
It stands for peripheral component interconnect.
Introduced by Intel.
Defines a local bus that allows up to ten PCI complaint expansion cards to
be plugged into the computer.
One of these ten cards must be the PCI controller card and others are video
card, network interface card etc.
PCI controller exchanges information with the computers processor as 32-
bit or 64-bit words and allows PCI adapters to perform certain tasks
concurrently with the main processor.
PCI can operate at a bus speed of 32MHz.
Adapters
Allow processor to communicate with and control I/O or
storage devices.
A set of hardware circuitry.
Connects to system bus.
Acts as an interface/bridge.
Example: serial port adapter, connects to system bus, and has
a port where a modem could be attached.
Port
Ports of adapters support attachment of I/O devices.
Expansion slots
Physical connectors.
Can be used to attach extra adapters to allow support of
various types of I/O devices.
Storage devices
Hard disks and CD-ROMS.
Display
Most common CRT
For laptops, LCD.
Needs the display adapter to attach the monitor.
7/11/2014 14
Keyboard
Has an 8-bit processor inside.
Used to detect key presses/releases.
The adapter itself has an 8-bit processor that gets
keystroke reports from the keyboard processor.
Printer
Attached to parallel port.
8 bits data transfer at a time.
Keyboard- serial mode transfer, bit-by-bit.
Parallel port adapter is normally integrated into the
computer motherboard.
3 popular printers: dot-matrix, laser, ink jet.
7/11/2014 15
Mouse
Preferred input device.
Used to be connected through serial port.
Now has dedicated PS/2 and USB mouse port.
Other ports and adapters
Most computers have 2 serial ports today : COM1 and
COM2
Has data rate 115 kbps.
Can be of 9 or 25 pins.
7/11/2014 16
Power supply
Converts standard 220v AC to DC for all the
components of the computer. +5v, -5v, +12v and 12v.
Sometimes supplies AC voltage directly to monitor.
Cooling
A fan to keep the power supply cool.
CPU also has a separate cooling fan.
Large and powerful computers may need cooling for
each individual adapters and the motherboard.
7/11/2014 Fahmida Hamid 17
Floppy disk drives (FDD)
Needed to support floppy disks.
Floppy is a magnetic storage medium.
Now floppy size = 3.5 in diameter and stores 1.44MB of
data.
PCs today have FDD adapter built-in.
Hard disk drives (HDD)
They attach to computer through IDE (intelligent drive
electronics) adapter port.
CD-ROM drives
Can store 700MB of data. 5 in size.
They attach to computer through IDE (intelligent drive
electronics) adapter port.
7/11/2014 Fahmida Hamid 18
Real-time clock and calendar
Its a chip.
Has small nonvolatile memory (64 bytes).
Power supplied by a small battery.
This chip supplies date & time and stores basic
system configuration.
Loss of this information destroys system
configuration.
7/11/2014 19
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Computer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersDocumento12 pagineComputer Motherboard Components and The Functions, Manufactures & OthersRohan DhawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Give All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipDocumento7 pagineGive All The Parts of The Motherboard and Give Each Part Description. 1. CPU (Central Processing Unit) ChipjanNessuna valutazione finora
- ITC Lec 3Documento31 pagineITC Lec 3josephNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Processing UnitDocumento5 pagineCentral Processing UnitssssmailnatNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment CS by ABRARDocumento9 pagineAssignment CS by ABRARThe King studioNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Notes 2Documento6 pagineBasic Notes 2jivan jyotNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Components and Their FunctionsDocumento4 pagineMotherboard Components and Their FunctionsRige Mae MuescoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento6 pagineChapter 4Lloyd RevesNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"Documento10 pagineStandard I/O Interfances Reference: Call Hamacher, "Computer Organization"JochumNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Components and FunctionsDocumento4 pagineMotherboard Components and FunctionsCheryl Dumaguit BelaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-II: Accessory BoardDocumento39 pagineUnit-II: Accessory BoardNavi KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No.4Documento12 pagineExperiment No.4Kshitij DudheNessuna valutazione finora
- MotherboardDocumento20 pagineMotherboardJeyc RapperNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of MotherboardDocumento63 pagineParts of MotherboardMarivic Omosura ItongNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter TwoDocumento36 pagineChapter TwoyonasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 8 - IO BusesDocumento70 pagineLecture 8 - IO BusesHydie CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento5 pagineChapter 1nashwah mahomedNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Component of The System UnitDocumento8 pagineChapter 4 Component of The System UnitAminiasi SalatovouNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocumento13 pagineBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of System Unit & MotherboardDocumento6 pagineParts of System Unit & MotherboardNonoy Enopena100% (2)
- Homework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetDocumento13 pagineHomework 1: John Kerby C. Corral X-GarnetJohn Kerby CorralNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper - History of Different Buses in A PCDocumento20 paginePaper - History of Different Buses in A PCammad ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocumento28 pagineMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- Parts of MotherboardDocumento86 pagineParts of MotherboardKurt BalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Major Parts and FunctionDocumento3 pagineMotherboard Major Parts and FunctionVic Picar0% (1)
- Chapter 4 - The Components of The System Unit - ReviewDocumento2 pagineChapter 4 - The Components of The System Unit - ReviewYūkiHaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer SystemDocumento10 pagineComputer Systemdhirendra lamsalNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Computer MotherboardDocumento5 pagine4 Computer MotherboardStar Boy DavieNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard Components and FunctionDocumento5 pagineMotherboard Components and FunctionnominnanaaespasolNessuna valutazione finora
- Latest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsDocumento3 pagineLatest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsSahil ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - 6 Input/output Organization Introduction To Bus ArchitectureDocumento14 pagineUnit - 6 Input/output Organization Introduction To Bus ArchitectureAyushi SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Processors (CPU) : Internal System Unit ComponentsDocumento5 pagineProcessors (CPU) : Internal System Unit ComponentsAnonymous ZzYOKUcONessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Hardware ComponentsDocumento5 pagineComputer Hardware ComponentscomputerwizNessuna valutazione finora
- Mohammad Alfaiz Khan-CSO Practical7Documento3 pagineMohammad Alfaiz Khan-CSO Practical7kmohammadalfaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Compter SystemsDocumento23 pagineBasics of Compter SystemsYogesh KuteNessuna valutazione finora
- A Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataDocumento11 pagineA Computer Is A Device That Can Receive, Process and Store DataPenchalaiah NarasapuramNessuna valutazione finora
- International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) Is An AmericanDocumento9 pagineInternational Business Machines Corporation (IBM) Is An AmericanClash ClansNessuna valutazione finora
- CHT Practical 1 KUKDocumento3 pagineCHT Practical 1 KUKDhruv SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper - History of Different Buses in A PCDocumento21 paginePaper - History of Different Buses in A PCammad ahmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Computer Architecture 1-1Documento4 pagineIntroduction To Computer Architecture 1-1Jedekia kicaNessuna valutazione finora
- CahmDocumento3 pagineCahmakkivish37Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organization of A ComputerDocumento12 pagineOrganization of A ComputerManjare Hassin RaadNessuna valutazione finora
- 21BCS11360 (Workshop Tech. 1.1)Documento6 pagine21BCS11360 (Workshop Tech. 1.1)Shreyank PushkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Typical Configuration of Computer SystemDocumento90 pagineTypical Configuration of Computer Systemgani100% (1)
- A+ Computing ConceptsDocumento8 pagineA+ Computing ConceptsMafiozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Computer Architecture (Autosaved)Documento128 pagineAdvance Computer Architecture (Autosaved)Sara KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Report-3 Computer Hardware: How The Processor Works?Documento6 pagineLab Report-3 Computer Hardware: How The Processor Works?COLD STUDIONessuna valutazione finora
- Computer System ComponentsDocumento11 pagineComputer System ComponentsNoone F. moonNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer MotherboardDocumento15 pagineComputer MotherboardElsabet KindeNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Instructions Computer Program: Exercise 111Documento6 pagineComputer Instructions Computer Program: Exercise 111rsac_1997Nessuna valutazione finora
- Inside A Computer CabinetDocumento14 pagineInside A Computer CabinetJavid HamdardNessuna valutazione finora
- Motherboard: The CPUDocumento10 pagineMotherboard: The CPU000pssNessuna valutazione finora
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocumento14 pagineIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Description of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Documento4 pagineDescription of Motherboard:: Q # 2. Identify Various Components of A Computer System On Motherboard?Nain khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware ConceptsDocumento28 pagineHardware ConceptsGeetha NamavaramNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing InformaticsDocumento13 pagineNursing InformaticsNursidar Pascual MukattilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chs Assignment 1Documento7 pagineChs Assignment 1Kiruba KaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryDocumento11 pagineLab Outcome: CO 1-Recall The Fundamentals of Computer Hardware. TheoryasavariNessuna valutazione finora
- II Puc CS 1st and 4th Chapters NotesDocumento17 pagineII Puc CS 1st and 4th Chapters NotesRyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre-Colonial Philippine ArtDocumento5 paginePre-Colonial Philippine Artpaulinavera100% (5)
- SAP HR and Payroll Wage TypesDocumento3 pagineSAP HR and Payroll Wage TypesBharathk Kld0% (1)
- Yemen Companies Contact DetailsDocumento5 pagineYemen Companies Contact DetailsYAGHMOURE ABDALRAHMAN78% (9)
- Model-Checking: A Tutorial Introduction: January 1999Documento26 pagineModel-Checking: A Tutorial Introduction: January 1999Quý Trương QuangNessuna valutazione finora
- Netflix Annual Report 2010Documento76 pagineNetflix Annual Report 2010Arman AliNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is NanoWatt TechnologyDocumento1 paginaWhat Is NanoWatt Technologyfolk_sharathNessuna valutazione finora
- Proposal Mini Project SBL LatestDocumento19 pagineProposal Mini Project SBL Latestapi-310034018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Site AnalysisDocumento4 pagineSite AnalysisS O NALNessuna valutazione finora
- Monster Energy v. Jing - Counterfeit OpinionDocumento9 pagineMonster Energy v. Jing - Counterfeit OpinionMark JaffeNessuna valutazione finora
- Prayer For Protection PDFDocumento3 paginePrayer For Protection PDFtim100% (1)
- Dual Nature and RadiationDocumento39 pagineDual Nature and RadiationWedger RealmeNessuna valutazione finora
- 3500 Ha027988 7Documento384 pagine3500 Ha027988 7Gigi ZitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Review Module 8Documento18 pagineBook Review Module 8Asherah Mica MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Personal Tutor: 11 + MATHS Test 6Documento10 paginePersonal Tutor: 11 + MATHS Test 6siddhant4uNessuna valutazione finora
- AC Hipots 15-200kVDocumento4 pagineAC Hipots 15-200kVfelipe.aounNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Different Laser Texture Configurations On Improving Surface Wettability and Wear Characteristics of Ti6Al4V Implant MaterialDocumento14 pagineEffect of Different Laser Texture Configurations On Improving Surface Wettability and Wear Characteristics of Ti6Al4V Implant Materialnitish kumar100% (1)
- Management of Odontogenic Infection of Primary Teeth in Child That Extends To The Submandibular and Submental Space Case ReportDocumento5 pagineManagement of Odontogenic Infection of Primary Teeth in Child That Extends To The Submandibular and Submental Space Case ReportMel FANessuna valutazione finora
- Ev Conversion PDFDocumento2 pagineEv Conversion PDFShannonNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Requirements CompressDocumento9 pagineSoftware Requirements CompressApni Duniya100% (1)
- G5 Series User ManualDocumento22 pagineG5 Series User ManualDaniel MekonnenNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Documento4 pagineA Simple and Reliable Submental Intubation.68Tîrban Pantelimon FlorinNessuna valutazione finora
- ACCA Strategic Business Reporting (SBR) Workbook 2020Documento840 pagineACCA Strategic Business Reporting (SBR) Workbook 2020Azba Nishath0% (1)
- Media EthicsDocumento11 pagineMedia EthicsSreekanth Reddy100% (2)
- Piezometers: Types, Functions, & How It Works?Documento38 paginePiezometers: Types, Functions, & How It Works?Encardio RiteNessuna valutazione finora
- 2002PCDFCADocumento78 pagine2002PCDFCATin NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Install Sensor Lsi Fl061Documento14 pagineInstall Sensor Lsi Fl061AlterSon Grafi KalayNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5: Number Systems: Introduction To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Documento16 pagineModule 5: Number Systems: Introduction To Networks v7.0 (ITN)Mihai MarinNessuna valutazione finora
- XIInfo Pract H Y 416Documento4 pagineXIInfo Pract H Y 416Neelima VijayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics For EconomicsDocumento58 pagineStatistics For EconomicsKintu GeraldNessuna valutazione finora
- Frankenstein ExtractDocumento1 paginaFrankenstein ExtractAnneNessuna valutazione finora