Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Segment
Caricato da
pluck_boyCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Segment
Caricato da
pluck_boyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Segmentation, Targeting,
and Positioning
Building the Right Relationships
with the Right Customers
Chapter 7
7 - 1
Learning Goals
1. Learn the three steps of target marketing,
market segmentation, target marketing, and
market positioning
2. Understand the major bases for segmenting
consumer and business marketing strategy
3. Know how companies identify attractive
market segments and choose target
marketing strategy
4. Realize how companies position their
products for maximum competitive
advantage in the marketplace
7 - 2
Sells multiple brands
within the same product
category for a variety of
products
Brands feature a
different mix of benefits
and appeal to different
segments
Has also identified
different niches within
certain segments
Product modifications
are useful: Tide offers
seven different product
formulations to serve
different niches needs
Case Study
Procter & Gamble
7 - 3
Steps in market segmentation,
targeting and positioning
Market Segmentation
Identify bases for segmenting the market
Develop segment profiles
Target Marketing
Develop measure of segment
attractiveness
Select target segments
Market Positioning
Develop positioning for target segments
Develop a marketing mix for each segment
Goal 1: Learn the three steps of target marketing
7 - 4
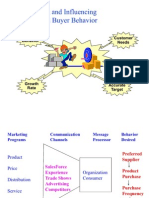
Figure 8-1:
Steps in Market
Segmentation, Targeting,
and Positioning
7 - 5
Definition
Market Segmentation:
Dividing a market into distinct
groups with distinct needs,
characteristics, or behavior who
might require separate products or
marketing mixes.
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 6
Segmenting Consumer
Markets
Geographical segmentation
Demographic segmentation
Most popular segmentation
Psychographic segmentation
Lifestyle, social class, and
personality-based segmentation
Behavioral segmentation
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 7
World region
or country
U.S. region
State
City
Neighborhood
City or
metro size
Density
Climate
Geographic Segmentation
Variables
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 8
Geographical climate is
a legitimate means of
segmentation for many
products or services.
Name several examples of
products for which need
(and demand) would vary
on a geographical basis.
Discussion Question
7 - 9
Demographic Segmentation
Variables
Age
Gender
Family size
Family life cycle
Income
Occupation
Education
Religion
Race
Generation
Nationality
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 10
What type of demographic segmentation
is reflected by this ad?
7 - 11
Occasions
Benefits
User Status
Attitude Toward
the Product
User Rates
Loyalty Status
Readiness Stage
Behavioral Segmentation
Variables
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 12
Swatch targets
those with an
active lifestyle
7 - 13
Occasion segmentation: Altoids Love
Tin is a curiously strong valentine
7 - 14
Segmenting Business
Markets
Demographic segmentation
Industry, company size, location
Operating variables
Technology, usage status, customer capabilities
Purchasing approaches
Situational factors
Urgency, specific application, size of order
Personal characteristics
Buyer-seller similarity, attitudes toward risk, loyalty
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 15
Segmenting International
Markets
Geographic segmentation
Location or region
Economic factors
Population income or level of economic
development
Political and legal factors
Type / stability of government, monetary
regulations, amount of bureaucracy, etc.
Cultural factors
Language, religion, values, attitudes, customs,
behavioral patterns
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 16
Requirements for Effective
Segmentation
Measurable
Size, purchasing power, and profile of segment
Accessible
Can be reached and served
Substantial
Large and profitable enough to serve
Differentiable
Respond differently
Actionable
Effective programs can be developed
Goal 2: Understand the major bases for segmentation
7 - 17
Target Marketing
Target Market
Consists of a set of buyers who share
common needs or characteristics
that the company decides to serve
Goal 3: Know how companies identify and target attractive segments
7 - 18
Target Marketing
Evaluating Market Segments
Segment size and growth
Segment structural attractiveness
Level of competition
Substitute products
Power of buyers
Powerful suppliers
Company objectives and resources
Goal 3: Know how companies identify and target attractive segments
7 - 19
Target Marketing
Selecting Target Market Segments
Undifferentiated (mass) marketing
Differentiated (segmented)
marketing
Concentrated (niche) marketing
Micromarketing (local or individual)
Goal 3: Know how companies identify and target attractive segments
7 - 20
Choosing a Target
Marketing Strategy
Considerations include:
Company resources
The degree of product variability
Products life-cycle stage
Market variability
Competitors marketing strategies
Goal 3: Know how companies identify and target attractive segments
7 - 21
Target Marketing
Socially Responsible Targeting
Some segments, especially children,
are at special risk
Many potential abuses on the
Internet, including fraud Internet
shoppers
Controversy occurs when the
methods used are questionable
Goal 3: Know how companies identify and target attractive segments
7 - 22
Positioning
Positioning:
The place the product occupies in
consumers minds relative to competing
products.
Typically defined by consumers on the
basis of important attributes.
Involves implanting the brands unique
benefits and differentiation in the
customers mind.
Positioning maps that plot perceptions of
brands are commonly used.
Goal 4: Realize how companies position their products
7 - 23
Porsche is
positioned on
the basis of
performance
and freedom.
7 - 24
Identifying possible
competitive advantages
Choosing the right
competitive advantage
Choosing a positioning
strategy
Differentiation can be based
on
Products
Services
Channels
People
Image
Topics
Choosing a Positioning
Strategy
Goal 4: Realize how companies position their products
7 - 25
Market Segmentation
How many differences to
promote?
Unique selling
proposition
Several benefits
Which differences to
promote? Criteria include:
Important
Distinctive
Superior
Communicable
Preemptive
Affordable
Profitable
Topics
Identifying possible
competitive advantages
Choosing the right
competitive advantage
Choosing a positioning
strategy
Goal 4: Realize how companies position their products
7 - 26
Market Segmentation
Value propositions
represent the full
positioning of the brand
Possible value propositions:
More for More
More for the Same
More for Less
The Same for Less
Less for Much Less
Topics
Identifying possible
competitive advantages
Choosing the right
competitive advantage
Choosing a positioning
strategy
Goal 4: Realize how companies position their products
7 - 27
Figure 8-3:
Possible Value Propositions
7 - 28
Developing a
Positioning Statement
Positioning statements summarize
the company or brand positioning
EXAMPLE: To (target segment and
need) our (brand) is (concept) that
(point-of-difference)
Goal 4: Realize how companies position their products
7 - 29
Communicating the
Positioning
Companies must be certain to
DELIVER their value propositions.
Positions must be monitored and
adapted over time.
Goal 4: Realize how companies position their products
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Building The Right Relationships With The Right CustomersDocumento23 pagineSegmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Building The Right Relationships With The Right CustomersSivapalan SivapirashanthNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch7 Segmentation, Targeting, PositioningDocumento18 pagineCh7 Segmentation, Targeting, PositioningShahid MushtaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Segmentation - KotlerDocumento23 pagineMarketing Segmentation - KotlerRajiv MondalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningDocumento23 pagineChapter 7 Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningHamid KhurshidNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning For Competitive AdvantageDocumento28 pagineMarket Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning For Competitive AdvantageSangeeta BaishyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmenting, Targeting and PositiongDocumento23 pagineSegmenting, Targeting and PositiongalikhayalNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2 - The Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessDocumento36 pagineTopic 2 - The Role of IMC in The Marketing ProcessShamal Shavneel SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- STP AnalysisDocumento5 pagineSTP AnalysissutharshanlkNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 - Market Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning (Revised - Sept 2013)Documento26 pagineUnit 4 - Market Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning (Revised - Sept 2013)Cherrell Lynch100% (1)
- MM - Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning252-Lecture5Documento27 pagineMM - Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning252-Lecture5Rahul RauniyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning NotesDocumento7 pagineSegmentation, Targeting, and Positioning NotesSavannah Simone Petrachenko100% (2)
- Segmentation Targeting and PositioningDocumento37 pagineSegmentation Targeting and PositioningdivyankNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning: MGT 252 - Lecture 5Documento30 pagineSegmentation, Targeting and Positioning: MGT 252 - Lecture 5eunicegaluraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 4Documento48 pagineChap 4abdullahkashiftkNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Segmentation, Targeting & PositioningDocumento216 pagineCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Segmentation, Targeting & PositioningVladimir ZahmanovNessuna valutazione finora
- STPDocumento22 pagineSTPzakirno19248Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Does STDP Stand ForDocumento4 pagineWhat Does STDP Stand ForForam ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7Documento34 pagineChapter 7Nurul Athirah GhazaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Market SegmentationDocumento10 pagineCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Market SegmentationNoman KhosaNessuna valutazione finora
- STPDocumento23 pagineSTPsarikawalia100% (1)
- Customer Driven Market StrategyDocumento51 pagineCustomer Driven Market StrategySWARUPA HAVALDARNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningDocumento33 pagineCustomer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningNoraSabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Customer-Driven Marketing StrategyDocumento18 pagineCustomer-Driven Marketing StrategyIndronil BanikNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2 POMDocumento35 pagineLecture 2 POMAnwar HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7Documento20 pagineCH 7mknightblaze139Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 Chapter 4 Customer Driven Marketing StrategyDocumento28 pagine2021 Chapter 4 Customer Driven Marketing StrategyAptHouL AzizNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 5 Learning MaterialDocumento6 pagineWeek 5 Learning MaterialFatema ZehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Marketing: Phillip Kotler & Gary ArmstrongDocumento38 paginePrinciples of Marketing: Phillip Kotler & Gary ArmstrongMāhmõūd ĀhmēdNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 - Marketing - ManagementDocumento28 pagineChapter 6 - Marketing - ManagementRakshit TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Phone Company Market Segmentation Plan0Documento35 pagineCell Phone Company Market Segmentation Plan0Shamsul ArefinNessuna valutazione finora
- C6 - Segment Target M LMSDocumento43 pagineC6 - Segment Target M LMShuuhung29032003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation & TargettingDocumento18 pagineSegmentation & Targettingmahakagrawal3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reporting Outline (Group4 12 Abm1)Documento3 pagineReporting Outline (Group4 12 Abm1)Rafaelto D. Atangan Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mod Kotler 07Documento42 pagineMod Kotler 07Muhieddine TabshNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Building The Right Relationships With The Right CustomersDocumento23 pagineSegmentation, Targeting, and Positioning: Building The Right Relationships With The Right CustomersFata HullaNessuna valutazione finora
- MKT 100 PPT SegmentationDocumento22 pagineMKT 100 PPT SegmentationbrandinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmenting, Targeting and Positioning: Building Right Relationships With Right CustomersDocumento51 pagineSegmenting, Targeting and Positioning: Building Right Relationships With Right CustomerschaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocumento77 pagineSegmentation, Targeting and PositioningShubham BawkarNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 5 - TargetingDocumento18 pagineUNIT 5 - TargetingMoses SwagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Strategy - STPDDocumento19 pagineMarketing Strategy - STPDSagar ChachondiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8: Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Creating Value For Target CustomersDocumento10 pagineChapter 8: Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy: Creating Value For Target CustomersDai HuuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Imc Planning ProcessDocumento35 pagineThe Imc Planning ProcessTRIXIA MAE B. ESPIRITUNessuna valutazione finora
- STP Market Segmentation Targeting PositioningDocumento34 pagineSTP Market Segmentation Targeting PositioningJaymss MirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy - Creating Value For Target CustomersDocumento45 pagineCH 7 Customer-Driven Marketing Strategy - Creating Value For Target CustomersMd. Rabiul AlomNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation and PostioningDocumento3 pagineMarket Segmentation and PostioningMuhammad FazilNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocumento18 pagineSegmentation, Targeting and PositioningHussain AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation Targeting PostioningDocumento80 pagineSegmentation Targeting PostioningNayana RajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- IM1019 L4 Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyDocumento44 pagineIM1019 L4 Customer Value-Driven Marketing StrategyDƯƠNG NGUYỄN THÁI BÌNHNessuna valutazione finora
- Market SegmentationDocumento16 pagineMarket SegmentationMohammad Rafeeq BhatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Five: Market Segmentation, Targeting and PositioningDocumento19 pagineChapter Five: Market Segmentation, Targeting and Positioningalazar suffaNessuna valutazione finora
- UGB229 Marketing Management: Segmentation, Targeting, and PositioningDocumento33 pagineUGB229 Marketing Management: Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioningjohnisco20044729Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 08 Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning For Competitive AdvantageDocumento22 pagineChapter 08 Market Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning For Competitive AdvantageHarini MuraliNessuna valutazione finora
- STPDocumento32 pagineSTPvishakha_rm2000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP)Documento18 pagineSegmentation, Targeting, Positioning (STP)Tanvir AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Segmentation (Module 4)Documento5 pagineMarket Segmentation (Module 4)tom jonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Segementatiion Targeting PositiongDocumento41 pagineSegementatiion Targeting PositiongVishal MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Marketing: Segmenting & Targeting MarketDocumento41 paginePrinciples of Marketing: Segmenting & Targeting MarketNorizati ReesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Coke STP Steps-By RobintbgDocumento9 pagineCoke STP Steps-By Robintbgintel0000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionDa EverandMarketing Management Concepts and Tools: A Simple IntroductionValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (7)