Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Diversity of Life
Caricato da
Rajiv Kabad0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
24 visualizzazioni44 paginelife
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentolife
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
24 visualizzazioni44 pagineDiversity of Life
Caricato da
Rajiv Kabadlife
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 44
Diversity of Modern Life
Kingdom Monera (Monerans)
Smallest and simplest
lifeforms
Unicellular (one-celled)
no nucleus
Bacteria and cyanobacteria
Bacteria
Three basic shapes:
round (cocci)
rod (bacilli)
spiral (spirilli)
Questions
What are two characteristics of
the organisms in Kingdom
Monera?
What is meant by unicellular?
What are the three shapes of
bacteria?
Kingdom Protista(Protists)
Single-celled or multicellular
more complex than organisms
in Kingdom Monera
nucleus
protozoans (animal-like)
algae (plant-like)
Protozoans
Kingdom Protista
no cell wall or chlorophyll
internal digestion
no locomotion (some)
Algae
Cell walls
Chlorophyll
Photosynthetic
Placed in groups according to
color and structure
Questions
What are some characteristics
of Protists?
What are the two types of
Protists?
How are the two types of
Protists different?
Kingdom Fungi
Multicellular; complex
cell walls, no chlorophyll
Threadlike fungi (bread mold)
club fungi (mushrooms)
sac fungi (yeast and mildew)
Questions
What are some characteristics
of Fungi?
What are the three groups of
fungi?
Kingdom Plantae
Multicellular, cell walls, and
chlorophyll
Largest and longest-living
things on Earth
Vascular or Nonvascular
Nonvascular Plants
CANNOT conduct water
Example: Moss
Moist environment
Vascular Plants
CAN conduct water
Capable of living in drier areas
Club mosses, Ferns, Horsetails,
Gymnosperms, and
Angiosperms
Gymnosperms
Seed plant
name means naked seed
Most are conifers
Angiosperms -Flowering Plants
Seed plant
name means covered seed
Seeds are produced inside
ovaries
A ripened ovary is a fruit
largest/most diverse plants
Questions
What is the major difference
between a gymnosperm and an
angiosperm?
What are three plant
characteristics?
How are vascular and non
vascular plants different?
Sponges (invertebrate)
Simplest of the animal groups
lives in salt water attached to
the bottom
Hollow central cavity
Two layers of body cells with
tiny pores
Coelenterates (invertebrate)
Jellyfish, hydras, and corals
two cell layers
Live in water
hollow body with a single
opening
Questions
What are three similarities
between coelenterates and
sponges?
Flatworms (invertebrate)
Flattened body; mostly
parasitic
one body opening
two eyespots (light detection)
Turbellarians (free-living)
Planarians (freshwater
Turbellarians)
Roundworms (invertebrate)
Rounded shaped
two body openings (eating and
waste expulsion)
mostly free-living
Ex: Nematodes and hookworms
Segmented Worms (invertebrate)
Rounded, segmented bodies
two body openings
has five hearts and a brain
Ex: leeches and marine tube
worms
Questions
In what major way are the three
types of worms different?
How are the segmented worms
MOST similar to the
roundworms?
Mollusks (invertebrate)
Soft-bodies, no shell:
(octopus/squid)
well-developed organs
some with shells:
(clams/oysters)
Arthropods (invertebrate)
Largest group of animals
multiple body segments
jointed appendages
(legs/arms)
exoskeleton (hard outer
covering)
Arthropods (continued)
Well-developed organs
insects, lobsters, crabs, and
spiders
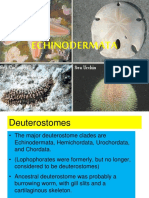
Echinoderms (invertebrate)
Spiny skinned animals
star fish (sea stars), sand
dollars, sea cucumbers
flexible arms; tube feet
known for regeneration (ability
to grow new body parts)
Questions
What is the major similarity
between mollusks,
echinoderms, and arthropods?
Which group of organisms are
known for regeneration?
What is regeneration?
Questions
What is the largest group of
animals?
Describe an invertebrate.
An octopus and a clam belong
to what group of invertebrates?
How is an endoskelton different
from an exoskeleton?
Vertebrates
Have backbones
body with a head and most have
appendages
endoskeleton (internal
skeleton for
support/protection)
Vertebrates (continued)
Endotherm (warm- blooded);
these organisms can control
their body temperature from
within despite changes in the
environment
Vertebrates (continued)
Ectotherm (cold-blooded); body
temperature changes with the
environment
Questions
What is the difference between
an ectotherm and an
endotherm?
How is a vertebrate different
from an invertebrate?
Jawless fishes
Ex: Sea lamprey
mouth is used for sucking
fluids; no appendages (fins)
flexible skeleton made of
cartilage
ectotherms
Cartilaginous Fishes
Two pairs of fins; gills
ectotherms
strong teeth (sharks)
SKELETON MADE OF CARTILAGE
stingrays, skates, sharks
Bony fishes
Flounder, eels, trout, and others
SKELETON MADE OF BONE
gills
streamlined bodies (narrow
shape)
most numerous group of fish
Questions
How are the cartilaginous
fishes mainly different from the
bony fishes?
What do the other fishes have
that the jawless fishes do not
have?
Amphibians
Frogs, toads, salamanders
part of their life is spent on land
and part of life is spent in the
water; (ectotherms)
smooth, moist skin
gills when they are young and
have lungs as adults
Reptiles
Adapted to live on land
(terrestrial)
breathe with lungs
body covered with plates or
scales
ectotherms
Reptiles
Dinosaurs
Turtles, snakes, lizards,
crocodiles, and alligators
lay eggs in a leathery shell
Birds
Bodies adapted for flight (light,
bones, feathers, and wings)
Scaly legs and feet
lay eggs in a hard shell
endotherms
Mammals
Advanced nervous system;
highly developed brain
Endotherms
Hairy bodies
can occupy several habitats
give birth to live young;
produce milk mammary glands
Questions
Which animals spend part of
their life on and part of it in the
water?
What type of animals have
scales or or hard plates?
Questions
Which two groups of animals
are warm-blooded?
What is the difference between
the eggs of reptiles and birds?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocumento3 pagineVertebrates and InvertebratesShar Nur JeanNessuna valutazione finora
- InvertebratesDocumento61 pagineInvertebratesJoyce Ann RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Animals AutosavedDocumento35 pagineClassification of Animals AutosavedjuliankobieplaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Classifying Living Organisms by Kingdoms & CharacteristicsDocumento61 pagineClassifying Living Organisms by Kingdoms & CharacteristicsMuhammad Amin SuhaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 6 Q2 Characteristics of InvertebratesDocumento46 pagineScience 6 Q2 Characteristics of InvertebratesDanski PomilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of Invertebrate AnimalsDocumento46 pagineCharacteristics of Invertebrate AnimalsNiel FelicildaNessuna valutazione finora
- SCIENCE 6 Q2 InvertebratesDocumento59 pagineSCIENCE 6 Q2 InvertebratesGlenda Abogadie PinguelNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic-12 - Arthropods 13Documento51 pagineTopic-12 - Arthropods 13Inaya ImranNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4 Features of organisms FDocumento45 pagine1.4 Features of organisms FqdxtcmvzgzNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Animals 2016Documento29 pagineClassification of Animals 2016BALQIS NURAZIZAHNessuna valutazione finora
- ClassificationDocumento13 pagineClassificationEdward DhlaminiNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal KingdomDocumento103 pagineAnimal KingdomAlexander Yeung100% (1)
- The 5 KingdomsDocumento23 pagineThe 5 Kingdomskj56djb38Nessuna valutazione finora
- #1 An Introduction To Living Organisms: Biology Study PaperDocumento8 pagine#1 An Introduction To Living Organisms: Biology Study PaperAkili ArmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 InvertebrateDocumento47 pagine12 InvertebrateAmelia Puji LestariNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-23-Animals SummaryDocumento28 pagineChapter-23-Animals SummaryJan Marlon GoritNessuna valutazione finora
- Systematics and Classification of AnimalsDocumento51 pagineSystematics and Classification of AnimalsJong CarsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Animals - Dec11Documento60 pagineAnimals - Dec11France Lee ManobanNessuna valutazione finora
- AnimalsDocumento28 pagineAnimalsEnaya MajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification (Third Years Sondervick)Documento85 pagineClassification (Third Years Sondervick)Oliver SlovenskoNessuna valutazione finora
- Coelomate phyla comparisonDocumento82 pagineCoelomate phyla comparisonHawltu MuluNessuna valutazione finora
- ch33 SlidesDocumento24 paginech33 Slidesapi-197124028Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biological TaxonomyDocumento6 pagineBiological TaxonomyfaezamushtaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal KingdomDocumento73 pagineAnimal KingdomIshika GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Organisms Bio 5090 Notes Chalani WijesuterendraDocumento19 pagineClassification of Organisms Bio 5090 Notes Chalani WijesuterendraChal WijeNessuna valutazione finora
- Arthropoda: The Largest Phylum of AnimalsDocumento50 pagineArthropoda: The Largest Phylum of AnimalsNicole de BellNessuna valutazione finora
- HURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-1 ClassificationDocumento39 pagineHURDCO International School: Subject-Biology Chapter-1 ClassificationMunmun AfnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Diversity in Living OrganismsDocumento35 pagineDiversity in Living OrganismsEdUcT-VKS100% (1)
- Characteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsDocumento3 pagineCharacteristics and Classification of Living OrganismsSulaf OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2nd Week2Documento37 pagine2nd Week2Kegie SulpotNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertebrates and Invertebrates ClassificationDocumento33 pagineVertebrates and Invertebrates ClassificationOtenciano MautganonNessuna valutazione finora
- Arthropods GR7 BioDocumento36 pagineArthropods GR7 Biosara ahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Classificationofanimals 5 9 2014 5 21 48 PMDocumento33 pagineClassificationofanimals 5 9 2014 5 21 48 PMCJ TuldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vertebrates 2020Documento62 pagineVertebrates 2020Julia MeirellesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One: Classification of Animal WorldDocumento31 pagineChapter One: Classification of Animal WorldLUBNA AKTERNessuna valutazione finora
- Kingdom AnimaliaDocumento16 pagineKingdom AnimaliaMarese PrietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Vertebrate and Invertebrate AnimalsDocumento33 pagineClassification of Vertebrate and Invertebrate AnimalsJanice Tañedo PancipaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification PDFDocumento34 pagineClassification PDFFaiaz AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Evelyn Hone College Lecture 7 2022 Kingdom AnimaliaDocumento101 pagineEvelyn Hone College Lecture 7 2022 Kingdom AnimaliaJoyce KapembwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diversity of Life: EBIO 1010Documento36 pagineDiversity of Life: EBIO 1010candy_fairy7Nessuna valutazione finora
- KCSE ONLINE REVISION NOTES FORM 3 BIOLOGYDocumento74 pagineKCSE ONLINE REVISION NOTES FORM 3 BIOLOGYDavid ToywaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1&2 - Intro, Protozoa, Por If EraDocumento60 pagineLecture 1&2 - Intro, Protozoa, Por If Eraapi-3827285Nessuna valutazione finora
- Invertebrateanimals 140331061236 Phpapp02Documento17 pagineInvertebrateanimals 140331061236 Phpapp02Cay C. CordovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Kingdom PPT 3 - Class 9Documento32 pagineAnimal Kingdom PPT 3 - Class 9vidushi rathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Eukaryotes (General Biology 1)Documento17 pagineEukaryotes (General Biology 1)King KayNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Animals: Vertebrates and InvertebratesDocumento33 pagineClassification of Animals: Vertebrates and Invertebratesrajeshmmahajan100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Lesson 1 What Are Protists PDFDocumento38 pagineChapter 8 Lesson 1 What Are Protists PDFElijah AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Fossils 3Documento36 pagineFossils 3Reddy SetyawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To InvertebratesDocumento7 pagineIntroduction To Invertebratesalejandra figueroaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8. InvertebratesDocumento142 pagineUnit 8. InvertebratesPika PiNessuna valutazione finora
- Annelids: Khristina J. CruzDocumento72 pagineAnnelids: Khristina J. CruzEthylNessuna valutazione finora
- Plant and Animal KingdomDocumento5 paginePlant and Animal KingdomMa. Liza Coralyn MundoNessuna valutazione finora
- Echinodermata PDFDocumento57 pagineEchinodermata PDFjerlimanmanalu100% (1)
- InvertebratesDocumento65 pagineInvertebratesHelena SaorinNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of OrganismsDocumento17 pagineClassification of OrganismsManula MuthunayakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 5 InvertebratesDocumento96 pagineUnit 5 InvertebratesMarga IglesiasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 32: Reptiles and BirdsDocumento69 pagineChapter 32: Reptiles and BirdsRaviNessuna valutazione finora
- EchinodermsDocumento13 pagineEchinodermsAtif RazaNessuna valutazione finora
- NBME 25 Questions VersionDocumento201 pagineNBME 25 Questions VersionManpreet KS100% (10)
- Rotational Dynamics Type 1Documento12 pagineRotational Dynamics Type 1AAVANINessuna valutazione finora
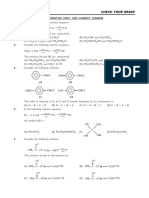
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: CH CL (A) CH CL (B) CHDocumento29 pagineExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: CH CL (A) CH CL (B) CHRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Study Guide PhysicsDocumento96 pagineAP Study Guide PhysicsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials 2018 Final Feb2018Documento45 pagineEssentials 2018 Final Feb2018Rajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Chemistry Tests AnsDocumento7 pagineComplete Chemistry Tests AnsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- SC2 - O'Malley SAT II Review (Organic)Documento2 pagineSC2 - O'Malley SAT II Review (Organic)Rajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Problems For NeetDocumento359 paginePractice Problems For NeetPrudhvi Nath0% (2)
- Rotational Dynamics Type 1Documento12 pagineRotational Dynamics Type 1AAVANINessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Math 2 Tests Answers PDFDocumento6 pagineComplete Math 2 Tests Answers PDFRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Unit9 Worksheet AnswersDocumento5 pagineAP Unit9 Worksheet AnswersAAVANINessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class 9 Social Science Question BankDocumento120 pagineCBSE Class 9 Social Science Question BankRajiv Kabad100% (2)
- Complete Chemistry Tests PDFDocumento136 pagineComplete Chemistry Tests PDFInder BalajiNessuna valutazione finora
- LogicgatesDocumento17 pagineLogicgatesRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsDocumento5 pagineLife Processes Class 10 Notes Science - MyCBSEguide - CBSE Papers & NCERT SolutionsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- ISBAR Communication PolicyDocumento2 pagineISBAR Communication PolicyRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- ISBAR Communication PolicyDocumento2 pagineISBAR Communication PolicyRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem RecordDocumento82 pagineChem RecordRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- 15-0648 Form QEWS Standard+Pediatric+Observation+Chart 5+to+11yrsDocumento2 pagine15-0648 Form QEWS Standard+Pediatric+Observation+Chart 5+to+11yrsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- CardiacDocumento1 paginaCardiacRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac CycleDocumento1 paginaCardiac CycleRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- NFO Note - Reliance Dual Advantage Fixed Tenure Fund XI - Plan ADocumento3 pagineNFO Note - Reliance Dual Advantage Fixed Tenure Fund XI - Plan ARajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Practical Record for Class XI StudentsDocumento1 paginaBiology Practical Record for Class XI StudentsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 1 3 5 1Documento36 pagine1 1 3 5 1rahulNessuna valutazione finora
- © Ncert Not To Be Republished: Principle of Mathematical InductionDocumento12 pagine© Ncert Not To Be Republished: Principle of Mathematical InductionSCReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Holiday HWDocumento4 pagineHoliday HWRajiv Kabad100% (1)
- Morp. of PlantsDocumento26 pagineMorp. of PlantsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Fundamentals: Understanding the BasicsDocumento3 pagineComputer Fundamentals: Understanding the BasicsRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Idi AminDocumento1 paginaIdi AminRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- 31-2-2 ScienceDocumento16 pagine31-2-2 ScienceRajiv KabadNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 11 - 1.4 Kingdoms and DomainsDocumento4 pagineBiology 11 - 1.4 Kingdoms and DomainsMinNessuna valutazione finora
- Protist GuideDocumento30 pagineProtist GuidemavicarigoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine Microbiology by CB MunnDocumento77 pagineMarine Microbiology by CB MunnjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 3rd Edition StarrDocumento10 pagineTest Bank For Biology Today and Tomorrow With Physiology 3rd Edition Starrhalcyonadelau7suNessuna valutazione finora
- Carolus LinnaeusDocumento30 pagineCarolus Linnaeusummu atiqah maisaraNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Kingdoms of OrganismsDocumento13 pagine5 Kingdoms of OrganismsChoirul Anam100% (2)
- Biology STAAR Review Stations Day 8Documento9 pagineBiology STAAR Review Stations Day 8excaliber4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Test Bank For Principles of Life 3rd Edition HillisDocumento42 pagineTest Bank For Principles of Life 3rd Edition Hillismangcornuntune6o9xNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento4 pagineUntitledAlice KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mcat Self PrepDocumento27 pagineMcat Self PrepAbdul Manan100% (1)
- Class XI Biology Study Material 2022-23-1Documento257 pagineClass XI Biology Study Material 2022-23-1ysNessuna valutazione finora
- Protozoa Unit Four F.YDocumento31 pagineProtozoa Unit Four F.YmousumimamunNessuna valutazione finora
- FSC 1st Year Smart Syllabus Punjab BoardsDocumento31 pagineFSC 1st Year Smart Syllabus Punjab BoardsRashid Nawaz100% (2)
- DLL of Grade 8, Quarter 4Documento51 pagineDLL of Grade 8, Quarter 4Rey Ann RubioNessuna valutazione finora
- Classifying Organisms into Kingdoms Based on Cell Structure and ReproductionDocumento20 pagineClassifying Organisms into Kingdoms Based on Cell Structure and ReproductionEmma AlexandersNessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Class Biology Mcqs Chapter n03 and 04Documento3 pagine9th Class Biology Mcqs Chapter n03 and 04RafiullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Protista LabDocumento2 pagineProtista Labapi-271250844Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiversity, Classification and ConservationDocumento17 pagineBiodiversity, Classification and Conservationmobasser sikderNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: Chapter 1 Invitation To BiologyDocumento9 pagineBiology: Chapter 1 Invitation To Biologyamstrghtr94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classlifewkst 1 1Documento2 pagineClasslifewkst 1 1api-25406961433% (3)
- Protists and Fungi Review: Key Terms and ConceptsDocumento8 pagineProtists and Fungi Review: Key Terms and ConceptsChris MackNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect.1 .BTE2410Lec. 1 1basics1Documento57 pagineLect.1 .BTE2410Lec. 1 1basics1Aleep YoungBaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Classification Class 11 Notes BiologyDocumento6 pagineBiological Classification Class 11 Notes BiologyVyjayanthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Diag. Exam in Sci - 7Documento3 pagineDiag. Exam in Sci - 7Joeab BayanbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Microbiology Syllabus and Lecture OverviewDocumento32 pagineIntroduction to Microbiology Syllabus and Lecture OverviewJihad Abou Ali WakedNessuna valutazione finora
- Sbi3u Mini Test 2 Unit 1 AnswersDocumento2 pagineSbi3u Mini Test 2 Unit 1 Answerschriston.mNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Parasitology OutlineDocumento5 pagineClinical Parasitology OutlineLynneth Mae Beranda CorpusNessuna valutazione finora
- Life - WikipediaDocumento59 pagineLife - WikipediaChaudhary TamannaNessuna valutazione finora
- LN Med Bact Final PDFDocumento444 pagineLN Med Bact Final PDFPrince HimansuNessuna valutazione finora
- Std11 Bot EM 1Documento236 pagineStd11 Bot EM 1Irshad Ali100% (1)