Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Balance Sheet and Ratio Analysis of A Bank
Caricato da
ArchanaHegde0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
112 visualizzazioni52 paginebank balance sheet analysis
Titolo originale
Balance Sheet and Ratio Analysis of a Bank
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentobank balance sheet analysis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
112 visualizzazioni52 pagineBalance Sheet and Ratio Analysis of A Bank
Caricato da
ArchanaHegdebank balance sheet analysis
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 52
Presented by
9164 Jenovah Carl Fernandes
9117 Ashwini Jadhav
9108 Amit Bhamare
1
Balance Sheet
Of
A bank
2
A Snap Shot
A photograph of financial worth of
the concern at certain time.
The study of the balance sheet reveal
whether the business of the
bank is healthy and growing and
has a promising future or not
3
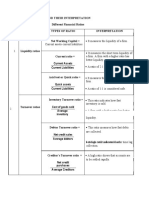
What is Balance Sheet
Liquid Assets
Loans
Marketable Securities
Investment Securities
Fixed Assets
Accrued Interest
Other Assets
Total Assets
4
Cash included cash in hand and RBI including
foreign currencies and balances with other
banks.
Cash is kept in hand by the banks to meet the
demand and obligation of the customer.
Cash is the primary reserve or first line of
defense against depositors
The banks advance short term loans to their
customers.
These loans are advanced on a normal
interest with the promise that these will be
returned to the bank on short notice
The amount advanced for short period is
called money at call and at short notice and is
regarded.
The bank invest funds in the govt. securities.
bonds, gold or other profitable commodities
or instrument for short and long term
investment
The investment in these items are quite liquid
and profit yielding
The advances includes loans, cash credits,
overdrafts, bills discounted.
Advances are the largest items on the assets
side of the commercial bank.
These advances have high yield but low
liquidity
Deposits
Bank Borrowings
Accrued Expenses
Other Liabilities
Shareholders Equity
Total Liabilities
9
Fixed deposits and saving ,etc
Liabilities Borrowing
This is the amount which the bank borrows
from RBI.
Loans may be obtained against securities.
Share Capital
Reserves
Retained Earnings
Revaluation Surplus
Share Premiums
Net Income
Total S/H Equity
11
The bank raises capital from its shareholder
and the sale of ordinary shares.
Reserves
This is the amount which is accumulated over
the years out of net undistributed profit.
That tries to give maximum profit to the
shareholders.
That lends rationally.
That give security to their depositors
Interest Rates
Interest Sensitivity
Due Dates
Foreign Currency
breakdown
Collateral
14
AMEL
This system was adopted in India since
1995
Under this system the rating of individual
banks is done along five key parameters.
Each of the five dimensions of performance
is rated on a scale of 1 to 5, varying from
fundamentally strong bank to
fundamentally weak bank.
15
Capital Adequacy
Asset Quality
Management
Earnings
Liquidity
16
17
The Capital of a
Bank protects the
Bank against
unexpected future
losses.
18
CAPITAL ADEQUACY
1. Is level of capital high enough ?
2. Is capital growing proportionate to
assets ?
3. Can additional debt be raised if needed
4. Is there pressure to pay high dividends
19
1.
Shareholders Equity
-----------------------------------
Total Assets
The ability of the present Capital to support
the further growth of Assets
20
2.
Shareholders Equity
------------------------
Risk Weighted Assets
21
TIER ONE CAPITAL:
Which can absorb losses without a bank being
required to cease trading
Tier I Capital = Ordinary Capital+Retained
Earnings& Share Premium - Intangible assets
22
TIER TWO CAPITAL : Which can absorb losses
in the event of a winding-up and so provides
a lesser degree of protection to depositors.
Tier II Capital = Undisclosed
Reserves+General Bad Debt Provision+
Revaluation Reserve + Subordinate debt+
Redeemable Preference shares
23
24
25
26
4.
Total Debt
--------------------------
Shareholders Equity
The ability to raise additional Debt Capital
27
5. Financial Leverage :
Total Assets
-----------------------
Shareholders Equity
28
6. Capital Formation Rate :
Retained Net Income (RNI)
------------------------------
Average Shareholders Equity
RNI = Net Income - Dividends to be paid
The internal growth of Equity Capital
29
Minimum requirements of capital fund in
India:
* Existing Banks 09 %
* New Private Sector Banks 10 %
* Banks undertaking Insurance business 10 %
* Local Area Banks 15%
30
Asset quality is another important aspect of
the evaluation of a banks performance under
the Reserve Bank of India guidelines.
Bank managers are concerned with the quality
of their loans since that provides earnings for
the bank. Loan quality and asset quality are
two terms with basically the same meaning.
31
ASSET QUALITY
1. Are net charge - off s reasonable ?
2. Is management slow to charge off loans?
3. Is loan growth reasonable ?
4. Is loan loss reserve level adequate ?
5. Do earnings comfortably cover loan
losses ?
32
1.
Loans
------------------
Total Assets
33
2. Non Performing Loans =
a) Loans past due more than 90 days
b) Loans not accruing interest
c) Loans with low interest rates
d) Loans on which repayment terms
have been renegotiated.
34
3. Non Performing Loans
------------------------
Total Loans
Indicates how much of the loan portfolio is
non performing.
35
4. Reserves for Non Performing Loans
--------------------------------
Non Performing Loans
Indicates the ability of the loan loss reserve to
absorb potential losses from currently non
performing loans.
36
5. Loan Loss Provision
--------------------
Average Loans
Shows current income reduction in
anticipation of loan losses.
37
6.
Interest Earning Assets
---------------------------
Total Assets
7. Non Interest Earning Assets
------------------------------
Total Assets
38
A bank can not sustain itself long without a
positive cash flow.
Earnings are essential to :
1.Absorb loan losses
2.Finance internal growth of capital
3.Attract investors to supply capital
EARNINGS
1. Are earnings at an adequate level ?
2. Does valid reporting exist for earnings?
IF POOR, ASCRIBABLE TO :
1. Low asset yield
2. High cost of funds
3. Inadequate non interest income
4. High loan charge off s
5. High loan loss provisions
6. Mismanaging taxes
7. High overhead costs
IF STRONG, ASCRIBABLE TO :
1. Strong asset yield
2. Low cost of funds
3. Adequate non - interest income
4. High loan charge off s
5. High loan loss provisions
6. Adequate taxes
7. Low overhead costs
1. Return on Assets ( ROA )
Net Income
---------------------------
Total Average Assets
2. Return on Equity ( ROE )
Net Income
----------------------------
Average Shareholders Equity
3. Net interest margin
net interest Income
--------------------------
Average Interest Earning Assets
4. Net non interest income
Non interest income- non interest expenses
-------------------------------------
Total average assets
5. Operating expense ratio
Total Operating Expense
--------------------------------
Total Operating Income
6. Efficiency Ratio
Non Interest Expense
----------------------------
Net total income
10. Interest Rate Sensitivity Gap :
Interest Rate Sensitive Assets
(-)
Interest Rate Sensitive Liabilities
11. Interest Rate Sensitivity Gap Ratio :
Interest Rate Sensitive Assets
---------------------------------
Interest Rate Sensitive Liabilities
A class of financial metrics that is used to
determine a bank's ability to pay off its short-
terms debts obligations.
LIQUIDITY
1. Is bank dependent on bought money ?
2. Is core deposit growth proportionate
to asset growth ?
4. Is volatile funds significant to assets?
1.Loan- deposit ratio
Loans
-----------------
Deposits
2.Liquid assets ratio
Liquid Assets
--------------
Deposits
3. Liquid Assets
--------------------
Large Liabilities
Measures the assets readily available to cover
a loss of large liabilities.
5. Core Deposits
----------------------
Earning Assets
Indicates the extend to which earning assets
are funded by those deposits considered
stable and not subject to interest rate
disintermediation.
THANK YOU
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Balance Sheet Analysis of Maruti SuzukiDocumento63 pagineBalance Sheet Analysis of Maruti Suzukikeyur5867% (6)
- Balance SheetDocumento30 pagineBalance SheetBhuvan GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Balance Sheet AnalysisDocumento42 pagineBalance Sheet Analysismusadhiq_yavarNessuna valutazione finora
- Segment AnalysisDocumento53 pagineSegment AnalysisamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratio Analysis - Tata and M Amp MDocumento38 pagineRatio Analysis - Tata and M Amp MNani BhupalamNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative Ratio Analysis of Two Companies: Bata & Apex 2011-14Documento21 pagineComparative Ratio Analysis of Two Companies: Bata & Apex 2011-14Arnab Upal100% (2)
- Handout # 1 Solutions (L)Documento10 pagineHandout # 1 Solutions (L)Prabhawati prasadNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.1-Hortizontal/Trends Analysis: Chapter No # 4Documento32 pagine4.1-Hortizontal/Trends Analysis: Chapter No # 4Sadi ShahzadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Balance Sheet AnalysisDocumento18 pagineBalance Sheet Analysisrajat ranjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Types Financial RatiosDocumento8 pagineTypes Financial RatiosRohit Chaudhari100% (1)
- Chapter 7 Notes Question Amp SolutionsDocumento7 pagineChapter 7 Notes Question Amp SolutionsPankhuri SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratio Analysis: Theory and ProblemsDocumento51 pagineRatio Analysis: Theory and ProblemsAnit Jacob Philip100% (1)
- Bond ImmunisationDocumento29 pagineBond ImmunisationVaidyanathan RavichandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Value Based Management BCG ApproachDocumento14 pagineValue Based Management BCG ApproachAvi AhujaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ratio AnalysisDocumento12 pagineRatio AnalysisSachinNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Statement Analysis and Valuation (Penman) FA2013Documento5 pagineFinancial Statement Analysis and Valuation (Penman) FA2013Saurabh VashistNessuna valutazione finora
- Advantages of Accounting RatiosDocumento3 pagineAdvantages of Accounting RatiosNeha BatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Pharma Is Considering The Manufacture of A New Drug, Floxin, For Which The FollowingDocumento7 pagineModern Pharma Is Considering The Manufacture of A New Drug, Floxin, For Which The FollowingbansalparthNessuna valutazione finora
- Relative Valuation JaiDocumento29 pagineRelative Valuation JaiGarima SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- SynopsisDocumento7 pagineSynopsisAnchalNessuna valutazione finora
- ICAI Corporate ValuationDocumento47 pagineICAI Corporate Valuationqamaraleem1_25038318Nessuna valutazione finora
- Company AnalysisDocumento11 pagineCompany AnalysisRamesh Chandra DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Continuous Assignments: Ram Kumar KakaniDocumento10 pagineContinuous Assignments: Ram Kumar KakaniKabeer KarnaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Valuing Real Assets in The Presence of Risk: Strategic Financial ManagementDocumento15 pagineValuing Real Assets in The Presence of Risk: Strategic Financial ManagementAnish Mittal100% (1)
- 3 Financial RatiosDocumento29 pagine3 Financial RatiosAB12P1 Sanchez Krisly AngelNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Standard IndiaDocumento114 pagineAccounting Standard IndiakprakashmmNessuna valutazione finora
- Receivable Management KanchanDocumento12 pagineReceivable Management KanchanSanchita NaikNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Analysis TATA STEElDocumento18 pagineFinancial Analysis TATA STEElneha mundraNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 09Documento34 pagineCH 09Azhar SeptariNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Project Format For Profitability Ratio Analysis of Company A, Company B and Company C in Same Industry For FY 20X1 20X2 20X3Documento15 pagineFinal Project Format For Profitability Ratio Analysis of Company A, Company B and Company C in Same Industry For FY 20X1 20X2 20X3janimeetmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment Valuation RatiosDocumento18 pagineInvestment Valuation RatiosVicknesan AyapanNessuna valutazione finora
- FM - 1 AssignmentDocumento6 pagineFM - 1 AssignmentBHAVEN ASHOK SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Valuation PresentationDocumento43 pagineBusiness Valuation PresentationNitin Pal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 6 Financial Statements Analysis and InterpretationDocumento58 pagineUnit 6 Financial Statements Analysis and Interpretationdaniel rajkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dabur IndiaDocumento37 pagineDabur IndiaBandaru NarendrababuNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11 Valuation Using MultiplesDocumento22 pagineChapter 11 Valuation Using MultiplesUmar MansuriNessuna valutazione finora
- BCG ApproachDocumento2 pagineBCG ApproachAdhityaNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Ratio Analysis Dec 2013 PDFDocumento13 pagineFinancial Ratio Analysis Dec 2013 PDFHạng VũNessuna valutazione finora
- Capital Budgeting Illustrative NumericalsDocumento6 pagineCapital Budgeting Illustrative NumericalsPriyanka Dargad100% (1)
- Chap 12Documento23 pagineChap 12Maria SyNessuna valutazione finora
- PHT and KooistraDocumento4 paginePHT and KooistraNilesh PrajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Financial AnalyticsDocumento11 pagine03 Financial AnalyticsII MBA 2021Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10Documento18 pagineCH 10prashantgargindia_93Nessuna valutazione finora
- SFM - Forex - QuestionsDocumento23 pagineSFM - Forex - QuestionsVishal SutarNessuna valutazione finora
- Case QuestionsDocumento5 pagineCase Questionsaditi_sharma_65Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture5 6 Ratio Analysis 13Documento39 pagineLecture5 6 Ratio Analysis 13Cristina IonescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Vegetron ExcelDocumento21 pagineVegetron Excelanirudh03467% (3)
- Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsDocumento23 pagineAnalysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsJohn HolmesNessuna valutazione finora
- A Note On Valuation in Entrepreneurial SettingsDocumento4 pagineA Note On Valuation in Entrepreneurial SettingsUsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- 395 37 Solutions Case Studies 4 Time Value Money Case Solutions Chapter 4 FMDocumento13 pagine395 37 Solutions Case Studies 4 Time Value Money Case Solutions Chapter 4 FMblazeweaver67% (3)
- A PPT On Money MarketDocumento25 pagineA PPT On Money MarketBrinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost of CapitalDocumento8 pagineCost of CapitalAreeb BaqaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Ratios and Their InterpretationDocumento10 pagineFinancial Ratios and Their InterpretationPriyanka_Bhans_7838100% (3)
- BR Act, 1949Documento7 pagineBR Act, 1949aki16288Nessuna valutazione finora
- ALM PPT FinalDocumento49 pagineALM PPT FinalNishant SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bfm-Mod - D PDFDocumento18 pagineBfm-Mod - D PDFparul yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of A Balance Sheet of A Bank: 2) Liabilities of The Commercial BanksDocumento4 pagineMeaning of A Balance Sheet of A Bank: 2) Liabilities of The Commercial BanksShilpan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study of Non Performing Assets in Bank of BarodaDocumento68 pagineA Study of Non Performing Assets in Bank of BarodaMohamed Tousif81% (21)
- Chapter 5Documento36 pagineChapter 5Baby KhorNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento127 pagineChapter 2Dung Hoàng Khưu VõNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Exchange Operations of Jamuna BankDocumento43 pagineForeign Exchange Operations of Jamuna BankHole StudioNessuna valutazione finora
- JAIIB Paper 4 RBWM Module C Support Services Marketing of Banking Services Products PDFDocumento39 pagineJAIIB Paper 4 RBWM Module C Support Services Marketing of Banking Services Products PDFAssr MurtyNessuna valutazione finora
- 15624702052231UoGssBO9TQOUnD5 PDFDocumento5 pagine15624702052231UoGssBO9TQOUnD5 PDFvenkateshbitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Delhi Co-Operative Housing Finance Corporation LTDDocumento6 pagineDelhi Co-Operative Housing Finance Corporation LTDLalit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Sebi, S M (P #1-C) : Hare Arket IllarDocumento19 pagine9 Sebi, S M (P #1-C) : Hare Arket IllarVCITYNessuna valutazione finora
- A BadulaDocumento4 pagineA Badulanotapernota101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Metrobank FoundationDocumento11 pagineMetrobank FoundationAbigail LeronNessuna valutazione finora
- European Central BankDocumento2 pagineEuropean Central BanknairpranavNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Peculiarity of CoopDocumento6 pagineAccounting Peculiarity of CoopRoann AguirreNessuna valutazione finora
- IBPS Po 2012 Exam Question Papers & AnswersDocumento12 pagineIBPS Po 2012 Exam Question Papers & AnswersVenkey Goud100% (2)
- Foreign Currency ValuationDocumento12 pagineForeign Currency ValuationAhmed ElhawaryNessuna valutazione finora
- BRM ProjectDocumento23 pagineBRM Projectrbhatter007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module - 2 Banking System and Operations: Rajneesh MishraDocumento51 pagineModule - 2 Banking System and Operations: Rajneesh MishramarianmadhurNessuna valutazione finora
- Bank StatementDocumento1 paginaBank Statementcodex hdNessuna valutazione finora
- POA Section 7 Part 1Documento4 paginePOA Section 7 Part 1kxng ultimateNessuna valutazione finora
- RE Financiers ListDocumento15 pagineRE Financiers ListAhmed Mobashshir SamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 01Documento2 pagine01ishtee894Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prudential Bank Vs IAC - G.R. No. 74886. December 8, 1992Documento13 paginePrudential Bank Vs IAC - G.R. No. 74886. December 8, 1992Ebbe DyNessuna valutazione finora
- MTech QROR InterviewDocumento3 pagineMTech QROR InterviewMohammadChharchhodawalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Loan Pricing 916Documento22 pagineLoan Pricing 916Gonçalo MadalenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Partnership Resolution SampleDocumento2 paginePartnership Resolution SamplePatrick John Salalila Paguio89% (9)
- Disbursement HandbookDocumento152 pagineDisbursement Handbookasf100% (1)
- Problem 3Documento3 pagineProblem 3Joyce GijsenNessuna valutazione finora
- Arbes Obs enDocumento12 pagineArbes Obs enAndy PhuongNessuna valutazione finora
- NomadGuide CHIANG MAI Guide Book PreviewDocumento33 pagineNomadGuide CHIANG MAI Guide Book PreviewMichael John Hughes100% (1)
- WL WL: Irctcs E Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)Documento1 paginaWL WL: Irctcs E Ticketing Service Electronic Reservation Slip (Personal User)amrit90320Nessuna valutazione finora
- SLM-19667-BBA - Fiancial Markets and InstitutionsDocumento155 pagineSLM-19667-BBA - Fiancial Markets and InstitutionsMadhusudanNessuna valutazione finora
- SidbiDocumento26 pagineSidbiAnand JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- History of EurobondsDocumento2 pagineHistory of Eurobondsterigand50% (2)
- D.V.V. Satya Prasad and Ors. vs. The Government of AndhraDocumento42 pagineD.V.V. Satya Prasad and Ors. vs. The Government of AndhrapraveenaNessuna valutazione finora