Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
2011 03 09 0237 2011 01 14 SAP Development Lif
Caricato da
Anik Jayan Raj Boddeda0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
83 visualizzazioni43 paginesap hana development
Titolo originale
2011_03_09_0237_2011_01_14_SAP_Development_Lif
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentosap hana development
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
83 visualizzazioni43 pagine2011 03 09 0237 2011 01 14 SAP Development Lif
Caricato da
Anik Jayan Raj Boddedasap hana development
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 43
2010 IBM Corporation
SAP TechED 2010 - Custom Development
Mihir R. Gor Senior Managing Consultant
Virgil Parenzee - Senior Managing Consultant
14 January 2011
2011 IBM Corporation 2
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management & Business Rules Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
Comments in chevron boxes are Point of Views
IBM Cattail URL link to slides:
http://cattail.boulder.ibm.com/cattail/download/EBBE0FE0D8873DDAAFB7414C093F23B6/4/SAP
+TechED+2010+-+Custom+Development+webinar+v1.0.ppt
2011 IBM Corporation 3
So whats different? Why do we need to know this stuff?
SAP are developing the technologies that underpin the custom development capabilities of the SAP
application requires a change in thinking from a Designers, an Architects and a Developers PoV.
Key focus areas are emerging:
WD-ABAP
WD-Java
WD-VC
Rich internet applications / mash-ups
Whats different - Why is it important to us? 2 key points:
Methodology
ASAP 7 Process modelling to UI components where traditional waterfall development method
is changing now MVC paradigm is taking hold BPx/Functional Analysts model the process
Processes become agnostic to the underlying implementation technology
Key to SAP is the definition of the Business Process this serves as the entry point to custom
development
Functional/Developers design UI screens/layout reducing coding effort
SAP WebDynpro technology serves to bind the Model to the View using WD controller
Tools
New upgraded versions of SAP enables designers/developers to integrate UI with pre-developed
apps and widgets via Rich Internet applications
What do we need to do now?
Appraise yourself of these new technical and tooling offerings
Develop the skills in these areas refresh and renew our capabilities
2011 IBM Corporation 4
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
2011 IBM Corporation 5
SAP Strategy Extending Core functionality to users
On-Premise Move to more process orientated view in the delivery of SAP. New ASAP Method is de-
facto approach. This has BPM / SOA enablement at the heart of the delivery method
On-Demand adding extensions to core on-premise by developing new SaaS based solutions e.g.
Business by Design; On-Demand Reporting
On-Device Exposing SAP to more people through improved UI/mobility; delivering UI for the way that
people are used to seeing apps i.e. no clunky WinGUI, but aligned to Smartphones; NW Business Client
SAP
Business Suite:
ERP 6.0, SEM,
SRM, PLM, FIM
2011 IBM Corporation 6
SAP Business Process Management and ASAP 7.0 Method
New, streamlined approach for more focused SAP
projects to accelerate time to value and lower TCO
The new ASAP 7.0 methodology provides
transparency of value realization through consistent
business case reflection.
It ensures efficient guidance for SOA and BPM and
traditional implementation projects through the entire
project life-cycle
It delivers revised content in all the traditional areas
needed for efficient project teams project
management, solution management, organizational
change management, training, blueprinting,
configuration, testing, cutover planning
ASAP 7.0 drives multi-lifecycle considerations, with
added complexity, but to drive a holistic approach:
Process Lifecycle
BPM, NetWeaver BPM
Enabling MVC development
Application Lifecycle
Implementation + Run
Project Lifecycle
PMI PMBOK, Agile, Governance
AscendantSAP
Value Lifecycle
BR/VR, EA and execution
2011 IBM Corporation 7
SAP Innovations
SAP are looking to continuously evolve the existing SAP landscape in a non-disruptive way
Leveraging existing SAP investments no forced upgrades
Upgrade now focused on business enablement rather than licensing drivers
SAP themes centred around : The era of AND
Delivery On-Premise AND unforeseen Demand
Speed AND Accuracy
Real Time AND Low Cost
Powerful AND Simple
Evolution AND New Horizons
In 2002, SAP announced Netweaver as a new Technical Platform for SAP with mantra :
People Data Process integration
Now in 2010, new SAP Netweaver 7.3 extends that message to offer
Interaction
SAP NW Portal Workspace
DUET Enterprise (MS Outlook integration)
Alloy (IBM Lotus Notes integration)
Extensibility
Java only ESB, JMS publish/subscribe
Reusable Business Rules Management with MS-Excel integration
Master Data Management : MDM + MDG
Adoption of Web Standards: WS Policy 1.2, SOAP 1.2, WS Trust 1.3 and Java SE6
Foundation for Process Integration
Multi-version landscape in Solution Manager
Java EE5 certified
2011 IBM Corporation 8
SAP Innovation themes
SAP Cloud and Collaboration
Aspirations
Each of Consumption AND
reliability
Private AND Public
New service consumption
Code AND extensions
Open AND Integrated
New SAP Offerings
SAP ByDesign mid-market cloud
based SaaS offering
On Demand e.g. Carbon Footprint
impact Industry application running
on Amazon Cloud
Stream Works real time
collaborative business process
using Google Wave
SAP NW CE Release 7.3 New
process composition tooling
SAP BI 7.3 with BO harmonised
and consolidated in new release
SAP Aurora BO 4.0 - Includes
Crystal, Xcellsius dashboards, one
integrated design time environment
Code Exchange - SAP SDN
community innovations social
networking of code snippets
Portal workspace - offering event
based insights
SAP Mobility
Aspirations
Native experience AND lower TCO
Unwired existing applications AND
fantastic new applications
Personal AND business
Facts and figures
1.5Tn messages globally 2010
with 700Bn min/month
In 2010, 4Bn mobile subscribers
exchange 2Bn messages/day
using 900 mobile operators
By 2012, 70% of the global
workforce will be using mobile
New SAP themes
New Duet Enterprise extended
integration with MS-apps e.g.
Sharepoint event -> Solution
Manager -> .NET -> ABAP ->
Sharepoint
Project Gateway 1H 2011
expose legacy SAP systems to
mobile via device agnostic
Gateway service
SAP Sybase unwired mobility
platform using Sybase offering
Mobile sales, Mobile workflow
SAP In-memory computing
Aspirations
Game changing innovation
Facts and figures
2003 HW computing power
improved by clock speed
2010 multi-core chips forced
redesign of SW/apps to utilise the
cores more effectively
HW Blade (no moving parts)
composed of 64 Core 2.5 Ghz
2 TB Main memory holding
operational data in main memory
Retailer has 460Bn rows of 1 year
aggregated sales data now has 20
x faster reporting speed
200 x faster price performance
analytics scanning 1m rec/ms/core
with aggregates 10m rec/sec
Super charged apps dunning is
100x faster, settlement 50x faster
Takes out layers of apps and
aggregation processing for
Operational data
New SAP themes
HANA In memory computing
non-disruptive attachment to BW
and BOBJ Nov 2010
2011 IBM Corporation 9
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
2011 IBM Corporation 10
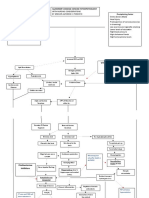
What do we know and do today?
IBM SAP practice has a well established
development methodology and lifecycle based
on Ascendant SAP (Project Lifecycle)
IBM has differentiating tools and accelerators
and proven SAP Custom Development
capabilities with IBM GD teams
These have matured into Technology
Assembly Centers (TAC) teams that
provide immediate accelerated value to
our clients with repeatable capabilities
with high quality yet at reduced
development costs
M
e
t
h
o
d
P
h
a
s
e
Communication & Coordination (all teams)
1. Document
Functional
Specification
Document
(FSD)
8.Create
Technical Design
and Unit Test Plan
13. Execute Unit
Test
16. Review
Test Results
C
l
i
e
n
t
18.Test ( Functional,
Integration and User
Acceptance )
14. Internal Code
Walkthrough
9. Internal Design
Walkthrough
17 SCR
10.Design
Review
Lege
nd
Task with Deliverable
Task without
Deliverable
Process checkpoint
Sign off and
Knowledge
Transfer
Handoff
A
B
A
P
T
A
C
19. Support
development
during
cutover and
testing
20. Complete Knowledge
management with Lessons Learnt
and update methods .
2. Decide
Delivery Cell
3. Compute
FSI
4. Interactive
Design Session
5. Determine
Complexity and
Effort
6. Perform TAC
capacity planning
and decide on
schedule and
resource
7. Identify
Reusable
Components that
can be used
11. Create
Program Structure
using RIC
Generator and plug
in reusable
components
12. Complete
code
Ongoing Issue Resolution (all teams)
15. Delivery
Review
Realization
Business
Blueprint
Final
Prep
Go Live
Code Optimizer
This ABAP based tool helps in detecting project naming and programming
standards .
Saves review and rework time thereby helping in reduced cost to delivery .
RIC Generator
This tool generates auto code for Reports , Interface and Conversion
taking .xml based
technical specification as input . Significantly reduces coding time .
Reduction in coding
time observed to the tune of 25 40%
Reusable Asset
Library (ReAL )
Contains harvested assets which will help in enhancing practitioner
knowledge . Delivery
method will institutionalize submitting as well as re-using these assets .
Auto TS
Generator
This tool will automatically generate the pseudo code , UTP and other
sections of a Technical Specification ( Selection Screen , Transport
section , Authorization Checks, Custom Function Modules,DDIC Objects ,
messages etc. ) . Development in progress. This will significantly reduce
total development efforts and can be positioned as a differentiator.
Code Snippet
Generator
Accelerator for ABAP Coding. Will provide guidance during ABAP
Development .
CTS Checker
(Dependency
and Naming
Conventions)
Will be used during Delivery Review by Cell Lead to check for dependent
transports as well as naming convention of transport contents . Planned
to be released shortly.
Continue to use and develop the IBM TAC
capabilities they differentiate us from the
competition
SAP is innovating in new areas of Custom
Development both in mainstream and
emerging technologies - we need to develop
our knowledge/skills to enhance our client
propositions in the marketplace
2011 IBM Corporation 11
Welcome to the Custom Development ZOO !
Mainstream : Custom Development options
Web Dynpro ABAP (WDA)
Netweaver Composition Environment (NWCE)
Web Dynpro Java (WDJ)
Web Dynpro Visual Composer (WDVC)
Composite Application Framework (CAF)
Guided Procedures (GP) now incorporated into Business Process Manager (BPM)
which includes Process Composer
Emerging : Custom Development options
Web Dynpro ABAP + CHIP + Page Builder
Web Dynpro ABAP + Floorplan Manager (FPM)
Rich Internet Applications :
WDA/WDJ - Adobe Flash Islands & Microsoft Silverlight Islands
WDA/WDJ - AJAX
Given the wide array of development tooling options,
use SAP Best Built apps guidelines to determine the
right Use Cases and apply development standards
Adhere to established methods in ASAP 7.0 /
Ascendant-SAP for delivery method guidance
2011 IBM Corporation 12
User Interface Recommendations
SAP recommends that SAP application development uses the following UI technologies:
Web Dynpro ABAP (WDA) with FPM for UI consistency
Web Dynpro Java (WDJ) and Web Dynpro for Visual Composer (WD4VC)
The Web Client UI Framework (required for continued development for SAP CRM)
SAP Interactive Forms by Adobe for forms that are printed or used online or offline.
SAP no longer encourages use of following UI tech:
Business Server Pages (BSP)
HTMLB
Portal Framework
XHTML or plain HTML
ITS flow logic
ABAP Dynpro (classic dynpro)
SAP Script (now replaced by Adobe Interactive forms)
Dont get religious about the development
technology : ABAP, Java, VC, etc
In terms of sunset technologies, Business suite has
over 100K classic ABAP Dynpros, so SAP are not
walking away from this completely but now there is
new features in WDA that make development on
classic dynpro redundant.
SAP are still investing in old technologies to ensure
integration capabilities can continue.
Be pragmatic - make tooling decisions based on
project requirements but avoid the obvious pitfalls :
Use WDA for ABAP Stack systems
Consider WDJ if you need more application
integration options
SAP say that there is no 'one size for all there
are different tools because there are multiple use
cases and different requirement each time.
2011 IBM Corporation 13
SAP Best Built Applications Guidelines for SAP Business Suite
SAP Architecture Community have produced
guidelines on application development called The
Best-Built Apps Guidelines.
The Best-Built Apps Guidelines are:
Recommendations from SAP about what SAP
technologies partners should leverage
Descriptions of what to do rather than how to
do it
Based on internal standards, best practices,
and architecture guidelines used by SAP
developers
Developed iteratively and incrementally
guidance about what partners should do to
best align their SW with SAP Business Suite
The Best-Built Apps Guidelines are not:
Statements of future direction
Qualification for a new brand or logo
Mandates that partners must follow - Partners
choose whether or not to follow the guidance
Develop solutions built on a single stack, whether ABAP, J ava, or a
third-party platform.
Create composite applications to support new business processes or
scenarios without the need to modify SAP Business Suite components.
SAP business solutions should allow customizations and extensions
of their functionality.
Create test plans and using state-of-the-art testing tools to ensure
functional correctness before releasing software.
The persistency (or database) layer should be free of application logic.
Partner/ISVs keep track of any open source software that is integrated
into their products. SAP also recommends that ISVs carefully analyze
the terms of the license of any open source software that is integrated
into their products, considering license terms from a business
perspective.
Use ABAP version as released in SAP NetWeaver 7.0.
Use ABAP Objects for new programming initiatives and for significant
refactoring of older programs.
Use SAP NetWeaver Developer Studio if you develop for and run on
SAP NetWeaver AS J ava.
.NET developers use one of the following versions, all of which have
been tested by SAP for interoperability:
.NET 2.0 with WS enh. 3.0, .NET 3.0, .NET 3.5
Use the BBA Guidelines to support the clients
Enterprise Architecture standards and project
delivery method and best practices
http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/sdn/bestbuiltapps
2011 IBM Corporation 14
SAP Technology Toolbox
The diagram below illustrates rich development opportunities in SAP Business Suite
All these tools offerings can be confusing at first, so
look at the process requirements to define the use
case that meets process requirements
2011 IBM Corporation 15
SAP Composition Environment 7.3
SAP Netweaver CE provides an Eclipse-based application composition environment , including all layers
to build and run composite applications
CE is used for all BPM, WDJ, WD4VC and CAF development using MCV principles
Provides Integrated tools to develop, implement, and run composite applications faster
Enables service, data , UI composition, and process choreography as used in BPM
Fully Java compatible so easier to create/adopt emerging technology standards and enable the
implementation of development projects based on Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 5 (J2EE5)
2011 IBM Corporation 16
What is Web Dynpro?
Web Dynpro is SAPs standard UI technology for developing business applications that have
Web-based user interfaces. Consists of:
a runtime environment
graphical development environment
Both have integrated tools for either the ABAP or Java development environments.
Web Dynpro is based on a powerful and flexible architecture that uses the Model-View-
Controller design pattern (MVC). This MVC ensures:
clear separation of user interfaces from backend services and business logic,
supports reuse and better maintenance, extensibility and flexibility (by using
components),
provides declarative and graphical tools to minimize development efforts.
The UI definition of Web Dynpro is independent of client technology so the Web Dynpro
application can run on different platforms e.g. browsers, rich clients, mobile devices & future
technologies clients, without additional development or configuration.
Model: BPM is used to define the business process model (where process abstracted from the
technology),
View: UI technologies like WD ABAP, WD Java and WD4VC define the view (look & feel with Islands /
widget etc)
Controller: WD is the binding layer to bring it all together (compilation)
2011 IBM Corporation 17
What is Web Dynpro ABAP (WDA)?
ABAP (Advanced Business Application Programming) is SAPs object oriented, proprietary
programming language for developing business applications within an SAP system.
Web Dynpro ABAP (WDA) is the main SAP standard UI technology for developing Web
application UIs in the ABAP environment. It consists of a runtime environment and a
graphical development environment with special tools that are completely integrated into the
ABAP development environment - the ABAP Workbench (transaction SE80):
This full integration with the ABAP development environment provides direct access to
ABAP data, business logic, and to Data Dictionary Search Helps.
WDA has been available since
October 2005 and is widely used by
the SAP Business Suite and will
continue to be the UI technology of
choice for mainstream Business
Suite applications
ABAP is here to stay !
However, classical ABAP skills now need
renovation and consider more WDA UI
features integration with RIA technologies
2011 IBM Corporation 18
WDA key features
Model-based UI development
Enforce clear separation between UI logic and business logic
Little coding, lots of design
Declarative UI development
Future Proof UI Declaration
Browser, Web Dynpro Client, Mobile Device
Client technology independent UI definition
Central implementation of UI standards
NW Portal Accessibility support
Adobe Forms and Adobe Flash integration
Centrally provided UI elements
Internationalization support
Supports major platforms
Java (as of SAP NetWeaver '04), ABAP (from NW 7.0)
Development completely integrated into ABAP Workbench
Graphical View Layout design
Declarative UI development
ABAP editor with forward navigation
ABAP dictionary data types directly available
Simple remote debugging
Functionality + services of the ABAP Dev Env directly usable
ABAP lifecycle management
Transport
Translation
Enhancements
SAP will continue to invest in WDA used in
all ABAP stack systems and will be enriched
to enable greater Integration capabilities e.g.
WDA for Eclipse
2011 IBM Corporation 19
What is WDA with Floor Plan Manager?
Floorplan Manager (FPM) is a Web Dynpro ABAP application that provides a framework for
developing new Web Dynpro ABAP application interfaces consistent with SAP UI guidelines.
To align and support the development of the ERP User interfaces, a Floorplan Manager
(FPM) for WDA framework is available within the ABAP stack.
FPM is a mandatory tool for the creation of new WDA apps in SAP Business Suite(i.e. ERP,
PLM, SCM, SRM, FIM).
The FPM provides central implementation of floor plans (Object Instance Floorplan, Quick
Activity Floorplan, and Guided Activity Floorplan), support for WDA screens integration, and
tools to adapt and configure the applications by the customers.
FPM is available since WDA 7.00 SP13 and is used by all ERP projects using WDA as of
SAP EhP4 for SAP ERP 6.0.
For all WDA development, SAP recommends
using the FPM to ensure consistency among
all custom + standard SAP user interfaces
2011 IBM Corporation 20
What is Web Dynpro Java (WDJ)?
Web Dynpro is a development toolset and a runtime environment for creating business
applications that have web-based user interfaces.
Recap : Java is a standard, platform independent and object-oriented programming
language used to develop web-based business applications.
WDJ has grown in prominence in last several
years, but SAP are investing just as much in
WDA as WDJ
2011 IBM Corporation 21
What is Web Dynpro Java (WDJ)?
WDJ is the SAP standard UI technology for developing Web application UIs in the Java
environment consisting of a Java (J2EE5) runtime environment and an Eclipse-based (3.x)
development environment (Eclipse is an open source integrated development environment)
WDJ uses the SAP NetWeaver Developer Studio (NWDS) as the integrated development
environment to easily design, develop, deploy and maintain business applications.
Eclipse framework also provides Web services
tools for connectivity based on open standards,
and a Java dictionary for centralised data type and
data structure management.
WDJ has been available since NW2004 (WAS
6.40), and is used within SAP to produce robust
and highly scalable J2EE applications e.g.
ESS/MSS and different SAP Portal applications
like User and Role management transaction and
Universal Work List (UWL).
WDJ is incorporated into the SAP NetWeaver
Composition Environment 7.x (CE), which
provides architectural improvements, new
capabilities, and integration with the other CE
modelling tools (BPM, Visual Composer, CAF)
2011 IBM Corporation 22
What is Web Dynpro for Visual Composer (WD4VC)
WD4VC is the runtime environment for Visual Composer for Composition Environment (CE)
7.1 applications. It is a subset of the of WDJ runtime and a ready to run WDJ application.
In SAP CE, there is strong interoperability between
WDJ and WD4VC, i.e. All development projects
can start with WD4VC, but once they hit a wall
(e.g. have a need for a complex data
transformation), WDJ component can be easily
created to pass around the wall, and consumed
by WD4VC. This integration (inside the NWDS)
means that it is no longer necessary to choose
between starting a project in WDJ or WD4VC, one
can do both, utilising the strengths of each of the
technologies where required.
WD4VC features:
used to rapidly develop business apps
consuming SOA/BI services without having
any Java knowledge
Easy-to-Use: fully model-based, no coding
required !!
BI Connectivity: out-of-the-box support for BI
data services using BI consumer service layer.
ALV-Table support
Create portal content (worksets, roles, pages,
and iViews) and creating Voice applications
Consider WD4VC for early visualisation
of the UI during Blueprint or Detail Design
phases - no coding required
2011 IBM Corporation 23
What are the similarities and differences between the tools?
WDJ and WDA similarities:
create web-based business application UIs and use the MVC design patterns to support a strict
separation of business and presentation logic.
support integration with high interactivity islands to enrich the basic Web Dynpro UI offering with pixel-
perfect high, animated, and improved UIs.
Use same Unified Rendering layer (look & feels same)
Use RIA and AJAX functions
WDJ and WDA differences:
WDJ is implemented in Java and uses CE 7.1.1+
WDA is implemented in ABAP stack NW 7.0+
WDJ developers can do the following:
create their UI applications based on multiple
various data sources
Enterprise services or EJBs
attach to UIs for E2E processes using BPM
WDA developers can do the following:
access standard business logic from the SAP
systems native ABAP coding.
Use MIME repository to manage and use different
objects such as graphics and icons.
Consider Use Case and requirement
Consider maturity of skills and capabilities
Consider timelines and accelerator assets
2011 IBM Corporation 24
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
2011 IBM Corporation 25
Rich Internet Applications for WDJ, WDA and CRM WebClient
UI Framework
RIA are widgets that allow web-apps to be integrated into SAP applications which enable
SAP application mash-up capabilities. Flavours are:
AJAX for WDA and WDJ
CHIPs for WDA
Islands enhancements for WDA and WDJ
These are emerging technologies SAP have
tried to standardise integration option within
Web Dynpro
2011 IBM Corporation 26
SAP NW WDA and AJAX client (Async Javascript for XML)
In WDA, you can install WD AJAX client to provide rich functions like:
based value suggestion as you type
Uses the DDic Search Help to retrieve the values
Values from the Personal Value List (PVL) get displayed with a star and PVL used
in-place of DropDown when you press F4
Drag&Drop, and Page Rearrangement
Validation of Simple Data Types
Extensive Keyboard Support for hot keys, access keys, function keys
In-place of editing, use more fluid animations
Enhanced client/server communication supporting on-demand JavaScript load and with
New Lightspeed rendering engine, with inline CSS and other performance
enhancements
More emphasis on WDA UI development with
Web 2.0 capabilities like Ajax new skill
development requirement
2011 IBM Corporation 27
WDA Collaborative Human Interface Part (CHIP) and Side panel
Collaborative Human Interface Part (CHIP) component model describes
These are like standard web widgets that can be integrated into the WDA application
CHIP capabilities with inports, outports and port contracts
Ports describe data structures of CHIP input or output data
Parameters of a port describe the corresponding data types
CHIPs can be connected to exchange data (wiring)
CHIPs can be integrated into WDA
Side Panel is a separated part of a Web Dynpro application screen
Can be opened / closed / resized
Side Panel CHIPs can access the application context and display additional information
Side Panel has Page-Builder-like runtime authoring capabilities
Can be assigned to Web Dynpro applications as configuration or customizing
2011 IBM Corporation 28
WDA CHIPs and Page Builder (PB)
WDA Page Builder, Side Panel and CHIPs provide
UI flexibility and mash-up capabilities to SAP
Business Suite applications (NO CODING !)
WDA PB is a tool on top of WDA used to
Design/enrish layout of UI screens using
CHIPs without coding
Connect loosely coupled CHIPS for data
transfer (wiring) without coding
a tool for both, runtime and design time.
CHIPs are
reusable UI components
Layout can be adapted and CHIPs can be
assigned from CHIP catalog
extensions allow to configure existing CHIPs
New in Web Dynpro ABAP with SAP NetWeaver
7.0 EhP2
ABAPers need to learn Web 2.0 UI components and
widgets to help enhance the WDA UI experience
See SAP SDN
http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/sdn/index?rid=/webcontent/
uuid/20e7f0de-5e02-2c10-c29a-8423cbdd82ff
See SAP TechED lecture CD163
2011 IBM Corporation 29
Web Dynpro Islands enabling Mash-ups
WDJ/WDA provides openness to other UI technologies like Islands - 3 types:
Adobe Flash Islands
MS-Silverlight Islands
HTML5 Islands (Project Phoenix)
Islands are self contained web apps (downloadable and reusable) that provide:
High-end business graphics
Direct user interactions with delightful performance, sliders, drag & drop etc.
Completely integrated in SAP development environment and lifecycle
Web Dynpro Developers can insert Flash Island Components into WD
Data binding + event propagation without leaving design constructs of WD
Adobe Flash Islands for Web Dynpro Java
Support rich user interaction with transition, drag & drop, sliders, tooltips etc.
Provide a Flash Island UI Element to integrate YahooMaps in Web Dynpro views.
Provide subset of WD4VC Analytics UI Elements like the AnalyticsChart UI Element in Web Dynpro
Java UI Element Library.
UI elements provided: checkboxes, trees, roadmaps, with specific properties and events
Some Implications:
maybe not for all business requirements
Adding custom properties/events to existing elements not possible
high development and maintenance efforts (over a long time)!
Specific UI programming skills needed.
Complex and difficult debugging (multi: system, development environment
and languages)
Performance issue: Do not use more than 3 Flash Islands on the screen, so
avoid data aggregation on client side and provide suitable paging of data
2011 IBM Corporation 30
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
2011 IBM Corporation 31
Recap: Reusability & Composition
Eat Order Pay Fast Food
Traditional Buffet
Restaurant, la carte
Dinner Party
Eat Order Pay
Eat
Pay
Eat
Eat as much as you like
Pay
Eat
Reusable business processes allow the same 3 processes to
be assembled differently to support different business models.
2011 IBM Corporation 32
What is Business Process Management?
BPM is all about defining best practice processes using industry
standard process modelling tools
Compose new innovative business process extensions
Integrate, adapt and extend core business processes
Services & event enablement -provisioning and consumption
End-to-end Process Orchestration
Process Modelling perspective for process sketching and hand-over
to Process Development perspective (build control)
Supports various stages of process design
Rapid prototyping (build & deploy of incomplete model) with default
tasks and mock services
2011 IBM Corporation 33
BPM overview
2011 IBM Corporation 34
BPM overview
Compose new processes via SAP CE 7.2 which harmonises BPM, processes, views, services on
Eclipse 3 or J2EE 5
SAP CE 7.3 = Eclipse based development environment which now includes NW BPM
More than workflow includes business friendly graphical modeller, rules and tasks using BPMN
(Business process modelling notation) standard.
Process Composer, Process Desk, Process Server
BPM output includes automatically generated UI components with process context (data objects) for
consumption by SAP WD4VC and/or SAP WDJ
BPM offers integrated design time for Forms and Dashboards
Once Level 3 Blueprint models are defined in BPM tool, outputs can be generated for consumption
into SAP VC or WDJ development
= Modelling
= Management
= Monitoring
= Measuring
= Meeting
2011 IBM Corporation 35
BPM and Analytics
2011 IBM Corporation 36
SAP BPM Composite Designer for SAP wall to wall
SAP CE 7.3 includes BPM/BRM and also Composite Designer to enable single point of entry
for modelling and assembling composite applications.
Spans across multiple composites to present via Graphical UI
2011 IBM Corporation 37
SAPs Agile Method for BPM
2011 IBM Corporation 38
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
2011 IBM Corporation 39
What are Business Rules?
Business Rules Management (BRM)
manages business rules for decision automation.
Business users participate and control rule definition
and changes,
BPx team can model, validate, deploy, update, and
archive business rules through their lifecycle.
IT organizations can work with business users to
manage business rules that drive process flow and
execution.
Benefits: improved decision-making, transparency,
efficiency, error reduction
Business Rules Framework Plus (BRFPlus)
Available in SAP NW 7.0 ABAP, a comprehensive
framework that helps users to model rules used for
automatic decision support in all business cases .
It has a flexible open API and advanced features
such as browser-based UI, traceability, and
simulation eases the effort and time invested in
implementing policies and rules.
2011 IBM Corporation 40
BRM overview
BRM provides graphical rules designer tool incorporating alerts, events, embedded sub
processes and enabling automatic decision making capability with Rules Flow
Rules flow is graphical modelling of complex rules execution sequence e.g. for analytical
reporting, BRM provides the process context
BRM uses boundary events evention which are events with exception handling
BRM rules are integrated with MS-Excel for ease of editing and portability
2011 IBM Corporation 41
IBM BPM Three Key Offerings
Websphere Dynamic Process Edition
Historically integration-centric and enterprise scale
Firmly layered on SOA
Focuses on composing existing services (or assets), but new too
Necessitate a more traditional implementation approach; encumbered playback capabilities (relatively)
Websphere Lombardi Edition
Historically human-centric and departmental scale
Focuses on Business Empowerment
Shared Model whats modelled at design-time is used at run-time
Has a useful playback facility; fosters collaboration
FileNet Business Process Manager
FileNet brand world-class Enterprise Content Management
Has full-feature BPMS, but has use in specific situations
Appropriate when documents are central to the process
Retention of documents and process data features
Standard SAP tools are great for
homogenous landscape, but in a
heterogeneous landscape, IBM can offer
competitive and / or complementary BPM
offerings
Evaluation of BPM tooling should be done
with SAP BBA guidelines and client
requirements and constraints
2011 IBM Corporation 42
Agenda
1
2
3
4
5
Key Themes from SAP TechED 2010
Custom Development tooling options
Rich Internet Applications
Business Process Management
Business Rules Management
6 Summary
2011 IBM Corporation 43
Summary
Clearly, SAP innovations are moving rapidly enhancing development tooling options with
WDA, WDJ, WD4VC, WDA-CHIP, Islands
For IBM SAP practitioners like BPx Functional lead, Architects and Developers, this
requires rapid learning curve to develop skills, knowledge and experience of:
SAP ASAP 7 methodology integration into IBM Ascendant-SAP
BPM with integration with BRM, WD4VC, WDJ in SAP CE for composition
Extensions to UI development tooling with WDJ/WDA RIA Islands and WDA CHIP
Understand impact on delivery methodology
Changes the way we deliver solutions to clients
Model View Controller paradigm less coding, more modelling
Understand what alternate IBM tools are available for use for BPM
SAP now talk about timeless software where Enterprise software solves fundamental
business problems, and it must do continually over generations of business and
technological change. We all need to do the same with our skills !
Read Best Built Apps and SAP SDN
Develop awareness and network see SAP Docupedia (successor to help.sap.com):
https://cw.sdn.sap.com/cw/community/docupedia
Collaborate and share within IBM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Notification of Workplace Violence Form Sarawak General HospitalDocumento2 pagineNotification of Workplace Violence Form Sarawak General HospitalRomuald Leo PiongNessuna valutazione finora
- 50 Apo Fruits Corp V Land Bank of The PhilippinesDocumento5 pagine50 Apo Fruits Corp V Land Bank of The PhilippinesRae Angela GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thief King's Vault PDFDocumento24 pagineThief King's Vault PDFCarlos Eduardo Schnorr100% (2)
- Mab, Boy, Son), Used in Patronymics See AlsoDocumento46 pagineMab, Boy, Son), Used in Patronymics See AlsoEilise IrelandNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesDocumento5 pagineMultiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesYosef Dwi Cahyadi SalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Baptism of ApostlesDocumento67 pagineBaptism of ApostlesaudubelaiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Graduation SpeechesDocumento9 pagineGraduation SpeechesSeun IsraelNessuna valutazione finora
- Hughes explores loss of childhood faithDocumento2 pagineHughes explores loss of childhood faithFearless713Nessuna valutazione finora
- Existing culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaDocumento9 pagineExisting culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaGilbert Gabrillo JoyosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDocumento10 paginePathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Nurses Qualityof Work LifeDocumento5 pagineNurses Qualityof Work LifeAnissa septianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Process Quiz AnswersDocumento3 pagineCommunication Process Quiz AnswersAbigail CullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Police Planning 2ndDocumento8 paginePolice Planning 2ndLester BalagotNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Daily Bible ReadingsDocumento5 pagine2011 Daily Bible ReadingsTraci GuckinNessuna valutazione finora
- No Going BackDocumento39 pagineNo Going BackandrophilemxNessuna valutazione finora
- Junkspace: Hilary PowellDocumento5 pagineJunkspace: Hilary PowellPilar PinchartNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocumento71 pagineUnderstanding Culture, Society and PoliticsAl Cheeno AnonuevoNessuna valutazione finora
- Back Order ProcessDocumento11 pagineBack Order ProcessManiJyotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bai Tap LonDocumento10 pagineBai Tap LonMyNguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lit Exam 2nd QuarterDocumento4 pagineLit Exam 2nd Quarterjoel Torres100% (2)
- POM Q1 Week 3 PDFDocumento10 paginePOM Q1 Week 3 PDFMary Ann Isanan60% (5)
- Interactive Textbook1 1whatis MatterDocumento7 pagineInteractive Textbook1 1whatis Matterapi-240094705Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mozart's Oboe Concerto in C Stage 2Documento4 pagineMozart's Oboe Concerto in C Stage 2renz_adameNessuna valutazione finora
- Semester 1 FinalDocumento29 pagineSemester 1 FinalBudi NugrohoNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Leadership TheoriesDocumento24 pagineApplication of Leadership TheoriesTine WojiNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper:: 14 Marketing Management 34, Pricing: Factors Affecting PricingDocumento9 paginePaper:: 14 Marketing Management 34, Pricing: Factors Affecting PricingstudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Mayo ClinicDocumento2 pagineMayo Clinicapi-3695725Nessuna valutazione finora
- SESSION 8 - Anti-Malaria DrugsDocumento48 pagineSESSION 8 - Anti-Malaria DrugsYassboy MsdNessuna valutazione finora
- Lista de Canciones de Los 80Documento38 pagineLista de Canciones de Los 80Maria Luisa GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora