Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
PHY12 Review Items Exit Exam
Caricato da
Rigel ZabateDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
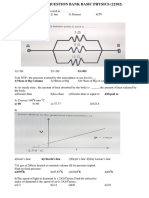
Formati disponibili
PHY12 Review Items Exit Exam
Caricato da
Rigel ZabateCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EXIT EXAM REVIEW
PHY12
By: fmn 06/06/14
THERMAL EXPANSION
Linear Expansion
Area Expansion
Change L to A and to : = 2
Volume Expansion
Change L to V and to : = 3
Stress = - Y o AT
Force,F = -Y A o
AT
THERMAL STRESS
2 Common Effects of Heat
1. Change in temperature
2. Change in Phase
Change in Temperature
m m
Where:
m = mass of the body
C = specific heat
t = change in temperature
HEAT AND HEAT MEASUREMENTS
Change in Phase
Fixed Points points at which a substance will have a
change its phase without a change in
temperature.
Freezing Point/Melting Point
water
Boiling Point/Steam Point
steam
Units CGS MKS FPS
C Cal/g-c Kcal/kg-c BTU/slug-
F
Note: CGS/MKS
C
ice
0.5
C
water
1.0
C
steam
0.48
Units and values of Specific Heat, C
Values of
L
cgs mks fps
80 cal/g 80 kcal/kg 144 BTU/slug
540
cal/g
540
kcal/kg
972 BTU/slug
Values of Latent Heat
Principle of calorimetry (Mixing Substances)
Hotter bodies will give off heat
Colder bodies will absorb heat
By conservation of heat energy
Heat lost by hotter body = heat gained by colder
bodies
Mode of Heat transfer
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
MECHANISM OF HEAT TRANSFER
H = Q/t
= rate of heat flow ( J or cal/s
WAVE MOTION
Wave Speed,
wavelength,
Velocity of Transverse Wave,
(for vibrating string)
n
L 2
=
L
m
T
v =
Frequency, f
L
m
T
L
n
f
2
=
(String)
t
T
dL
n
f =
(Wire)
Mathematical Description of a Wave
( ) ( ) t kx A t x y = = cos , Sinusoidal wave moving in (+) x direction
SOUND WAVE
Speed of Sound in a Liquid,
Speed of Sound in a Solid Rod,
Speed of Sound in Air,
B
v
=
=
Y
v
t s m V
t s cm V
6 . 0 / 332
60 / 200 , 33
+ =
+ =
Resonance in an Air Column
Closed at One End
Open at Both Ends
Doppler Effect
1
1, 3, 5,
4
n
v
f n n n
L
= = =
1
1, 2, 3,
2
n
v
n n n
L
= = =
Electricity
Ohms Law,
Electric Power, P
Electrical Energy,E
V IR =
V
I
R
E = P X T
(Watts,W)
(KWH)
Voltage,V (V)
Current,I (Ampere, A)
Resistance,R (Ohm,)
Kirchhoffs Laws
1. Kirchhoffs Point (or Junction) Rule I in = I out
2. Kirchhoffs Loop (or circuit) Rule
= s IR s emf ' '
1. Complete the following statement: A temperature decrease of 30 C is
equal to a temperature decrease of
A) 30 F.
B) 30 K.
C) 17 F.
D) 26 F.
2. An aluminum tank of volume 0.0300 m
3
is filled to the top with mercury
at 20.0 C. The tank is placed inside a chamber with an interior
temperature of 70.0 C. The coefficient of volume expansion for mercury
is 1.82 10
4
/C; and the coefficient of linear expansion of aluminum is
23.0 10
6
/C. After the tank and its contents reach thermal equilibrium
with the interior of the chamber, how much mercury has spilled?
A) 2.52 10
5
m
3
B) 6.60 10
5
m
3
C) 1.69 10
4
m
3
D) 1.92 10
4
m
3
3. A 0.30-kg lead ball is heated to 90.0 C and dropped into an ideal
calorimeter containing 0.50 kg of water initially at 20.0 C. What is the
final equilibrium temperature of the lead ball? The specific heat capacity
of lead is 128 J/(kg C); and the specific heat of water is 4186 J/(kg
C).
A) 84.8 C
B) 20.8 C
C) 21.3 C
D) 27.8 C
4. The ends of a cylindrical steel rod are maintained at two different
temperatures. The rod conducts heat from one end to the other at a rate
of 10 cal/s. At what rate would a steel rod twice as long and twice the
diameter conduct heat between the same two temperatures?
A) 5 cal/s
B) 10 cal/s
C) 20 cal/s
D) 40 cal/s
5. A periodic wave is produced on a stretched string. Which one of the
following properties is not related to the speed of the wave?
A) frequency
B) amplitude
C) wavelength
D) tension in the string
6. What is the distance to the nearest antinode from the fixed end of a
guitar string vibrating at its first harmonic?
A) l
B) 2l
C) l/2
D) l/4
7. What is the wavelength of a wave with a speed of 9.0 m/s and a period of
0.33 s?
A) 0.33 m
B) 1.5 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 13 m
The displacement of a vibrating string versus position along the string is
shown in the figure. The periodic waves have a speed of 10.0 cm/s. A and
B are two points on the string.
9. What is the amplitude of the wave?
A) 2 mm
B) 4 mm
C) 8 mm
D) 12 mm
10. What is the wavelength of the wave?
A) 3.0 cm
B) 6.0 cm
C) 9.0 cm
D) 12 cm
Two point charges are held at the corners of a rectangle as shown in the
figure. The lengths of sides of the rectangle are 0.050 m and 0.150 m.
Assume that the electric potential is defined to be zero at infinity.
11. Determine the electric potential at corner A.
A) +6.0 10
4
V
B) 2.4 10
5
V
C) +4.6 10
5
V
D) 7.8 10
5
V
12. What is the potential difference, V
B
V
A
, between corners A and B?
A) 8.4 10
5
V
B) 7.8 10
5
V
C) 7.2 10
5
V
D) 6.0 10
5
V
13. Which one of the following circuits has the largest resistance?
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d
E) e
14. A resistor dissipates 1.5 W when it is connected to a battery with a
potential difference of 12 V. What is the resistance of the resistor?
A) 220 W
B) 18 W
C) 8.0 W
D) 96 W
Three resistors are connected as shown in the figure. The potential
difference between points A and B is 26 V.
15. What is the equivalent resistance between the points A and B?
A) 3.8 W
B) 4.3 W
C) 5.1 W
D) 6.8 W
16. How much current flows through the 3- resistor?
A) 2.0 A
B) 4.0 A
C) 6.0 A
D) 8.7 A
17. Three resistors and two batteries are connected as
shown in the circuit diagram. What is the magnitude of
the current through the 12-V battery?
A) 0.82 A
B) 0.30 A
C) 0.67 A
D) 0.52 A
18. A train is moving toward a stationary observer with a speed of 30
m/s. The whistle of the locomotive has a frequency of 500 Hz and
the speed of sound of 340 m/s. What is the frequency heard by the
observer.
A) 458 Hz C) 458 Hz
B) 548 Hz D) 495 Hz
19. It is found out that 100 kcal of heat is just sufficient in changing a
certain amount of ice at -20
o
C to steam at 130
o
C. Determine the
mass of the ice. Ans. m = 0.13 kg
20. One end of the insulated metal rod is maintained at 100
o
C, and
the other end is maintained at 0
o
C by an ice-water mixture. The
rod is 60 cm long and has cross-sectional area of 1.25 cm
2
. The
heat conducted by the rod melts 8.50 g of ice in 10 min.
A) Find the thermal conductivity k of the metal.
B) What is the temperature at a point 25 cm from the hotter end
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CW3 - 3Documento2 pagineCW3 - 3Rigel Zabate54% (13)
- CW3 - 3Documento2 pagineCW3 - 3Rigel Zabate54% (13)
- BDA30603 Tutorial 4Documento7 pagineBDA30603 Tutorial 4Firdaus JannahNessuna valutazione finora
- CW2 Bayani CaseDocumento10 pagineCW2 Bayani CaseRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- CW3 - 4Documento2 pagineCW3 - 4Rigel Zabate0% (1)
- CW2 Bayani CaseDocumento10 pagineCW2 Bayani CaseRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- CW3 Mind ControlDocumento2 pagineCW3 Mind ControlRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- Reviewer Ece102Documento8 pagineReviewer Ece102Rigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy12 Exit Exam ReviewDocumento9 paginePhy12 Exit Exam ReviewAngelo Joshua De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- VVIMP QUESTIONS Basic Physics (22102)Documento5 pagineVVIMP QUESTIONS Basic Physics (22102)Prathamesh Nawale100% (1)
- Ame - 1126 - Heat Transfer, 20-05-2013, May - 2013 PDFDocumento2 pagineAme - 1126 - Heat Transfer, 20-05-2013, May - 2013 PDFMichael PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- DRDO ME Downloaded FromDocumento23 pagineDRDO ME Downloaded FromAvneet MaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer Gate QuestionsDocumento5 pagineHeat Transfer Gate QuestionsAshok Kumar SNessuna valutazione finora
- NR 310803 Heat TransferDocumento8 pagineNR 310803 Heat TransferSrinivasa Rao GNessuna valutazione finora
- πt− π πt− π πt− π πt−: A 23 o B -23 o 3 3Documento4 pagineπt− π πt− π πt− π πt−: A 23 o B -23 o 3 3Sun SopheakNessuna valutazione finora
- Iecep I Geas QaDocumento6 pagineIecep I Geas QaJerry LubiNessuna valutazione finora
- 8S 2105 Mepc22 1Documento2 pagine8S 2105 Mepc22 1Challa YachendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Conductvity Matal RodDocumento7 pagineThermal Conductvity Matal RodTheOPGarriXNessuna valutazione finora
- MIDTERMSDocumento3 pagineMIDTERMSMiya GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- 12th Phy QP Set 1 To 5Documento21 pagine12th Phy QP Set 1 To 5Samiullah ShaikhNessuna valutazione finora
- Phys 125 Pracexam 4Documento7 paginePhys 125 Pracexam 4Moad EloustaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock7 p1 SourceDocumento9 pagineMock7 p1 SourceDewan Olin ChotepadaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Atkins P 787-788Documento2 pagineAtkins P 787-788charls00Nessuna valutazione finora
- Heat & Mass Transfer Jan 2014Documento2 pagineHeat & Mass Transfer Jan 2014Prasad C M100% (1)
- Physics ss3Documento9 paginePhysics ss3classikNessuna valutazione finora
- Btech Model QuestionsDocumento22 pagineBtech Model QuestionsAkshayKannanNessuna valutazione finora
- Jipmer 2015 Solved QPDocumento67 pagineJipmer 2015 Solved QPS Balagopal Sivaprakasam67% (3)
- 9A14403 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransferDocumento8 pagine9A14403 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- PPDCDocumento8 paginePPDCJordan taylorNessuna valutazione finora
- T.Y.B.tech Mech Sem VDocumento24 pagineT.Y.B.tech Mech Sem VChirag JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Bansal CLasses Physics Study Material For IIT JEEDocumento521 pagineBansal CLasses Physics Study Material For IIT JEEmuno93% (14)
- Heat TransferDocumento15 pagineHeat Transferaddtadd6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Mock 2Documento3 pagineFinal Mock 2Subho SenguptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved Problems Heat TransferDocumento12 pagineSolved Problems Heat TransferFaisal SadaatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2013 (M.S.)Documento2 pagine2013 (M.S.)Arun SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- R07 Set No. 2Documento8 pagineR07 Set No. 2bhaskar5377Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cusat 2016Documento37 pagineCusat 2016sreejitha KNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiple Choice Questions On Mechanics and HeatDocumento21 pagineMultiple Choice Questions On Mechanics and HeatGodwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Transfer: Anna University Question BankDocumento6 pagineHeat Transfer: Anna University Question BankaeroacademicNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYSICS 12th Sci Prelim Question PaperDocumento4 paginePHYSICS 12th Sci Prelim Question PaperAditya Deshmukh0% (1)
- Extended SurfacesDocumento13 pagineExtended SurfacesDirkMyburghNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet IIDocumento2 pagineWorksheet IIgiziew belayNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ExamA1-2019-1Documento4 pagineFinal ExamA1-2019-1trinh.lenukieuNessuna valutazione finora
- Viteee - 2017 - Sample Questions PhysicsDocumento1 paginaViteee - 2017 - Sample Questions PhysicsRaghuvendra SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Ejercicios de Corriente ContinuaDocumento8 pagineEjercicios de Corriente ContinuaJohn pazsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Current and Resistance-1Documento5 pagineCurrent and Resistance-1Burcu TemirNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam Physics1 - SampleDocumento4 pagineFinal Exam Physics1 - Samplethảo nguyễn thanhNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables Are PermittedDocumento4 pagineUse of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables Are Permitted3rajaNessuna valutazione finora
- HMT IMP Questions NewDocumento3 pagineHMT IMP Questions NewRavi PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Solved ISRO Scientist or Engineer Mechanical 2009 Paper With SolutionsDocumento21 pagineSolved ISRO Scientist or Engineer Mechanical 2009 Paper With SolutionsAB RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 3 QsDocumento3 pagineTutorial 3 QsWan HafizaNessuna valutazione finora
- KCT 2010-2011 HTDocumento4 pagineKCT 2010-2011 HTask4krishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics 73 PS 1 - OriginalDocumento13 paginePhysics 73 PS 1 - OriginalJay VeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Measurement of TemperatureDocumento3 pagineMeasurement of TemperatureUmesh ShivappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Aieee Test ViiDocumento17 pagineAieee Test ViiKarm VeerNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Conduction Tutorial 1Documento11 pagine2 Conduction Tutorial 1GnazGoragod100% (1)
- 2222Documento3 pagine2222ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- 2222Documento3 pagine2222ArunNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsDa EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Da EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Da EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Advances in Magnetohydrodynamics: Proceedings of a Colloquium Organized by the Department of Fuel Technology and Chemical Engineering at Sheffield University, October 1961Da EverandAdvances in Magnetohydrodynamics: Proceedings of a Colloquium Organized by the Department of Fuel Technology and Chemical Engineering at Sheffield University, October 1961I. A. McGrathNessuna valutazione finora
- HW1Documento4 pagineHW1Rigel Zabate50% (2)
- HW2Documento2 pagineHW2Rigel Zabate0% (1)
- ECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTDocumento48 pagineECE199R-C12 Final Document OJTRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- CW3 - 1Documento2 pagineCW3 - 1Rigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- Reaction in The Business Code Ethics of PLDT: Dela Rea, Kimmi FDocumento6 pagineReaction in The Business Code Ethics of PLDT: Dela Rea, Kimmi FRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE70 SyllabusDocumento5 pagineECE70 SyllabusRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- HW1Documento4 pagineHW1Rigel Zabate50% (2)
- CW3 MindControlDocumento6 pagineCW3 MindControlRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- HW2Documento2 pagineHW2Rigel Zabate0% (1)
- Reaction in The Business Code Ethics of PLDT: Dela Rea, Kimmi FDocumento6 pagineReaction in The Business Code Ethics of PLDT: Dela Rea, Kimmi FRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- CW3 Q&aDocumento2 pagineCW3 Q&aRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- CW3 - 2Documento2 pagineCW3 - 2Rigel Zabate88% (8)
- CW3 - 4Documento2 pagineCW3 - 4Rigel Zabate100% (1)
- Case Analysis On Mind Control: Dela Rea, Kimmi FDocumento6 pagineCase Analysis On Mind Control: Dela Rea, Kimmi FRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- Liveloud SongsDocumento148 pagineLiveloud SongsRigel Zabate90% (10)
- Procurement and Safety Laws Pertaining To ECE Equipment/Services in The PhilippinesDocumento33 pagineProcurement and Safety Laws Pertaining To ECE Equipment/Services in The PhilippinesRigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece107l Exp 1Documento3 pagineEce107l Exp 1Rigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- CW3 - 1Documento2 pagineCW3 - 1Rigel ZabateNessuna valutazione finora
- Liveloud SongsDocumento148 pagineLiveloud SongsRigel Zabate90% (10)
- Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocumento5 pagineIdentify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Questiontwinckel mae bienes100% (1)
- Proposal and Analysis of A Novel Single-Drive Bearingless MotorDocumento10 pagineProposal and Analysis of A Novel Single-Drive Bearingless MotorMohsenHonarNessuna valutazione finora
- ELE637 Chapter1Documento19 pagineELE637 Chapter1supermannonNessuna valutazione finora
- Base Isolation - Final ReportDocumento23 pagineBase Isolation - Final ReportYati Tank76% (25)
- RADIOSS For Impact Analysis v12 Rev20130214 PDFDocumento328 pagineRADIOSS For Impact Analysis v12 Rev20130214 PDFKevin ChackochanNessuna valutazione finora
- Erzilia Lozneanu and Mircea Sanduloviciu - Minimal-Cell System Created in Laboratory by Self-OrganizationDocumento9 pagineErzilia Lozneanu and Mircea Sanduloviciu - Minimal-Cell System Created in Laboratory by Self-OrganizationHilltopss0% (1)
- Chapter 13: Kinetics of A Particle: Force and Acceleration: 13.1 Newton's Laws of MotionDocumento5 pagineChapter 13: Kinetics of A Particle: Force and Acceleration: 13.1 Newton's Laws of MotionideepujNessuna valutazione finora
- Scotch 3cdmas Mock ExamDocumento32 pagineScotch 3cdmas Mock ExamFredNessuna valutazione finora
- Destructive TestingDocumento42 pagineDestructive TestingHyori AnapadaNessuna valutazione finora
- BennettDocumento271 pagineBennettLew MingNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/42 May/June 2020Documento17 pagineCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/42 May/June 2020Tino KambaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid PowerDocumento88 pagineFluid PowerGabriel Ak100% (3)
- Geotechnical Aspects of Building Design (EN 1997) : Eurocode 2Documento55 pagineGeotechnical Aspects of Building Design (EN 1997) : Eurocode 2margitorsiNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Physics NotesDocumento16 pagineIGCSE Physics NotesMhdAboualy84% (32)
- 3.0 Material Properties of Metals and FailureDocumento29 pagine3.0 Material Properties of Metals and FailureHasmitthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Moment-Rotation Characterization of Cold-Formed Steel Beam in Box SectionDocumento1 paginaMoment-Rotation Characterization of Cold-Formed Steel Beam in Box SectionXavier NietoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCESC Structural Engineering and Construction ManagementDocumento23 pagineMCESC Structural Engineering and Construction ManagementsonofalexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- CFD Report: Submitted by Vipul Agrawal 2018H1410129H M.E Design EngineeringDocumento12 pagineCFD Report: Submitted by Vipul Agrawal 2018H1410129H M.E Design EngineeringVipul AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Loss in PipesDocumento8 pagineEnergy Loss in PipesRo Win83% (6)
- Flange CouplingDocumento16 pagineFlange CouplingARUN VNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0149197018301525 MainDocumento10 pagine1 s2.0 S0149197018301525 Mainait hssainNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution: Principle of Work and Energy: Referring To The Free-Body Diagram of TheDocumento5 pagineSolution: Principle of Work and Energy: Referring To The Free-Body Diagram of TheESTHEFANI PAOLA FONSECA MENDOZANessuna valutazione finora
- IScodes Soil DynamicsDocumento128 pagineIScodes Soil DynamicsRajashekar.PNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12Documento59 pagineChapter 12Martunis TomyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4-Symmetry and Group Theory ApplicationsDocumento98 pagineChapter 4-Symmetry and Group Theory ApplicationsJohn Edward Zapater100% (1)
- Descriptions of Fluid FlowsDocumento2 pagineDescriptions of Fluid FlowsdarshanNessuna valutazione finora
- 02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214Documento20 pagine02.1-WCDMA Basic Principle of Radio Propagation - 20051214kltowerNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Fuzzi-Pid Tracking Controller For IndustDocumento8 pagineDesign of Fuzzi-Pid Tracking Controller For IndustBernadetteNessuna valutazione finora
- 1) Modal Analysis Over An Aircraft Wing During Cruise SpeedDocumento3 pagine1) Modal Analysis Over An Aircraft Wing During Cruise SpeedSanjayNessuna valutazione finora
- IS800 2007 I-Section 1 Detailed CalculationDocumento5 pagineIS800 2007 I-Section 1 Detailed CalculationJigar Piyush ShahNessuna valutazione finora