Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Quality Management System Introduction To Auditing
Caricato da
ravindra_jivaniTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Quality Management System Introduction To Auditing
Caricato da
ravindra_jivaniCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Quality Management System
Introduction to Auditing
Quality System Audit
Effectiveness of an organisations Quality
Management System is assessed
Why Audit
Required by the standard
Determine quality system effectiveness
Identify existing nonconformities
Highlight areas of strength
Point out areas for improvement
Indicate requirements for corrective and /or
preventive action
Management System
Management System:
to establish objectives and to achieve those
objectives
Quality Management System:
to direct and control an organisation with
regard to quality
System:
set of interrelated or interacting elements
Quality System Audit
The process of assessment has to be
OBJECTIVE
Quality System Audit
Assessment is a comparison of implemented
Quality System with Quality System
Standards like ISO 9000
However results depend on Auditor
hence this training
What is sought by Auditor
Established Policy and Objectives
Developed appropriate systems
Necessary documentation of the system
Effective implementation of those systems
Since we can never expect absolute
perfection the auditor can only assess
The Degree of Compliance
Quality System Standards
Lay down principles that require
interpretation
The auditor must have very strong
understanding of principles to be able to
assess whether the standard has been
understood
interpreted
and can demonstrate adequate control
Questions in an auditors mind
Is the system right and sufficient?
Does the organisation do the right things to
adequately control quality of products?
Does the organisation do things properly all
the time?
What is the evidence that things are done
correctly?
Nagging questions
What is adequate?
When is a thing properly done?
How much evidence is required?
Auditor
Needs to judge whether an organisation has
arrived at a sensible and acceptable
interpretation of the standard; therefore he
must
study the standard to improve understanding
objective of the system is that quality must be
consistently achieved
consider possible consequences of something
going wrong due to inadequacy
take account of others opinion
Auditor
Looks for:
established policies and objectives
developed appropriate systems
documentation to ensure adequate control
effective implementation of the system
Since we can never expect absolute perfection,
the auditor can only assess
THE DEGEREE OF COMPLI ANCE
Quality Audit
Systematic, independent and documented
process for obtaining evidence and
evaluating it objectively to determine the
extent to which the audit criteria is fulfilled
Types of Audit
Internal Audit
External Audit
Third Party Audit
Auditor Competence
Auditors demonstrated capability to apply
knowledge and skills
based on
education
experience
training
Qualification process:
process to demonstrate the ability to fulfil specified
requirements (in this case the auditors qualification)
Audit conventions
Audits create stress. Uncertainty amplifies
stress
Act predictably
Why conventions?
To reduce stress
To have clear methods of audits
Audit conventions
Start at the top
Audit must be planned
Examination/Evaluation
Reports
Follow up action
Types of audit
Process
Product
Quality System
Compliance
Health & Safety
Environmental
Financial
Quality Management System
ISO 9000:2000 - AUDITOR
TRAINING
Quality Management
Principle
Comprehensive and fundamental rule or
belief, for leading and operating an
organisation, aimed at continually
improving performance over the long
term by focusing on customers while
addressing the needs of all other
stakeholders
ISO/TC176/WG15
Quality Management Principles
Customer-Focused Organisation
Leadership
Involvement of People
Process Approach
System Approach by Management
Continual Improvement
Factual approach to decision making
Mutually beneficial supplier relationships
Customer - Focused Organisation
Understanding customer needs and
expectations
Communicating these needs and
expectations throughout the organisation
Measuring customer satisfaction and acting
on results
Managing customer relationships
Leadership
Being proactive & leading by example
Establishing a clear vision of the
organisations future
Providing people with required resources
and freedom to act with responsibility and
accountability
Promoting open and honest communication
Educating, training and coaching people
Setting challenging goals and targets
Involvement of People
Accept ownership and responsibility to solve problems
Actively seek opportunities to make improvements
Actively seek opportunities to enhance their
competencies,knowledge and experience
Freely share knowledge and experience in teams and
groups
Focus on creation of value for customers
Better represent the organisation to customers
Derive satisfaction from their work
Process Approach
Define Processes needed to achieve desired results
Identify & Measure Inputs & Outputs
Identify interfaces
Evaluate risk, consequence and impact on
customers
Establish responsibility authority and
accountability for managing processes
Consider methods, training, resources etc to
achieve desired result
System Approach
Define & Develop processes
Structure the System in most efficient way
Understand interdependencies of processes
in the system
Continually improve through measurement
and evaluation
Continual Improvement
Products,Processes & Systems
Incremental & Breakthrough Concepts
Periodic Assessment against established Criteria
Efficiency & Effectiveness of processes
Promote prevention-based activities
Provide training on continual improvement tools
Establish measure & goals to guide & track
improvements
Continual improvement
Quality
Management
System
support to
achieve the
objectives
Act
Plan
Check
Do
Achieve
objectives
Moving
target
Continual improvement
Analysing and evaluating the existing situation to
identify areas for improvement;
Establish the objectives for improvement;
Searching for possible solutions to achieve the
objectives;
Evaluating these solutions and making a selection
Implementing the selected solution;
Measuring, verifying, analysing and evaluating
results of the implementation to determine that the
objectives have been met;
Formalising changes.
Factual Approach to Decision-
Making
Measuring & Collecting Data &
Information
Ensure accurate, reliable & accessible
Analyse data and information
Understand value of Statistical Techniques
Make Decisions and Take Actions on
results of analysis
Mutually Beneficial Supplier
Relationships
Identify and Select key suppliers
Establish relationships that balance short term
gains with long-term considerations
Create clear and open communications
Initiate joint development and improvement of
products and processes
Establish joint understanding of customer needs
Share information and future plans
Introductory Sections
Scope
Normative Reference
Terms Definitions
Who Survives?
ISO 9001 9002 9003
ISO 9004 9004-1 9004-2
Adopted from ISO14001:
Statutory & regulatory requirements
Commitment, awareness
Communication
Continual Improvement
2000 Family
ISO 9000: Fundamentals Vocabulary(normative)
ISO 9001: Requirements
ISO 9004 Guidelines for Performance
Improvement
ISO 19011: Guidelines for Auditing
management Systems
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Quality
Ability of a set of inherent characteristics of a
product, system or process to fulfil
requirements of customers and other
interested parties
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Requirement
need or expectation that is stated,
customarily implied or obligatory
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Quality Requirement
Requirement for
inherent characteristics of a product,
process or system
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Inherent Characteristic is part of the product
e.g. diameter of bolt
Assigned Characteristic (e.g. price of
product) is not and inherent characteristic
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Quality Improvement
part of quality management,
focused on increasing
effectiveness and efficiency
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Quality Objective
something sought, or aimed for,
related to quality
Terminology (ISO 9000)
1994 2000
Customer Customer
Supplier Organisation
Subcontractor Supplier
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Procedure
Specified way to carry out an
activity or a process
Terminology (ISO 9000)
Document
Information and its support
medium
The Charges - General
ISO9001:1994
20 elements
ISO9001:2000
Quality Management System
Management Responsibility Resource
Management Product Realization
Measurement, Analysis & Improvement
4.1 QMS General Requirements
Establish, document, implement, maintain
and continually improve the effectiveness of
a quality management system
Establishing the System
Determine processes needed
sequence and interaction
criteria and methods for operation and
control
information available for operation and
monitoring
measure, monitor, and analyse
implement action to achieve planned results
and continual improvement
4.2 General Documentation
Requirements
QMS shall include:
documented quality policy and objective
documented quality manual
documented procedures required by 9001
documented required by the organisation to
ensure effective planning operation and control
of processes
Types of Documents
Quality Policy and Objective
Quality Manual
Scope of System(incl. exclusions)
Procedures or Reference to them
Description of sequence/interaction of
processes
Types of Documents
Quality Manuals
information, both internally and externally, about the
organizations quality management system
Quality Plans
how the quality management system is applied to a specific
product, project or contract
Procedures
how to perform activities
Records
objective evidence of activities performed or results
achieved
Extent of Documentation
Size of the organisation and type of activity
complexity and interaction of processes
competence of personnel
Control of Documents
Approve, Review, Update
Identify Current Revision Status and
changes
Ensure availability,
Legible Identifiable, Reirlevable
Control External Documents
Control Obsolete Documents
Records are a special type of document
Control of Quality Records
To provide evidence of conformity to
requirements and system
Legible, identifiable retrievable
Retention time specified
Disposition specified
Requires a documented procedure
5.1 Management Commitment
Demonstrate Commitment to Development
Implementation & Continually Improving
the effectiveness of System (Including
statutory and regulatory requirements)
Communicating Importance of Meeting
Customer Requirements
Establishing Quality Policy & Objectives
Conducting Management Reviews
Providing Necessary Resources
5.2 Customer Focus
Requirements (replaces needs and
expectations)
Aim of enhancing Customer
Satisfaction
5.3 Quality Policy
Appropriate to purpose for organisation
Commitment to Continually Improve the
effectiveness of the system
Framework for setting and reviewing
Quality Objectives
5.4 Planning
5.4.1 Quality Objectives
Measurable
Consistent with Policy
The objectives include those needed to meet
requirements for product
5.4 Planning
5.4.2 Quality Planning
Processes of the System
Resources needed
Continual Improvement
Change management
5.5 Responsibility, Authority and
Communication
5.5.1 Responsibility & Authorities
Top Management define and communicate
Responsibilities, Authorities &
Interrelations
5.5 Responsibility, Authority and
Communication
5.5.2 Management Representative
Only one member of management
Processes Established implemented &
Maintained
Report to Top Management
Promote Awareness of Customer
Requirements
5.5 Responsibility,Authority and
Communication
5.5.3 Internal Communications
Top management shall ensure
communication between various levels and
functions regarding effectiveness of system
5.6 Management Review (Inputs)
Current Performance and Improvement
Opportunities
Audit Results
Customer Feedback
Process/Product Conformance
Preventive/Corrective Actions
Actions from previous reviews
Planned changes
Recommendations for improvement
5.6 Management Review
(Outputs)
Actions related to:
improvement of the QMS and its processes,
Improvement of product related to customer
requirements,
resource needs
6.1 Resource Management
Determine & Provide in Timely Manner to
Implement, Maintain & Continually Improve
Processes
Enhance Customer Satisfaction
6.2 Human Resources
6.2.1 General:
Persons competent to perform work
affecting quality
6.2.2 Competence Awareness & Training,
determine competency needs;
provide training or other actions;
evaluate effectiveness of training
ensure awareness of relevance and
importance of activities;
maintain records
6.3 Infrastructure
Determine, provide & Maintain
Buildings, Workspace and Utilities
Equipment, hardware & software
Supporting Services (transport or
communication)
6.3 Work Environment
Identify & Maintain conditions to achieve
conformity of product
7. Product Realization
7.1 Planning of Realization Processes
Quality Objectives
Processes, Documentation, Resources
Facilities
Verification/Validation and Criteria for
Acceptance
Records
Planning should be suitable for
organisation,s operations
7.2 Customer Related Processes
Identify Requirements
Review Requirements not stated but
necessary
Any other requirement of organisation
7.2.1 Identification of Customer
Requirements
Specified by the customer
Not specified by the customer
Obligations
7.2.2 Review of Requirement
Tenders and Contracts
Requirements defined
Anomalies resolved
Ability confirmed
Amendments controlled
Internet sales addressed
7.2.3 Customer Communication
Product information
enquiries, contracts or order handing,
including amendments;
customer feedback, including customer
complaints
7.3 Design and/or Development
7.3.1 Planning 7.3.5 Verification
7.3.2 Inputs 7.3.6 Validation
7.3.3 Outputs 7.3.7 Changes
7.3.4 Review
7.4 Purchasing
7.4.1 Purchasing Control
7.4.2 Purchasing Information
7.4.3 Verification of Purchased Product
7.5 Production and Service
Provision
7.5.1 Control of production and service provision
Availability of information
Work Instructions, where necessary
Use & Maintenance of suitable equipment
Availability & Use of Monitoring & Measuring
equipment
Implement Monitoring Activities
Processes for Release, Delivery & Post Delivery
Activities
7.5 Production & Service
Provision
7.5.2 Validation of Processes
7.5.3 Identification & Traceability
7.5.4 Customer Property
7.5.5 Preservation of Product
7.6 Control of Monitoring &
Measuring Devices
Determine Measurements
Identify Devices Required
Use & Control
Where applicable
Calibrate or verified, Safeguard, Project, etc
includes software
8. Measurement, Analysis &
Improvement
8.1 Planning
Define, Plan, Implement
Measurement & Monitoring Activities
conformity of product and system Improve
effectiveness of system
Applicable Methodologies (inc. Statistical
Techniques)
8.2 Monitoring & Measurement
8.2.1 Customer Satisfaction (monitor customer
perception to requirements fulfilment)
8.2.2 Internal Audits
Monitoring/Measurement
8.2.3 Processes (correction & corrective action
8.2.4 Product
8.2.1 Customer Satisfaction
Monitor Information
Customer Perception
Defined Methods
Proactive not Reactive
8.2.2 Internal Audit
Quality System
Effectively Implemented
Effectively maintained.
Conform to ISO9001
8.2.3 Monitoring & Measurement
of Processes
Suitable Methods
Realisation Processes
Demonstrate Ability
Achieve planned results
Correction and Corrective action
8.2.4 Monitoring & Measurement
of Product
Measure and monitor characteristic of the
product to verify that requirements are met
Appropriate Stages
Evidence of conformity (records)
No release/delivery until all OK (approved
by relevant authority)
8.2.3 Control of Nonconforming
Product
Related to Product
Identified and Controlled
Prevent Unintended Use or Delivery
Corrected and re verified
Applies to post delivery problems which
will require
appropriate action
8.4 Analysis of Data
Customer Satisfaction
Conformance to Product Requirements
Characteristics and Trends of Processes, &
Products
Suppliers
8.5 Improvement
8.5.1 Planning for Continual Improvement
Plan and Manage the processes necessary
for continual improvement
(quality policy, quality objectives, audit
results, data, corrective/preventive action
Continual Improvement
Defining, measuring and analysing existing
situation;
Establishing objectives for improvement;
Searching for possible solutions;
Evaluating solutions;
Implementing, selected solution;
Measuring verifying, and analysing results
of implementation;
Formalising changes.
8.5 Improvement
8.5.2 Corrective Action
Review Nonconformities (incl. Complaints)
Determine Cause
Evaluate Need for Action
Determine &Implement Action including
prevention of recurrence
Record Results
Review Corrective action
8.5 Improvement
8.5.3 Preventive Action
Action
Implement Action
Record Results
Review Preventive action Identification
Determine Cause
Determine
INTERNAL AUDIT
WHAT IS
AUDIT?
WHAT IS AN AUDIT
A health check
Key words
- Systematic
- Documented
- Periodic
- Objective
- Verification
KEY CONCEPTS
Verification Evaluate compliance to requirements
Systematic Carried out in accordance to set protocols
Periodic Conducted to established schedule
Objective Auditors have some independence,
Evidence for audit findings.
Documented Reports are prepared
WHY AUDIT?
Required by the standards.
To identify and define AREAS OF
IMPROVEMENT
TERMINOLOGY: AUDITS
AUDITS
- Period over which ALL
parts
of organisation checked to
planned arrangements
- determine whether MS has
been properly
implemented
and maintained
AUDIT TERMINOLOGY
Audit Cycle
period over which ALL parts or organisation
are audited
Audit Programme
time table within audit cycle
shows whats audited, when and by
whom
AUDIT TERMINOLOGY
Audit Protocol/Procedure:
detail of individual audit including
- audit scope
- audit frequency
- audit methodologies
- personnel and experience
- documentation required
- reporting and distribution
AUDIT SCHEDULING
Scheduled - routine auditing
- High risk/potential for harm
( I.e significant aspects)
e.g. every 6 months
AUDIT SCHEDULING
Unscheduled - usually prompted by:
Significant change in personnel
Change in regulations
Process change
AUDIT APPROACH
Product line
By work area / activity
AUDIT PROGRAMME
HOW TO ACHIEVE
CONTINUAL IMPROVEMENT
Actual
Performance
Time
Preparatory
quality review
AUDIT TEAM
AUDIT TEAM
SELECTION
AUDIT TEAM PERSONNEL
REQUIREMENTS
Independent from area / activity under audit
Experience and expertise including:
Management system and standards
System auditing
Product requirements
Technical knowledge of area/activity
AUDITOR QUALIFICATION
Education
- at least secondary or equivalent
with
5 years work experience
or
- degree with 4 years work
experience
AUDITOR SKILLS
Personnel Attributes
Open mined
Mature/sound judgement
analytical skills/tenacity
perceives situations in a realistic way
Understands complex operations from a broad
perspective
Understands role in individual units
AUDITOR REQUIREMENTS
Personal Attributes
Obtains and assesses objective evidence faidy
Remains true to purpose of audit
Evaluates audit observations and personal
interactions during audit
Treats concerned personnel with humility
Reacts with sensitivity to national
conventions/customs
Performs audit audit without distractions
AUDITOR REQUIREMENTS
Personal Attributes
Ability to listen - Test
Gives full attention to audit process
Reacts effectively in stressful situations
Arrives at generally acceptable conclusions
based on audit observations
Remain true to a conclusion
Able to organize and conduct and audit
AUDITOR GUIDELINES
Maintains competence
Knowledge of standards and
requirement is current
knowledge of audit procedure and
methods is current
Participates in refresher training where
necessary
AUDIT TEAM SELECTION
Process should consider:
- qualifications as identified in the standard
- type or organisation, processes, activities or
function
being audited
- number and composition of audit teams
- language skills and expertise of the individual
audit team
members
AUDIT TEAM SELECTION
Process should consider:
- potential conflict of interest between audit team
members
and auditee
- requirements of clients, certification and
accreditation
boards
- need for skill in management the team
- skills needed to deal with a particular auditee
AUDIT TEAM
REQUIREMENTS
Audit team should include experience as:
- Team leader
- Systems auditor
- Product Quality specialist
- Technical specialist
- if not resourced internally then externally
INTERNAL AUDIT
Audit
Methodology
STAGES OF AN AUDIT
Pre - audit activities
Audit activities
Post audit activities
CONDUTING AN AUDIT
Pre - Audit
- Agree the scope of the audit
- Establish methods of assessment
- Select auditors, Team leader
- Briefly review documented MS and other
background information
- Plan the audit (checklists etc.) Conduct a pre-
audit meeting
CONDUCTING AN AUDIT
USE OF CHECKLIST DISADVANTAGES
ADVANTAGES
- useful guide to the audit process - preparation time
needed
- records evidence - blinkered view
- record of audit - somewhat cumbersome
- part or report
- good help for beginners
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
Opening meeting
Review documents
Interview
Collect evidence/site inspection
Closing meeting
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
Explain why asking a particular question
Ask a question in different ways if not
understood
If auditee becomes stressed - take a break!
Speak to supervisor first
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
5 Ws and 1 H
What ?
Why ?
When ?
How ?
Where ?
Who ?
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
Do you know how to carry out thickness
checking of this plate?
How thickness measurement of this plate is
done?
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
DEVELOPING A QUESTION TECHNIQUE
- Show me!
- I dont understand, please explain.
- What if ..
- Are you saying that?
- Silent approach
- Puzzled look
- Good or You have under control !
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
ASK LOOK
Mainly open ended Observe what is
questions which happening
provide information
REORD CHECK
objective evidence- instructions
positive and negative
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
Ensure interviewee:
Hears or sees what you tell or show them
Understands what they have heard
Agrees with what they have heard or seen
Takes action
Provides feedback
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
If something is wrong:
Do not criticise
Investigate
Do not undermine supervisor
Record specific details
Also record compliance!
AUDIT ACTIVITIES
Be objective
Persist if a non-conformity exists
Dont get annoyed
Dont take sides
Make your own judgements
Plan time effectively
Be positive
INTERVIEWING SKILLS
On completion
- say Thanks!
POST - AUDIT ACTIVITIES
Audit reporting
- facts
- probabilities
- uncertainties
POST AUDIT ACTIVITIES
Audit reporting - distinguish between
- observations
- interpretations
- assessments
- opinions
- advice
- recommendations
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ISO 9001 Basic FundamentalDocumento35 pagineISO 9001 Basic FundamentalIstimawan_Bagus100% (2)
- World Class Manufacturing: Session 2 Quality Systems: ISO 9000-2000, ISO 14000, Frame Work For BusinessDocumento8 pagineWorld Class Manufacturing: Session 2 Quality Systems: ISO 9000-2000, ISO 14000, Frame Work For BusinessPrashant KadamNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Internal AuditsDocumento44 pagineModern Internal AuditsJoshua HardinNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidance On Conforming To ISO9001Documento46 pagineGuidance On Conforming To ISO9001vethamanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Iqa Training PDFDocumento103 pagineIqa Training PDFkimNessuna valutazione finora
- Implementing and Validating The Quality SystemDocumento23 pagineImplementing and Validating The Quality SystemΑυτός είμαι εγώNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal QMS Auditing: Why Is It So Difficult?Documento51 pagineInternal QMS Auditing: Why Is It So Difficult?Adhavan M AnnathuraiNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO PresentationDocumento64 pagineISO PresentationManu Madaan100% (2)
- Quality Management System Software A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandQuality Management System Software A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandManufacturing Facilities A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Auditing TechniquesDocumento42 pagineRevised Auditing Techniquessaurabh choudhary100% (2)
- Auditing QMS IQA PresentationDocumento128 pagineAuditing QMS IQA PresentationJeaneth Dela Pena Carnicer100% (1)
- Audit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19Da EverandAudit Risk Alert: Government Auditing Standards and Single Audit Developments: Strengthening Audit Integrity 2018/19Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ISODocumento26 pagineWhat Is ISOISO Consultant NomanNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Management Systems: QMS, EMS, OHSMS, FSMS including Aerospace, Service, Semiconductor/Electronics, Automotive, and FoodDa EverandIntegrated Management Systems: QMS, EMS, OHSMS, FSMS including Aerospace, Service, Semiconductor/Electronics, Automotive, and FoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Management for Medical Device Manufacturers: [MD and IVD]Da EverandRisk Management for Medical Device Manufacturers: [MD and IVD]Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Management System Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDa EverandQuality Management System Process A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 9001 10 Clauses InterpretationDocumento34 pagineIso 9001 10 Clauses InterpretationJojo DollolasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Approach A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionDa EverandProcess Approach A Complete Guide - 2019 EditionNessuna valutazione finora
- Section 2Documento117 pagineSection 2باسل العدوانNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To CGMP Compliance CourseDocumento111 pagineIntroduction To CGMP Compliance CourseHend maarofNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001-2015 Transition Workshop (Auditors)Documento96 pagineISO 9001-2015 Transition Workshop (Auditors)S K GARGNessuna valutazione finora
- GMP Good Manufacturing Practices For Quality StandardsDocumento2 pagineGMP Good Manufacturing Practices For Quality StandardsShailesh GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso9001 2015Documento33 pagineIso9001 2015EzkizofrenikaNessuna valutazione finora
- ISO 9001 Training MaterialDocumento248 pagineISO 9001 Training MaterialBuddharaju Kiran100% (2)
- Quality Management SystemDocumento29 pagineQuality Management SystemArunNessuna valutazione finora
- QMS ISO 9001 2008 OverviewDocumento16 pagineQMS ISO 9001 2008 Overviewvipul_gupta1835100% (1)
- ISO 14000 Quality StandardsDocumento4 pagineISO 14000 Quality Standardsmastercontroldotcom100% (1)
- What Are Differences Between Reprocessing and Reworking?Documento1 paginaWhat Are Differences Between Reprocessing and Reworking?Prince MoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cost of QualityDocumento21 pagineCost of QualitymaherkamelNessuna valutazione finora
- 8D Training: Quality Department Quality Training Corrective Action, 8D & Concern ReportingDocumento16 pagine8D Training: Quality Department Quality Training Corrective Action, 8D & Concern ReportingKarl SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Aplac TC 003 Issue 4Documento7 pagineAplac TC 003 Issue 4nawal2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 000 Quality Control-Lec 1Documento153 pagine000 Quality Control-Lec 1Arwa HusseinNessuna valutazione finora
- Qci VersionDocumento47 pagineQci VersionMelissa MurrayNessuna valutazione finora
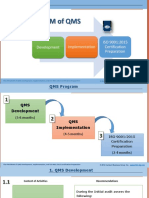
- The Program of QmsDocumento16 pagineThe Program of QmsHamza Sharif AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview 9001 2015 Presentation 23 Sep 15 Web Compatibility ModeDocumento33 pagineOverview 9001 2015 Presentation 23 Sep 15 Web Compatibility ModeAsmat KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Managing The Process Flow With ISO9000 FamilyDocumento6 pagineManaging The Process Flow With ISO9000 FamilyVC100% (1)
- 5952 Frequently Asked Questions 9001 2015Documento4 pagine5952 Frequently Asked Questions 9001 2015ramanadkNessuna valutazione finora
- Final AssignmentDocumento6 pagineFinal Assignmentmhk665Nessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On GMP Requirements For Ophthalmic PreparationsDocumento57 pagineSeminar On GMP Requirements For Ophthalmic Preparationsvkguptajss100% (1)
- TS16949 Training OverviewDocumento23 pagineTS16949 Training OverviewPraveen CoolNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 - Exercises - Participant HandoutDocumento33 pagine03 - Exercises - Participant Handoutnandhu sampathNessuna valutazione finora
- Total Quality ManagementDocumento97 pagineTotal Quality ManagementRodiemerNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaceutical Quality Management SystemDocumento13 paginePharmaceutical Quality Management SystemShailesh Gupta100% (1)
- CAPA Change ManagementDocumento22 pagineCAPA Change ManagementMuhammadAmdadulHoque100% (1)
- Tools and Quality Measurement and ImprovementDocumento39 pagineTools and Quality Measurement and Improvementanishaharsh0% (1)
- ISO-TS 16949 IQA Course MaterialDocumento31 pagineISO-TS 16949 IQA Course Materialazadsingh1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Quality AuditsDocumento13 pagineChapter 10 Quality Audits12007856100% (1)
- APQPDocumento33 pagineAPQPAtul SURVENessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 9001 2015Documento21 pagineIso 9001 2015Sapan Kansara100% (1)
- Change Management ProcedureDocumento4 pagineChange Management ProcedureBryan Moore100% (1)
- Iso9001 2015 Quality Manual Template 1 1024Documento1 paginaIso9001 2015 Quality Manual Template 1 1024Adhi GunantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Good Manufacturing PracticeDocumento27 paginePrinciples of Good Manufacturing PracticeabdrhmanNessuna valutazione finora
- RecordsDocumento23 pagineRecordsPamela Acosta GerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 188 What Is Explosive CladdingDocumento1 paginaPart 188 What Is Explosive Claddingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 190 Techniques To Weld Repair Hot Section Gas Turbine BladesDocumento1 paginaPart 190 Techniques To Weld Repair Hot Section Gas Turbine Bladesravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 191 Material Issues and Repair of Hot Section Gas Turbine BladesDocumento2 paginePart 191 Material Issues and Repair of Hot Section Gas Turbine Bladesravindra_jivani100% (1)
- Part 189 What Is GalvanisingDocumento2 paginePart 189 What Is Galvanisingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 185 Project Saves Time and Money For Amerada HessDocumento1 paginaPart 185 Project Saves Time and Money For Amerada Hessravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 184 Hydrogen Embrittlement TestingDocumento1 paginaPART 184 Hydrogen Embrittlement Testingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 187 Material Performance in Hydrogen Chloride EnvironmentsDocumento2 paginePart 187 Material Performance in Hydrogen Chloride Environmentsravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 173 What Is Friction WeldingDocumento3 paginePART 173 What Is Friction Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 166 What Is Spot WeldingDocumento4 paginePART 166 What Is Spot Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 182 What Is Polymer WeldingDocumento3 paginePART 182 What Is Polymer Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 180 Ir and BCF Weld Differences For Thermoplastic PipingDocumento1 paginaPart 180 Ir and BCF Weld Differences For Thermoplastic Pipingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 181 What Thermoplastic Materials Can Be Hot Plate WeldedDocumento1 paginaPart 181 What Thermoplastic Materials Can Be Hot Plate Weldedravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 183 What Is Orbital Welding of ThermoplasticsDocumento1 paginaPART 183 What Is Orbital Welding of Thermoplasticsravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 177 BS en 287-1 and BS en Iso 9606-1 For Welder QualificationDocumento2 paginePart 177 BS en 287-1 and BS en Iso 9606-1 For Welder Qualificationravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 179 What Are The Typical Applications For Hot Plate WeldingDocumento1 paginaPART 179 What Are The Typical Applications For Hot Plate Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 171 When Manual Metal Arc Welding, Which Electrode Polarity Should I UseDocumento2 paginePART 171 When Manual Metal Arc Welding, Which Electrode Polarity Should I Useravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 172 Are There Any Differences Between Fracture Toughness Tests Carried Out To BS 7448 and Those Using Astm E1820Documento2 paginePart 172 Are There Any Differences Between Fracture Toughness Tests Carried Out To BS 7448 and Those Using Astm E1820ravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 168 How Can I Minimise Electrode Wear in Resistance Spot WeldingDocumento2 paginePART 168 How Can I Minimise Electrode Wear in Resistance Spot Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 170 How Can I Minimise Weld Splash, For Resistance Spot Weld Quality and Safety ReasonsDocumento2 paginePART 170 How Can I Minimise Weld Splash, For Resistance Spot Weld Quality and Safety Reasonsravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 164 Welding Consumables - Part 4 - GAS SHIELDED CONSUMABLESDocumento3 paginePART 164 Welding Consumables - Part 4 - GAS SHIELDED CONSUMABLESravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 167 What Electrode Material Should I Use For Resistance Spot WeldingDocumento1 paginaPART 167 What Electrode Material Should I Use For Resistance Spot Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 169 How Do I Resistance Spot Weld Aluminium AlloysDocumento2 paginePART 169 How Do I Resistance Spot Weld Aluminium Alloysravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 165 Welding Consumables - Part 5 - MIG MAG AND CORED CARBON STEEL WIRESDocumento5 paginePART 165 Welding Consumables - Part 5 - MIG MAG AND CORED CARBON STEEL WIRESravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 160 What Is Plasma Arc WeldingDocumento1 paginaPART 160 What Is Plasma Arc Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 159 What Is Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) WeldingDocumento4 paginePART 159 What Is Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 163 Welding Consumables - Part 2Documento3 paginePART 163 Welding Consumables - Part 2ravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 164 Welding Consumables - Part 3Documento6 paginePART 164 Welding Consumables - Part 3ravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 162 Welding Consumables - Part 1Documento3 paginePART 162 Welding Consumables - Part 1ravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 161 Resistance and Mechanical JoiningDocumento2 paginePART 161 Resistance and Mechanical Joiningravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- PART 158 What Is Narrow Gap WeldingDocumento1 paginaPART 158 What Is Narrow Gap Weldingravindra_jivaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fix 2Documento11 pagineFix 2lutfiyatunNessuna valutazione finora
- Sami Lodi Resume (COMPATIBLE)Documento3 pagineSami Lodi Resume (COMPATIBLE)Malinda ContrerasNessuna valutazione finora
- Tina Li Xiaomi - Final ThesisDocumento62 pagineTina Li Xiaomi - Final ThesisEshvin KrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Research PaperDocumento69 pagineResearch PaperChembie Mariquit LaderaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iram High School: Department of Education Division of City Schools Olongapo CityDocumento3 pagineIram High School: Department of Education Division of City Schools Olongapo CityJeran Angel FacalNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepare Second Edition Level 1: List It!Documento2 paginePrepare Second Edition Level 1: List It!Mar PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Lesson PlanDocumento6 pagineSoil Lesson Planapi-295505041100% (3)
- ĐỀ 1 LỚP 4Documento5 pagineĐỀ 1 LỚP 4Chiến NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Autism PhysiotherapyDocumento4 pagineAutism PhysiotherapyPooja ChhabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Siew Yue Killingley - BiographyDocumento5 pagineSiew Yue Killingley - Biographyphreak90210Nessuna valutazione finora
- Rules For The Student English Speech CompetitionDocumento2 pagineRules For The Student English Speech CompetitionCitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tardiness 1Documento4 pagineTardiness 1Ley 31Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Prepositions Lesson PlanDocumento4 pagine2 Prepositions Lesson Planapi-279690289100% (3)
- Delf Lecture 1Documento36 pagineDelf Lecture 1Nazia Begum100% (1)
- E10tim106 PDFDocumento64 pagineE10tim106 PDFhemacrcNessuna valutazione finora
- HomeworkDocumento36 pagineHomeworkMae DacerNessuna valutazione finora
- Legends Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineLegends Lesson Planapi-489169715100% (2)
- Measuring & Evaluating Learning OutcomesDocumento122 pagineMeasuring & Evaluating Learning OutcomesDennis Bautista88% (17)
- Read Aloud Lesson Plan Kindergarten AutorecoveredDocumento6 pagineRead Aloud Lesson Plan Kindergarten Autorecoveredapi-455234421Nessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching MethodDocumento14 pagineTeaching MethodBiruk EshetuNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Lucky Scramble 3x3 (PB)Documento3 pagineBest Lucky Scramble 3x3 (PB)Simple Circle100% (1)
- Narrative Report in SWTDocumento13 pagineNarrative Report in SWTQuarentai Siete LptNessuna valutazione finora
- Russia Under Stalin ReviewDocumento11 pagineRussia Under Stalin Reviewcreyes25100% (1)
- Global PerspectiveDocumento47 pagineGlobal PerspectiveRenato PanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Functional VocabularyDocumento179 pagineFunctional VocabularyEmily Thomas50% (2)
- KsasDocumento5 pagineKsasapi-268236603Nessuna valutazione finora
- Names InformationDocumento136 pagineNames InformationLatifah EmamNessuna valutazione finora
- Bible Introduction PDFDocumento13 pagineBible Introduction PDFmanuelgonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuhn, The Phenomenological Concept of HorizonDocumento18 pagineKuhn, The Phenomenological Concept of HorizonaliscolantuoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Parental Involvement Questionare PDFDocumento11 pagineParental Involvement Questionare PDFAurell B. SantelicesNessuna valutazione finora


















![Risk Management for Medical Device Manufacturers: [MD and IVD]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/602872428/149x198/825d3b5cd7/1666718194?v=1)