Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
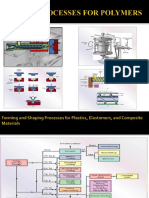
Forming and Shaping Plastics & Composite Materials: Chapter - 18
Caricato da
Muddu Alaparthi0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
100 visualizzazioni35 pagineRapid prototyping
Titolo originale
Rapid prototyping
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoRapid prototyping
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
100 visualizzazioni35 pagineForming and Shaping Plastics & Composite Materials: Chapter - 18
Caricato da
Muddu AlaparthiRapid prototyping
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 35
Chapter - 18
Forming and shaping plastics
& composite materials
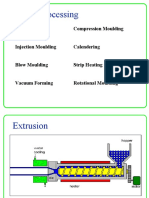
Topics
Introduction
Extrusion
Injection molding
Structured foam molding
Blow molding
Rotational molding
Thermoforming
Compression molding
Casting
Process of composite materials
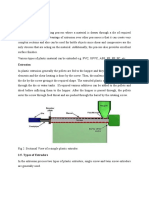
Extrusion
Raw materials in the form if thermoplastic
pallets,granules,or powder, placed into a hopper and fed
into extruder barrel.
The barrel is equipped with a screw that blends the pallets
and conveys them down the barrel
Heaters around the extruders barrels heats the pellets and
liquefies them
Screw has 3-sections
Feed section
Melt or transition section
Pumping section.
Complex shapes with constant cross-section
Solid rods, channels, tubing, pipe, window frames,
architectural components can be extruded due to
continuous supply and flow.
Plastic coated electrical wire, cable, and strips are also
extruded
Pellets :extruded product is a small-diameter rod which is
chopped into small pellets
Sheet and film extrusion :
Extruded parts are rolled on water and on the rollers
Extruder
Fig : Schematic illustration of a typical extruder for plastics, elastomers, and composite materials.
Sheet and Film Extruder
Fig : Die geometry (coat-hanger) for extruding sheet.
Fig : Schematic illustration of the production of
thin film and plastic bags from tube first
produced by an extruder and then blown
by air.
Injection molding
Fig : Injection molding with (a) plunger, (b) reciprocating rotating screw, (c) a typical part made from
an injection molding machine cavity, showing a number of parts made from one shot, note also
mold features such as sprues, runners and gates.
Similar to extrusion barrel is heated
Pellets or granules fed into heated cylinder
Melt is forced into a split-die chamber
Molten plastic pushed into mold cavity
Pressure ranges from 70 Mpa 200 Mpa
Typical products : Cups, containers, housings, tool
handles, knobs, electrical and communication
components, toys etc.
Injection molding
Injection molding
Injection molds have
several components such
as runners, cores,
cavities, cooling
channels, inserts, knock
out pins and ejectors
3-basic types of molds
Cold runner two plate
mold
Cold runner three plate
mold
Hot runner mold
Fig : Examples of injection molding
Injection Molding Machine
Fig : A 2.2-MN (250-ton) injection molding machine. The tonnage is the force applied
to keep the dies closed during injection of molten plastic into the mold cavities.
Process capabilities :
High production rates
Good dimensional control
Cycle time range 5 to 60 secs
Mold materials- tool steels, beryllium - Cu, Al
Mold life- 2 million cycles (steel molds)
10000 cycles ( Al molds)
Machines :
Horizontal or vertical machines
Clamping hydraulic or electric
Reaction Injection molding :
Mixture of resin with 2 or more reactive
fluids forced into the mold cavity at high
speed .
Applications : Bumpers, tenders, thermal
insulation, refrigerators and freezers,
water skis, stiffness
Reaction-Injection Molding
Fig : Schematic illustration of
the reaction-injection
molding process.
Blow molding
Modified extrusion and Injection Molding process.
A tube extruded then clamped to mold with cavity
larger than tube diameter.
Finally blown outward to fill the cavity
Pressure 350Kpa-700Kpa
Other Blow Molding processes
Injection Blow molding
Multi layer Blow molding
Fig : Schematic
illustration of (a)
the blow-
molding process
for making
plastic beverage
bottles, and (b)
a three-station
injection blow-
molding
machine.
Blow
molding
Rotational Molding
Thermo plastics are thermosets can be formed into
large parts by rotational molding
A thin walled metal mold is made of 2 pieces
Rotated abut two perpendicular axes
Pre-measured quantity of powdered plastic material
is rotated about 2-axes
Typical parts produced-Trash cans, boat hulls,
buckets, housings, toys, carrying cases and foot
balls.
Rotational
Molding
Fig: The rotational molding
(rotomolding or
rotocasting) process.
Trash cans, buckets, and
plastic footballs can be
made by this process.
Slush-molding
Plastisols are used in slush molding
Plastic materials are forced against the inside
walls of the heated mold by tumbling action.
The part is cooled while it is still rotating and then
removed by opening the mold
Thermoforming
Series process for forming thermoplastic sheet or film over a mold by
applying heat and pressure.
Typical parts : advertising signs, refrigerator liner, packaging , appliance
housing, and panels for shower stalls .
Fig : Various Thermoforming processes for thermoplastic sheet. These processes are
commonly used in making advertising signs, cookie and candy trays, panels for shower
stalls, and packaging.
Compression molding
Pre-shaped charge ,pre-measured volume of powder and viscous mixture
of liquid resin and filler material is placed directly into a heated mold cavity.
Compression mold results in a flash formation which is a n excess material.
Typical parts made are dishes, handles, container caps fittings, electrical
and electronic components and housings
Materials used in compression molding are thermosetting plastics &
elastomers
Curing times range from 0.5 to 5 mins
3- types of compression molds are
Flash type
Positive type
Semi-positive
Compression
Molding
Fig : Types of compression
molding, a process
similar to forging; (a)
positive, (b) semi
positive, (c) flash (d) Die
design for making
compression-molded
part with undercuts.
Transfer molding
Transfer molding is an improvement if compression
molding
Uncured thermosetting material placed in a heated
transfer pot or chamber, which is injected into heated
closed molds
Ram plunger or rotating screw feeder forces material
into mold cavity through narrow channels
This flow generates heat and resin is molten as it
enters the mold
Typical parts : Electrical & electronic components,
rubber and silicone parts
Transfer molding
Fig : Sequence of operations in transfer molding for thermosetting plastics. This
process is particularly suitable for intricate parts with varying wall thickness.
Casting
Conventional casting of thermo plastics :
Mixture of monomer, catalyst and
various additives are heated and poured
into the mould
The desired part is formed after
polymerization takes place.
Centrifugal casting :
Centrifugal force used to stack the
material onto the mold
Reinforced plastics with short fibers are
used
Fig : Casting
Potting & Encapsulation
Casting the plastic
around an electrical
component to embed it
in the plastic is potting
In both the plastic is
Dielectric
Fig : Potting & Encapsulation
Cold forming
Processes such as rolling ,deep drawing extrusion closed die forging ,coining
and rubber forming can be used for thermoplastics at room temperatures
Typical materials used : Poly propylene, poly carbonate, Abs, and rigid PVC
Considerations :
Sufficiently ductile material at room temperature
Non recoverable material deformation
Solid Phase forming
Temperatures from 10
o
c to 20
o
c are maintained, which is below melting point
Advantages :
Spring-back is lower
Dimensional accuracy can be maintained
Calendaring and Examples of Reinforced
Plastics
Fig : Reinforced-plastic components for a Honda
motorcycle. The parts shown are front and
rear forks, a rear swing arm, a wheel, and
brake disks.
Fig : Schematic illustration of calendaring,
Sheets produced by this process are
subsequently used in thermoforming.
Prepegs
Fig : (a) Manufacturing process for polymer-matrix
composite. (b) Boron-epoxy prepeg tape.
a
b
Tape Laying
Fig : (a) Single-ply lay-up of boron-epoxy tape for
the horizontal stabilizer for F-14 fighter aircraft. (b)
A 10 axis computer-numerical controlled tape-
laying system. This machine is capable of laying
up 75 mm and 150 mm (3 in. and 6 in.) wide
tapes, on contours of up to 30 and at speeds of
up to 0.5m/s.
Sheet Molding
Fig : The manufacturing process for producing reinforced-plastic sheets. The
sheet is still viscous at this stage; it can later be shaped into various products.
Examples of Molding processes
Fig : (a) Vacuum-bag forming.
(b) Pressure-bag
forming.
Fig : Manual methods of
processing reinforced
plastics: (a) hand lay-
up and (b) spray-up.
These methods are
also called open-mold
processing.
Filament Winding
Fig : (a) Schematic illustration of the filament-winding process. (b) Fiberglass being wound over
aluminum liners, for slide-raft inflation vessels for the Boeing767 aircraft.
Pultrusion
Fig: Pultrusion Process
Design Modifications to Minimize Distortions
Fig : Examples of design conditions to eliminate or minimize distortion of plastic parts. (a) Suggested design changes
to minimize distortion. (b) Die design for extrusion of square sections.Without this design, product cross sections swell
(c) Design change in a rib,to minimize pull-in caused by shrinkage during cooling. (d) Stiffening the bottoms of thin
plastic containers by the bottoms of thin plastic containers by doming-this technique is similar to the process used to
make the bottoms of Al. beverages cans.
THE END
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FormingAndShapingPlasticsDocumento30 pagineFormingAndShapingPlasticsM PraveenNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 19 Plastics and Composite Materials1Documento28 pagineCH 19 Plastics and Composite Materials1Cham AmirruddinNessuna valutazione finora
- UnitVI Injection - Compressiona ND Blow MoldingDocumento48 pagineUnitVI Injection - Compressiona ND Blow Moldingharrywilson.harish77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume III: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #3Da EverandPlastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers - Volume III: Plastic Injection Mold Design for Toolmakers, #3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Forming & Shaping Processes For Plastics: Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222Documento41 pagineForming & Shaping Processes For Plastics: Manufacturing Processes Manufacturing Processes ME ME - 222 222shahnawaz875Nessuna valutazione finora
- PlasticsDocumento48 paginePlasticsPavan MehataNessuna valutazione finora
- BTM4723 Plastic Composite FormingDocumento55 pagineBTM4723 Plastic Composite FormingMas Ayu HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-5 - Plastic Processing (51-94)Documento44 pagineUnit-5 - Plastic Processing (51-94)jasvinder singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing of PlasticsDocumento39 pagineManufacturing of PlasticsShivani MedarapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrusion MoldingDocumento16 pagineExtrusion Moldingalihyderabro166Nessuna valutazione finora
- BMP2Documento121 pagineBMP2sid sNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics and CompositesDocumento23 paginePlastics and CompositesAamir RashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Proc 28 May 09 FinalDocumento59 paginePlastic Proc 28 May 09 FinalAinun ZulfikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Processing: Extrusion Compression MouldingDocumento88 paginePlastic Processing: Extrusion Compression MouldingBhushan Shankar Kamble100% (2)
- Plastics: Extrusion MoldingDocumento21 paginePlastics: Extrusion Moldingluan_baNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1-2Documento70 pagineChapter 1-2Shivpoojan SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers PPT PDFDocumento47 paginePolymers PPT PDFShivani RajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2Documento21 pagineModule 2ABIGAIL OLAJUMOKE JOSEPHNessuna valutazione finora
- Injection Moulding New.Documento156 pagineInjection Moulding New.krishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento29 pagineChapter 5Tamirat NemomsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 - Extrusion-Based Processes (Part 1)Documento45 pagineChapter 13 - Extrusion-Based Processes (Part 1)hirenpatNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 (BCHE-602)Documento14 pagineUnit 4 (BCHE-602)Garima TamtaNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymerextrusion 180721114925Documento17 paginePolymerextrusion 180721114925Athlur Sai KiranNessuna valutazione finora
- Shaping Processes For Polymers 1Documento43 pagineShaping Processes For Polymers 1Masa FuadNessuna valutazione finora
- New ThermoformingDocumento20 pagineNew ThermoformingVijay S PNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics PDFDocumento18 paginePlastics PDFV Phanindra BoguNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics: by Dr. V Phanindra Bogu Dept. of Mech. EnggDocumento18 paginePlastics: by Dr. V Phanindra Bogu Dept. of Mech. EnggV Phanindra BoguNessuna valutazione finora
- 202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingDocumento9 pagine202004032240236827nksingh Polymer ProcessingMuhammad Umair Akbar GujjarNessuna valutazione finora
- Roll FormingDocumento11 pagineRoll FormingthirumalaikumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-6 Plastic MouldingDocumento12 pagineUnit-6 Plastic MouldingManav Patel100% (1)
- Zones of ScrewDocumento111 pagineZones of Screwzubi0585100% (2)
- Plastic Manufacturing ProcessesDocumento6 paginePlastic Manufacturing ProcessesHimanshu TiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Injection Molding Cetak PlastikDocumento63 pagineInjection Molding Cetak PlastikRaihan FirdausNessuna valutazione finora
- Mt1 Unit 5 NotesDocumento11 pagineMt1 Unit 5 NotesvelavansuNessuna valutazione finora
- Injection Moulding: Dharmendra Kumar Yadav Mtech, Rubber Technology IIT KharagpurDocumento30 pagineInjection Moulding: Dharmendra Kumar Yadav Mtech, Rubber Technology IIT KharagpurlawrenziNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 6-Common Manufaturing Processes IDocumento29 pagineLecture 6-Common Manufaturing Processes IKamal SurenNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13Documento109 pagineChapter 13SaAhRaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic of Mould DesignDocumento79 pagineBasic of Mould DesignKamal Krishna Kashyap100% (4)
- Blow Molding ProcessDocumento184 pagineBlow Molding ProcessShubham ChaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrusion Die DesignDocumento67 pagineExtrusion Die DesignShubham Chaudhary100% (1)
- Extrusion of Thermoplastics EXTRUSION Plays A Prominent Part On The Plastics Industry. Extrusion, UnlikeDocumento21 pagineExtrusion of Thermoplastics EXTRUSION Plays A Prominent Part On The Plastics Industry. Extrusion, UnlikeParag NambiarNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Procession Term Test-1Documento90 paginePolymer Procession Term Test-1সাইদুর রহমানNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3: Plastic Processing: 1. State The General Properties of PlasticsDocumento13 pagineUnit 3: Plastic Processing: 1. State The General Properties of PlasticsSagar DhageNessuna valutazione finora
- BMM3643 CHP 1 Forming and Shaping Polymer ProcessesDocumento30 pagineBMM3643 CHP 1 Forming and Shaping Polymer Processesemadaddin alezzaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Injection MoldingDocumento10 pagineInjection MoldingKalam Kulai100% (1)
- Ch3 Forming Shaping Plastics and CompositeDocumento64 pagineCh3 Forming Shaping Plastics and CompositeRusydi JamainNessuna valutazione finora
- Shaping Processes For PlasticsDocumento92 pagineShaping Processes For PlasticsmindmaczaNessuna valutazione finora
- Process Parameters in Injection Moulding: by Devang NaikDocumento24 pagineProcess Parameters in Injection Moulding: by Devang NaikAmit PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch13 1 PolymerMelt&ExtrusionDocumento32 pagineCh13 1 PolymerMelt&ExtrusionPrabhu MechNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Plastics WordDocumento9 pagineMCQ Plastics Wordsrujankala100% (4)
- Polymer Processing HandoutDocumento68 paginePolymer Processing HandoutibraheemNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics ExtrusionDocumento9 paginePlastics ExtrusionFITIWINessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental of Manufacturing by Groover Cahpter 13Documento125 pagineFundamental of Manufacturing by Groover Cahpter 13ali kingNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 4-ODL-2Documento46 pagineWeek 4-ODL-2aymaNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrusion and DrawingDocumento19 pagineExtrusion and DrawingBatuhan YildizNessuna valutazione finora
- Compression MoldingDocumento12 pagineCompression MoldingSuyog BhoyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic InjectionDocumento39 paginePlastic InjectionRishav KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is AbaqusDocumento41 pagineWhat Is AbaqusmshambooliNessuna valutazione finora
- An Evaluation of Plastic Flow Stress Models For The Simulation of High-Temperature and High-Strain-Rate Deformation of MetalsDocumento43 pagineAn Evaluation of Plastic Flow Stress Models For The Simulation of High-Temperature and High-Strain-Rate Deformation of MetalsMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- 053 PDFDocumento28 pagine053 PDFMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of Chemtech ResearchDocumento8 pagineInternational Journal of Chemtech ResearchMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- User SubDocumento542 pagineUser SubGiannis-Sama VazaiosNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 1 Appsc TipsDocumento1 paginaGroup 1 Appsc TipsMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite Structures: Chi-Seung Lee, Jeong-Hyeon Kim, Seul-Kee Kim, Dong-Man Ryu, Jae-Myung LeeDocumento14 pagineComposite Structures: Chi-Seung Lee, Jeong-Hyeon Kim, Seul-Kee Kim, Dong-Man Ryu, Jae-Myung LeeMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Multiphase Finite Element Modeling of Machining Unidirectional Composites: Prediction of Debonding and Fiber DamageDocumento12 pagineMultiphase Finite Element Modeling of Machining Unidirectional Composites: Prediction of Debonding and Fiber DamageMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- PDFDocumento25 paginePDFMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- PDFDocumento25 paginePDFMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Abaqus - Cae Users ManualDocumento1.306 pagineAbaqus - Cae Users ManualSarhan Karray100% (1)
- Civil Services EnglishDocumento4 pagineCivil Services EnglishMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- UVAMT ProgrammDocumento12 pagineUVAMT ProgrammMuddu AlaparthiNessuna valutazione finora
- Creo Parametric ManualDocumento105 pagineCreo Parametric ManualDanilo BorgesNessuna valutazione finora
- Hdpe Butt Fusion Welding TheoryDocumento294 pagineHdpe Butt Fusion Welding TheoryNAVANEETH NAVANI100% (2)
- Extrusion of PlasticsDocumento49 pagineExtrusion of PlasticsDenys MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics Blown Film Extrusion: Manufacturing IntelligenceDocumento6 paginePlastics Blown Film Extrusion: Manufacturing IntelligenceMark SternNessuna valutazione finora
- 55 Dynamic Modeling of Blown Film ExtrusionDocumento21 pagine55 Dynamic Modeling of Blown Film ExtrusionFacundo CarmonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Co-Extruded Multi-Polymer Protective Tapes: 2A25 2A26 2A29 (Clear)Documento3 pagineCo-Extruded Multi-Polymer Protective Tapes: 2A25 2A26 2A29 (Clear)Mario Daniel ConejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Blown Film ManualDocumento20 pagineBlown Film ManualJohn P. Bandoquillo100% (2)
- Other Types of Injection MoldingDocumento22 pagineOther Types of Injection MoldingKodhansNessuna valutazione finora
- HatfieldDocumento33 pagineHatfieldAlex ForrestNessuna valutazione finora
- MidSouth Packaging, Inc. PREMIUM QUALITY PLASTIC BAGS & ROLLSDocumento32 pagineMidSouth Packaging, Inc. PREMIUM QUALITY PLASTIC BAGS & ROLLSmichaeljscudderNessuna valutazione finora
- World Standard Sheet LinesDocumento4 pagineWorld Standard Sheet LinesAlejandro RubianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Shear Rate CalculationDocumento8 pagineShear Rate CalculationMdAliRazuNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 1 ExtrusionDocumento69 pagine2 1 ExtrusionSingh Anuj0% (1)
- Rassegna Ing - Bassa PDFDocumento18 pagineRassegna Ing - Bassa PDFNajlepsaJagodaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acknowledgment: Aastu EPIDocumento35 pagineAcknowledgment: Aastu EPIbernabasNessuna valutazione finora
- Extrusion of PlasticDocumento6 pagineExtrusion of Plasticdasani93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of The Development of A Plastic Recycling MachineDocumento15 pagineOptimization of The Development of A Plastic Recycling MachinePhilip ArpiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastics Technology Handbook, Volume 2Documento135 paginePlastics Technology Handbook, Volume 2Momentum Press88% (17)
- What Are PolymersDocumento51 pagineWhat Are PolymerspatwarcNessuna valutazione finora
- Extruding Plastics A Practical Processing Handbook PDFDocumento2 pagineExtruding Plastics A Practical Processing Handbook PDFBrian0% (1)
- Experiment 3 (BFL)Documento7 pagineExperiment 3 (BFL)wajahat rasoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting and Mitigating Gels in Polyethylene Film ProductsDocumento24 pagineTroubleshooting and Mitigating Gels in Polyethylene Film ProductsTHEREZA TORRES BLANCASNessuna valutazione finora
- Barrier FilmsDocumento37 pagineBarrier FilmsJulio GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- LECTURE 6-Forming and Shaping of Plastics and CompositesDocumento52 pagineLECTURE 6-Forming and Shaping of Plastics and CompositesM.k. VarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- FilmDocumento2 pagineFilmDhileepan KumarasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Blow Molding Handbook (Print-on-Demand)Documento21 pagineBlow Molding Handbook (Print-on-Demand)RaynerNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Notes 2014 Parts 8-11 PDFDocumento42 paginePolymer Notes 2014 Parts 8-11 PDFRadhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers in Flexible PackagingDocumento9 paginePolymers in Flexible PackagingGul' Love100% (2)
- MTT655 W2 ExtrusionDocumento13 pagineMTT655 W2 ExtrusionCitra Adelina SitorusNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-27.8 PlasticsDocumento98 pagineCh-27.8 PlasticsasjfgauojfgfNessuna valutazione finora