Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
Caricato da
xinying94Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
Caricato da
xinying94Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Carboxylic acids and their derivatives
Learning Objectives
Students should be able to
Interpret and use the nomenclature, general
formula and displayed formula of the carboxylic
acids and esters
Describe the formation of carboxylic acids from
alcohols, aldehydes and nitriles
Describe the reactions of carboxylic acids in the
formation of
(i) salts
(ii) Esters
continued on next page....
Carboxylic acids and their derivatives
Learning Objectives continued...
Describe the formation of esters from carboxylic
acids , using ethyl ethanoate as an example
Describe acid and base hydrolysis of esters
State the major commercial uses of esters e.g.
Solvents , perfumes and flavourings
STRUCTURE OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
contain the carboxyl functional group -COOH
the bonds around carbon atom are in a planar arrangement
include a carbonyl (C=O) group and
a hydroxyl (O-H) group
are isomeric with esters :- RCOOR
Carboxylic acids form a homologous series
HOMOLOGOUS SERIES
HCOOH CH
3
COOH C
2
H
5
COOH
With more carbon atoms, there can be structural isomers
C
3
H
7
COOH (CH
3
)
2
CHCOOH
Greater branching causes inter-molecular forces to be
weaker giving rise to lower boiling points
Boiling point is higher for straight chain isomers.
101C 118C 141C 164C
164C 154C
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
BOILING POINT
Increases as molecular size increases - due to increased strength of van
der Waals forces
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
BOILING POINT
Carboxylic acids have high boiling points for their relative molecular mass
This is caused by inter-molecular hydrogen bonding due to polar OH
bonds
DIMERISATION
stronger inter-molecular attraction means more energy is needed to
separate molecules
HYDROGEN
BONDING
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
SOLUBILITY
carboxylic acids are soluble in organic solvents
they are also soluble in water due to hydrogen bonding
small molecules dissolve readily in cold water
as mass increases, the solubility decreases
benzoic acid is fairly insoluble in cold water but is soluble in hot water
HYDROGEN
BONDING
PREPARATION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
Oxidation of aldehydes RCHO + [O] > RCOOH
Hydrolysis of esters RCOOR + H
2
O RCOOH + ROH
Hydrolysis of acyl chlorides RCOCl + H
2
O > RCOOH + HCl
Hydrolysis of nitriles RCN + 2 H
2
O > RCOOH + NH
3
Hydrolysis of amides RCONH
2
+ H
2
O > RCOOH + NH
3
Oxidation of 1alcohols RCH
2
OH + 2[O] > RCOOH + H
2
O
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
ACIDITY
weak acids RCOOH + H
2
O(l) RCOO(aq) + H
3
O
+
(aq)
form salts RCOOH + NaOH(aq) > RCOONa
+
(aq) + H
2
O(l)
2RCOOH + Mg(s) > (RCOO)
2
Mg
2+
(aq) + H
2
(g)
The acid can be liberated from its salt by treatment with a stronger acid.
e.g. RCOO Na
+
(aq) + HCl(aq) > RCOOH + NaCl(aq)
Conversion of an acid to its water soluble salt followed by acidification of
the salt to restore the acid is often used to separate acids from a mixture.
Carboxylic acids are strong enough acids to liberate CO
2
from carbonates
ESTERIFICATION
Reagent(s) alcohol + strong acid catalyst (e.g conc. H
2
SO
4
)
Conditions reflux
Product ester
Equation e.g. CH
3
CH
2
OH(l) + CH
3
COOH(l) CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
(l) + H
2
O(l)
ethanol ethanoic acid ethyl ethanoate
Notes Conc. H
2
SO
4
is a dehydrating agent - it removes water
causing the equilibrium to move to the right and thus
increases the yield of the ester
Naming esters Named from the original alcohol and carboxylic acid
CH
3
OH + CH
3
COOH CH
3
COOCH
3
+ H
2
O
METHYL ETHANOATE
ESTERS
Structure Substitute the H in carboxylic acid by an organic group
Nomenclature first part from alcohol, second part from acid
e.g. methyl ethanoate CH
3
COOCH
3
Preparation From carboxylic acids and acyl chlorides
Reactivity Unreactive compared with acids and acyl chlorides
Isomerism Esters are structural isomers of carboxylic acids
ETHYL METHANOATE
METHYL ETHANOATE
Classification CARBOXYLIC ACID ESTER
Functional Group R-COOH R-COOR
Name PROPANOIC ACID METHYL ETHANOATE
Physical properties O-H bond gives rise No hydrogen bonding
to hydrogen bonding; insoluble in water
get higher boiling point
and solubility in water
Chemical properties acidic fairly unreactive
react with alcohols hydrolysed to acids
STRUCTURAL ISOMERISM FUNCTIONAL GROUP
PREPARATION OF ESTERS - 1
Reagent(s) alcohol + carboxylic acid
Conditions reflux with a strong acid catalyst (e.g. conc. H
2
SO
4
)
Equation e.g. CH
3
CH
2
OH(l) + CH
3
COOH(l) CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
(l) + H
2
O(l)
ethanol ethanoic acid ethyl ethanoate
Note Conc. H
2
SO
4
is a dehydrating agent - it removes water
causing the equilibrium to move to the right and thus
increases the yield of the ester
PREPARATION OF ESTERS - 2
Reagent(s) alcohol + acyl chloride
Conditions reflux under dry conditons
Equation e.g. CH
3
OH(l) + CH
3
COCl(l) > CH
3
COOCH
3
(l) + HCl(g)
methanol ethanoyl methyl
chloride ethanoate
Note Acyl chlorides are very reactive
but must be kept dry as they react
with water.
CHLORINATION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS ( Acylation)
Chlorination involves replacing the OH with a Cl
Product acyl chloride
Reagent thionyl chloride SOCl
2
Conditions DRY conditions
Equation CH
3
COOH + SOCl
2
> CH
3
COCl + SO
2
+ HCl
Alternative
method CH
3
COOH + PCl
5
> CH
3
COCl + POCl
3
+ HCl
phosphorus(V) chloride
HYDROLYSIS OF ESTERS
Hydrolysis is the opposite of esterification
ESTER + WATER CARBOXYLIC ACID + ALCOHOL
HCOOH + C
2
H
5
OH
METHANOIC ETHANOL
ACID
CH
3
COOH + CH
3
OH
ETHANOIC METHANOL
ACID
ETHYL METHANOATE
METHYL ETHANOATE
HYDROLYSIS OF ESTERS
The products of hydrolysis depend on the conditions used...
acidic CH
3
COOCH
3
+ H
2
O CH
3
COOH + CH
3
OH
alkaline CH
3
COOCH
3
+ NaOH > CH
3
COO Na
+
+ CH
3
OH
If the hydrolysis takes place under alkaline conditions,
the organic product is a water soluble ionic salt
The carboxylic acid can be made by treating the salt with HCl
CH
3
COO Na
+
+ HCl > CH
3
COOH + NaCl
USES OF ESTERS
Despite being fairly chemically unreactive, esters are useful as ...
flavourings apple 2-methylbutanoate
pear 3-methylbutylethanoate
banana 1-methylbutylethanoate
pineapple butylbutanoate
rum 2-methylpropylpropanoate
solvents nail varnish remover - ethyl ethanoate
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Documento67 pagineChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNessuna valutazione finora
- ArenesDocumento5 pagineArenes林琪Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leeson 17Documento5 pagineLeeson 17MarcTnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Mass SpecDocumento6 pagineMass Specapi-182809945Nessuna valutazione finora
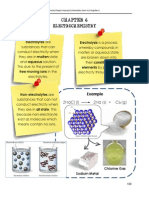
- ElectrolysisDocumento25 pagineElectrolysisMuhammad UmerNessuna valutazione finora
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 1 - Answer SchemeDocumento12 paginet2 Chem Revision Ex 1 - Answer SchemeNicholas OwNessuna valutazione finora
- CrackingDocumento5 pagineCrackingnorlin facultadNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 3Documento1 paginaTest 3Windellea WongNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.phenols (915-968)Documento54 pagine13.phenols (915-968)AbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lattice Energy ExplainedDocumento22 pagineLattice Energy Explainednotabc gamerNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure 1 QPDocumento10 pagineAtomic Structure 1 QPAsif AmdadNessuna valutazione finora
- Addition Polymers and Polyester Student NotesDocumento8 pagineAddition Polymers and Polyester Student Notesapi-277345420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic ReactionsDocumento16 pagineOrganic Reactionsyie_793Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry: Metall RgyDocumento136 pagineChemistry: Metall Rgymukesh kannaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Kinetics QuestionsDocumento18 pagineChemical Kinetics QuestionsAakaash C.K.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Structure: Rutherford Atomic Model, Planck's Quantum Theory, Bohr Atomic Model, de Broglie Dual Nature, Heisenberg's Uncertainty PrincipleDocumento15 pagineAtomic Structure: Rutherford Atomic Model, Planck's Quantum Theory, Bohr Atomic Model, de Broglie Dual Nature, Heisenberg's Uncertainty PrincipleBedojyoti BarmanNessuna valutazione finora
- First Row Transition MetalsDocumento39 pagineFirst Row Transition MetalsArielle LewisNessuna valutazione finora
- IMPORTANT Solution and OrganicDocumento121 pagineIMPORTANT Solution and OrganicShri GuhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Halides and organic compounds identificationDocumento37 pagineHalides and organic compounds identificationAishwarya NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- JC1 Atomic Structure NotesDocumento35 pagineJC1 Atomic Structure NotesLeng RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsDocumento19 pagineOxford Resources For IB: Structure 3.1 - The Periodic Table: Classification of ElementsGian Paolo GerzonNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDocumento8 pagineEdexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMaliha Ishrat JarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cie QDocumento17 pagineCie Qinternationalmakkhayar100% (1)
- Tutorial 1.1 (PG 1-2)Documento3 pagineTutorial 1.1 (PG 1-2)Supia NazmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry WordDocumento19 pagineOrganic Chemistry Wordisnaini safitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding and StructureDocumento199 pagineChemical Bonding and StructureRichard NestorNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 10 Organic Chemistry SL 2021Documento41 pagineTopic 10 Organic Chemistry SL 2021HotTornado XDNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Chemistry Exam Q1 Calculating Enthalpy ChangeDocumento8 pagineAS Chemistry Exam Q1 Calculating Enthalpy ChangeJake RobinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrolysis Products Grade 9 WorksheetDocumento1 paginaElectrolysis Products Grade 9 WorksheetDhriti GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Assignment 2Documento2 pagine11 Chemistry Chapter 3 Assignment 2g_ayyanar0% (1)
- Chemistry of Period IIDocumento6 pagineChemistry of Period IIPAUL KOLERENessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Carbon CompoundsDocumento306 pagineTypes of Carbon CompoundsJerry Sumok WalterNessuna valutazione finora
- EAMCET QR Chemistry SR Chem 17.organic Chemistry Carboxylic AcidsDocumento5 pagineEAMCET QR Chemistry SR Chem 17.organic Chemistry Carboxylic AcidsJagadeesh Goli100% (2)
- Group IV Trends - Carbon To LeadDocumento76 pagineGroup IV Trends - Carbon To LeadRhondene WintNessuna valutazione finora
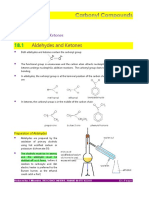
- Aldehydes and Ketones ReactionsDocumento9 pagineAldehydes and Ketones ReactionsKudzayi Tusaumwe100% (1)
- Bottom of Pyramid - Test # 1 - Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles & TechniquesDocumento5 pagineBottom of Pyramid - Test # 1 - Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles & TechniquesJay PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- GRP VII Tutorial AnsDocumento9 pagineGRP VII Tutorial AnslayssourcreamNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocumento14 pagine02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrolysisDocumento31 pagineElectrolysisteddaboyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 - Atoms-Saju-Hsslive PDFDocumento9 pagineChapter 12 - Atoms-Saju-Hsslive PDFAmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework QuestionsDocumento2 pagineChapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework Questionservaldi0% (1)
- Pioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsDocumento31 paginePioneer Junior College H2 Chemistry (9647) An Introduction To The Chemistry of Transition ElementsTimothy HandokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to HydrogenDocumento36 pagineIntroduction to HydrogenAryaman VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: Hydroxy Compounds (II)Documento3 pagineLesson Plan: Lesson: Hydroxy Compounds (II)MarcTnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of Main Group Elements-Group 1 and 2, 13 To 18Documento126 pagineChemistry of Main Group Elements-Group 1 and 2, 13 To 18nalla casuga100% (1)
- F324 Condensation PolymersDocumento7 pagineF324 Condensation PolymersDoc_CrocNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 49Documento3 pagineLesson 49MarcTnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17 - Hydroxy CompoundsDocumento8 pagineChapter 17 - Hydroxy CompoundsNabindra RuwaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocumento11 pagineHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Module Form 4Documento30 pagineChemistry Module Form 4mohd faisol100% (1)
- Peculiar Behaviour of CarbonDocumento7 paginePeculiar Behaviour of Carbonhussail sarmadNessuna valutazione finora
- F325 Transition ElementsDocumento18 pagineF325 Transition ElementsDoc_CrocNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 19H NotesDocumento40 pagineCH 19H NotesHello HelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Combustion Analysis QuestionsDocumento2 pagineExtra Combustion Analysis QuestionsAnshu MovvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionDa EverandElectron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
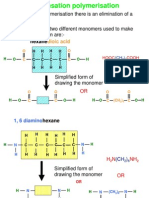
- Condensation PolymerisationDocumento14 pagineCondensation Polymerisationafoo1234100% (2)
- Hydrocarbons: Sources, Classification and PropertiesDocumento22 pagineHydrocarbons: Sources, Classification and PropertiesManan TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- P Block2012 457Documento143 pagineP Block2012 457Abhishek Bansal100% (1)
- Transition Metal ToxicityDa EverandTransition Metal ToxicityG. W. RichterNessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 Text 1Documento5 pagine2010 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Text 1Documento5 pagine09 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2010 Text 2Documento5 pagine2010 Text 2xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 95 Text1234Documento19 pagine95 Text1234xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Text 2Documento4 pagine08 Text 2xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- How to Blueprint Your Career PathDocumento19 pagineHow to Blueprint Your Career Pathxinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 98 Text1234Documento4 pagine98 Text1234xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 97 Text1234Documento21 pagine97 Text1234xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 96 Text 1234Documento21 pagine96 Text 1234xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Text 4Documento4 pagine09 Text 4xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 94 Text 1Documento4 pagine94 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Text 1Documento4 pagine08 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Research Progress and ChallengesDocumento4 pagineCancer Research Progress and Challengesxinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 95 Text 1Documento19 pagine95 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Text 3Documento4 pagine08 Text 3xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Text 2Documento4 pagine09 Text 2xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Text 4Documento5 pagine06 Text 4xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Text 3Documento4 pagine09 Text 3xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Text 1Documento4 pagine07 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Text 3Documento4 pagine07 Text 3xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08 Text 4Documento3 pagine08 Text 4xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Text 2Documento4 pagine07 Text 2xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Text 4Documento5 pagine07 Text 4xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Text 3Documento4 pagine06 Text 3xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Text 1Documento3 pagine06 Text 1xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Text 2Documento3 pagine05 Text 2xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Text 4Documento3 pagine05 Text 4xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Text 3Documento4 pagine05 Text 3xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Text 3Documento4 pagine05 Text 3xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Text 2Documento4 pagine05 Text 2xinying94Nessuna valutazione finora