Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lecture 8
Caricato da
Strider TeepeeCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lecture 8
Caricato da
Strider TeepeeCopyright:
Formati disponibili
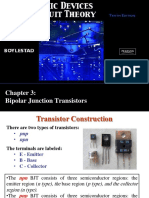
Chapter 8:
FET Amplifiers
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
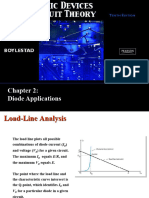
Introduction
FETs provide:
Excellent voltage gain
High input impedance
Low-power consumption
Good frequency range
2
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
FET Small-Signal Model
Transconductance
The relationship of a change in I
D
to the corresponding change in
V
GS
is called transconductance
Transconductance is denoted g
m
and given by:
GS
D
m
V
I
g
=
3
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Graphical Determination of g
m
4
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Mathematical Definitions of g
m
GS
D
m
V
I
g
A
A
=
(
=
P
GS
P
DSS
m
V
V
1
V
2I
g
P
DSS
m0
V
2I
g =
(
=
P
GS
m0 m
V
V
1 g g
DSS
D
P
GS
I
I
V
V
1 =
DSS
D
m0
P
GS
m0 m
I
I
g
V
V
1 g g =
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
Where V
GS
=0V
Where
5
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
O =
i
Z
os
d o
y
1
r Z = =
constant V
D
DS
d
GS
I
V
r
=
=
A
A
Input impedance:
FET Impedance
Output Impedance:
where:
y
os
= admittance parameter listed on FET specification sheets.
6
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
FET AC Equivalent Circuit
7
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Source (CS) Fixed-Bias Circuit
The input is on the gate and the
output is on the drain
8
There is a 180 phase shift
between input and output
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Calculations
G i
R Z =
d D o
r || R Z =
10R r
D o
D d
R Z
>
~
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
9
) R || (r g
V
V
A
D d m
i
o
v
= =
D d
10R r
D m
i
o
v
R g
V
V
A
>
= =
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Source (CS) Self-Bias Circuit
This is a common-source amplifier
configuration, so the input is on the gate
and the output is on the drain
10
There is a 180 phase shift between
input and output
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Calculations
G i
R Z =
D d o
R || r Z =
10R r
D o
D d
R Z
>
~
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
11
) R || (r g A
D d m v
=
D d
10R r
D m v
R g A
>
=
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Source (CS) Self-Bias Circuit
Removing C
s
affects
the gain of the circuit.
12
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Calculations
G i
R Z =
10R r
D o
D d
R Z
>
~
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
13
d
S D
S m
D m
i
o
v
r
R R
R g 1
R g
V
V
A
+
+ +
= =
) R (R 0 1 r
S m
D m
i
o
v
S D d
R g 1
R g
V
V
A
+ >
+
= =
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Source (CS) Voltage-Divider Bias
This is a common-source
amplifier configuration, so the
input is on the gate and the
output is on the drain.
14
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Impedances
2 1 i
R || R Z =
D d o
R || r Z =
10R r
D o
D d
R Z
>
~
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
15
) R || (r g A
D d m v
=
D d
10R r
D m v
R g A
>
=
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Source Follower (Common-Drain) Circuit
In a common-drain amplifier
configuration, the input is on the
gate, but the output is from the
source.
16
There is no phase shift between
input and output.
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Impedances
m
S d o
g
1
|| R || r Z =
S d
10R r
m
S o
g
1
|| R Z
>
~
G i
R Z =
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
17
) R || (r g 1
) R || (r g
V
V
A
S d m
S d m
i
o
v
+
= =
10 r
S m
S m
i
o
v
d
R g 1
R g
V
V
A
>
+
= =
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Gate (CG) Circuit
The input is on the source
and the output is on the
drain.
18
There is no phase shift
between input and output.
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Calculations
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
(
+
+
=
d m
D d
S i
r g 1
R r
|| R Z
D d
10R r
m
S i
g
1
|| R Z
>
~
d D o
r || R Z =
10 r D o
d
R Z
>
~
19
(
+
(
+
= =
d
D
d
D
D m
i
o
v
r
R
1
r
R
R g
V
V
A
10R r D m v
D d
R g A
>
=
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
D-Type MOSFET AC Equivalent
20
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
E-Type MOSFET AC Equivalent
g
m
and r
d
can be found in
the specification sheet for
the FET.
21
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Source Drain-Feedback
22
There is a 180 phase shift
between input and output.
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Calculations
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
) R || (r g 1
R || r R
Z
D d m
D d F
i
+
+
=
D d D d F
10R r , R || r R
D m
F
i
R g 1
R
Z
> >>
+
~
D d F o
||R r || R Z =
D d D d F
10R r , R || r R D o
R Z
> >>
~
23
) R || r || (R g A
D d F m v
=
D m v
D
10R
d
,r
D
| | R
d
r
F
R
R g A
> >>
~
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Common-Source Voltage-Divider Bias
24
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Calculations
2 1 i
R || R Z =
D d o
R || r Z =
Input impedance:
Output impedance:
10 r D o
d
R Z
>
~
25
) R || (r g A
D d m v
=
D d
10R r D m v
R g A
>
~
Voltage gain:
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Summary Table
more
26
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Summary Table
27
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Troubleshooting
.
Check the DC bias voltages:
If not correct check power supply, resistors, FET. Also check to ensure
that the coupling capacitor between amplifier stages is OK.
Check the AC voltages:
If not correct check FET, capacitors and the loading effect of the next
stage
28
Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved.
Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e
Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelsky
Practical Applications
Three-Channel Audio Mixer
Silent Switching
Phase Shift Networks
Motion Detection System
29
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Da EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-8 FET AmplifiersDocumento29 pagineChapter-8 FET AmplifiersFranklin Rey PacquiaoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 02 Aplikasi DiodaDocumento63 pagineCH 02 Aplikasi DiodaBenedictus BayuNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT AC AnalysisDocumento22 pagineBJT AC AnalysisDonna OrqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 02 - Diode ApplicationsDocumento28 pagineLecture 02 - Diode ApplicationsazizNessuna valutazione finora
- B-Stad CH 08Documento30 pagineB-Stad CH 08lakshmipoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ene212 CH 15 Power SupplyDocumento24 pagineEne212 CH 15 Power SupplyposktovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 PDFDocumento32 pagineChapter 9 PDFVince Felipe OlivarNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAP2 ADocumento26 pagineCHAP2 AKyte Valerie SamonteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch5 Power Supplies Voltage Regulator Pp15aDocumento38 pagineCh5 Power Supplies Voltage Regulator Pp15aeddyonnNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Edition Boylestad Louis Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsDocumento26 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Edition Boylestad Louis Chapter 2 Diode ApplicationsengitalomedeirosNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulators PDFDocumento24 pagineRegulators PDFH Aries OñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter2 p2 NITHDocumento21 pagineChapter2 p2 NITHPriyanshu GargNessuna valutazione finora
- Diodes Applications: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis NashelskyDocumento23 pagineDiodes Applications: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis Nashelskyasiri201912Nessuna valutazione finora
- Floyd CH 5Documento40 pagineFloyd CH 5aishahsuciutomo100% (1)
- Clipper and Clamper LessonDocumento21 pagineClipper and Clamper LessonJeffery DungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch05 Transistor Bias Circuits (37 PP)Documento19 pagineCh05 Transistor Bias Circuits (37 PP)junaidnazirNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter4 p2Documento19 pagineChapter4 p2mayankardeshanaNessuna valutazione finora
- B-Stad CH 05Documento46 pagineB-Stad CH 05lakshmipoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12Documento30 pagineChapter 12Aditi BardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 10Documento40 pagineCH 10Dr-Muhammad Aqeel AslamNessuna valutazione finora
- DeviceDocumento29 pagineDeviceAkhtarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter2 p1 NITHDocumento22 pagineChapter2 p1 NITHPriyanshu GargNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT AC AnalysisDocumento44 pagineBJT AC AnalysisSmadi Rana2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Ed Boylestad Chapter 13Documento28 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory 10th Ed Boylestad Chapter 13Calix LeonelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 13 Linear Digital IcsDocumento28 pagineChapter 13 Linear Digital IcsAlyssa RabaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 06Documento41 pagineChap 06Hidayah HadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter4 p1Documento24 pagineChapter4 p1mayankardeshanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Amplifiers: BENE 2163 Electronic SystemsDocumento39 paginePower Amplifiers: BENE 2163 Electronic SystemszafirahNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistor CharacteristicsDocumento25 pagineTransistor Characteristicsmanish100% (1)
- Ed - 2022 - Chap 03Documento126 pagineEd - 2022 - Chap 03Đăng Trần QuốcNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagram Power Supply: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis NashelskyDocumento10 pagineDiagram Power Supply: Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory, 10/e Robert L. Boylestad and Louis NashelskyanggotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transistors PDFDocumento28 pagineTransistors PDFubaidNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT DC Biasing 4 - p2Documento20 pagineBJT DC Biasing 4 - p2FajarNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics FundamentalstransistorsDocumento81 pagineElectronics FundamentalstransistorsSandeep Varma's67% (3)
- Electronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Semiconductor DiodesDocumento35 pagineElectronic Devices and Circuit Theory: Semiconductor DiodesEzsilvasilva SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Da EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisDa EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesDa EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Da EverandElectronic Devices and Circuits: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering Division, Volume 1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Multiple Choice Questions in Electronics and Electrical EngineeringDa EverandMultiple Choice Questions in Electronics and Electrical EngineeringValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsDa EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNessuna valutazione finora
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorDa Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Electronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesDa EverandElectronics 3 Checkbook: The Checkbooks SeriesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Electronic Devices and CircuitsDa EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Electronic Devices and CircuitsNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics: Switches and ConvertersDa EverandPower Electronics: Switches and ConvertersValutazione: 2 su 5 stelle2/5 (1)
- Beginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsDa EverandBeginning Digital Electronics through ProjectsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsDa EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- BooleanDocumento89 pagineBooleanStrider TeepeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12: Kinematics of A ParticleDocumento10 pagineChapter 12: Kinematics of A ParticleStrider TeepeeNessuna valutazione finora
- SeatDocumento1 paginaSeatStrider TeepeeNessuna valutazione finora
- C Chap01Documento21 pagineC Chap01Michael MagpantayNessuna valutazione finora
- Super Computers by Phuong VoDocumento16 pagineSuper Computers by Phuong VoStrider TeepeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Microprocessors & Microcontrolers: H. Sabaghian BDocumento27 pagineMicroprocessors & Microcontrolers: H. Sabaghian BStrider TeepeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Guppa - Se Ultra300x Servicemanual PDFDocumento560 pagineGuppa - Se Ultra300x Servicemanual PDFPatrik Benjaro100% (1)
- Answer Sheet A2Documento3 pagineAnswer Sheet A2Alba FernándezNessuna valutazione finora
- Strapack I-10 Instruction-Parts Manual MBDocumento26 pagineStrapack I-10 Instruction-Parts Manual MBJesus PempengcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Booster Unit Auto Backwash FilterDocumento5 pagineBooster Unit Auto Backwash FilterFardin NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 6351 - Electrical Drives and Controls (EDC) QBDocumento160 pagineEE 6351 - Electrical Drives and Controls (EDC) QBkannanchammyNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Asylum ApplicationDocumento2 pagineTraining Asylum Applicationec_eiucNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification Tree - Utkarsh Kulshrestha: Earn in G Is in Learnin G - Utkarsh KulshresthaDocumento33 pagineClassification Tree - Utkarsh Kulshrestha: Earn in G Is in Learnin G - Utkarsh KulshresthaN MaheshNessuna valutazione finora
- 1602.07360v1 - SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level Accuracy With 50x Fewer Parameters and 1MB Model Size - 2016Documento5 pagine1602.07360v1 - SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level Accuracy With 50x Fewer Parameters and 1MB Model Size - 2016ajgallegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Language UnderstandingDocumento41 pagineNatural Language Understandingankurgarg123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 w95 LRT OverallDocumento100 pagine02 w95 LRT OverallPRASARANA LRTJNessuna valutazione finora
- Mastery 3 (MIL)Documento2 pagineMastery 3 (MIL)Jude Mandal MetanteNessuna valutazione finora
- Visual Foxpro Bsamt3aDocumento32 pagineVisual Foxpro Bsamt3aJherald NarcisoNessuna valutazione finora
- ByD DemoScript Project MGMTDocumento21 pagineByD DemoScript Project MGMTLakhbir SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Apd Summer Institute ApplicationDocumento3 pagineApd Summer Institute ApplicationFNessuna valutazione finora
- Junos Telemetry InterfaceDocumento150 pagineJunos Telemetry InterfacedeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8: Future Outlook: Central Business Configuration For SAP S/4HANA CloudDocumento9 pagineUnit 8: Future Outlook: Central Business Configuration For SAP S/4HANA CloudKarina San MartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Aman Choudhary BCA-1 C PracticalDocumento65 pagineAman Choudhary BCA-1 C PracticalPoras ChahandeNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 3Documento4 pagineQuiz 3Kereen Pearl PascuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ahb7816t ElDocumento3 pagineAhb7816t ElcjtrybiecNessuna valutazione finora
- Oracle K Gudie For RAC11g - Install - WindowsDocumento180 pagineOracle K Gudie For RAC11g - Install - WindowsMuhammad KhalilNessuna valutazione finora
- Primavera P6 Version 20.12 Is Out. Here's What's New 1Documento14 paginePrimavera P6 Version 20.12 Is Out. Here's What's New 1meshmeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 4 Paper - Cellular Neural NetworkDocumento13 pagineLec 4 Paper - Cellular Neural NetworkPraveena AnnaduraiNessuna valutazione finora
- Principle of LCD DisplayDocumento23 paginePrinciple of LCD DisplayZulhilmi BalokolosNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspire Company Profile:, Aspire Exam Cracking KITDocumento17 pagineAspire Company Profile:, Aspire Exam Cracking KITChandrasekhar Uchiha100% (1)
- Chapter 12Documento34 pagineChapter 12Thanh Van DaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Access The GUI On Unity Array With No Network access-KB 501073Documento3 pagineAccess The GUI On Unity Array With No Network access-KB 501073Алексей ПетраковNessuna valutazione finora
- F7400 Vs BHT8048Documento1 paginaF7400 Vs BHT8048Arief RahardjoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Conceptualized InteractionDocumento32 pagineChapter 2 Conceptualized InteractionnancyNessuna valutazione finora
- PPM Pulse-Position ModulationDocumento2 paginePPM Pulse-Position ModulationfiraszekiNessuna valutazione finora
- DELEM Install GBDocumento81 pagineDELEM Install GBSylwester C.Nessuna valutazione finora