Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Urinary System: Rita Rosita
Caricato da
Eko PrasTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Urinary System: Rita Rosita
Caricato da
Eko PrasCopyright:
Formati disponibili
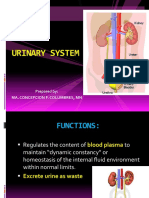
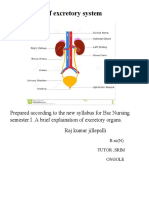
Urinary System
Rita Rosita
Three Functions of the Urinary System
1. Excretion:
removal of organic wastes from body
fluids
2. Elimination:
discharge of waste products
3. Homeostatic regulation:
of blood plasma volume and solute
concentration
Components of the Urinary System
Kidney :
Function :
Excrete final product of metabolic
activities & excess watercontrol
concentration substances in body fluid
Release : erythropoitin, renin, 1,25
hydrocholecalciferol
Location of the kidneys
Are located on either
side of vertebral
column T
12
L
3
):
The right kidney is
slightly lower than the
left kidney because of
the liver's size and
position.
superior surface capped
by suprarenal gland
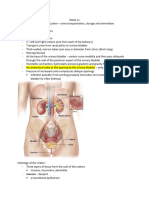
Kidney
Is about 10 cm long, 5.5 cm wide, and
3 cm. thick
Weighs about 150 g
Hilum
Point of entry for renal artery and renal
nerves
Point of exit for renal vein and ureter
Renal Surface Projection
Anterior surface :
Hillar centre at transpyloric plane, 5cm lateral
from midline, slightly medial from cart 9
th
costae
Reniform : upper pole 2,5cm from midline, lower
7,5cm
Posterior surface :
Hillar centre : Lower border of V.L1, 5cm from
midline
Reniform : lower pole 2,5cm from crista iliaca
Renal Relation
Kidneys concentric layers
Renal Capsule
A layer of collagen fibers
Covers outer surface of entire organ
Adipose Capsule
A thick layer of adipose tissue
Surrounds renal capsule
Renal Fascia
A dense, fibrous outer layeranterior and posterior
layer
Anchors kidney to surrounding structures
Gross Anatomy
Shape
Two bean-shaped organs
Lateral surface -- convex
Medial surface -- concave
Renal Pelvis
Large, funnel-shaped chamber
Consists of 2 or 3 major calyces
Connected to ureter, which drains kidney
The Structure of the Kidney
VASKULARISASI
A. RENALIS
CABANG AORTA ABDOMINALIS VL2
PECAH MENJADI DIVISI ANT. & DIVISI
POST. 5 CAB. UNTUK 5 SEGMEN
VASKULARISASI :
APICAL (SUP.) POLUS CRANIALIS
(V&D)
ANTERIOR SUPERIOR
ANTERIOR INFERIOR
INFERIOR 1/3 BAG. BAWAH (V&D)
POSTERIOR
LINEA BRODEL avascular
S35
S36
Blood Supply :
A.renalis
A.segmentalis
A.interlobaris
A.arcuata
A.interlobularis
A.afferent
Upper urinary tract
Renal calyces and
pelvis
Located : sinus
renalis
Pelviureteric
junction
extrahillar, lower
part of medial
border of kidney
Ureters
Pair of muscular tubes 30 cm. (12 in)
Each ureter begins at the funnel-
shaped renal pelvis
Tubular organs that transport urine
Move urine from the kidneys to
urinary bladder
Radiography
Descending or excretion pyelography
Ascending or retrograde pyelography
Normal capping of the minor
calyces clinically important
obliterated hydronephrosis
The constriction of
ureter
PELVIS RENALIS URETER
PARS ABD. PARS PELVINA
BEFORE ENTER URINARY
BLADDER
Urinary Bladder
Functions as
temporary reservoir
urine storage
Full bladder can
contain 1 liter of urine
Lining the urinary
bladder has folds
(rugae) that disappear
as bladder fills
The Trigone of the
Urinary Bladder :Is a
triangular area
bounded by:
openings of ureters
entrance to urethra
VESICA URINARIA
BENTUK/UKURAN/POSISI SGT. BERVARIASI
KAPASITAS : RATA2 120 - 320 CC ( 280 CC)
NORMAL MAX 500 CC
BAGIAN2: 4 FACIES : SUPERIOR
POST.(FUNDUS = BASIS)
2 INFEROLAT. COLLUM
APEX
EXCAVATIO : VESICORECTALIS
VESICOUTERINA
SYMPHYSEO-VESICALIS
Bladder capacity
125-320 cc
Mictie : 280 cc
> 500cc pain
caused by tension
Reffered pain :
T11- L2, S2-4
lower ant abd wall,
perineum, penis
Begins at the neck of the
urinary bladder
Moves urine from urinary
bladder to the outside of the
body
Females = 4 cm. (1.5 in.) long
Males = 20 cm. (8 in.) long
Divided into prostatic,
membranous, and spongy
(penile) portions.
Male urethra also
transports semen during
ejaculation
Urethra
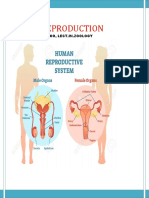
Reproductive System
The Reproductive System
Gonads:
organs that produce gametes and
hormones
Ducts:
receive and transport gametes
Accessory glands:
secrete fluids into ducts
Perineal structures:
collectively known as external genitalia
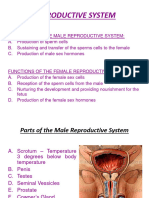
Male Reproductive System
Production and Pathway
of Spermatozoa :
Testes
Epididymis
Ductus deferens
vas deferens
Ejaculatory duct
Urethra
Accessory Organs
Secrete fluids into ejaculatory
ducts and urethra:
seminal vesicles
prostate gland
bulbourethral glands
External Genitalia
Scrotum
Encloses testes
Is a fleshy pouch
Suspended inferior to perineum
Anterior to anus
Posterior to base of penis
Penis
erectile organ
contains distal portion of urethra
Testes
Egg-shaped
5 cm long, 3 cm wide, 2.5 cm thick
Weighs 1015 g
Hangs in scrotum
The Structure and Function of Testes
Structure Seminiferous
tubules
Produce sperm
Each is about 80 cm long
Testis contains about 1/2 mile of
tightly-coiled seminiferous tubules
Spermatogenesis
Is the process of sperm production
Begins at outermost cell layer in
seminiferous tubules
Proceeds toward lumen
Hormone Production
Testosterone
TESTES LAYERS
TUNICA VAGINALIS :
Lamina parietalis
Lamina visceralis
TUNICA ALBUGINEA.
- MEDIASTINUM TESTIS.
SEPTA 250
LOBULUS
Lamina parietalis
tunica vaginalis
Lamina visceralis
tunica vaginalis
Tunica albuginea
The beginning of male reproduction tract
Spiral form canal and have 7 m long
Attachment at margo posterior testis
Have three segment :caput, corpus, and
cauda
EPIDIDYMIS.
Cauda epidydimis-
ductus ejaculatorius
Each about 4045 cm
long
Start form cauda
epididymis
Storage of sperm
Ductus Deferens
About 2 cm long
Merger of ampula
ductus deferens and
ductus vesica seminalis
Passing through
prostate gland
Enter the urethra pars
prostatica
Ductus ejaculatorius
Glandula Prostate
Organ berotot dengan
diameter kl 4 cm.
Melingkari urethra
proximalis:
Berada ddi bawah
versica urinaria
Terdiri dari 30- 50
glandular
tubuloalveoler.
Dibungkus otot polos.
Membentuk 20 30 %
volume semen.
PROSTAT.
BAGIAN BAGIAN:
PERMUKAAN : POSTERIOR
ANTERIOR
INFEROLATERAL (2).
LOBUS: SATU LOBUS MEDIUS.
DUA LOBUS LATERAL.
SCROTUM
Contains of:
1. TESTES
2. EPIDIDYMIS
3. FUNICULUS SPERMATICUS.
FUNICULUS SPERMATICUS
Consist of:
1. DUCTUS DEFERENS.
2. A.TESTICULARIS
3. PLEXUS PAMPINIFORMIS.
4. A.CREMASTERICA.
5. LYMPH
PEMBUNGKUS FUNICULUS
SPERMATICUS.
SCROTUM
FASCIA SPERMATICA EXTERNA
(fascia M.obliquus abdominis externus)
FASCIA/M. CREMASTERICA
(fascia m.obliquus abdominis internus)
FASCIA SPERMATICA INTERNA
(fascia transversalis)
TUNICA VAGINALIS (peritoneum)
VASCULARISASI
A.CREMASTERICA
A.SPERMATICA INTERNA
R.SCROTALIS ANTERIOR
CABANG DARI A. PUDENDA EXTERNA.
R.SCROTALIS POSTRIOR
CABANG DARI A.PUDENDA INTERNA.
Penis
Tubular Organ :
Passed by urethrae
Passages urine
Introduces semen into
female vagina
Three segment:
Radix penis
Corpus penis
Glans penis
Blood Supply of Penis
A. BULBOURETHRALIS
A. PROFUNDA PENIS.
A. DORSALIS PENIS.
INNERVATION
N.DORSALIS PENIS.
R.PROFUNDA N.PERINEALIS.
R.ANTERIOR N.ILIOINGUINALIS.
SPERM TRANSPORT
TUBULUS SEMINIFERUS TUB.RECTI
RETE TESTIS DUCTUS EFFEREN
EPIDYDIMIS (storages and maturation)
DUCTUS DEFERENS DUCTUS
EJACULATORIUS URETHRA
Organs of the Female Reproductive
System
Ovaries
Uterine tubes
Fallopian tubes
Uterus
Vagina
External
genitalia
The Female Reproductive
System
Produces sex hormones and functional
gametes
Protects and supports developing
embryo
Nourishes newborn infant
Ovaries
The functions :
Production of
immature female
gametes
(oocytes)
Secretion of
female sex
hormones
(estrogens,
progestins)
Oogenesis
Also called ovum
production
Begins before birth
Accelerates at puberty
Ends at menopause
Ovarian Cycle
Includes monthly
oogenesis:
between puberty and
menopause
Uterine (Fallopian) Tubes
Fallopian tubes or
oviducts
Are hollow, muscular
tubes about 13 cm long
Transport oocyte from
ovary to uterus
Three Segments of the Uterine
Tube
1. Infundibulum:
an expanded funnel near ovary
fimbriae fingerlike processes
surrounding entrance to
uterine tube
Inner surfaces lined with cilia:
beat toward middle segment
2. Ampulla:
middle segment
smooth muscle layers in wall
become thicker approaching
uterus
3. Isthmus:
a short segment between
ampulla and uterine wall
Functions of the Uterine Tubes
Involves:
ciliary movement
peristaltic contractions in walls of uterine tube
From infundibulum to uterine cavity:
normally takes 34 days
For fertilization to occur:
secondary oocyte must meet spermatozoa during
first 1224 hours
Fertilization typically occurs:
near boundary between ampulla and isthmus
Uterus
Provides for
developing embryo
(weeks 18) and fetus
(week 9 through
delivery):
1. mechanical protection
2. nutritional support
3. waste removal
Regions of the Uterus
1. Body
Also called corpus
Is largest portion of uterus
Ends at isthmus
2. Fundus
Is rounded portion of uterine
body:
superior to attachment of uterine
tubes
3. Cervix
Is inferior portion of uterus
Extends from isthmus to vagina
Distal end projects about 1.25 cm
into vagina
Vagina
Is an elastic, muscular tube
Extends between cervix and
vestibule
7.59 cm long
Highly distensible
Cervix
projects into vaginal canal
Fornix
is shallow recess surrounding
cervical protrusion
Lies parallel to:
rectum, posteriorly
urethra, anteriorly
Functions of the Vagina
1. Passageway for elimination of
menstrual fluids
2. Receives spermatozoa during sexual
intercourse
3. Forms inferior portion of birth canal
The Female External Genitalia
Mons Pubis and Labia
Majora
Form outer limits of vulva:
protect and cover inner
structures
contain adipose tissue
Sebaceous glands and
apocrine sweat glands:
secrete onto inner surface
of labia majora
The Female External Genitalia
Labia Minora
Small folds
Covered with smooth, hairless skin
Clitoris
A small protruberance in vestibule
Has same embryonic structures as penis
Extensions of labia minora:
form prepuce or hood
The Female External Genitalia
Vestibule
Is a central space bounded by the labia
minora
Glands
Paraurethral (Skenes) glands :discharge
into urethra near external opening
Vestibularis (Bartholins) glands :
discharge into vagina opening
Mammary Glands - Breast
Lie in pectoral fat pads deep
to skin of chest
Modified apocrine sweat
glands
15 to 20 lobes divided by
connective tissue
Radial arrangement around nipple
Nipple on each breast
contains ducts from mammary
glands to surface
Areola
reddish-brown skin around each
nipple
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- General Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento62 pagineGeneral Anatomy of Urinary SystemSARABIA, ARVIN JR.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Male Reproductive Tract: Kristel Paulane Fleur Lubrin-Oandasan MD DpogsDocumento28 pagineMale Reproductive Tract: Kristel Paulane Fleur Lubrin-Oandasan MD DpogsFaith CarylaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi Blok 17Documento34 pagineAnatomi Blok 17Lintang SuroyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System AnatomyDocumento43 pagineUrinary System AnatomyAmelia AnjaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Urogenital SystemDocumento33 pagineUrogenital SystemimaninjaloenkosiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System: Prepared By: Ma. Concepcion F. Columbres, MNDocumento38 pagineUrinary System: Prepared By: Ma. Concepcion F. Columbres, MNAl Serenoso100% (1)
- Uretra & GinjalDocumento47 pagineUretra & GinjalHeka Putri JayantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Digestive and UrinaryDocumento23 pagineDigestive and UrinarySamantha EllaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Ureters Urinary Bladder UrethraDocumento20 pagineUreters Urinary Bladder UrethraFlora PopaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System TheoryDocumento29 pagineUrinary System Theoryوجد عمرNessuna valutazione finora
- General Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento43 pagineGeneral Anatomy of Urinary Systemiqra riazNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction MaleDocumento57 pagineReproduction MalealidudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive System (Week 17)Documento95 pagineReproductive System (Week 17)Krisha Mabel TabijeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento34 pagineAnatomy of Urinary Systemhana100% (1)
- Urinary System and Male Genital OrgansDocumento28 pagineUrinary System and Male Genital Organsapi-19641337Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocumento39 pagineGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- #1 Anatomi Fisiologi Urogenital SystemDocumento24 pagine#1 Anatomi Fisiologi Urogenital SystemNur azriyati PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- Human ReproductionDocumento15 pagineHuman ReproductionAnkit PruthwirajNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Dr. Aguirre Pancreas: ND RDAlbert CorderoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraDocumento16 pagineAnatomy of Urinary Bladder and UrethraAmalina ZolkefleeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento6 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Male and Female Reproductive System Female Reproductive Anatomy and PhysiologyJustJ ThingsNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento10 pagineReproductive SystemMatt MasilonganNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen (Repaired)Documento174 pagineAbdomen (Repaired)Merellyn Hurtado PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocumento44 pagineThe Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityRahmawati HamudiNessuna valutazione finora
- Urogenital (UG) Is Derived FromDocumento7 pagineUrogenital (UG) Is Derived FromSushant SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Inisiasi VIIDocumento42 pagineInisiasi VIIjoan wanadriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary SystemDocumento8 pagineThe Urinary SystemOlivia MorrisonNessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Documento7 pagineHandouts - Urinary System Sp11 BIO 160Kelly Trainor100% (2)
- Anatomy of Excretory SystemDocumento12 pagineAnatomy of Excretory SystemSANJEEVA REDDYNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 Urinary System: Lesson 1Documento23 pagineChapter 9 Urinary System: Lesson 1Tia AriantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bladder&UrethraDocumento36 pagineBladder&UrethraBalaji KarunakaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System: Anatomy and Physiology IiiDocumento48 pagineUrinary System: Anatomy and Physiology IiiShelby Dawn100% (1)
- Topik 2 2021Documento26 pagineTopik 2 2021AnnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy & Physiology URINARY TRACTDocumento28 pagineAnatomy & Physiology URINARY TRACTabdullatifNessuna valutazione finora
- LECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Documento45 pagineLECT 2anatomy and Physiology of Pregnancy 2Umer RafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- Tractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu MedanDocumento29 pagineTractus Urinarius: Departemen Anatomi Fk-Usu Medanjazira rezkikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 Genital SystemDocumento32 pagineChapter 6 Genital Systemapi-19916399Nessuna valutazione finora
- General Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento41 pagineGeneral Anatomy of Urinary Systemtriana_niman100% (2)
- Reproductive System - CompressedDocumento109 pagineReproductive System - CompressedNoel Calvo Macarine100% (2)
- Ma. Elizabeth F. FontanillaDocumento48 pagineMa. Elizabeth F. Fontanillatam mei100% (1)
- Abdomen (Repaired)Documento172 pagineAbdomen (Repaired)OstazNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive System 1Documento9 pagineReproductive System 1Marvel NnaemekaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy N Physiology of UtiDocumento6 pagineAnatomy N Physiology of UtiMarjorie PalaganasNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive SystemDocumento7 pagineReproductive Systemcollege code - 5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento12 pagineUrinary System Anatomy and PhysiologyCris Vincent Suma-oy100% (1)
- General Urinary SystemDocumento41 pagineGeneral Urinary SystemCollin LucasNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento4 pagineUrinary SystemRoiland Atienza BaybayonNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Development of UrethraDocumento18 pagineAnatomy and Development of UrethraSameer MahakalkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Reproduction Logo NotesDocumento25 pagineHuman Reproduction Logo Notespajice8959Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology The Female Reproductive SystemDocumento11 pagineAnatomy and Physiology The Female Reproductive Systemmelody_kaye272000Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Male Reproductive SystemDocumento4 pagineThe Male Reproductive Systemmbok diyirNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento31 pagineUrinary SystemAyro Business CenterNessuna valutazione finora
- The Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocumento41 pagineThe Urinary System: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin Universityraynhard b. fandresNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento40 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemSAYMABANUNessuna valutazione finora
- Ap Reprod MasculinoDocumento87 pagineAp Reprod MasculinoMelani Saravia ortizNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary Excretory System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.DDocumento15 pagineUrinary Excretory System: Ma. Minda Luz M. Manuguid, M.Dchocoholic potchiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Renal SystemDocumento8 pagineThe Human Renal SystemRobert CaseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Lower Urinary TractDocumento27 pagineAnatomy of The Lower Urinary Tractمحمد حميدانNessuna valutazione finora
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineDa EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNessuna valutazione finora
- 258 509 1 SMDocumento7 pagine258 509 1 SMEko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pi Is 0272638616302645Documento9 paginePi Is 0272638616302645Eko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysate Sodium Prescription and Blood Pressure in Hemodialysis PatientsDocumento10 pagineDialysate Sodium Prescription and Blood Pressure in Hemodialysis PatientsEko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension in HemodialysisDocumento7 paginePrevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension in HemodialysisEko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal PendukungDocumento7 pagineJurnal PendukungEko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Pendukung 2Documento13 pagineJurnal Pendukung 2Eko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension in HemodialysisDocumento7 paginePrevalence and Risk Factors of Hypertension in HemodialysisEko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- 340 2407 1 PBDocumento7 pagine340 2407 1 PBEko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Documentatin & Reporting Nurses by M.fathoni 2013Documento66 pagine9 Documentatin & Reporting Nurses by M.fathoni 2013Eko PrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Vision Medilink Product DetailsDocumento4 pagineVision Medilink Product DetailsRaj SekarNessuna valutazione finora
- AnswersDocumento4 pagineAnswersamitmehta29Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusDocumento4 pagine4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusZia Ammarah SaripNessuna valutazione finora
- Hoja Tecnica IS 320.1 Zona 1Documento2 pagineHoja Tecnica IS 320.1 Zona 1susanivar adrianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Villavilla Vs CADocumento6 pagineVillavilla Vs CABobby ParksNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse Production in India: Major Constraints and Way ForwardDocumento33 paginePulse Production in India: Major Constraints and Way ForwardDeus EXNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Quality Parameters A Case Study of Karnafully - Dr. A K MajumderDocumento6 pagineWater Quality Parameters A Case Study of Karnafully - Dr. A K MajumderMd. Badrul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Steri - Cycle I 160 New GenDocumento16 pagineSteri - Cycle I 160 New GenLEO AROKYA DASSNessuna valutazione finora
- 100518-Concrete Roof Installation Manual 0515Documento26 pagine100518-Concrete Roof Installation Manual 0515Moe Oo HtunNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Conduct A Situation AnalysisDocumento10 pagineHow To Conduct A Situation AnalysisÂmany AymanNessuna valutazione finora
- Denon DHT-T100 Ver 3 PDFDocumento34 pagineDenon DHT-T100 Ver 3 PDFboroda241083% (6)
- The Consumption of WaterDocumento2 pagineThe Consumption of WaterasungapeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mouse HardyweinbergDocumento5 pagineMouse Hardyweinbergapi-477617112Nessuna valutazione finora
- Northern NVProvider DirectoryDocumento82 pagineNorthern NVProvider DirectoryGuru NandeshwarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S0378517311000226 MainDocumento9 pagine1 s2.0 S0378517311000226 MainFIRMAN MUHARAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Green Rating System - Ritik JainDocumento6 pagineGreen Rating System - Ritik Jainmayuresh barbarwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ink Presentation Final (TOYO)Documento34 pagineInk Presentation Final (TOYO)komal100% (1)
- Pneumatic Oscillator Valve - Pneumatic Controls - Impulse Automation LTDDocumento3 paginePneumatic Oscillator Valve - Pneumatic Controls - Impulse Automation LTDDindin NajmudinNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Laxmi Niwas PalaceDocumento72 pagineReport On Laxmi Niwas PalaceRenu MahayachNessuna valutazione finora
- Valerie Tillard Murder: Probable CauseDocumento11 pagineValerie Tillard Murder: Probable CauseLeigh EganNessuna valutazione finora
- ThreeDocumento6 pagineThreeapi-340425056Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comparitive Study of Pile Foundations With Foundations On Stone Column Treated Ground 170704090313Documento23 pagineComparitive Study of Pile Foundations With Foundations On Stone Column Treated Ground 170704090313anurag hazarikaNessuna valutazione finora
- Index: General Notices (1) Apply To All Monographs and Other TextsDocumento36 pagineIndex: General Notices (1) Apply To All Monographs and Other TextsGhenaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-1FlowCharts For HaccpDocumento3 pagine1-1FlowCharts For HaccpPeter George0% (1)
- Diesel Generator 350-To-500-Kw-Specs-SheetDocumento9 pagineDiesel Generator 350-To-500-Kw-Specs-SheetamrNessuna valutazione finora
- Cocoa Nursery Manual Feb 2013Documento51 pagineCocoa Nursery Manual Feb 2013jeffreyNessuna valutazione finora
- wk8 Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Immune Disorders Part 2Documento32 paginewk8 Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has An Immune Disorders Part 2claire yowsNessuna valutazione finora
- Carcinoma of Prostate: Dr. Saadat Hashmi Consultant UrologistDocumento48 pagineCarcinoma of Prostate: Dr. Saadat Hashmi Consultant UrologistMuhammad ArsalNessuna valutazione finora
- Important Topics RTCDocumento18 pagineImportant Topics RTCjoydeep12Nessuna valutazione finora