Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Gas Dehydration
Caricato da
MahendraToratiDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Gas Dehydration
Caricato da
MahendraToratiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
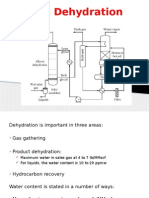
Dehydration is important in three areas:
Gas gathering
Product dehydration:
Maximum water in sales gas at 4 to 7 lb/MMscf
For liquids, the water content is 10 to 20 ppmw
Hydrocarbon recovery
Water content is stated in a number of ways:
Mass of water per volume of gas, lb/MMscf
Concentration, parts per million by volume
(ppmv)
In any mixture, where both the gas and liquid
phases are in equilibrium, each component, i,
in the mixture obeys the relationship
Calculate the water content of the sweet
natural gas shown in Table 6.1at 300 psia and
80F
The MW of the gas mixture is 18.41
Specific gravity : Sp. Gr.= 18.41/28.96 = 0.636
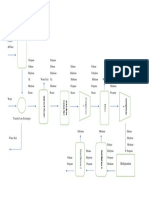
Two processes, absorption and adsorption, are the most common
ABSORPTION PROCESSES:
Water levels in natural gas can be reduced to the 10 pmmv range in a physical
absorption process.
The solvent used for the absorption should have the following properties:
A high affinity for water and a low affinity for hydrocarbons
A low volatility at the absorption temperature to reduce vaporization
Losses
A low viscosity for ease of pumping and good contact between the gas and liquid
phases
A low potential for corrosion
The two types of adsorption are physical adsorption and
chemisorption.
In physical adsorption, the bonding between the adsorbed
species and the solid phase is called van der Waals forces.
Physical adsorption is an equilibrium process like
vaporliquid equilibria
Two steps are involved in adsorbing a trace gas
component.
The first step is to have the component contact the surface
The second step is to have it travel through the pathways
inside the adsorbent
When used as a purification process,
adsorption has two major disadvantages:
o It is a fixed-bed process that requires two or
more adsorption beds for continuous
operation.
o It has limited capacity and is usually
impractical for removing large amounts of
impurity.
Three types of commercial adsorbents are in
common use in gas processing plants:
Silica gel, which is made of pure SiO2
Activated alumina, which is made of Al2O3
Molecular sieves
To minimize MTZ thickness, the bed diameter
should be kept small.
This feature also reduces the wall thickness
of the high-pressure vessels and increases
the superficial velocity, which improves mass
transfer in the gas phase.
An existing 4A molecular sieve bed has been
processing 80 MMscfd on a 12-hour cycle with two
beds. Exit gas goes to a cryogenic turboexpander
section. Gas flow is increased to 100 Mscfd.
Estimate the increased pressure drop and
determine whether the bed capacity allows
continued operation on a 12-hour cycle or the
cycle time should be changed. The gas enters the
bed at 120F and 950 psig. Water content is 60% of
saturation at 120F. The molar mass of the gas is
18.5, with a viscosity of 0.014 cP and a
compressibility factor of 0.84. The adsorption bed
contains 41,000 lbs of 1/8-inch diameter beads
with a bulk density of 44 lb/ft3. The inside wall
diameter of the bed is 7.5 ft. The absorbent was
installed 2 years ago.
Desiccant Processes:
Can reduce the water content down to 20 ppmv
Membrane Processes
Refrigeration Processes
Twister Technology
Vortex Tube Technology
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Gas DehydrationDocumento15 pagineGas DehydrationRama Krishna PillaNessuna valutazione finora
- PETE 460 Natural Gas TechnologyDocumento34 paginePETE 460 Natural Gas TechnologyatiyosdeNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas DehydrationDocumento7 pagineGas DehydrationChemical.AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrates Part 3b-Dehydration-Glycol Rev2 (Oct03)Documento26 pagineHydrates Part 3b-Dehydration-Glycol Rev2 (Oct03)gad480Nessuna valutazione finora
- Queries On TEG Gas Dehydration - Industrial Professionals - CheresourcesDocumento6 pagineQueries On TEG Gas Dehydration - Industrial Professionals - CheresourcesCH1253Nessuna valutazione finora
- Desalter Operation OptimizationDocumento3 pagineDesalter Operation OptimizationRexx MexxNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment Catalogue API Oil SeparatorDocumento2 pagineEquipment Catalogue API Oil Separatorbesant vargheesNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Crude Oil RefiningDocumento57 pagine6 Crude Oil RefiningAkashNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatic Coalescer (Laminar Flow)Documento3 pagineElectrostatic Coalescer (Laminar Flow)Yusof SundangNessuna valutazione finora
- Control Valve Sizing Theory, Cavitation, FlashingDocumento45 pagineControl Valve Sizing Theory, Cavitation, FlashingVitória MarcenariaNessuna valutazione finora
- ETI Electrostatic BrochureDocumento6 pagineETI Electrostatic BrochureHector RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Crude Oil BlendingDocumento20 pagineCrude Oil BlendingRajan BalkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Petroleum IndustryDocumento39 paginePetroleum IndustryQuenie Rose RontalNessuna valutazione finora
- Vis BreakingDocumento21 pagineVis BreakingAhmed Hassan RashedNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Field Engineering - Gas Well PerformanceDocumento20 pagineGas Field Engineering - Gas Well PerformanceLoh Chun LiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Desalter OperationDocumento19 pagineDesalter OperationmohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- IPTC 10735 Process Optimization in Gas Sweetening Unit-A Case StudyDocumento7 pagineIPTC 10735 Process Optimization in Gas Sweetening Unit-A Case StudyGary Kiel Palacios EspinozaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Quick Look at DesaltingDocumento12 pagineA Quick Look at Desaltingananth2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas DehydrationDocumento61 pagineGas Dehydrationraja.mtNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study of Foaming and Carry-Over Problems in Oil and Gas SeparatorsDocumento6 pagineA Study of Foaming and Carry-Over Problems in Oil and Gas SeparatorsWendy V. DomínguezNessuna valutazione finora
- PETRECO Bilectric Desalters: State-Of-The-Art Efficient SystemsDocumento2 paginePETRECO Bilectric Desalters: State-Of-The-Art Efficient SystemsRoyster CabralNessuna valutazione finora
- MEG Scaling in Oil Gas EnvironmentDocumento209 pagineMEG Scaling in Oil Gas EnvironmentAdrian YongNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil Ref Walk ThroughDocumento7 pagineOil Ref Walk ThroughSumedh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Petroleum & Energy StudiesDocumento5 pagineUniversity of Petroleum & Energy Studieskrishnaswamy9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crude Oil Refinery-Short VersionDocumento14 pagineCrude Oil Refinery-Short Versionligia hancuNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Compressible FlowDocumento14 pagineIntroduction To Compressible Flowram kishor singhNessuna valutazione finora
- The Progress of Desulfurization Technology For Crude OilDocumento6 pagineThe Progress of Desulfurization Technology For Crude OiljoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Pumping of LiquidsDocumento20 paginePumping of Liquidsahmedyashar67% (3)
- 8 I LK? L 5 5: (19) United StatesDocumento14 pagine8 I LK? L 5 5: (19) United StatesKeysler PonceNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Gas Cleaning and TreatmentDocumento13 pagineNatural Gas Cleaning and Treatmentvamsix100% (1)
- Lecture 1 IntroductionDocumento26 pagineLecture 1 IntroductionRozh SartipNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Is The Result of Industry 'S Move To Use Higher PressuresDocumento2 pagineProblem Is The Result of Industry 'S Move To Use Higher PressuresFadhliNessuna valutazione finora
- Science and Technology of Novel Process For Deep Desulfurization of Oil Refinery StreamsDocumento25 pagineScience and Technology of Novel Process For Deep Desulfurization of Oil Refinery StreamsJorge L. Rivero S.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Gas Liquids RecoveryDocumento17 pagineNatural Gas Liquids Recoveryabdur rehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Advances in Electrostatic Treatment of Crude OilDocumento5 pagineAdvances in Electrostatic Treatment of Crude OilAnonymous bHh1L1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Debutaniser OptimisationDocumento5 pagineDebutaniser OptimisationAntonNessuna valutazione finora
- Improving Hydrotreater OperationsDocumento5 pagineImproving Hydrotreater Operationssaleh4060Nessuna valutazione finora
- Separator Sizing - PPTDocumento21 pagineSeparator Sizing - PPTD K SNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Transportation Storage I 2018Documento52 pagineGas Transportation Storage I 2018Johny ImitazNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric CO2 To MethanolDocumento16 pagineAtmospheric CO2 To MethanolMUTHU KESHAV KNessuna valutazione finora
- Lawal KA 2011 PHD Thesis PDFDocumento327 pagineLawal KA 2011 PHD Thesis PDFpedro aguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Eletrochemicaldesalter 191231094907Documento6 pagineEletrochemicaldesalter 191231094907ShakerMahmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- BRENT ALSPACH - Produced Water and Salinity Management The Desalination FrontierDocumento7 pagineBRENT ALSPACH - Produced Water and Salinity Management The Desalination FrontierPAOLANessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Fundamentals of Gas Dehydration Design and Operation With Glycol Solutions by Pearce and Sivalls PDFDocumento83 pagine5 Fundamentals of Gas Dehydration Design and Operation With Glycol Solutions by Pearce and Sivalls PDF许凉发Nessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Gas Processing - Summary & IntroductionDocumento7 pagineNatural Gas Processing - Summary & IntroductiondndudcNessuna valutazione finora
- Reforming and IsomerizationDocumento17 pagineReforming and Isomerizationhala mrayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Natural Gas Dehydration-Netusil & DitlDocumento20 pagineNatural Gas Dehydration-Netusil & DitlClemenNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Conversion ProcessesDocumento24 pagineThermal Conversion ProcessesAl JawadNessuna valutazione finora
- 18CH036 Hydrotreating ProcessDocumento17 pagine18CH036 Hydrotreating ProcessSuleka RanasingheNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated Gasification Combined Cycle: Acid Gas RemovalDocumento3 pagineIntegrated Gasification Combined Cycle: Acid Gas RemovaljuhriloverNessuna valutazione finora
- s3 - Sweetening ProcessDocumento38 pagines3 - Sweetening ProcessMd Abid AfridiNessuna valutazione finora
- Group Seminar On DesalterDocumento21 pagineGroup Seminar On Desalterinderdip75% (4)
- Ethylene CrackerDocumento28 pagineEthylene CrackerAbhinav AjmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- A-Analysis of Crude Oil Electrostatic Desalters Performance PDFDocumento5 pagineA-Analysis of Crude Oil Electrostatic Desalters Performance PDFLuis CortesNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Cracker PFDDocumento1 paginaSteam Cracker PFDMUHAMMAD NUR KHAIRINessuna valutazione finora
- Anaerobic TreatmentDocumento6 pagineAnaerobic TreatmentChandra JyotiNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid Desiccant DehydrationDocumento5 pagineSolid Desiccant Dehydrationca_minoNessuna valutazione finora
- Purge Gas RecoveryDocumento9 paginePurge Gas RecoveryMithilesh ShamkuwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Tubular Membrane-Maintenance and CleaningDocumento16 pagineTubular Membrane-Maintenance and CleaningM TNessuna valutazione finora
- Ion Exchange: Application of Ion Exchanger Water SofteningDocumento7 pagineIon Exchange: Application of Ion Exchanger Water SofteningListo A4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Propylene DerivativesDocumento25 paginePropylene DerivativesMahendraTorati100% (1)
- C4 and C5 Compounds: B.V.R.BhaskarDocumento12 pagineC4 and C5 Compounds: B.V.R.BhaskarMahendraToratiNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllabusDocumento7 pagineSyllabussaleem32Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Computer SystemsDocumento92 pagineIntroduction To Computer SystemsAmit SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Hydrates As An Unconventional Resource Asian PerspectiveDocumento44 pagineGas Hydrates As An Unconventional Resource Asian PerspectiveMahendraToratiNessuna valutazione finora
- M.tech ISM SyllabusDocumento38 pagineM.tech ISM SyllabusMahendraToratiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistryproject 170204054007Documento18 pagineChemistryproject 170204054007Roy BoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Report LalPirDocumento45 pagineBoiler Report LalPirAleem UllahNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Engineering Tools Gas Natural Gas DensityDocumento5 pagineHome Engineering Tools Gas Natural Gas Densityrafik1995Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blowout (Well Drilling) : Differential Sticking Is A Problem That Occurs When Drilling ADocumento6 pagineBlowout (Well Drilling) : Differential Sticking Is A Problem That Occurs When Drilling AMEUBRONessuna valutazione finora
- Upstream & Downstream PDFDocumento100 pagineUpstream & Downstream PDFIsd BambNessuna valutazione finora
- Cryogenic Tanks CatalogueDocumento14 pagineCryogenic Tanks Cataloguejayakumar04985Nessuna valutazione finora
- Minerals and Energy ResourcesDocumento7 pagineMinerals and Energy ResourcesPRASHANT SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Energy From Volcanoes: Submitted By: John Philip Rodero Submitted To: Tr. Medy PatajoDocumento4 pagineEnergy From Volcanoes: Submitted By: John Philip Rodero Submitted To: Tr. Medy PatajoAlvin Joshua RullNessuna valutazione finora
- Petron CorporationDocumento16 paginePetron CorporationzaineNessuna valutazione finora
- Mmy 170Documento4 pagineMmy 170thotalnNessuna valutazione finora
- C0210101-02-11-EN Installation - manuals - Generale - EN - 印刷 PDFDocumento20 pagineC0210101-02-11-EN Installation - manuals - Generale - EN - 印刷 PDFNhật Phong NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Coal and Petroleum (Notes) - Version 2.0-1Documento8 pagineCoal and Petroleum (Notes) - Version 2.0-1Akshat OberoiNessuna valutazione finora
- 28.01.22 Answer Key Lesson 12 - Doing WorkDocumento2 pagine28.01.22 Answer Key Lesson 12 - Doing WorkGitansh KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Current Affairs 2013Documento181 pagineCurrent Affairs 2013renu_kaushik_3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Safety ValvesDocumento11 pagineSafety ValvesMohamed AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethylene GlycolDocumento8 pagineEthylene GlycoljeswinNessuna valutazione finora
- Incident Report of Pneumatic Test FatalityDocumento3 pagineIncident Report of Pneumatic Test FatalityCarlos Jose Sibaja CardozoNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomass Conversion TechnologiesDocumento3 pagineBiomass Conversion TechnologiesYoy Sun Zoa0% (1)
- Ran K H1B Visa Sponsor Number of LCA Average SalaryDocumento7 pagineRan K H1B Visa Sponsor Number of LCA Average SalaryKitty FitzgeraldNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar Lab: Diesel Hydrotreaing Unit (DHT)Documento21 pagineSeminar Lab: Diesel Hydrotreaing Unit (DHT)Shahzen KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Captive Power Plant Anand HiraniDocumento43 pagineCaptive Power Plant Anand HiraniAnand HiraniNessuna valutazione finora
- Controlling Anti-Surge Valves in Low Flow Load Balancing OperationDocumento7 pagineControlling Anti-Surge Valves in Low Flow Load Balancing Operationmasimaha1379100% (1)
- Chemistry Crude Oil WorksheetDocumento23 pagineChemistry Crude Oil WorksheetJOEL VIVIANNessuna valutazione finora
- GF Group Project PresentationDocumento29 pagineGF Group Project PresentationTony LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Y Mahindra World City Chennai PDFDocumento31 pagineY Mahindra World City Chennai PDFGopi KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Miscible FloodingDocumento53 pagine6 - Miscible FloodingAndi Susetio100% (1)
- FM Data Sheet CompressorsDocumento14 pagineFM Data Sheet Compressorsralph1949Nessuna valutazione finora
- Simple DistillationDocumento2 pagineSimple DistillationHarvey A. JuicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Transition in PJM Resource Retirements Replacements and RisksDocumento20 pagineEnergy Transition in PJM Resource Retirements Replacements and RisksZerohedge100% (1)
- COREX MIDREX An Ideal Concept For Economic and Environmental Steel Production BoehmDocumento15 pagineCOREX MIDREX An Ideal Concept For Economic and Environmental Steel Production BoehmFernanda Brito100% (3)