Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Female Reproductive Anatomy
Caricato da
Sasikala MohanCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Female Reproductive Anatomy
Caricato da
Sasikala MohanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
1
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
ANATOMY
This information is important because it will raise your level
of awareness and understanding about your physical body.
It is imperative that you learn the changes you can expect to
experience from menarche to menopause as you live with
your female reproductive system
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
2
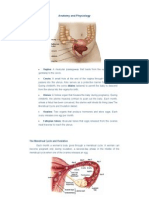
EXTERNAL GENTILIA
The vulva refers to those parts
that are outwardly visible
The vulva includes:
Mons pubis
Labia majora
Labia minora
Clitoris
Urethral opening
Vaginal opening
Perineum
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
3
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
4
MONS PUBIS
The triangular mound of fatty tissue that
covers the pubic bone
It protects the pubic symphysis
During adolescence sex hormones trigger
the growth of pubic hair on the mons pubis
Hair varies in coarseness curliness, amount,
color and thickness
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
5
LABIA MAJORA
Referred to as the outer lips
They have a darker pigmentation
The Labia Majora:
Protect the introitus and urethral openings
Are covered with hair and sebaceous glands
Tend to be smooth, moist, and hairless
Become flaccid with age and after childbirth
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
6
LABIA MINORA
Referred to as the inner lips
Made up of erectile, connective tissue that
darkens and swells during sexual arousal
Located inside the labia majora
They are more sensitive and responsive to
touch than the labia majora
The labia minora tightens during intercourse
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
7
CLITORIS
Highly sensitive organ composed of nerves, blood
vessels, and erectile tissue
Located under the prepuce
It is made up of a shaft and a glans
Becomes engorged with blood during sexual
stimulation
Key to sexual pleasure for most women
Urethral opening is located directly below
clitoris
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
8
FEMALE
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
9
VAGINAL OPENING
INTROITUS
Opening may be covered by a thin sheath
called the hymen
Using the presence of an intact hymen for
determining virginity is erroneous
Some women are born without hymens
The hymen can be perforated by many
different events
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
10
PERINEUM
The muscle and tissue located between the vaginal
opening and anal canal
It supports and surrounds the lower parts of the
urinary and digestive tracts
The perinium contains an abundance of nerve
endings that make it sensitive to touch
An episiotomy is an incision of the perinium used
during childbirth for widening the vaginal opening
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
11
INTERNAL GENITALIA
The internal genitalia consists of the:
Vagina
Cervix
Uterus
Fallopian Tubes
Ovaries
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
12
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
13
VAGINA
Fibro muscular tube, about 10 cm long
Extends from the cervix to the external genitals
It is located between the bladder,urethra and rectum,anal
canal
It functions :
As a passageway for the menstrual flow
For uterine secretions to pass down through the introitus
As the birth canal during labor
With the help of two Bartholins glands becomes
lubricated
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
14
CERVIX
The cervix connects the uterus to the vagina
The cervical opening to the vagina is small
This acts as a safety precaution against
foreign bodies entering the uterus
During childbirth, the cervix dilates to
accommodate the passage of the fetus
This dilation is a sign that labor has begun
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
15
PERINEUM
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
16
UTERUS
Commonly referred to as the womb
A pear shaped organ about the size of a clenched fist
It is made up of the endometrium, myometrium and
perimetrium
Consists of blood-enriched tissue that sloughs off each
month during menstrual cycle
The powerful muscles of the uterus expand to
accommodate a growing fetus and push it through the birth
canal
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
17
Uterus
Situated in the pelvis between bladder and
rectum
Two parts: body- upper expandable part and
cervix- lower cylindrical part
Body- fundus, anterior and posterior surface
and two lateral borders
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
18
Uterus
Arterial supply
Uterine artery
Venous drainage
Internal iliac veins
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
19
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
20
OVIDUCTS
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
21
FALLOPIAN TUBES
Serve as a pathway for the ovum to the uterus
Are the site of fertilization by the male sperm
Often referred to as the oviducts or uterine tubes
Fertilized egg takes approximately 6 to 10 days to
travel through the fallopian tube to implant in the
uterine lining
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
22
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
23
OVARIES
The female gonads or sex glands
They develop and expel an ovum each month
A woman is born with approximately 400,000 immature
eggs called follicles
During a lifetime a woman release @ 400 to 500 fully
matured eggs for fertilization
The follicles in the ovaries produce the female sex
hormones, progesterone and estrogen
These hormones prepare the uterus for implantation of the
fertilized egg
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
24
BREASTS
Organs of sexual arousal
Contain mammary glands
Consist of connective tissue that
serves as support
Each breast contain 15-25
clusters called lobes
Each lobule is connected by
ducts that open into the nipples
The nipples are made up of
erectile tissue
The pigmented around the
nipples are called the areola
Breast size is determined
primarily by heredity
Size also depends on the
existing fat and glandular tissue
Breasts may exhibit cyclical
changes, including increased
swelling and tenderness prior to
menstruation
Benign breast changes refer to
fibrocystic disease
Lumps or masses that are
noncancerous
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
25
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
26
BREAST SELF-
EXAMINATION
Women need to examine their breasts
monthly BSE
This is a proactive approach to detect
possible breast cancer
A supplement to clinical exams and
mammography
Best time for a BSE is a week after
menstruation
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
28
MENSTRUATION
Menarch, the onset of
menstruation signals the bodily
changes that transform a female
body
Average age is 12.8
Amount of bleeding varies from
woman to woman
Expulsion of blood clots
Blood color can vary from
bright red to dark maroon
Usually occurs every 25 to 32
days
Women can experience fluid
retention, cramping, mood
swings, weight gain, breast
tenderness, diarrhea, and
constipation
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
29
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
30
PITUITARY HORMONES
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
31
FOLLICLE DEVELOPMENT
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
32
OVULATION
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
33
OVARIAN HORMONES
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
34
SEX HORMONES
Follicle stimulating hormone
FHS-
Luteinizing hormone LH-
signals ovulation
Estrogen- produced throughout
the menstrual cycle
Progesterone-produced during
second half of cycle
Contributes to thickening of the
endometrium which is shed
during menstrual phase if
fertilization does not take place
Both FHS and LH are
produced in the
pituitary gland
Both estrogen and
progesterone are
produced by the
follicles in the ovaries
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
35
DYSMENORRHEA
Painful menstrual cramps
Painful menses without evidence of a physical abnormality
Believed to be normal body response to uterine
contractions
Other symptoms :
Nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal disturbances, and
fainting
Prostaglandins cause forceful, frequent uterine contractions
called cramps
Fibroids, polyps, IUD, PID, or endometriosis
UNIT 3: FEMALE
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
36
ENDOMETRIOSIS
Common cause of dysmennorrhea, dyspareunia,
and infertility
Endometrium fragments and lodges in other parts
of the pelvic cavity
Causes inflammation, bleeding, scarring,and
adhesions
Causes are still being studied
Treated through hormonal therapy, laparoscopic
surgery, or major surgical management
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Physiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Documento57 paginePhysiology of Female Reproductive System 01092010Azry MustapaNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento28 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemjeicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocumento4 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemIanne RanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocumento11 pagineAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemLenovo Legion Y520Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2-Anatomy of Reproductive SystemDocumento53 pagine2-Anatomy of Reproductive SystemMustafa SHawkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Embryology 1Documento72 pagineIntroduction To Embryology 1Sam MumoNessuna valutazione finora
- External Reproductive OrganDocumento19 pagineExternal Reproductive Organmistry100% (1)
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento6 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemAlyanna L. ArquillanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Reproductive Organs 2018Documento80 pagineMale Reproductive Organs 2018yasrul izad100% (1)
- Anatomy of Male Reproductive OrgansDocumento18 pagineAnatomy of Male Reproductive OrgansPutri HolmesNessuna valutazione finora
- Oogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in TheDocumento7 pagineOogenesis Oogenesis Is The Process Whereby Oogonia Differentiate Into Mature Oocytes. It Starts in ThebarbacumlaudeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The BreastDocumento6 pagineAnatomy of The BreastJuliana Andres100% (1)
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento34 pagineAnatomy of Urinary Systemhana100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocumento42 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemLiangkiuwiliuNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy 101 EmbryologyDocumento4 pagineHuman Anatomy 101 EmbryologyKonstantinos TheodosiadisNessuna valutazione finora
- PPP Anatomy of Endocrine SystemDocumento23 paginePPP Anatomy of Endocrine SystemMarisol AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive System: UterusDocumento44 pagineFemale Reproductive System: UterusBeni KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lymphatic SystemDocumento25 pagineLymphatic Systemumar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal MembranesDocumento17 pagineFetal MembranesQaiser InayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Gynecological Anatomy & PhysiologyDocumento39 pagineGynecological Anatomy & Physiologynursereview100% (3)
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocumento68 pagineAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemdodoNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Male Reproductive SystemDocumento45 pagineHuman Male Reproductive Systemcyber secNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary System AnatomyDocumento43 pagineUrinary System AnatomyAmelia AnjaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive System PDFDocumento48 pagineFemale Reproductive System PDFTeppy the GreatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Human Renal SystemDocumento15 pagineThe Human Renal SystemChuche SustentoNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento17 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemJasmaine RivoNessuna valutazione finora
- Gyne - Congenital AnomaliesDocumento170 pagineGyne - Congenital Anomaliesonijino100% (1)
- Review Anatomy of Endocrine SystemDocumento23 pagineReview Anatomy of Endocrine SystemAngkatan EmpatbelasNessuna valutazione finora
- Joints Anatomy PresentationDocumento41 pagineJoints Anatomy Presentationahmadnaveed99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: BY DR: AhmedDocumento82 pagineReproductive Anatomy and Physiology: BY DR: AhmedAhmed ElryahNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive Cycle: Reproductive Health I Clinical Medicine ClassDocumento77 pagineReproductive Cycle: Reproductive Health I Clinical Medicine Classmoreen kipkemoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocumento8 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAdor AbuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive SystemDocumento23 pagineFemale Reproductive SystemSheena PasionNessuna valutazione finora
- GametogenesisDocumento25 pagineGametogenesisJoanne Crishna MiguelNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiDocumento17 pagine1st Lecture On The Histology of Female Reproductive System by Dr. RoomiMudassar RoomiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocumento52 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAjay DNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive Physiology (Female)Documento23 pagineReproductive Physiology (Female)هدى قحطان جليل100% (1)
- Anatomy of Urinary SystemDocumento43 pagineAnatomy of Urinary SystemIrfan Ali JunejoNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproduction KBK 2009 - DR - DickyDocumento43 pagineFemale Reproduction KBK 2009 - DR - DickydicqszNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONDocumento67 paginePresented By, P.Jeyanthi, M.SC (N) I Year Apollo CONPaul AndersonNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal SystemDocumento18 pagineRenal SystemS GNessuna valutazione finora
- Submitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDocumento9 pagineSubmitted By: Diana M. Resultay A301/Group-3B Submitted To: Ms. ReyesDiannetotz MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelainan Penis Pada AnakDocumento23 pagineKelainan Penis Pada AnakAndrew SoerijadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproductive PhysiologyDocumento40 pagineReproductive PhysiologyBaiq Trisna Satriana100% (1)
- General Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekDocumento143 pagineGeneral Embryology Lecture 1 and 2 - Day 1-Third WeekSam MumoNessuna valutazione finora
- EmbryologyDocumento12 pagineEmbryologyIrene Sulinsia NapitupuluNessuna valutazione finora
- Female Reproductive HistologyDocumento59 pagineFemale Reproductive HistologyIta Indriani100% (2)
- Histology of Endocrine SystemMKDocumento54 pagineHistology of Endocrine SystemMKDo Ra EmonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-Fertilization & ImplantationDocumento20 pagine2-Fertilization & ImplantationMochammad Rizal Attamimi0% (1)
- Spermatogenesis, OogenesisDocumento16 pagineSpermatogenesis, Oogenesisannita100% (1)
- 1-Obs&Gynae - Anatomy and Embryology of The Female Reproductive SystemDocumento52 pagine1-Obs&Gynae - Anatomy and Embryology of The Female Reproductive Systemfadiawwad100% (3)
- The Reproductive SystemDocumento15 pagineThe Reproductive SystemMostafa Galal El Din100% (1)
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Documento36 pagineFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentDocumento54 pagineGenetic, Conception, and Fetal DevelopmentBiraito TakanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Foetal Development and CirculationDocumento7 pagine2 Foetal Development and CirculationJay PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Spermatogenesis and FertilizationDocumento21 pagineSpermatogenesis and FertilizationAyen FornollesNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.introduction To EmbryologyDocumento63 pagine8.introduction To EmbryologyAhmed OrabyNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysfunctional Uterine BleedingDocumento7 pagineDysfunctional Uterine BleedingNhorz Love UNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Nerves: DR Vinit K Ashok Adjunct FacultyDocumento27 pagineCranial Nerves: DR Vinit K Ashok Adjunct FacultySasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Urinary SystemDocumento4 pagineAnatomy Urinary Systemmmmm31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of Adrenal GlandDocumento22 pagineHistology of Adrenal GlandSasikala Mohan100% (3)
- Congenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Documento48 pagineCongenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Sasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Joints: 0 Bones Are Joined by Fibrous Tissue 0 Either Immovable or Permit Slight Degree of MovementDocumento8 pagineJoints: 0 Bones Are Joined by Fibrous Tissue 0 Either Immovable or Permit Slight Degree of MovementSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unravelling The Mystery of The BrainDocumento17 pagineUnravelling The Mystery of The BrainSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Documento48 pagineCongenital Heart Defects: Module F Chapter Eleven Cardiac System Pages 348 - 359Sasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Function Autonomic Nervous SystemDocumento33 pagineFunction Autonomic Nervous SystemSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBS Scheme Feb2014Documento23 pagineMBBS Scheme Feb2014Sasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidDocumento120 pagineAnatomy of Meninges Ventricles CerebrospinalfluidSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Brain AnatomyDocumento32 pagineIntroduction To Brain AnatomySasikala Mohan100% (1)
- Rectus SheathDocumento16 pagineRectus SheathSasikala Mohan100% (1)
- Brain Anatomy HemispheresDocumento37 pagineBrain Anatomy HemispheresSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversityDocumento21 pagineCerebellum: John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center For Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia UniversitySasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationDocumento67 pagineLecture 19 - Vessels and CirculationSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Vinayaka Mission'S University Aarupadai Veedu Medical College, PuducherryDocumento3 pagineVinayaka Mission'S University Aarupadai Veedu Medical College, PuducherrySasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiDocumento122 pagineAutonomic Nervous System: Dr. Lawrence A. OlatunjiSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cubital FossaDocumento19 pagineThe Cubital FossaSasikala MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Cover Letter Samples For Your Scientific ManuscriptDocumento11 pagine5 Cover Letter Samples For Your Scientific ManuscriptAlejandra J. Troncoso100% (2)
- Mms Health Recovery Guidebook 1 October 2016Documento346 pagineMms Health Recovery Guidebook 1 October 2016omar hazard94% (50)
- Rdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For PortfolioDocumento1 paginaRdramirez Aota 2018 Poster For Portfolioapi-437843157Nessuna valutazione finora
- Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment: November 14 Public-Health Order UpdateDocumento9 pagineColorado Department of Public Health and Environment: November 14 Public-Health Order UpdateMichael_Roberts2019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alprazolam: Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Documento1 paginaAlprazolam: Why Is This Medicine Prescribed To You?Jerome GeronimoNessuna valutazione finora
- Readycult Coliforms 100: Ordering Number: 1.01298.0001Documento4 pagineReadycult Coliforms 100: Ordering Number: 1.01298.0001Maria Alejandra VillalbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chinese Medicine Eng BrochureDocumento12 pagineChinese Medicine Eng BrochuretanasedanielaNessuna valutazione finora
- 80020120LITPDFDocumento37 pagine80020120LITPDFPraistonNessuna valutazione finora
- Health 8 Q3 Week 7-8 Module 1-6Documento22 pagineHealth 8 Q3 Week 7-8 Module 1-6Richard CoderiasNessuna valutazione finora
- MarriottDocumento4 pagineMarriottSheikh Farhan AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Summarised Clinchers Created For The Exam - Credits - Audi Maglalang-ReedDocumento9 pagineSummarised Clinchers Created For The Exam - Credits - Audi Maglalang-ReedflashjetNessuna valutazione finora
- Assisting Delivery Name: - Grade: - Year and Section: - DateDocumento5 pagineAssisting Delivery Name: - Grade: - Year and Section: - DateCrisia Jane LotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Literature Review Kangaroo Mother CareDocumento7 pagineLiterature Review Kangaroo Mother CareafdtuwxrbNessuna valutazione finora
- VF-VT AlgorithmDocumento10 pagineVF-VT AlgorithmPuskesmas Pinang JayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6 QuestionsDocumento2 pagineChapter 6 QuestionsGabo DanteNessuna valutazione finora
- First Year Student Orientation: University of DenverDocumento3 pagineFirst Year Student Orientation: University of DenverRyan DonovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter I 1Documento8 pagineChapter I 1Krizalyn BacongNessuna valutazione finora
- About The Author-James Herriot: A Triumph of Surgery Chapter - 1 Footprint Without FeetDocumento4 pagineAbout The Author-James Herriot: A Triumph of Surgery Chapter - 1 Footprint Without FeetSunil rathi100% (3)
- Physical Fitness Test Individual Score CardDocumento12 paginePhysical Fitness Test Individual Score CardJunessa TadinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter I Related Literature Teenage PreDocumento12 pagineChapter I Related Literature Teenage PreWilkenn Tuazon100% (3)
- Full Employee ReportDocumento3 pagineFull Employee ReportXYZNessuna valutazione finora
- Intentional InjuriesDocumento30 pagineIntentional InjuriesZyryx BartolomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University: Course Outline (Second Semester) ZOO 208Documento1 paginaAteneo de Zamboanga University: Course Outline (Second Semester) ZOO 208Almira AhamadNessuna valutazione finora
- Position PaperDocumento2 paginePosition Paperiscream230% (1)
- MR Mohan LalDocumento5 pagineMR Mohan LalRajkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Postharvest Technology-Importance: Eufemio G. Barcelon, PHDDocumento56 paginePostharvest Technology-Importance: Eufemio G. Barcelon, PHDJohanna Amor L. AdaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Validity and Reliability Study of The Turkish Version of Ego Identity Process QuestionairreDocumento6 pagineValidity and Reliability Study of The Turkish Version of Ego Identity Process QuestionairreSergio F. GonzalezNessuna valutazione finora
- Potsdam Village Police Dept. Blotter Sept. 10, 2017Documento2 paginePotsdam Village Police Dept. Blotter Sept. 10, 2017NewzjunkyNessuna valutazione finora
- Jdo Vol 59 New PDFDocumento100 pagineJdo Vol 59 New PDFLex MNessuna valutazione finora
- Ganglions Clinical Presentation - History and Physical ExaminationDocumento3 pagineGanglions Clinical Presentation - History and Physical ExaminationAnonymous vOJH2hLMh6Nessuna valutazione finora