Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Marxian Poltical Economy-New
Caricato da
blah blah 56743Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Marxian Poltical Economy-New
Caricato da
blah blah 56743Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Marxian Political Economy
Marxist political economy states that capitalism will eventually fail because factory owners and CEOs exploit labor to generate wealth for themselves. He believed that such exploitation leads to social unrest and class conflict. To ensure social and economic stability, he theorized, laborers should own and control the means of production. It treats class as tool of appropriation. State is seen as an agency or institution that manages and protects and advances the interests of capitalist.
Marxian Political Economy
It contests the idea of classical economists like Adam Smith and Ricardo that market operates according to social division of labour, which shows that individuals within market act independently and according to their desire. Further Smith-Recardo argued that market laws are independent of the will and wish of persons. The market and individual wants directly determine what happens in the market. In the neoclassical theories, individuals have an interest in maximising their well being defined by their preference ordering.
Marxian Political Economy
But Marxian method tries to find answers to the question of how we connect individual interests to social order.
To find answers to above question, we need to look at following proposition.
What is the relationship of individuals material interests to social order (It is here the link between politics and economics is established).
Marxian Political Economy
To understand this link, we have to focus on the three strands or streams of Marxian theory of political economy.
Revolutionary politics (route suggested by Marx himself)
The politics of class compromise social democracy (Karl Kautsky) Marxist State Theory.
Marxian Political Economy
We will discuss these theories latter. Let us discuss first the Class, interests and conflict from Marxian view point. The concept of class interests is central to Marxian theory. In Marxism, Marxian class theory asserts that an individuals position within a class hierarchy is determined by his role in the production process, and argues that political and ideological consciousness is determined by class position.
Marxian Political Economy
Within Marxian class theory, the structure of the production process forms the basis of class construction. First individuals see themselves as isolated agents pursing self interests on their own. But capitalist economy worked in such a way as to establish commonality of interests within classes of persons. The more individuals become aware of their common conditions and purpose, the more they see their material interests in broader light.
Marxian Political Economy
This process marks transition from individual to class interests and ultimately turns material economic interests into political one.
Therefore Marxian interpretation of relationship between economic and politics centres on the idea of economic interests and the part they play in defining political agendas.
Marxian Political Economy
How capitalism affects material conditions of workers.
According to Marx material conditions determine class consciousness.
Marx argues that the process of economic growth takes place through competition and competition operates on the basis of price system. Capitalists expand markets at the expense of competitors by reducing prices Capitalism benefits the workers so long as it maintains high level of investment.
Marxian Political Economy
According to Marx, competition tends to be selftiming when it effect is to drive the weaker producer out of business. As the competition weakens, the process that translates into productivity gains also weakens, which means demand does not expand. Marx attributes this to the failure to stimulate market growth which results from failure to enhance real wages. With stagnant market, no investment comes in.
Marxian Political Economy
The result is economic stagnation. When economy stagnates, the capitalist make little profit and accumulate little capital When wages dont improve, the workers suffer from high level of unemployment. This situation is characterized as economic crisis of the system.
Marxian Political Economy
According to Marx, a capitalist economy appears to be consisting of vast accumulation of commodities and individual tied together through the thread of exchange in the market place According to him market economy is more about appropriation of surplus value than maximisation of private welfare.
Marxian Political Economy
Material interests, class conflict and capitalism. Since material interests holds key to Marxian economy and focus on material interest raises following questions.
1. 2. Are those material best served under capitalism Are the material interests of workers and capitalist in conflict under capitalism or both (workers and capitalist) benefits or lose together.
3.
4.
Do the material interests of individual within the classes of workers and capitalists converge or conflict
Does the conflict that arises over material interests lead to challenge to social order of capitalism, or merely involve a shifting of power and benefit within capitalism.
Marxian Political Economy
In the scheme of Marxian political economy, worker appears to be loser because they are being paid less than their value of labour subsistence . Greater the cost of subsistence, less the surplus or profit for capitalist.
Marx argues that the profit motive drives the capitalist to seek ways of increasing their share of output.
Marxian Political Economy
Capitalist secure those profits either by increasing the value of output or reducing the value of subsistence. Marx argues that capitalist attempt to find ways to make workers work harder, longer and more efficiently without altering subsistence.
As a result profit increases, the real wage (subsistence) remains the same, as such his (worker) share of the product declines.
Marxian Political Economy
Economic interests and class consciousness
In Marxian theory, class refers to group of people who have similar position in the production process. Political agenda come to surface only when capitalist and worker have different economic interests. Class consciousness is behind the political agenda.
According to him in the production process there are two forces working class and Capitalist class.
Marxian Political Economy
Capitalist class drives to amass more wealth which set them (capitalist) into competition with each other, which has destructive implications for social order and individual well being.
For investors/capitalists if profit making is not satisfactory, then they refrain from investing in new business activity. To him, falling wages means falling demand for consumption of good, implying falling aggregate demand.
Marxian Political Economy
Individual capitalist benefits by lowering wages because he considers wage as cost. By working against wage increase, capitalists deprive workers of purchasing power in the capitalists system. According to Marx Capitalist have two interests.
1. Interests in wealth 2. Interest in the security of social system that allows pursuit of accumulation of wealth.
Marxian Political Economy
Revolutionary Politics:
It was set out in communist manifesto (1848).
Marx attempted to explain revolution by reference to the laws of motion of capitalism what he called historical materialism. According to Marx, laws of motions of capitalism work independently of the particular history, class situation and political institutions of different countries. Marx did not believe in the durability of self organising or self-regulating character of capitalism. According to him capitalist markets contained very forces that would eventually bring about their demise.
Marxian Political Economy
According to Marx Capitalist development involves the production of commodities (goods exchanged on market) whose value is enough to reproduce surpluses capital than its cost. The surplus capital is invested in productive capital, and this he called accumulation. Capital remains concentrated in fewer economic units of large size. As it advances, it displaces more and more workers creating industrial reserve army of labour.
Marxian Political Economy
Availability of abundant labour drives down wages of workers and they are willing to work for less wages. As the capital become more concentrated, workers are drawn closer together in large factories and urban areas. They organize themselves politically. According to Marx, the efforts of capitalist to increase his profit has harmful effects on the ability of workers to satisfy their material interests.
Marxian Political Economy
In order to raise profits, capitalists work to raise the productivity of labour. In this regard, they introduce more mechanized methods of production, which replaces workers with machines.
And introduction of machinery affects working conditions of workers and increase unemployment.
This leads Marx to conclude that capitalist development produces immiseration and polarization of material conditions of two classes.
Marxian Political Economy
According to Marx, this law creates an accumulation of misery, corresponding with accumulation of wealth.
Finally he concludes that accumulation of wealth at one pole produces at the same time accumulation of misery, agony of toil, slavery, ignorance, brutality, mental degradation at the opposite pole.
Marxian Political Economy
This situation, according to Marx, finally leads to revolution. In this regard he said : Let the ruling classes tremble at a Communistic revolution.... Workers of the world unite; you have nothing to lose but your chains It was in the context, he had said force is the midwife of the old society pregnant with new one. Marx was the advocate of the use of force.
Historical Materialism
Source : International Political Economy by Raymond C. Miller, P-182
Historical materialism
Source : International Political Economy by Raymond C. Miller, P-183
Marxian Political Economy
Marx and Social Democratic Policies.
There are some Marxists who believe that revolution is not inevitable as a result of the laws of motions of capitalist economy.
This strand or stream of Marxist strategy involves workers participation in interest groups, parties and electoral-legislative process.
Marxian Political Economy
The goal is to alter the position of labour and capital within system by establishing institutions and political democracy ensuring the participation of workers. Social Democracy is different from revolutionary politics. Former attempts to achieve goals by peaceful means within bourgeoisie institutions and politics whereas later uses violent means without (outside bourgeoisie institutions). The main idea of the reformist social democratic approach is to foster the material interests of workers with the frame work of capitalism and liberal democracy.
Marxian Political Economy
It attempts to tame capitalism and make it beneficial for more people, not just narrow capitalist class.
The core belief is that the welfare of citizen (worker and citizen) can be advanced by gradually rationalizing the economy.
Marxian Political Economy
Marxian State Theory.
This theory discuss how state is related to economy under capitalism According to this theory state exists to preserve and advance the order that protects the social order created under capitalism.
Marxian Political Economy
State works to define social order that favours one class, that is , bourgeoisie or capitalist class (Poulantzas) State works as agent to represent political interest of bourgeoisie. According to Marx, state is part of the super structure, the political shell of capitalism that is ultimately responsive to economic forces.
Base-Superstructure Analysis of Marx
Marxian Political Economy
Conclusion
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Objectives of Economic PlanningDocumento13 pagineObjectives of Economic PlanningNivriti SethNessuna valutazione finora
- Neo MarxismDocumento3 pagineNeo Marxismpakito100% (1)
- Dependency Theory and PakistanDocumento30 pagineDependency Theory and PakistanHamzah Bhatti71% (7)
- Pigou Welfare Economics 2Documento5 paginePigou Welfare Economics 2vikram inamdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Marxian Theory of Population GrowthDocumento3 pagineMarxian Theory of Population GrowthNikhil YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Plato Education System NewDocumento4 paginePlato Education System NewKhadija ZehraNessuna valutazione finora
- Liberalism in IrDocumento5 pagineLiberalism in IrEvelyn Lusiana TobingNessuna valutazione finora
- Decentralisation in Kerala: Problems and ProspectsDocumento19 pagineDecentralisation in Kerala: Problems and ProspectsK Rajasekharan75% (4)
- Challenges For DemocracyDocumento7 pagineChallenges For DemocracyShivendra SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Women in PakistanDocumento7 pagineWomen in PakistanSyed Zulqarnain100% (3)
- Nozick's Entitlement Theory of Distributive JusticeDocumento3 pagineNozick's Entitlement Theory of Distributive JusticeamritallbNessuna valutazione finora
- Foreign Aid Blessing or CurseDocumento25 pagineForeign Aid Blessing or CursePrashanth PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Political Parties: Unit - 3 Chapter-6Documento26 paginePolitical Parties: Unit - 3 Chapter-6Tripti Singha100% (1)
- Political History of NepalDocumento4 paginePolitical History of NepalAshish DhakalNessuna valutazione finora
- 2) Scope and Importance of EconomicsDocumento19 pagine2) Scope and Importance of EconomicsNimisha Beri0% (1)
- 3 Political CultureDocumento22 pagine3 Political CultureElena VoinovanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Concept of EconomicsDocumento7 pagineBasic Concept of EconomicsAshish DhakalNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 Public Administration TheoriesDocumento30 pagineChapter 2 Public Administration TheoriesSyed Zohaib KazmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Viden Io Du Ba Pol SC Hons Notes Neo Realism PDFDocumento18 pagineViden Io Du Ba Pol SC Hons Notes Neo Realism PDFSonali RaghuvanshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bureaucracy - Role and Challenges in IndiaDocumento12 pagineBureaucracy - Role and Challenges in IndiaRda RenthleiNessuna valutazione finora
- Merits of CapitalismDocumento2 pagineMerits of CapitalismFaisal NiaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Colonial Mode of ProductionDocumento4 pagineColonial Mode of ProductioninnakkNessuna valutazione finora
- Political Culture of BangladeshDocumento32 paginePolitical Culture of BangladeshBishawnath Roy100% (2)
- Alternative Interpretations of DevelopmentDocumento8 pagineAlternative Interpretations of DevelopmentAnonymous oQEx3z100% (1)
- The Four Basic Elements of Governance According To 1Documento14 pagineThe Four Basic Elements of Governance According To 1ShaiPH GamingNessuna valutazione finora
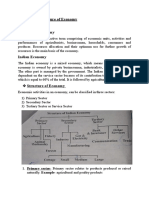
- Nature and Structure of EconomyDocumento3 pagineNature and Structure of EconomyAnkita Kumari SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomy Vs IntegrationDocumento31 pagineAutonomy Vs IntegrationWahid KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonmy Vs Integration and Gender Vs Women StudiesDocumento18 pagineAutonmy Vs Integration and Gender Vs Women StudiesshujahkianiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rise and Fall of the Faraizi Movement in BengalDocumento8 pagineThe Rise and Fall of the Faraizi Movement in Bengalfarhan munawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Administrative Ethics PDFDocumento14 pagineAdministrative Ethics PDFN Irina100% (1)
- Women in DevelopmentDocumento1 paginaWomen in DevelopmentZain Ul Abideen100% (1)
- Development Meaning and DefinitionDocumento18 pagineDevelopment Meaning and DefinitionShreyansh PriyamNessuna valutazione finora
- Meaning of Development-TodaroDocumento9 pagineMeaning of Development-TodaroAnonymous oQEx3z100% (1)
- Caste System in PakistanDocumento7 pagineCaste System in Pakistanuzma batool100% (1)
- Karl Marx AlienationDocumento5 pagineKarl Marx AlienationTom Makarov100% (1)
- State Council of ChinaDocumento2 pagineState Council of ChinaManjira Kar0% (1)
- Planning CommissionDocumento12 paginePlanning CommissionLata100% (1)
- Why Empowerment Alone Cannot Help Our WomenDocumento2 pagineWhy Empowerment Alone Cannot Help Our WomenVasundhara VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Economic Growth and DevelopmentDocumento17 pagineEconomic Growth and DevelopmentSachin Methree100% (1)
- Pakistan Education System IssuesDocumento4 paginePakistan Education System IssuesWaris Arslan0% (1)
- Globalization Essay Outline and ToolsDocumento7 pagineGlobalization Essay Outline and Toolstahi69Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1.4.3.1 Social Action PDFDocumento9 pagine1.4.3.1 Social Action PDFAnonymous gf2aAKNessuna valutazione finora
- Innovative Panaceas For Pakistan's Corruption Ills by M. Tariq WaseemDocumento64 pagineInnovative Panaceas For Pakistan's Corruption Ills by M. Tariq WaseemAbu AbdullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Problem in India by Ram AhujaDocumento241 pagineSocial Problem in India by Ram Ahujachem_iaf100% (1)
- Panchayati Raj - 73rd Constitutional Amendment ActDocumento7 paginePanchayati Raj - 73rd Constitutional Amendment ActSania SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Stratification in Pakistan, Social Difference, Social ClassDocumento22 pagineSocial Stratification in Pakistan, Social Difference, Social ClassMuti ullah100% (1)
- Uses of Analytical Approach in Political ScienceDocumento8 pagineUses of Analytical Approach in Political Sciencechutku1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sociology of Development TheoriesDocumento2 pagineSociology of Development Theoriessupriya guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Point Circular FlowDocumento30 paginePower Point Circular FlowRoselle Perez- Bariuan75% (4)
- Understanding IPEDocumento3 pagineUnderstanding IPEAnns Rehman100% (1)
- Lecture 8 The Invisible Hand in Action2Documento43 pagineLecture 8 The Invisible Hand in Action2GiuseppeNessuna valutazione finora
- Marx Class StruggleDocumento34 pagineMarx Class Strugglefaryal100% (1)
- Industrial Development in IndiaDocumento17 pagineIndustrial Development in IndiaSiddharth VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Discuss The Limitations and Improvements of The National Rural Development Policy-2001 PDFDocumento10 pagineDiscuss The Limitations and Improvements of The National Rural Development Policy-2001 PDFBushra Khatun Jannat100% (1)
- Authoritarian GovernmentDocumento11 pagineAuthoritarian GovernmentAnn SaNessuna valutazione finora
- Librelization, Privatization and GlobalizationDocumento12 pagineLibrelization, Privatization and GlobalizationYugam JoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Name-B.A.L.L.B.Ivth Sem Subject - Sociology Teacher - Dr. Niru Jain Topic - Sanskritization, Westernization, ModernizationDocumento24 pagineCourse Name-B.A.L.L.B.Ivth Sem Subject - Sociology Teacher - Dr. Niru Jain Topic - Sanskritization, Westernization, ModernizationClark KennttNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circular Flow of Output & IncomeDocumento6 pagineThe Circular Flow of Output & IncomeanandkasirajankakNessuna valutazione finora
- Political Economy EssayDocumento6 paginePolitical Economy EssayYassmina Adham OrbanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Development of German SociologyDocumento21 pagineThe Development of German SociologyVENKATANATH BATHININessuna valutazione finora
- MODULES RUNNING CORE AND OPTIONAL 2014-15Documento2 pagineMODULES RUNNING CORE AND OPTIONAL 2014-15blah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- ANTHROPOLOGICAL THEORY THROUGH HISTORYDocumento9 pagineANTHROPOLOGICAL THEORY THROUGH HISTORYblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gender-Biased Interaction in The Classroom: The Influence of Gender and Age in The Relationship Between Teacher and PupilDocumento12 pagineGender-Biased Interaction in The Classroom: The Influence of Gender and Age in The Relationship Between Teacher and Pupilblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Žižek Seminar Spring 2014Documento2 pagineŽižek Seminar Spring 2014blah blah 56743100% (1)
- Gil Anidjar PDFDocumento26 pagineGil Anidjar PDFblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Imperial Ideologies, Transnational Activism: Questioning The Place of Religious Freedom From British IndiaDocumento17 pagineImperial Ideologies, Transnational Activism: Questioning The Place of Religious Freedom From British Indiablah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- AdfsdDocumento24 pagineAdfsdblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- ANTH 101 Syllabus Spring08Documento30 pagineANTH 101 Syllabus Spring08blah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- SadsadDocumento20 pagineSadsadblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Writings and Speeches OF Sir Syed Ahmad Khan: Compiled and Edited byDocumento17 pagineWritings and Speeches OF Sir Syed Ahmad Khan: Compiled and Edited byblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT 382-Social Entrepreneurship-Jameel Goheer-Zehra AliDocumento8 pagineMGMT 382-Social Entrepreneurship-Jameel Goheer-Zehra AliFarhan HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthropology of South Asia: Anth 3334-001: Fall 2014 UH09: TUE/THU 12: 30-1:50Documento8 pagineAnthropology of South Asia: Anth 3334-001: Fall 2014 UH09: TUE/THU 12: 30-1:50blah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lahore University of Management Sciences SOC 223 - Sociology of EducationDocumento6 pagineLahore University of Management Sciences SOC 223 - Sociology of Educationblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Social Psychology CourseDocumento4 pagineSocial Psychology Courseblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Pedagogy Course Focuses on Social JusticeDocumento7 pagineCritical Pedagogy Course Focuses on Social Justiceblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- SS 102 - Pakistan Studies-Culture & Heritage (ZS) PDFDocumento7 pagineSS 102 - Pakistan Studies-Culture & Heritage (ZS) PDFblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDU 212 Critical Pedagogy SYLLABUSDocumento10 pagineEDU 212 Critical Pedagogy SYLLABUSblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Music of PakistanDocumento2 pagineClassical Music of Pakistanblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- A.K. Ramanujan "Annayyas Anthropology"Documento7 pagineA.K. Ramanujan "Annayyas Anthropology"Rei MagosakiNessuna valutazione finora
- International Scholarships HandbookDocumento48 pagineInternational Scholarships Handbookaatif_iba20086409Nessuna valutazione finora
- ANTH 101 Syllabus Spring08Documento30 pagineANTH 101 Syllabus Spring08blah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- KKKDocumento60 pagineKKKblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stole R 2008Documento29 pagineStole R 2008augustobianchiNessuna valutazione finora
- JHKJDocumento5 pagineJHKJblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- DfadfDocumento27 pagineDfadfblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Islamiat Presentation FinalDocumento32 pagineIslamiat Presentation Finalblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- RSCPB3 Statelessness PDFDocumento62 pagineRSCPB3 Statelessness PDFblah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brand Pakistan REPORTDocumento26 pagineBrand Pakistan REPORTSaddam HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Enrique Peñalosa Was The Mayor of ColumbiaDocumento2 pagineEnrique Peñalosa Was The Mayor of Columbiablah blah 56743Nessuna valutazione finora
- Distorted History of PakistanDocumento34 pagineDistorted History of PakistanAreeb HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- By-Pratya Mishra Astha Vajpai Damini Singh Priya PandeyDocumento16 pagineBy-Pratya Mishra Astha Vajpai Damini Singh Priya PandeyDishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Everything About The MarxismDocumento23 pagineEverything About The MarxismVilijaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Female Eunuch by Germaine GreerDocumento5 pagineThe Female Eunuch by Germaine GreerTejas KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- FascismDocumento3 pagineFascismMark FarodenNessuna valutazione finora
- Feminism The Power of Being HeardDocumento5 pagineFeminism The Power of Being HeardCarmela BorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Anastasia Flouli AUTH 3 Waves of FeminismDocumento11 pagineAnastasia Flouli AUTH 3 Waves of FeminismMehroz BalochNessuna valutazione finora
- Argument EssayDocumento3 pagineArgument Essayapi-492073476Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: The Democratic RepublicDocumento9 pagineChapter 1: The Democratic Republicnalla_lykan100% (1)
- Confronting Power Theorizing Gender Interdisciplinary Perspectives in The CaribbeanDocumento19 pagineConfronting Power Theorizing Gender Interdisciplinary Perspectives in The CaribbeanDiana IbarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tony Cliff - Permanent Revolution PDFDocumento24 pagineTony Cliff - Permanent Revolution PDFROWLAND PASARIBUNessuna valutazione finora
- Anarchism and Fascism - AntagonistsDocumento3 pagineAnarchism and Fascism - AntagonistsHugãoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Feministic - Approach To AwoodDocumento6 pagine6 Feministic - Approach To AwoodbibaNessuna valutazione finora
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN Marxist ApproachDocumento7 pagineDETAILED LESSON PLAN Marxist ApproachBilly Joe Ortile67% (3)
- The End of The AFZ The End of Meaningful PDFDocumento83 pagineThe End of The AFZ The End of Meaningful PDFSanja HorvatinčićNessuna valutazione finora
- Marxism For DummiesDocumento8 pagineMarxism For DummiesShraddha Ranganathan0% (3)
- Feminist Books & ReviewsDocumento3 pagineFeminist Books & ReviewsSohail KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Althusser's Theory of Ideology and Ideological State ApparatusesDocumento4 pagineAlthusser's Theory of Ideology and Ideological State ApparatuseskainoaxNessuna valutazione finora
- Regimes of The Modern World ASSIGNMDocumento8 pagineRegimes of The Modern World ASSIGNMNauman Raza100% (2)
- Aurat March 8-March-2020: Some Newspapers and Their Article About Aurat March: According To Daily Times NewsDocumento2 pagineAurat March 8-March-2020: Some Newspapers and Their Article About Aurat March: According To Daily Times NewschristyNessuna valutazione finora
- More Than A Woman - Caitlin MoranDocumento6 pagineMore Than A Woman - Caitlin MorannofymajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento3 pagineChapter 4Aeb Asib GbhertNessuna valutazione finora
- Gabriel Palma - World Development Dependency 1978Documento44 pagineGabriel Palma - World Development Dependency 1978Gabriel RolembergNessuna valutazione finora
- Race, Class, and Agency: A Return To Marxist Feminism: Shahrzad Mojab - Afiya S. ZiaDocumento15 pagineRace, Class, and Agency: A Return To Marxist Feminism: Shahrzad Mojab - Afiya S. ZiaRevivalist CoffeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Noam Chomsky-Chomsky On ConservatismDocumento2 pagineNoam Chomsky-Chomsky On ConservatismJames KroKantNessuna valutazione finora
- Roberto VivarelliDocumento16 pagineRoberto VivarelliGayle Fernandes100% (2)
- THE SINO-SOVIET DISPUTE ' WITHIN THE COMMUNIST MOVEMENT IN LATIN AMERICA (Reference CIA ESAU XXVIII)Documento187 pagineTHE SINO-SOVIET DISPUTE ' WITHIN THE COMMUNIST MOVEMENT IN LATIN AMERICA (Reference CIA ESAU XXVIII)nelson duringNessuna valutazione finora
- SocialismDocumento7 pagineSocialismlenard steve nisasNessuna valutazione finora
- BordigaDocumento540 pagineBordigaHari Madhavan Krishna KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Propaganda of The Deed PDFDocumento12 paginePropaganda of The Deed PDFdavv10Nessuna valutazione finora
- Project PT.Rapp Chemical Salary SlipsDocumento14 pagineProject PT.Rapp Chemical Salary SlipsAcepNessuna valutazione finora