Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
DSLP
Caricato da
vikasrajput1989Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
DSLP
Caricato da
vikasrajput1989Copyright:
Formati disponibili
When the electric field becomes strong enough, an electrical discharge occurs within clouds or between clouds and
the ground is called lightning stroke.
Assumption: No Shielding and No Lightning Mast Possible Insulation Flashover (depends primarily on the stroke current magnitude) Damage to Major Substation Equipment Substation Outage Cost
Minimize the possibility of direct lightning strike to bus and/or major equipment in the substation and hence, the outage and possible failure of major electrical equipment.
Lightning conductor consists of the lightning receiver projecting above the object to be protected, the earthing grid and the conductor which connects the receiver with the earthing grid and carry the lightning current safely to the ground.
In substations we use two type of
lightning media:
Lightning Masts Ground Wires (Shield Wire)
A column or narrow base structure containing a vertical conductor from its tip to earth. Its purpose is to intercept lightning strokes so that they do not terminate on objects located within its zone of protection.
A wire suspended above the phase conductors to protect phase conductor, objects from lightning strike located within its protective zone.
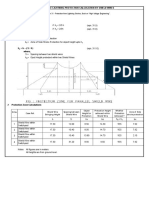
Lightning Masts Shield Wires Combination of Masts & Shield Wires Calculation Dr. Razevigs Method Fixed Angles Method: 45/60 degrees Electrogeometric methods IEEE Std. 998-1996
The space around a lightning conductor in which the probability of lightning stroke is small is called protective zone.
Projection of height of the lightning conductor above the height of the object to be protected is called the active height of the lightning conductor. H1=H-h H1 is active height
IVG-Impulse Voltage generator 1- Electrode(For Discharge) 2- Model of the lightning Conductor 3- Grounded metallic plane
H= Height of Diode h= Height of Lightning Rod R= Radius of Zone r=radius of Protective Zone h1= Height of object to be protected
H= Height of Diode h= Height of Lightning Rod B= Radius of Zone b=radius of Protective Zone
If h1<2/3h Radius of protective zone is r1=1.5h(1-h1/0.8h) h1 object height h LM height If h1>2/3h r1=0.75h(1-h1/h) if height of Lightning Mast h>30mt. Then r1 must be multiplied by the coefficient p=5.5/h
For 2 LM Distance between two LM a<=7(h-h1) h-h1 is active height of LM h1=h-a/7 For 3 LM a circle of diameter D is passing through the tips of the LM D=8(h-h1)
Minimum active height of LM 1,2,4 is h2=60/8=7.5mt (h2 is active height) Minimum active height of LM 2,4,5 is h2=55/8=6.9mt Minimum active height of LM 1,3,4 is h2=50/8=6.4mt Minimum active height of LM 4,5,7,8 is h2=57/8=7.2mt LM of Active height =7.5mt is able to protect the area. Maximum height of equipment to be protected is 11mt So height of LM h=7.5+11=18.5mt
If h1<2/3h Radius of protective zone is b1=1.2h(1-h1/0.8h)
If h1>2/3h b1=0.6h(1-h1/h)
X= (B-A)Tan60 or X= (B-A) Tan
S=8kIs0.65 S is strike distance Is stroke current in kA k is coefficient k=1 for shield wire k=1.2 for Lightning Mast
The Protective area of shield wire or mast depends on the amplitude of the stroke current Is. Allowable stroke current : Is=2.2(BIL)/Zs Is is allowable stroke current in kA Zs is surge impedance of the conductor through which the surge is passing in ohms.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Advances in High Voltage Insulation and Arc Interruption in SF6 and VacuumDa EverandAdvances in High Voltage Insulation and Arc Interruption in SF6 and VacuumNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP (11 3m)Documento7 pagineDSLP (11 3m)Ashutosh MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP Calculation by LMDocumento8 pagineDSLP Calculation by LMPrasad YeluripatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing Calculation As Per Ieee 80Documento10 pagineEarthing Calculation As Per Ieee 80Ben HurNessuna valutazione finora
- Razevig Method DSLPDocumento19 pagineRazevig Method DSLPsunny171083_901235920% (2)
- CT Requirements - Summary - Rev 3p2 - 090121 - ABB Relays - New - v0p5Documento20 pagineCT Requirements - Summary - Rev 3p2 - 090121 - ABB Relays - New - v0p5goalex100% (1)
- DSLP Calculation by LMDocumento8 pagineDSLP Calculation by LManilmarturiNessuna valutazione finora
- Substation Design and LayoutDocumento9 pagineSubstation Design and Layoutsurag1982Nessuna valutazione finora
- Substation EarthingDocumento6 pagineSubstation Earthingjpsridhar100% (1)
- Fault Level Calculation (Base MVA Methode) : DataDocumento2 pagineFault Level Calculation (Base MVA Methode) : DataTreesa Archnana100% (4)
- Substation Earthing by JGNDocumento49 pagineSubstation Earthing by JGNrupamNessuna valutazione finora
- Jamalpur Earthing Calculation Final PDFDocumento10 pagineJamalpur Earthing Calculation Final PDFarafinNessuna valutazione finora
- Busbar Sizing For SubstationDocumento22 pagineBusbar Sizing For Substationdundi_kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthing CalculationDocumento4 pagineEarthing CalculationNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP CalculationDocumento7 pagineDSLP Calculationravi shankar100% (1)
- DSLP-Mast AndraDocumento10 pagineDSLP-Mast AndraBNessuna valutazione finora
- A Presentation ON Direct Stroke Lightning Protection (DSLP) FOR SubstationsDocumento34 pagineA Presentation ON Direct Stroke Lightning Protection (DSLP) FOR SubstationsNageswar Makala100% (2)
- 2 - 220kv - Warangal - Nagaram 1Documento42 pagine2 - 220kv - Warangal - Nagaram 11453h100% (2)
- 33 SCF Tower Span 18mDocumento25 pagine33 SCF Tower Span 18mamrit90320Nessuna valutazione finora
- Calculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50 - 51) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocumento5 pagineCalculate IDMT Over Current Relay Setting (50 - 51) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesThức VõNessuna valutazione finora
- Design A Protection System of 220-33 KV Ramah Grid StationDocumento51 pagineDesign A Protection System of 220-33 KV Ramah Grid StationAnand Kumar100% (2)
- Earth Design-33kV-Assignment-Rev1Documento9 pagineEarth Design-33kV-Assignment-Rev1Vipinraj KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Earthmat Calculations For WTG HT YardDocumento3 pagineEarthmat Calculations For WTG HT YardSanthosh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- SLD 02 03 17Documento1 paginaSLD 02 03 17Hari HaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Part - I - SLD, BB & LayoutDocumento50 paginePart - I - SLD, BB & LayoutGargi100% (2)
- 33kV Line Loss Estimation - KaradikondaDocumento8 pagine33kV Line Loss Estimation - Karadikondasomdatta chaudhury0% (1)
- 220 KV AIS - TSDocumento34 pagine220 KV AIS - TSBilal AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil Soak Pit CalculationDocumento2 pagineOil Soak Pit CalculationROHIT MCNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP of Sub-Station Using Shield Wire by Razevig MethodDocumento1 paginaDSLP of Sub-Station Using Shield Wire by Razevig MethodSomen Sarkar100% (2)
- Aluminium Busbar Sizing Software OutputDocumento3 pagineAluminium Busbar Sizing Software Outputkapil100% (4)
- Short Circuit Force Calculation For 132 KV Substation at Noida-Sector 62Documento7 pagineShort Circuit Force Calculation For 132 KV Substation at Noida-Sector 62raghvendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Method For Calculation of Short-CircuitDocumento8 pagineEngineering Method For Calculation of Short-CircuitHakkim Sheik Thauth J100% (1)
- Permanent / Fixed Technical LossesDocumento11 paginePermanent / Fixed Technical Lossesyogesh100% (1)
- High Voltage Engineering Prof D V RazevigDocumento20 pagineHigh Voltage Engineering Prof D V RazevigSaroj100% (1)
- Calculation For Earthing MatDocumento11 pagineCalculation For Earthing Matpvpavan0% (1)
- Earthing of Gis Type ElkDocumento21 pagineEarthing of Gis Type ElkJairo Morales100% (1)
- DSLP CalculationDocumento23 pagineDSLP CalculationMunusamyKarthikeyan100% (1)
- Iec 865-1Documento23 pagineIec 865-1rahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Grid Earthing For EHV Switchyards As Per IEEE-80Documento3 pagineGrid Earthing For EHV Switchyards As Per IEEE-80kapilNessuna valutazione finora
- Aluminium Tubular Busbar Sizing Calculations - 132kVDocumento24 pagineAluminium Tubular Busbar Sizing Calculations - 132kVsitifarhani67% (3)
- Points To Be Consider While Selecting of Vector GroupDocumento3 paginePoints To Be Consider While Selecting of Vector GroupNanban VkyNessuna valutazione finora
- 33 KV TowerDocumento4 pagine33 KV TowerJayabalan R KNessuna valutazione finora
- KEC LT XLPE Cables BrochureDocumento28 pagineKEC LT XLPE Cables Brochureabhishek_918100% (1)
- Short Circuit Force For Equipment InterconnectionDocumento17 pagineShort Circuit Force For Equipment Interconnectionudayakumart100% (4)
- Update Final ReportDocumento18 pagineUpdate Final Reportanjes1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dokumen - Tips - Lightning Discharge and Fundamentals of Lightning ProtectionDocumento18 pagineDokumen - Tips - Lightning Discharge and Fundamentals of Lightning ProtectionBlazing RaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised Final Lightning Protection PDFDocumento37 pagineRevised Final Lightning Protection PDFkhaldoun samiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rolling Sphere Method Application For HV Lines: D. Machidon, M. Istrate, M. Guşă and M. DragomirDocumento4 pagineRolling Sphere Method Application For HV Lines: D. Machidon, M. Istrate, M. Guşă and M. DragomirDharam Sar HembramNessuna valutazione finora
- Lightning Protection Technology & HumanityDocumento48 pagineLightning Protection Technology & HumanityNguyen Phu LocNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP CalcDocumento5 pagineDSLP CalcPalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Selection of Surge Protective Device (SPD) - (Part 3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocumento8 pagineSelection of Surge Protective Device (SPD) - (Part 3) - Electrical Notes & ArticlesRahul ItaliyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Tips For Installing Surge Protection Devices in Low Voltage PanelDocumento19 paginePractical Tips For Installing Surge Protection Devices in Low Voltage PanelCesar SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- OVR SPD CatalogueDocumento12 pagineOVR SPD CatalogueHusnain AssociatesNessuna valutazione finora
- DSLPDocumento9 pagineDSLPjack paglaNessuna valutazione finora
- SCHIRTEC - Technical InformationDocumento16 pagineSCHIRTEC - Technical Information_MerlinNessuna valutazione finora
- Suggestion On Lightning Protection DesignDocumento45 pagineSuggestion On Lightning Protection DesignChien VuNessuna valutazione finora
- 220 to132KV GSS (Training Report)Documento17 pagine220 to132KV GSS (Training Report)Abhishek Dave0% (1)
- Microstrip Line Patch AntennaDocumento18 pagineMicrostrip Line Patch AntennaPrakash RanjanNessuna valutazione finora
- LPS Design Kaushi ElectricalDocumento10 pagineLPS Design Kaushi ElectricalYazhisai SelviNessuna valutazione finora
- CRB Lightning ProtectionDocumento1 paginaCRB Lightning Protectionvikasrajput1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- DSLP Calculation by VikasDocumento7 pagineDSLP Calculation by Vikasvikasrajput1989100% (2)
- Annexure D Additional Nors Conditions PlansDocumento19 pagineAnnexure D Additional Nors Conditions Plansvikasrajput1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- SCF and Cantiliver Strenth AnalysisDocumento68 pagineSCF and Cantiliver Strenth Analysisvikasrajput1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- SCF CalculationDocumento158 pagineSCF Calculationvikasrajput1989100% (2)
- Standard For Connectivity To Grid (CEA)Documento22 pagineStandard For Connectivity To Grid (CEA)vikasrajput1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cable SizingDocumento25 pagineCable Sizing54045114100% (1)
- Sag Tension 765kVDocumento11 pagineSag Tension 765kVvikasrajput1989100% (1)
- Neetpassionate Aiats 1 2021Documento26 pagineNeetpassionate Aiats 1 2021Hasmukh Ravat100% (1)
- Gs 64 TerminalDocumento28 pagineGs 64 TerminalJkp BukuljaNessuna valutazione finora
- SpeedStile Installation Guidlines Rev 1Documento14 pagineSpeedStile Installation Guidlines Rev 1WERMERMNessuna valutazione finora
- 555 Timer (Important)Documento76 pagine555 Timer (Important)money_kandan2004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Zelio Control Reg48pun1rhuDocumento4 pagineZelio Control Reg48pun1rhuAlexis Algüerno ContrerasNessuna valutazione finora
- Eaton Iluminat Urgenta Catalog Corpuri Baterie IndividualaDocumento8 pagineEaton Iluminat Urgenta Catalog Corpuri Baterie IndividualaAdrian MușatNessuna valutazione finora
- MRCT DS en V08Documento9 pagineMRCT DS en V08Anonymous 2l8XJIVNessuna valutazione finora
- Bat 41Documento3 pagineBat 41Fernando QueirozNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 21 PDFDocumento8 pagineLec 21 PDFVictor CantuárioNessuna valutazione finora
- Ime Fs1570Documento82 pagineIme Fs1570Fet TransistörNessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DST4601PX Dichron Eng PDFDocumento4 pagineDC-DST4601PX Dichron Eng PDFMarco GardinaliNessuna valutazione finora
- EE360 - Electric Circuit (Basics Needs To Revise For The Course)Documento66 pagineEE360 - Electric Circuit (Basics Needs To Revise For The Course)بدون اسمNessuna valutazione finora
- PowerElectronics Grid-Forming Case Studies 15.20Documento17 paginePowerElectronics Grid-Forming Case Studies 15.20Steven Leif EsselNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardinal Health MedSystem III Infusion Pump - Service BulletinDocumento12 pagineCardinal Health MedSystem III Infusion Pump - Service BulletinFábio Vitor MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.current ElectricityDocumento147 pagine1.current ElectricityYogy YNessuna valutazione finora
- 74HC241Documento12 pagine74HC241jnax101Nessuna valutazione finora
- CMF 300 ManualDocumento2 pagineCMF 300 ManualFrancisco AlonsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rayto 1904 Manual InstructionsDocumento39 pagineRayto 1904 Manual InstructionsHenry Kaunang60% (5)
- Technical SpecificationDocumento14 pagineTechnical SpecificationbinodeNessuna valutazione finora
- CST Application Note RfidDocumento15 pagineCST Application Note RfidAbohicham AbhNessuna valutazione finora
- Knock Knock Lock DoorDocumento52 pagineKnock Knock Lock DoorTasnim NabilahNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave RectifierDocumento15 pagineFull Wave Rectifiermandeep singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapiter3 - Mig Mag Welding50931Documento22 pagineChapiter3 - Mig Mag Welding50931Augusto SoaresNessuna valutazione finora
- HP 5328A Service ManualDocumento219 pagineHP 5328A Service ManualDragan LazicNessuna valutazione finora
- Denso Spark Plug Catalog 2015-CompressedDocumento12 pagineDenso Spark Plug Catalog 2015-CompressedFarrukh SharfiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Development of Flexible Integrated Circuits Based On Thin-Film TransistorsDocumento10 pagineThe Development of Flexible Integrated Circuits Based On Thin-Film TransistorsJOAM MANUEL RINCÓN ZULUAGANessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Multimedia 5Documento44 pagineElectrical Multimedia 5ding0398100% (1)
- External Electrical - BOQDocumento41 pagineExternal Electrical - BOQroy_nhp100% (1)
- Overexcitation ProtectionDocumento13 pagineOverexcitation Protectionalonso100% (1)
- Ec 301Documento1 paginaEc 301Meet ShahNessuna valutazione finora