Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
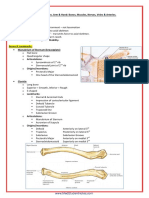
Topographical Anatomy of Lower Limb
Caricato da
Idrissou FmsbDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Topographical Anatomy of Lower Limb
Caricato da
Idrissou FmsbCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TOPOGRAPHICAL ANATOMY OF LOWER LIMB
N,1
Introduction
The lower limb:- thigh with three compartments - gluteal region - leg with three compartments - foot wth a dorsum and a sole
Interests
Man is bipodal Support and propulsion function of lower limb Transmission of weight and propulsion functions
GLUTEAL REGION
Boundaries: Behind pelvis From iliac crest to the gluteal fold Greater trochanter in front Lower part by gluteal fold - rounded buttock Two buttocks separated by natal cleft
Contents:Muscles: gluteal maximus, medius,minimus and deeply placed piriformis,obturator internus, superior and inferior gemellus as well as quadratus femoris Nerve: Sciatic Artery: Gluteals
The thigh region
Enclosed by deep fascia and fascia lata Anterior compartment Boundaries: Inguinal ligament above Knee below Laterally and medially by intermuscular septa Contents: Muscles: Sartorius, tensor fascia lata, quadriceps Nerve: Femoral Artery: Femoral Veins: Femoral and great saphenous
The femoral triangle
Boundaries:- Upper third of thigh just below the inguinal ligament which forms the base -Laterally, medial border of sartorius muscle - Medially the medial border of adductor longus -Inferiorly, the adductor canal through which femoral vessels pass into the popliteal fossa -Anterior wall is composed of the skin and fascia lata - Posterior wall is composed of muscles; adductor longus,pectineus,psoas major,and iliacus from medial to lateral side - Central hollow occupied by femoral vessels
Contents of the femoral triangle
The femoral vessels,the vein medial to the artery The profunda femoral artery from the posterolateral side of the femoral artery The lateral and medial circumflex arteries The deep external pudendal artery Three or four deep inguinal lymph nodes The femoral branch of genito femoral nerve The lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh The femoral nerve
Medial compartment of thigh
Bounderies:- Medially, is the medial intermuscular septum -No septum between it and posterior compartment Contents:- Muscles; gracilis, the three adductors longus brevis and magnus. Deeply lies obturator externus -Nerve; Obturator -Artery; Profunda femoris assisted proximally by obturator artery
The posterior compartment
Boundaries:- From buttock to back of knee -Separated from anterior compartment by the intermuscular septum - Not separated from the medial compartment by a septum since adductor magnus has two components fused from the adductors and from the hamstring. Contents:- Muscles; The hamstring muscles; semi tendinosus, the semi membranosus, and the biceps femoris - Nerve; Tibial component of the sciatic nerve except short head of the biceps femoris which comes from the common fibular part - Artery; Profunda femoris and its perforating branches. The upper part receives blood from the gluteal artery and the lower from the popliteal artery.
Popliteal fossa
Boundaries:- Above; semi membranosus and the semitendinosus on the medial side and the biceps femoris on the lateral side, diverging from the apex - Heads of gastrocnemus muscles below - Roof by the fascia lata - The floor by the popliteal surface of the femur, the capsule of the knee joint, renforced by the oblique popliteal ligament and the popliteus muscle covered by its fascia. Contents:- Muscles; Heads of gastrocnemus, popliteus, -Nerve; tibial and fibular - popliteal lymph nodes - Popliteal artery and vein
The anterior compartment of the leg region
Boundaries:- Medially, the subcutaneous surface of the tibia -Anterolaterally, the extensor muscular compartment Contents:- -Two intermuscular septae pass from deep fascia to enclose the peroneal compartment - Between the anterior intermuscular septum and the tibia lies the extensor compartment and between the posterior intermuscular septum and the tibia posteriorly lies the much bulky flexor compartment or calf.
Extensor compartment of the leg
Boundaries:- Between the deep fascia and the interosseous membrane -medially by extensor surface of tibia - Laterally by the extensor surface of the fibula Contents:-Muscles;tibialis anterior,extensor hallucis longus, extensor digitorum longus, and peroneus tertius -Nerve;fibular artery; anterior tibial vessels Lower end there is the extensor retinaculum
Dorsum of foot
Main veins form here: Great and short saphenous veins Nerve from the peroneal as the saphenous nerve Inferior extensor retinaculum prevents bowstringing of extensor tendons
Lateral compartment of the leg
Boundaries:- Between the peroneal surface of the fibula and deep fascia of the leg -In front and behind by the anterior and posterior intermuscular septum Contents:-Muscles; peroneus longus, and brevis - Nerve;superficial peroneal nerve - Artery; peroneal artery - vein; small saphenous vein
Posterior compartment of the leg
Boundaries:- The calf is medially limited by the medial border of the tibia, and laterally by the lateral border of the fibula Contents:- Muscles; two layers are found here separated by an intermuscular septum . Superficial muscles are the two gastrocnemus the plantaris, and the soleus. Deep muscles are the flexors, popliteus,flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus and tibialis posterior Nerve; tibial Artery: posterior and peroneal branches of posterior tibial artery.
Sole of foot
Essentially for strength and resilience Strength by massive tarsal bones and toe bones Resilience assured by multiple joints, arch arrangement and the powerful ligaments and the tie-beam aponeurosis Presence of sesamoid bones for the transmission of pull of small muscles.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Vessels of The Lower LimbDocumento60 pagineVessels of The Lower LimbAyalewNessuna valutazione finora
- The Upper LimbDocumento100 pagineThe Upper LimbAhmed Raza KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Femoral Region, Anterior and Medial Compartments of The ThighDocumento49 pagineFemoral Region, Anterior and Medial Compartments of The ThighNolanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gluteal RegionDocumento34 pagineGluteal Regionlion2chNessuna valutazione finora
- Popliteal Fossa: Dr.P.Sasikala, Assistant Professor of AnatomyDocumento18 paginePopliteal Fossa: Dr.P.Sasikala, Assistant Professor of AnatomySasikala Mohan100% (1)
- 7th Week Femoral Sheath, Femoral Triangle and Adductor CanalDocumento17 pagine7th Week Femoral Sheath, Femoral Triangle and Adductor CanalShah NawazNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper Limb: Organization FunctionDocumento33 pagineUpper Limb: Organization FunctionAhmed Nabiel El-Jaliel100% (1)
- 1st Lecture On Vascular Histology by Dr. ROOMIDocumento15 pagine1st Lecture On Vascular Histology by Dr. ROOMIMudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Anatomy of HeartDocumento46 pagineAnatomy of HeartDeepakNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesDa EverandNervous System: The Dog Stole the Professor's NotesNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionDocumento15 pagineBones of Upper and Lower Limbs - RevisionChess Nuts100% (1)
- Peritoneal SpaceDocumento54 paginePeritoneal Spacehsah radiologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighDocumento20 pagineGross Anatomy of Posterior Compartment of The ThighOnah ArinzeNessuna valutazione finora
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Da EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Lecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1Documento54 pagineLecture 3 Cardiovascular System 1hafiz patah100% (1)
- Atlas of Human Anatomy: Splanchnology · Ductless Glands · HeartDa EverandAtlas of Human Anatomy: Splanchnology · Ductless Glands · HeartValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Grip Strength and ElectromyogramDocumento8 pagineGrip Strength and ElectromyogramChandra Murali100% (1)
- Blood Vessels and Lymphatics in Organ SystemsDa EverandBlood Vessels and Lymphatics in Organ SystemsDavid AbramsonNessuna valutazione finora
- OIA-SA-H Cat Muscles MegatableDocumento6 pagineOIA-SA-H Cat Muscles MegatablePerseus Evangelio100% (2)
- Vascularization of Lower and Upper ExtermitesDocumento40 pagineVascularization of Lower and Upper Extermiteszainab sawan100% (1)
- Hand and WristDocumento5 pagineHand and WristcpNessuna valutazione finora
- Axilla Boundaries and ContentDocumento47 pagineAxilla Boundaries and Contentchzaheer72Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Human ThoraxDocumento71 pagineThe Human Thoraxbayenn100% (2)
- Upper Limb - Pectoral Region, Scapular Region, Axilla & Brachial PlexusDocumento12 pagineUpper Limb - Pectoral Region, Scapular Region, Axilla & Brachial Plexusewijayapala100% (1)
- Lower Limb Lab SheetDocumento3 pagineLower Limb Lab SheetKelly TrainorNessuna valutazione finora
- Ana 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Documento119 pagineAna 201 (Axilla N Axillary Artery) - 1Favour OnyeaboNessuna valutazione finora
- Upper LimbDocumento20 pagineUpper LimbsamzailNessuna valutazione finora
- AXILLADocumento8 pagineAXILLAImmunity RABOTANessuna valutazione finora
- How To Remember The Brachial PlexusDocumento4 pagineHow To Remember The Brachial PlexusAmanda PachecoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior & Medial Compartment of ThighDocumento25 pagineAnterior & Medial Compartment of ThighnasibdinNessuna valutazione finora
- A Practical Physiology: A Text-Book for Higher SchoolsDa EverandA Practical Physiology: A Text-Book for Higher SchoolsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bio Mechanics Lecture NotesDocumento53 pagineBio Mechanics Lecture NotesscdubalNessuna valutazione finora
- Regulation RespirationDocumento34 pagineRegulation Respirationkiedd_04100% (2)
- ANAT3411Documento51 pagineANAT3411Kai Dong ChoongNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelvis and Perineum - Anatomy, Vessels, Nerves - KenhubDocumento11 paginePelvis and Perineum - Anatomy, Vessels, Nerves - KenhubDhika100% (1)
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDocumento13 pagineUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- 01 Emryology The BeginningDocumento117 pagine01 Emryology The BeginningOsman Saidu SesayNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Biochemistry of Tissues and PhysiologicalDocumento214 pagineModule 5 Biochemistry of Tissues and PhysiologicalIna Guinar50% (2)
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento13 pagineCell Structure and FunctionNatalie KwokNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideDa EverandEndocrine System: A Tutorial Study GuideValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Anatomy of Upper LimbDocumento112 pagineAnatomy of Upper LimbUzma KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy 101 EmbryologyDocumento4 pagineHuman Anatomy 101 EmbryologyKonstantinos TheodosiadisNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Notes Week3Documento18 pagineAnatomy Notes Week3Zainab Ali100% (1)
- Osteology of Upper LimbDocumento13 pagineOsteology of Upper Limbdie1only100% (1)
- Dissection Guide For Human AnatomyDocumento170 pagineDissection Guide For Human Anatomyamazona89100% (1)
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Documento4 pagineSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaNessuna valutazione finora
- MSKDocumento7 pagineMSKKY KimberlyNessuna valutazione finora
- Aorta AnatomyDocumento41 pagineAorta AnatomySingey LhendupNessuna valutazione finora
- A&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)Documento42 pagineA&P - 7. Shoulder Girdle & Upper Limb Detailed Anatomy (42p)andreeaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Three Anatomical Planes: Anatomy TermsDocumento3 pagineThe Three Anatomical Planes: Anatomy TermsArman NaufalNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology of Respiratory System NotesDocumento3 pagineEmbryology of Respiratory System NotesJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy - Anterior Forearm and Palm PDFDocumento5 pagineAnatomy - Anterior Forearm and Palm PDFAngel Kim100% (2)
- Respiratory Physiology SenthilDocumento67 pagineRespiratory Physiology SenthilSenthilkumarNessuna valutazione finora
- EmbryologyDocumento39 pagineEmbryologyRukshan Ranatunga100% (1)
- Lifern's Anatomy: Limbs & Trunk: Thorax.................................................. 32Documento162 pagineLifern's Anatomy: Limbs & Trunk: Thorax.................................................. 32natheNessuna valutazione finora
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocumento28 pagineAutonomic Nervous Systemglad mohesh100% (1)
- AnatomyDocumento45 pagineAnatomyrkoppikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Reynaldo V. Lopez Senior Lecturer Department of AnatomyDocumento55 pagineDr. Reynaldo V. Lopez Senior Lecturer Department of AnatomyMohammad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Embryology of Musculoskeletal SystemDocumento14 pagineEmbryology of Musculoskeletal SystemdiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Islamic MonthsDocumento2 pagineIslamic MonthssheikTCSNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascularisation of The Lower LimbDocumento8 pagineVascularisation of The Lower LimbIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Muslim, Blessed, Months, Days, Nights, FestivalsDocumento9 pagineMuslim, Blessed, Months, Days, Nights, FestivalsabrahammahNessuna valutazione finora
- Citation Guidelines: MLA (Modern Language Association) Citation FormatDocumento7 pagineCitation Guidelines: MLA (Modern Language Association) Citation Formatdmh1976Nessuna valutazione finora
- Summary OfLower Limb AnatoDocumento6 pagineSummary OfLower Limb AnatoIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Folong PistDocumento1 paginaFolong PistIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Plantain PileDocumento1 paginaPlantain PileIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Renovascular Hypertension (M2) : G. Ashuntantang-SoméDocumento23 pagineRenovascular Hypertension (M2) : G. Ashuntantang-SoméIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- PK-PD of Antimicrobial Therapy-Lecture12 Oct11Documento37 paginePK-PD of Antimicrobial Therapy-Lecture12 Oct11Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbapenems and Monobactams - 090ct2012Documento6 pagineCarbapenems and Monobactams - 090ct2012Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Alggeo 20130213eDocumento3 pagineAlggeo 20130213eIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Alggeo 20130802eDocumento3 pagineAlggeo 20130802eIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 11-Protein Synthesis Inhibitors - Lincomycin & OthersDocumento21 pagine11-Protein Synthesis Inhibitors - Lincomycin & OthersIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 16 Anti Protozoal Drugs Lecture9 (0ct10)Documento18 pagine16 Anti Protozoal Drugs Lecture9 (0ct10)Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Penicillines Oct2012Documento19 pagine3 Penicillines Oct2012Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Anti Angina Agents Nov2010Documento12 pagine5 Anti Angina Agents Nov2010Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 6-LACTAMASE Inhibitors - Oct2013Documento4 pagine6-LACTAMASE Inhibitors - Oct2013Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Inhibitors PhenicolsDocumento11 pagine10 Antibiotics Protein Synthesis Inhibitors PhenicolsIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 5-Carbapenems and Monobactams - 090ct2012Documento5 pagine5-Carbapenems and Monobactams - 090ct2012Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Introduction To Pharmacology of Cardiovascular Drugs 0ct10Documento12 pagine1-Introduction To Pharmacology of Cardiovascular Drugs 0ct10Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Opioid AnalgesicsDocumento13 pagineOpioid AnalgesicsIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.7-Vasodilators Nov10Documento14 pagine4.7-Vasodilators Nov10Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Local Anesthetic May2010Documento26 pagineLocal Anesthetic May2010Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Opioid AnalgesicsDocumento13 pagineOpioid AnalgesicsIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Franco-Cameroon Congress 3Documento9 pagineFranco-Cameroon Congress 3Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Antacids and Anti-Ulcer Agents: Gastrointestinal PharmacologyDocumento56 pagineAntacids and Anti-Ulcer Agents: Gastrointestinal PharmacologyIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation (Hemopoietic Pharm) Jan 2010lDocumento2 pagineEvaluation (Hemopoietic Pharm) Jan 2010lIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Franco-Cameroon Congress 3Documento9 pagineFranco-Cameroon Congress 3Idrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug List For Health CampaignDocumento1 paginaDrug List For Health CampaignIdrissou FmsbNessuna valutazione finora
- Systems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesDocumento34 pagineSystems of Linear Equations With Two VariablesFatima KausarNessuna valutazione finora
- GTE LAB MANUAL Ver 4 - 1Documento135 pagineGTE LAB MANUAL Ver 4 - 1akhilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rangtong Shentong ViewDocumento19 pagineRangtong Shentong Viewlongjim31100% (1)
- 2020 Sustainabilty Report - ENDocumento29 pagine2020 Sustainabilty Report - ENGeraldNessuna valutazione finora
- Ok TC FlotationDocumento4 pagineOk TC FlotationWilliam SalcedoNessuna valutazione finora
- External Otitis (OE)Documento24 pagineExternal Otitis (OE)Hannah BLissNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn Horse Riding: at HPRCDocumento16 pagineLearn Horse Riding: at HPRCAkashNessuna valutazione finora
- INTERVIEW QUESTIONS - Verilog - PART-1Documento9 pagineINTERVIEW QUESTIONS - Verilog - PART-1charan tejaNessuna valutazione finora
- 24 - Al Nahda The Sheffeild Privat To International City, Greece K12 Dubai Bus Service TimetableDocumento10 pagine24 - Al Nahda The Sheffeild Privat To International City, Greece K12 Dubai Bus Service TimetableDubai Q&ANessuna valutazione finora
- Worktips 01 Priming of PavementsDocumento2 pagineWorktips 01 Priming of PavementsDilhara WickramaarachchiNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Brakes PDFDocumento6 pagine06 Brakes PDFAKILI PSINessuna valutazione finora
- Commissioning Valve Product BrochureDocumento14 pagineCommissioning Valve Product BrochureblindjaxxNessuna valutazione finora
- Shravana CharacterDocumento5 pagineShravana CharacterSuresh SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Figure Eight Island Homeowners' Association, Inc. Case StudyDocumento16 pagineFigure Eight Island Homeowners' Association, Inc. Case StudyYoong YingNessuna valutazione finora
- Bolt Group Coefficient For Eccentric Loads PDFDocumento5 pagineBolt Group Coefficient For Eccentric Loads PDFdvelchevNessuna valutazione finora
- Traina 250Wp PDFDocumento2 pagineTraina 250Wp PDFSherifImamNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk Assesment FOR PIPING WORKDocumento1 paginaRisk Assesment FOR PIPING WORKsunil100% (2)
- Ecological Fire MGMT Guidelines V5Documento40 pagineEcological Fire MGMT Guidelines V5MeNessuna valutazione finora
- Genmega G2500Documento103 pagineGenmega G2500tchindaforentNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Rex A Kaiju Thriller (Matthew Dennion) (Z-Library)Documento163 pagineAtomic Rex A Kaiju Thriller (Matthew Dennion) (Z-Library)Strictly Aviator Amritansh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- ATF - List of Explosive MaterialsDocumento8 pagineATF - List of Explosive MaterialsxiaotaoscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Advent of SkyscrapersDocumento27 pagineAdvent of SkyscrapersJoshua AlboNessuna valutazione finora
- Doxiadis, Constantinos (1968) EkisticsDocumento556 pagineDoxiadis, Constantinos (1968) EkisticsCelje1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- FPS Module 1Documento28 pagineFPS Module 1RickNessuna valutazione finora
- Zbus and Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDocumento20 pagineZbus and Symmetrical Fault Analysishj203800Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction On Photogrammetry Paul R WolfDocumento33 pagineIntroduction On Photogrammetry Paul R Wolfadnan yusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Nature Generator (Emtech Concept Paper)Documento3 pagineNature Generator (Emtech Concept Paper)Min SugaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Virudhunagar: Department: Semester: Vi SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 6602Documento34 pagineSri Vidya College of Engineering & Technology Virudhunagar: Department: Semester: Vi SUBJECT CODE / Name: CE 6602JEYA KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatric Airway ManagementDocumento2 paginePediatric Airway ManagementSilvy AmaliaNessuna valutazione finora