Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basics of Dialysis
Caricato da
Anicet VincentCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basics of Dialysis
Caricato da
Anicet VincentCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BASICS OF DIALYSIS
Basics of Dialysis
Healthy Kidney
Location and Structure Functions
Physical Basis
Transport through Membranes
Situation in a healthy human?
Functioning of solute transport?
Diseased Kidney
Causes Symptoms and Sequelae Renal Failure
Renal Replacement
Hemodialysis Peritonealdialysis Kidney Transplantation
Situation with a diseased kidney?
Functioning of replacement therapy?
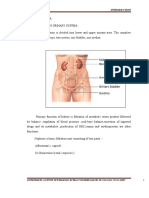
Location and Structure
Location of the Kidneys inside of the Body
Superior Vena Cava
Lung
Liver
Heart Aorta Spleen
Right Kidney
Large Intestine
Right Ureter
Left Kidney
Small Intestine
Left Ureter Bladder
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Location and Structure
Cross-Section of the Kidney
Nephron
Renal Medulla Papilla
Renal Vein Renal Artery Renal Pelvis Ureter
Renal Cortex
Branch of the Renal Vein
Branch of the Renal Artery
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Location and Structure
Nephron - Functional Unit of the Kidney
Distal Tubule Proximal Tubule
Collecting Duct Capillary Network
Plasma Ultrafiltrate Glomerulus Afferent Arteriole Efferent Venule
Urinary Outflow
Henles Loop
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Location and Structure
Details of a Glomerulus - The Membrane for Filtration
Proximal Tubule
Inside of the Capillary - Blood Side -
Bowmans Capsule Capillary Loops Efferent Arteriole Afferent Arteriole
Detail of the Capillary Wall
Capillary Wall - Filter-
Outside of the Capillary - Urine Side -
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Functions of the Kidney
Manifold Tasks of the Kidney
Bone Structure
Metabolic End Products
Blood Formation
Calcium Balance
Vitamin D Activation
Erythropoietin Synthesis
Removal of Urea, Creatinine etc.
Functions
Water Balance
Potassium Balance
Recovery of Bicarbonate Cardiac Activity Regulation of Blood pH
Healthy Kidney Diseased Kidney Physical Basis Renal Replacement
Sodium Removal Blood Pressure
Functions of the Kidney
Water Balance
0,3 l Water from metabolism 0,9 l Water contained in solid food 1,3 l Beverages
Water intake and water excretion must be balanced. This task is done by the kidneys and by thirst.
2,5 l Intake
0,1 l Water bound in stool 0,9 l Sweating and respiration 1,5 l Urine
2,5 l Removal
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Functions of the Kidney
Filtration and Reabsorption
60 l urine per day at the end of the proximal tubules 20 l urine per day at the beginning of the distal tubules 10 l urine per day at the end of the distal tubules
180 l filtrate per day in the glomeruli
1,5 l urine per day at the end of the collecting ducts real removal: 1,5 l urine
1500 l blood per day through the renal arteries
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Causes for Kidney Failure
Examples
Hypertension
Cysts, Anomalies
Diabetes
Autoimmune Diseases
Kidney Failure
Heavy Blood Loss
Nephritis
Accident / Trauma
Neurogenic Problems
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Causes for Kidney Failure
Location of the Cause?
Upstream of the Kidney - prerenal Heavy Blood Loss Stenosis of the Renal Artery ...
Within the Kidney - intrarenal Drugs Diabetes Inflammatory Diseases ...
Downstream of the Kidney - postrenal Prostatic Hypertrophy Renal Calculus ...
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Causes for Kidney Failure
Risk Factors of Renal Failure
Overweight Smoking
High Cholesterol
Hypertension Diabetes
Atherosclerosis
Kidney Failure
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Symptoms and Signs of Renal Diseases
Early Signs of Renal Disease
Blood in the Urine Protein in the Urine (Heavily Frothing Urine)
Fatigue
Signs and Symptoms at the beginning of renal disease are not specific, i.e. they occur also in other circumstances. A medical examination and simple tests are able to diagnose a renal disease early. Thus the progress of the renal disease can be stopped or at least slowed down.
Edema
Very Little Urin or Very Much Urine
Feeling of Weakness
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Symptoms and Signs of Renal Diseases
Renal Failure, e.g. Water Removal
Reduced Water Removal Peripheral Edema Fluid Overload in the Body Hypertension Fluid Lung
Reduction of Oxygen Intake
Reduction of Cardiac Performance
Without therapy the fluid overload of the body and its consequences are progressing, leading finally to the death of the patient. Renal replacement therapy is life-saving.
Healthy Kidney Diseased Kidney Physical Basis Renal Replacement
Renal Failure
Acute Renal Failure
Dialysis Treatments
Creatinine M/l Urine l/day
Time / days
Zllner, Innere Medizin, modified
1. Damage Damage to Renal Tissue (minutes to days)
Healthy Kidney
2. Oliguria / Anuria Complete Loss of Renal Function (up to 6 weeks)
3. Polyuria Uncontrolled Urine Quantities (1 - 2 weeks)
4. Recovery slow Recovery of Renal Function (several months)
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Renal Failure
Chronic Renal Failure - Stages
1
Renal Insufficiency
only minor clinical symptoms residual renal function is sufficient without treatment further deterioration
Renal Failure
increasing clinical symptoms multiple and serious deviations in blood chemistries residual renal function is borderline possible decompensation, e.g. due to a cold
severe clinical symptoms Acute-on-Chronic residual renal function is suddenly insufficient Renal Failure with adequate therapy a recompensation is often possible (return to stage 2)
Uremia
severe clinical symptoms renal replacement therapy is permanently needed, if untreated patient will die
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Physical Basis of Dialysis
Semipermeable Membrane
Erythrocyte, Red Blood Cell
Albumin, as Example of a Big Protein Molecule Electrolytes
Medium sized Molecules, e.g. b2-Microglobulin
Water Flow is Easily Possible
The semipermeable membrane functions similar to a fine sieve, only molecules that are small enough can pass.
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Physical Basis of Dialysis
Diffusion
Start: Different Concentrations End:
Time
Equal Concentrations
Diffusion is a consequence of the random movement of all molecules (Brownian Movement).
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Physical Basis of Dialysis
Ultrafiltration
Time
Pressure
Exertion of pressure on one side of the membrane produces filtration of water with solutes, as long as they can pass the membrane.
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Physical Basis of Dialysis
Osmosis
Time
Different to diffusion the dissolved particles cannot pass the membrane, nevertheless the concentrations tend to equal out, thus water passes the membrane.
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Physical Basis of Dialysis
Reverse Osmosis
Time Pressure
Similar to ultrafiltration pressure is applied to one side of the membrane. Reverse osmosis is especially important for the purification of water for the production of dialysate.
Healthy Kidney Diseased Kidney Physical Basis Renal Replacement
Hemodialysis
Flow Scheme Hemodialysis
Dialyzer Anti-Coagulation Blood Pump
Blood to the Patient Fresh Dialysate
Used Dialysate
Blood from the Patient
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Hemodialysis
Flow Scheme Hemofiltration
Dialyzer Sterile Infusion Solution Blood from the Patient Anti-Coagulation Blood Pump
Ultrafiltrate
An exact balancing of infused and ultrafiltrated volumes is mandatory when using Hemofiltration !
Blood to the Patient
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Hemodialysis
Vascular access
Dilated Vein - Shunt Twinlumen Catheter Jugular Vein (V. jugularis interna) Aorta
Connection: Vein and Artery Closure of the Distal End of the Vein
The vascular access using peripheral veins of the forearm has the big advantage of long usage, but it needs some weeks waiting time after the operation before the first use.
Healthy Kidney Diseased Kidney
The access by a catheter inserted in a central vein can be immediately used, but its lifetime is limited to a few weeks.
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Hemodialysis
Dialyzer
Bundle of Capillaries in the Housing Dialysate Inflow
Dialysate Outflow
Blood Outflow Solute Transfer across the Capillary Walls
Blood Inflow
The dialysate flows outside of the capillaries, blood within the capillaries countercurrently.
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Peritoneal Dialysis
How is Peritoneal Dialysis Done?
Bag with Fresh Solution
Peritoneal dialysis is done by filling specially composed peritoneal dialysis solution into the abdominal cavity.
The solute transfer between blood and the solution happens by diffusion. The water removal from the patient is an osmotic process.
Peritoneum
Implanted Catheter
Peritoneal Dialysis Solution Bag for Used Solution
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneum as Semipermeable Membrane
Transport from the Blood into the Solution Capillary Peritoneum
Connective Tissue Epithelial Layer Transport from the Solution into the Blood
Peritoneal Dialysis Solution
The solute transfer across the Peritoneum takes place in both directions, e.g. metabolic end products from the blood into the solution and e.g. buffers in the opposite direction.
Healthy Kidney Diseased Kidney Physical Basis Renal Replacement
Kidney Transplantation
Location of a Kidney Transplant
Liver Aorta
Kidney Transplant in the Fossa Iliaca, Not at the Position of Healthy Kidneys Connection of Renal Artery and Vein to the Pelvic Vessels
Connection of the Ureter to the Bladder of the Recipient
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Kidney Transplantation
Advantages of Kidney Transplantation
Continuous Treatment No Fixed Time Schedule
Advantages of Kidney Transplantation
Less Sequelae
Mobility
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Kidney Transplantation
Problems of Kidney Transplantation
Rejection Immunosuppression
Compatibility of Tissues
Disadvantages of Kidney Transplantation
Suitability of the Recipient
Shortage of Organ Donors
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Which Mode of Renal Replacement Therapy?
Kidney Transplantation Hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis
Each mode has its advantages and disadvantages. The selection is made in a discussion between patient and physician.
Healthy Kidney
Diseased Kidney
Physical Basis
Renal Replacement
Thank you for your kind attention.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Dialysis CompactDocumento16 pagineDialysis CompactTue100% (1)
- Dialysis TermsDocumento2 pagineDialysis TermsmagillaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Membranes for Life SciencesDa EverandMembranes for Life SciencesKlaus-Viktor PeinemannNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodialysis Dose and Adequacy GuideDocumento5 pagineHemodialysis Dose and Adequacy Guidedhianne_garcia2001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis DrugsDocumento51 pagineDialysis Drugslimkokhui100% (2)
- What You Should Know About Dialyzer Reuse: A Guide For Hemodialysis Patients and Their FamiliesDocumento8 pagineWhat You Should Know About Dialyzer Reuse: A Guide For Hemodialysis Patients and Their FamiliesDewiyanti TodingNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodialysis Adequacy DwiDocumento27 pagineHemodialysis Adequacy Dwiryo_ninukNessuna valutazione finora
- Adequacy of HaemodialysisDocumento82 pagineAdequacy of Haemodialysisshouvik chowdhury100% (1)
- Business Proposal - Dialysis - FiroDocumento17 pagineBusiness Proposal - Dialysis - FiroMuzri Muhammood100% (1)
- How To Measure Dialysis Adequacy - Edit 3Documento42 pagineHow To Measure Dialysis Adequacy - Edit 3Dicky SaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis Types and Processes ExplainedDocumento38 pagineDialysis Types and Processes ExplainedNish Macadato BalindongNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis Access Guidlines XenosDocumento69 pagineDialysis Access Guidlines Xenoslucian_panfilNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis Notes 1Documento3 pagineDialysis Notes 1Kavidu KeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Home Hemodialysis ManualDocumento279 pagineHome Hemodialysis ManualDabah KwakuphilipNessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of DialysisDocumento7 pagineComplications of DialysisDilessandro PieroNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug DialysabilityDocumento61 pagineDrug DialysabilityMohamed Essam ElraggalNessuna valutazione finora
- KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline Hemodialysis Update - Public Review Draft FINAL - 20150204 PDFDocumento78 pagineKDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline Hemodialysis Update - Public Review Draft FINAL - 20150204 PDFศักดิ์ชัย พูนศรีเจริญกุลNessuna valutazione finora
- Adequacy of HemodialysisDocumento42 pagineAdequacy of Hemodialysiswael abodiabNessuna valutazione finora
- Fresenius 2008T Dialysis System - Service ManualDocumento768 pagineFresenius 2008T Dialysis System - Service ManualEquipos HemodiálisisNessuna valutazione finora
- Interventional NephrologyDocumento5 pagineInterventional Nephrologyfouad tabet100% (1)
- DialysisDocumento63 pagineDialysisDhonat Flash100% (1)
- How Haemodialysis WorksDocumento19 pagineHow Haemodialysis WorksMaxence KouessiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis: Notes MS Vol. 2 Krizza Myrrh Gomera Balcita, RNDocumento52 pagineDialysis: Notes MS Vol. 2 Krizza Myrrh Gomera Balcita, RNWhimsey CipresNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis: Navigation SearchDocumento48 pagineDialysis: Navigation SearchCalimlim KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis Outcomes in India A Pilot Study PDFDocumento22 pagineDialysis Outcomes in India A Pilot Study PDFVashistmohan A.P.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Complications of HemodialysisDocumento34 pagineComplications of HemodialysisElza GeorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis: Duaa Farooq Khan 11634 Amina Bashir 11283 Syed Uzair Iftikhar 13608 Qamar Ud Din 13071Documento11 pagineDialysis: Duaa Farooq Khan 11634 Amina Bashir 11283 Syed Uzair Iftikhar 13608 Qamar Ud Din 13071Aimal SafdarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis and OsmosisDocumento10 pagineDialysis and OsmosisValerie Anne AstorgaNessuna valutazione finora
- DialyzerDocumento10 pagineDialyzerfatima rasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief Look at Renal AnatomyDocumento15 pagineA Brief Look at Renal AnatomyKristina De Peralta Willy100% (1)
- Renal Replacement Therapy HD, PD, Renal TransplantationDocumento65 pagineRenal Replacement Therapy HD, PD, Renal TransplantationparciNessuna valutazione finora
- PD Prescription Present 4-8-52Documento74 paginePD Prescription Present 4-8-52Kong Kong KongNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Unit HandbookDocumento105 pagineRenal Unit HandbookPBoxmNessuna valutazione finora
- Peritoneal DialysisDocumento23 paginePeritoneal Dialysismakyofrancis20Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis PrescriptionDocumento23 pagineDialysis PrescriptionMercy Juliana Jacqualine100% (1)
- Dialysis Basics: DR - Ashutosh Ojha MD, DNB (Gen Med) PDCC-Nephro (Student) GMCH..GuwahatiDocumento36 pagineDialysis Basics: DR - Ashutosh Ojha MD, DNB (Gen Med) PDCC-Nephro (Student) GMCH..GuwahatiManish Arya JaiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment OptionsDocumento60 pagineBPH Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment OptionsMaddox EdeyajNessuna valutazione finora
- Standards For Renal DialysisDocumento18 pagineStandards For Renal DialysisIbrar Ahmad100% (1)
- How Does Haemodialysis WorkDocumento19 pagineHow Does Haemodialysis Workhello_khay100% (1)
- PD Adequacy AssessmentDocumento33 paginePD Adequacy AssessmentKong Kong KongNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodialysis, Phosphorus and Calcium, Peritoneal DialysisDocumento29 pagineHemodialysis, Phosphorus and Calcium, Peritoneal DialysisTrizha MaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Peritoneal DialysisDocumento23 paginePeritoneal DialysisNur Aida JoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis and reverse osmosis technologies explainedDocumento9 pagineDialysis and reverse osmosis technologies explainedK.D. PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodialysis: By: Liana Lee SenciónDocumento14 pagineHemodialysis: By: Liana Lee SenciónKavidu KeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodialysis 2nd Final 171120Documento94 pagineHemodialysis 2nd Final 171120jaime berces hospitalNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Dialysis Fourth EditionDocumento2 pagineHandbook of Dialysis Fourth EditionMădălina Rădulescu50% (2)
- DIALYZERDocumento2 pagineDIALYZERassilamorNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Dialysis Training CentersDocumento6 pagineTop Dialysis Training CenterssakuraleeshaoranNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop CRRT PDFDocumento88 pagineWorkshop CRRT PDFDesy rahmatNessuna valutazione finora
- Alternate Dialysis Platforms:: Sorbents SorbentsDocumento17 pagineAlternate Dialysis Platforms:: Sorbents SorbentsJoe Single100% (2)
- Preoperative Vein Diameter Predicts AVF OutcomesDocumento40 paginePreoperative Vein Diameter Predicts AVF OutcomesMikael AngelooNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The KidneysDocumento7 pagineAnatomy of The KidneysSanthu SuNessuna valutazione finora
- Dialysis Event Surveillance ManualDocumento56 pagineDialysis Event Surveillance ManualAnitha SNessuna valutazione finora
- Genitourinary: Drafnan Abdirahman MohamedDocumento163 pagineGenitourinary: Drafnan Abdirahman MohamedMuse MuseNessuna valutazione finora
- Peritoneal Dialysis Adequacy & Prescription ManagementDocumento49 paginePeritoneal Dialysis Adequacy & Prescription Managementsurya kristyoadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemodialysis in ChildrenDocumento28 pagineHemodialysis in ChildrenKarna Yuli sitanggangNessuna valutazione finora
- Discover kidney disease care and nephrology nursingDocumento64 pagineDiscover kidney disease care and nephrology nursingvirnzrobzNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocumento33 pagineChronic Kidney DiseasesexiiimammaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Urinary System:-: Antilithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Dried Leaves of Fragaria Vesca Linn."Documento41 pagineIntroduction To Urinary System:-: Antilithiatic Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Dried Leaves of Fragaria Vesca Linn."Rohit PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Create - Interactive PDFDocumento9 pagineHow To Create - Interactive PDFAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- CPL-G01 Anti Curruption HandbookDocumento22 pagineCPL-G01 Anti Curruption HandbookAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- The Logical Framework ApproachDocumento4 pagineThe Logical Framework ApproachAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Health Book 2019 VfinalDocumento15 pagineSafety Health Book 2019 VfinalAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- The Logical Framework ApproachDocumento4 pagineThe Logical Framework ApproachAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- AAQS Standard Method of Measuring Building Work 2014Documento105 pagineAAQS Standard Method of Measuring Building Work 2014Janesha100% (1)
- Safety Health Book 2019 VfinalDocumento15 pagineSafety Health Book 2019 VfinalAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidance For Standard Form Contract - Sri Lanka PDFDocumento301 pagineGuidance For Standard Form Contract - Sri Lanka PDFNuwantha UduwageNessuna valutazione finora
- Substation Construction ManualDocumento63 pagineSubstation Construction ManualAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Load in Refrigeration SystemsDocumento72 pagineHeat Load in Refrigeration Systemsforeverdiesel100% (8)
- 3 Overhead Line and Substation Construction MethodologyDocumento34 pagine3 Overhead Line and Substation Construction MethodologyNurul Islam Faruk100% (4)
- Project Risk Assessment ExamplesDocumento10 pagineProject Risk Assessment Examples1094Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fire Fighting DrawingsDocumento6 pagineFire Fighting DrawingsAnicet Vincent0% (1)
- Project Risk Assessment ExamplesDocumento10 pagineProject Risk Assessment Examples1094Nessuna valutazione finora
- NORPLAN Tanzania Geotechnical EngineerigDocumento20 pagineNORPLAN Tanzania Geotechnical EngineerigAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Biogas Digestor ConstructionDocumento48 pagineBiogas Digestor ConstructionAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- NORPLAN Tanzania BrochureDocumento20 pagineNORPLAN Tanzania BrochureAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Compressed Air Systems - The Secret Is in The PipeDocumento5 pagineCompressed Air Systems - The Secret Is in The PipeAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-TB - Basic Dehumidification Refrigeration Flow Diagrams PDFDocumento4 pagine2-TB - Basic Dehumidification Refrigeration Flow Diagrams PDFAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- HTM 2022Documento92 pagineHTM 2022masoodaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Design Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo PDFDocumento7 pagineDesign Examples 1 2 of Circular Silo PDFAnicet Vincent70% (10)
- Fire Hydrant Spacing and Flow RatesDocumento3 pagineFire Hydrant Spacing and Flow RatesTanya Paira GamalloNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Drawings PDFDocumento3 pagineTechnical Drawings PDFAnicet Vincent33% (3)
- Natural Gas Installation Standards HandbookDocumento80 pagineNatural Gas Installation Standards HandbookAnicet Vincent100% (1)
- Tujenge 2012Documento1 paginaTujenge 2012Anicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Dehumidification of Fertilizer - Storage PDFDocumento2 pagineDehumidification of Fertilizer - Storage PDFAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial HosereelsDocumento4 pagineIndustrial HosereelsAnicet VincentNessuna valutazione finora
- (Subcellular Biochemistry 73) Baoxue Yang, Jeff M. Sands (Eds.) - Urea Transporters-Springer Netherlands (2014)Documento267 pagine(Subcellular Biochemistry 73) Baoxue Yang, Jeff M. Sands (Eds.) - Urea Transporters-Springer Netherlands (2014)Alejandro Rojas GómezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pediatrics NephrologyDocumento25 paginePediatrics NephrologyNujhat TabassumNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 26Documento7 pagineChapter 26jess waldenNessuna valutazione finora
- A&P Target ScoresDocumento72 pagineA&P Target ScoresMercurie8592% (12)
- MCQ FMS 3 (2016) With Answers-1Documento17 pagineMCQ FMS 3 (2016) With Answers-1stella pangestikaNessuna valutazione finora
- DiureticsDocumento49 pagineDiureticsamara cheemaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 5090Documento29 pagineBiology 5090iPhone InamNessuna valutazione finora
- Biochemistry 1.01 Cell MembraneDocumento8 pagineBiochemistry 1.01 Cell MembraneApril AramNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento64 pagineUrinary Systemazlidai ismailNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaesthesia Q Review 2014Documento33 pagineAnaesthesia Q Review 2014ChandanJha100% (8)
- Chapter 7. The Excretory System: Short QuestionsDocumento23 pagineChapter 7. The Excretory System: Short QuestionsAshwieen Kumar PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study Nephrotic SyndromeDocumento26 pagineCase Study Nephrotic SyndromeDimpal Choudhary0% (2)
- Kidney function and structure explainedDocumento7 pagineKidney function and structure explainedLisa EllisNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Histology MCQs GuideDocumento6 pagineRenal Histology MCQs GuideMohammad zreadNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes From Dental Articles ANATOMYDocumento6 pagineNotes From Dental Articles ANATOMYpatelpurvivNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 29 Urine Formation PDFDocumento15 pagineExpt 29 Urine Formation PDFGene PabayosNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Fluid RegulationDocumento10 pagineBiology Fluid RegulationArcely EchaniqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Pharmacology 2023Documento116 pagineRenal Pharmacology 2023sami MesfinNessuna valutazione finora
- ESRD Secondary To Diabetic Nephropathy CASE STUDYDocumento42 pagineESRD Secondary To Diabetic Nephropathy CASE STUDYRalph Pelegrino75% (4)
- HipofosfatemiaDocumento12 pagineHipofosfatemiamiguelalmenarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal Blood Flow Until Regulation of RBF and GFRDocumento5 pagineRenal Blood Flow Until Regulation of RBF and GFRDoogie ReynaldoNessuna valutazione finora
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Documento7 paginePathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Plant and human excretion systems explainedDocumento9 paginePlant and human excretion systems explainedJoy FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- M16 Biology HL Paper 2 MarkschemeDocumento18 pagineM16 Biology HL Paper 2 MarkschemeClaudia Angelica Bonilla EscobarNessuna valutazione finora
- RenalDocumento81 pagineRenalandreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fish Histology Manual v4Documento357 pagineFish Histology Manual v4vdcastillo13100% (1)
- Feedback MechanismDocumento25 pagineFeedback Mechanismkaloy domanaisNessuna valutazione finora
- Pex 09 01Documento5 paginePex 09 01Gerardien Elham AfifahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter No. 15 - Homeostasis (By Faisal Zada Khan)Documento36 pagineChapter No. 15 - Homeostasis (By Faisal Zada Khan)Pubg Killer15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Primer: Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento17 paginePrimer: Acute Kidney InjuryDiana AngelesNessuna valutazione finora