Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Resurce Provisioning
Caricato da
kamleshadhauTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Resurce Provisioning
Caricato da
kamleshadhauCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Euro-TM meeting 19-20 May 2011
WG5: Applications & Performance Evaluation
S. Distefano, M. Fazio, A. Puliafito (sdistefano, mfazio, apuliafito) @ unime.it
Applications/services and basic functions provided in a Cloud are based on the Virtual Resources which are abstracted from Physical Resources.
Virtual physical resources, such as V-CPUs, V-Storages, V-Networks etc.
V-Networks can be further divided into V-Routers, V-Switches, V-Firewalls, VPNs, V-Interfaces, V-Links based on physical Router/ Switch equipments.
Computational resources are managed in terms of Virtual Machines(VMs) and/or Virtual Clusters (VCs).
To prepare VMs with appropriate resources and make them ready for user applications
To prepare a virtual cluster with appropriate instances and make it ready for virtual cluster computation To manage changes in resources availability through VMs restore or migration
Allocating resources to VMs to match the workloads
Goals:
High resource utilization Energy efficiency reliability of services Low performance interference
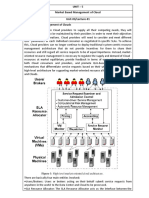
VM VM VM VM
Virtualized Service
Resource Broker 1
VM VM VM
Virtualized Service
Resource Broker 2
VM VM VM VM
Virtualized Service
Resource Broker 3
VM VM
Virtualized Service
Resource Providers (RPs) Clients
Business companies, cluster managers and even hosts which provide physical resources as IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service).
Users/Application that are interested in resource provisioning. They do not have knowledge regarding or control over the underlying data center infrastructures of the Clouds allocate resources for applications/services on multiple VMs in order to fulfill requests of different Clients manage resources provided by several RPs deploying VMs on several Physical Servers in the same Cloud, or even different Clouds. resource allocation in order to obtain the most cost-effective resources
Resource Brokers (RBs)
collecting and indexing all the resources available from several cloud providers translating the application requirements (expressed in terms of high-level parameters such as execution time, throughput, transaction rate) into low-level criteria related to computing, storage and network distributed resources estimating the capacity needs of Virtual Machines (VMs), managing the available resources in order to ensure specific requirements of QoS monitoring the usage of allocated resources in order to guaratee the SLA with the user performing load balancing based on resource consumption. dynamically reallocating resources, so to have a more efficiently use of available resources when Application/Services request to allocate (extra) resources, checking whether they are authorized managing VMs migration among different physical sites.
Transactions can be proposed as a lightweight mechanism to synchronize all the activities of resource Brokers Transactions alleviates many of the problems associated with the locking of VRs during the allocation task
STM implementation to protect shared VRs
Managing concurrent allocations from different RBs
Consistency of information whenever RPs update their resources RBs can force some kind of priorities among transactions
cut off locks and their related problems in process concurrence
Depending on the implementation, this priority could either be the age of a transaction or the type of activity (e.g. VM allocation, VM migration, resource discovery...)
Granularity of transactions is object-based, where objects are VMs.
Objects are shadowed, rather than changed in place. Commit tries to set the clone as the current object. Abort destroy the current clone and tries to set a new clone from the current objects.
Buffering Conflict detection Abort/Recovery Commit
Abort/Recovery
Local cache of available VR clones Cache coherence protocol Invalidate transactional cache activity Validate transactional cache activity
Buffering
VM
Transaction Manager
Resource Broker
VM VM VM VM
Resource Discovery
VM
Conflict detection
VM VM
VM VM
Virtualized Service
Commit
CM is an agent in the Transaction Manager. Notified of transaction events Decides what to do on a conflict: Several available policies
Abort a transaction or spin-wait Which transaction to abort, if any
In Cloud systems, new policies need to be designed to manage different types of activities
user-oriented policy provider-oriented policy economy-driven policy
Aggressive, Polite, Randomized, Greedy, Karma, Timestamp
Representation of VRs
VMs and VCs
Atomization strategies
to design RB tasks
Managing dynamic resources
resources abruptly disappear during a transaction
Clever
Virtual Infrastructure management layer to access and administrate private/hybrid clouds. Provider of Iaas https://clever.unime.it
Cloud@Home
volunteer computing into the Cloud computing paradigm C@H architecture works as a Cloud Broker https://cloudathome.unime.it/
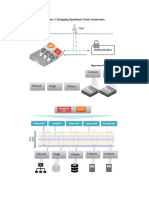
RQM is responsible for the management of resources and services needed to achieve the application requirements imposed by the SLA manager.
SLA
Cloud Providers
Discovery Layer Front end Request Handler
Front end Interface
Resource Manager
Discovery Layer Interface
State Tracker
State Tracker It keeps the state of the requests stored by the Request Handler and their associated resources It also acts as the essential event dispatcher into which other components can hook routines.
Deuce:
runtime environment for Java Software Transactional Memory (STM) http://www.deucestm.org
STM to support resource provisioning in Cloud environments: Managing concurrent RBs activities and resource updates from RPs Increasing VMs allocation efficiency Specific policies in the CM to design transaction management strategies Use case: C@H project
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessDa EverandThe Ultimate Guide to Unlocking the Full Potential of Cloud Services: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminarv HGHJFDCDocumento8 pagineSeminarv HGHJFDCDeepaDunderNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionDa EverandCloud Computing: Harnessing the Power of the Digital Skies: The IT CollectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Architectural Design of Compute and Storage Clouds: Unit - IiiDocumento13 pagineArchitectural Design of Compute and Storage Clouds: Unit - Iii0901IO201015 ANKIT PATELNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing Unit 3Documento30 pagineCloud Computing Unit 3Vinayak UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- (IJCST-V1I2P6) : K K Shahabanath, T Sreekesh NamboodiriDocumento4 pagine(IJCST-V1I2P6) : K K Shahabanath, T Sreekesh NamboodiriIJETA - EighthSenseGroupNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud ParadigmDocumento17 pagineCloud ParadigmMohammed YousifNessuna valutazione finora
- Resource Usage Monitoring in Clouds: Mohit Dhingra, J. Lakshmi, S. K. NandyDocumento7 pagineResource Usage Monitoring in Clouds: Mohit Dhingra, J. Lakshmi, S. K. NandysunilsmcsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Models and PlatformsDocumento36 pagineCloud Models and PlatformsGilbert GobiyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Models and PlatformsDocumento35 pagineCloud Models and PlatformsnoddynoddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3Documento24 pagineUnit 3Viraj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT IV-Cloud ComputingDocumento40 pagineUNIT IV-Cloud Computing19CS038 HARIPRASADRNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT III - Cloud Computing-1Documento34 pagineUNIT III - Cloud Computing-1struthika DNessuna valutazione finora
- International Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)Documento6 pagineInternational Refereed Journal of Engineering and Science (IRJES)www.irjes.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento90 pagineUnit 4DJ editzNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Machines Provisioning and Migration ServicesDocumento43 pagineVirtual Machines Provisioning and Migration ServicesNeha SrinivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud QnA For MTEDocumento64 pagineCloud QnA For MTELoL CluBNessuna valutazione finora
- CCSP Master Notes V2Documento54 pagineCCSP Master Notes V2Moazzam ChNessuna valutazione finora
- VIRTUALIZATIONDocumento4 pagineVIRTUALIZATIONCitac KnjigaNessuna valutazione finora
- CC Winter 2021 SolutionDocumento13 pagineCC Winter 2021 SolutionVivekNessuna valutazione finora
- CC-KML051-Unit IVDocumento16 pagineCC-KML051-Unit IVFdjsNessuna valutazione finora
- A Taxanomy of Live Migration in Cloud ComputingDocumento35 pagineA Taxanomy of Live Migration in Cloud ComputingGudivada LokeshsainathNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4Documento38 pagineUnit 4Dharmik SuchakNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud CMPTNG 2Documento6 pagineCloud CMPTNG 2Asad AliNessuna valutazione finora
- CC-KML051-Unit IIIDocumento18 pagineCC-KML051-Unit IIIFdjsNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Machines Provisioning and Migration ServicesDocumento64 pagineVirtual Machines Provisioning and Migration Servicesbhargavi100% (4)
- CC Unit 3Documento61 pagineCC Unit 3prassadyashwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Resource AllocationDocumento4 pagineCloud Resource Allocationnidee_nishokNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Computing Unit - Ii: Mohammed Sharfuddin, Assistant Professor, Csed, MjcetDocumento61 pagineCloud Computing Unit - Ii: Mohammed Sharfuddin, Assistant Professor, Csed, MjcetMohammed Abdul BariNessuna valutazione finora
- UIT1522-DS-U02S04-VM PROVISIONING AND MIGRATION-NetVDocumento50 pagineUIT1522-DS-U02S04-VM PROVISIONING AND MIGRATION-NetVBrain ChandlerNessuna valutazione finora
- Characterization of Elasticity With Promise of SLAsDocumento8 pagineCharacterization of Elasticity With Promise of SLAsSudha PelluriNessuna valutazione finora
- Market Based Management of CloudDocumento19 pagineMarket Based Management of Cloudjaijohnk100% (1)
- Iaa SCloud ArchitecturesDocumento35 pagineIaa SCloud ArchitecturesGhofrane FerchichiNessuna valutazione finora
- Architectural Overview of Cloud Computing: B.M. RaoDocumento37 pagineArchitectural Overview of Cloud Computing: B.M. RaoJyotiranjanDasNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IvDocumento20 pagineUnit Ivrachananandhan3007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IvDocumento20 pagineUnit Ivrachananandhan3007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4-Cloud Computing Notes-1Documento40 pagineUnit 4-Cloud Computing Notes-1HOD IT100% (3)
- UNIT III - Cloud ComputingDocumento35 pagineUNIT III - Cloud ComputingMagneto Eric Apollyon ThornNessuna valutazione finora
- Tempest - Soft State Replication in The Service TierDocumento10 pagineTempest - Soft State Replication in The Service TierDaniel ValadezNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 2Documento20 pagineLecture 2Faridullah SahilNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Virtual Machine Provisioning and Migration ServicesDocumento31 pagine4 Virtual Machine Provisioning and Migration ServicesSaravanaKumar MNessuna valutazione finora
- Architectures in Cloud ComputingDocumento35 pagineArchitectures in Cloud Computingsuga1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 4 FinalDocumento40 pagineUNIT 4 FinalSivakumar SathasivamNessuna valutazione finora
- Comp Sci - IJCSEITR - POLVMParallel Optimized Live VM Migration - Jayasree PDocumento16 pagineComp Sci - IJCSEITR - POLVMParallel Optimized Live VM Migration - Jayasree PTJPRC PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT III - Cloud ComputingDocumento35 pagineUNIT III - Cloud Computing19CS038 HARIPRASADRNessuna valutazione finora
- Base PaperDocumento8 pagineBase PaperRaminsha RafeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud ComputingDocumento9 pagineCloud ComputingAkshatNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 NotesDocumento42 pagineUnit 4 NotesViNiE .RNessuna valutazione finora
- Irjet V4i3151Documento3 pagineIrjet V4i3151Arthee PandiNessuna valutazione finora
- CloudDocumento5 pagineCloudmarcotony14Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6 - Approaches For Optimizing VM Placement and Migration in Cloud Environments A SurveyDocumento29 pagine6 - Approaches For Optimizing VM Placement and Migration in Cloud Environments A SurveyhasniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud ComputingDocumento53 pagineCloud ComputingashishNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2 CloudDocumento7 pagineModule 2 Cloudsreelakshmi sajeevNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtualization and Cloud Computing-U3Documento8 pagineVirtualization and Cloud Computing-U3Prabhash JenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Emerging Cloud Computing: Vol. 1 Issue 2 January 2011Documento17 pagineEmerging Cloud Computing: Vol. 1 Issue 2 January 2011admin2146Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enhanced Throttled Balancing Algorithm For Cloud ComputingDocumento13 pagineEnhanced Throttled Balancing Algorithm For Cloud ComputingAlmazeye MedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 CCDocumento40 pagineUnit 4 CCsivapunithan SNessuna valutazione finora
- Resourceful Multideployement and Multisnapshotting To Retroduce Traffic and Burden in Cloud Agent-Based Metropolitan Transport SystemsDocumento5 pagineResourceful Multideployement and Multisnapshotting To Retroduce Traffic and Burden in Cloud Agent-Based Metropolitan Transport SystemsinventionjournalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Cloud Quiz Question AnswerDocumento12 pagineCloud Quiz Question Answertayyab bsra juttNessuna valutazione finora
- A Framework For Establishing Trust in Cloud Provenance: Imad M. AbbadiDocumento18 pagineA Framework For Establishing Trust in Cloud Provenance: Imad M. AbbadivikasbhowateNessuna valutazione finora
- CS856 F15 SDN NFV ResearchDocumento59 pagineCS856 F15 SDN NFV ResearchSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Puppetcamp Geneva Talk Dan BodeDocumento43 paginePuppetcamp Geneva Talk Dan BodeSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- SDN TutorialDocumento31 pagineSDN TutorialSaravanaRaajaa100% (1)
- Ovs SlidesDocumento18 pagineOvs SlidesSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Object StorageDocumento45 pagineObject StorageSaravanaRaajaa100% (1)
- 20130407-LOAD Puppet TutorialDocumento93 pagine20130407-LOAD Puppet TutorialSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Hat Enteprise Linux Openstack Platform: Product Overview & UpdateDocumento32 pagineRed Hat Enteprise Linux Openstack Platform: Product Overview & Updatekrishna56hNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1: Designing Openstack Cloud ArchitectureDocumento65 pagineChapter 1: Designing Openstack Cloud ArchitectureSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- CS856 F15 SDN NFV ResearchDocumento59 pagineCS856 F15 SDN NFV ResearchSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deploying RDO On Red Hat Enterprise LinuxDocumento55 pagineDeploying RDO On Red Hat Enterprise LinuxSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Deploying RDO On Red Hat Enterprise LinuxDocumento55 pagineDeploying RDO On Red Hat Enterprise LinuxSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- 390alecture03 12spDocumento3 pagine390alecture03 12spSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Cloud Computing?Documento26 pagineWhat Is Cloud Computing?SaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Hat Enteprise Linux Openstack Platform: Product Overview & UpdateDocumento32 pagineRed Hat Enteprise Linux Openstack Platform: Product Overview & Updatekrishna56hNessuna valutazione finora
- RedHat Linux 9 Security GuideDocumento106 pagineRedHat Linux 9 Security GuideSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grep Awk SedDocumento9 pagineGrep Awk SedvishnuselvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grep Awk SedDocumento9 pagineGrep Awk SedvishnuselvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cathrow Thu 450 RhevDocumento47 pagineCathrow Thu 450 RhevSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceilometer Introduction PDFDocumento25 pagineCeilometer Introduction PDFSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutron UpdateDocumento16 pagineNeutron UpdateSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 05 22 Cloudday Amazon Aws Premiers Pas Carlos Conde 120618021543 Phpapp02Documento109 pagine2012 05 22 Cloudday Amazon Aws Premiers Pas Carlos Conde 120618021543 Phpapp02SaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amazon AWS Tutorial II: Windows and Linux On EC2Documento69 pagineAmazon AWS Tutorial II: Windows and Linux On EC2SaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Summary: Exercise: Make It So That OurDocumento4 pagineLecture Summary: Exercise: Make It So That OurSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamil Font Install HelpDocumento2 pagineTamil Font Install HelpSêlvâkûmâr JayabalaNessuna valutazione finora
- BCounts SetupTutorialDocumento26 pagineBCounts SetupTutorialSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Summary: Course Introduction and SyllabusDocumento4 pagineLecture Summary: Course Introduction and SyllabusSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Summary: Directory Description Command DescriptionDocumento3 pagineLecture Summary: Directory Description Command DescriptionSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- The CCA Component Model For High-Performance Scientific ComputingDocumento15 pagineThe CCA Component Model For High-Performance Scientific ComputingSaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shells and Shell Scripts: COMP 444/5201 Revision 1.3 January 25, 2005Documento34 pagineShells and Shell Scripts: COMP 444/5201 Revision 1.3 January 25, 2005SaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 TSCloud CamerareadyDocumento7 pagine2011 TSCloud CamerareadySaravanaRaajaaNessuna valutazione finora
- WiTECH KB ArticlesDocumento1 paginaWiTECH KB ArticlesServicios TecnicosNessuna valutazione finora
- Printing - What's New in WINFIOL 7Documento2 paginePrinting - What's New in WINFIOL 7hvicenteNessuna valutazione finora
- SystemDocumento4 pagineSystemseahorse2301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Info De3 Ba JaraneDocumento8 pagineInfo De3 Ba JaraneAmerBurekovicNessuna valutazione finora
- Resume C++ ExampleDocumento3 pagineResume C++ ExamplesergeypandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Systems Security CS 628A: Pramod Subramanyan Indian Institute of Technology KanpurDocumento66 pagineComputer Systems Security CS 628A: Pramod Subramanyan Indian Institute of Technology KanpurMohan RaghuNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical No.24,26,27,28,30Documento10 paginePractical No.24,26,27,28,30Abhishek JaikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab: Kubernetes Metrics ServerDocumento6 pagineLab: Kubernetes Metrics ServerSoujanyana SanagavarapuNessuna valutazione finora
- Password Guide To Use KeygenDocumento1 paginaPassword Guide To Use KeygenMelvin EsguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- A728542518 - 16469 - 30 - 2019 - Flume CompleteDocumento13 pagineA728542518 - 16469 - 30 - 2019 - Flume CompletevivekNessuna valutazione finora
- User-ID LabDocumento23 pagineUser-ID LabHenryNessuna valutazione finora
- Task Command April11Documento19 pagineTask Command April11debidash2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- COBOL Compilers 2004Documento8 pagineCOBOL Compilers 2004Cipta Ageung MahdiarNessuna valutazione finora
- 8-2-SP1 Administering My WebMethods ServerDocumento434 pagine8-2-SP1 Administering My WebMethods ServerShahbaz KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Installations DetailsDocumento8 pagineInstallations DetailsWesal RefatNessuna valutazione finora
- PDFDocumento22 paginePDFJosé MarquesNessuna valutazione finora
- BESR2010 Patch LogDocumento733 pagineBESR2010 Patch LogvasusarasNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Enable EB Tax in RequisitionsDocumento2 pagineHow To Enable EB Tax in Requisitionsvenkatrs63532Nessuna valutazione finora
- C01 Intro To Petrel 2004Documento32 pagineC01 Intro To Petrel 2004Henry Reynolds Darcy100% (1)
- Hyper V TDP Install UserGuide PDFDocumento270 pagineHyper V TDP Install UserGuide PDFimenhidouriNessuna valutazione finora
- TLE - ICTCSS10 - Q1 - Clas2 - Identifying Materials in Accordance With System RequirementsDocumento18 pagineTLE - ICTCSS10 - Q1 - Clas2 - Identifying Materials in Accordance With System RequirementsMARIES IMEE VENTURILLONessuna valutazione finora
- Endpoint Central Requirements and PortsDocumento9 pagineEndpoint Central Requirements and PortsZakariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manish KumarDocumento3 pagineManish Kumarmanish sharma1989Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roland Cloud Manager Eng01 WDocumento8 pagineRoland Cloud Manager Eng01 WPablo Martinez MasipNessuna valutazione finora
- HcwclearDocumento51 pagineHcwclearavin_kNessuna valutazione finora
- TocDocumento6 pagineTocTugas UtomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Autocad Webcast One - Getting StartedDocumento28 pagineAutocad Webcast One - Getting StartedMarcos AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Call Logging Interface User Manual PDFDocumento17 pagineCall Logging Interface User Manual PDFWagdy KhaterNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Hat OpenStack Platform-9-Director Installation and Usage-En-USDocumento190 pagineRed Hat OpenStack Platform-9-Director Installation and Usage-En-USMarcio José de OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- 914 E1 WebLogic12c Clustering-JASDocumento58 pagine914 E1 WebLogic12c Clustering-JASOscarJaimesNessuna valutazione finora