Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
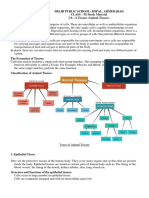
Tissues
Caricato da
Tedi HoxhaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tissues
Caricato da
Tedi HoxhaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
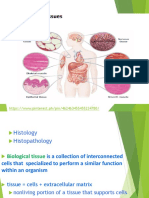
Histology- Study of Tissues
Physiological systems are made up of organs that serve specific functions. Organs are made up of tissues, which are then made up of cells.
Four types of tissue:
Epithelial Connective Muscle Nervous
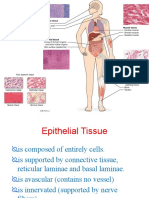
Epithelial tissues are sheets of tightly connected epithelial cells. The tissues form skin and line hollow organs.
Function of Epithelial cells
Some epithelial cells can: Secrete substances, like hormones Move substances with cilia Act as chemical receptors Create boundaries Control filtration and transport
Cells in Epithelial Tissue
Squamous
Cells- Simple /Stratified Columnar Cells- Simple/pseudostratified Cuboidal Cells- Simple/stratified Transitional Cells
Classification of Epithelial Tissue
Epithelial Tissue (A)
Stratified squamous epithelium, nonkeratinized, from human mouth. LM, H&E stain.
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Simple Columar Epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium from human intrahepatic bile duct. LM, trichrome stain.
Simple cuboidal epithelium lining follicles of human thyroid gland. LM, H&E stain.
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium lining a human bronchus; cilia on many cells. LM.
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
Transitional epithelium line the urethra of a male infant. LM, H&E stain.
Pigmented epithelium from a person of African descent. LM, H&E stain.
Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Non-Keratinized Stratified Squamous Epithelium
Transitional Epithelium
Skin from human foot; note thick keratin layer. LM, H&E stain.
Sweat glands in human skin. LM, H&E stain.
Epithelial Tissue (B)
Simple
cuboidal epithelium is found in glandular tissue and in the kidney tubules.
Muscle tissues consist of elongated cells that generate force and cause movement. Three types of muscle tissues: Skeletal Cardiac Smooth
Skeletal:
responsible for locomotion and other body movements (e.g., breathing, shivering). Cardiac: makes up the heart and is responsible for the heartbeat and blood flow. Smooth: involved in movement and generation of forces in internal organs (e.g., gut, blood vessels).
Figure 40.4 Filaments in Skeletal Muscle Cells
Types of Muscle Tissue
Connective tissues are dispersed cells in an extracellular matrix that they secrete. The matrix contains protein fibers: Collagen: strong and resistant to stretch, supports skin and connections between muscles and bones Elastin: can be stretched and then recoils; found in tissues that stretch (e.g., lungs, arteries)
Diagram of Loose CT
Connective Tissue
Areolar connective tissue; elastic and collagenic fibers in a rat. LM, silver stain.
Connective tissues: Cartilage provides structural support and is flexible: has chondrocytes; cells that secrete the extracellular matrix. Bone: provides support and is hardened by calcium phosphate deposition in the matrix. Bone cells are osteocytes.
Hyaline cartilage in cat larynx. LM, H&E stain.
Cartilage
Fibrocartilage in a mammalian intervertebral disc. LM, H&E stain.
Elastic cartilage from a pig's ear.
Human compact bone, transverse section. LM, Schmorl's stain.
More connective tissues: Adipose tissue: includes adipose cells that form and store lipids. Cells are adipocytes. Blood: consists of cells in a very liquid extracellular matrix, the blood plasma. There are red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and platelets (thrombocytes).
Blood cells from domestic chicken (Gallus gallus). LM,
Giemsa stain.
Normal human adipose cells. LM, H&E stain.
Nervous tissues contain two basic cell types: neurons and glia. Neurons encode information as electrical impulses that travel over axons to their targets. Chemical signals from the neuron stimulate a response in the target cell, via receptors. Glia provide support for neurons.
Neurons
Nervous Tissue Includes Neurons and Glia (A)
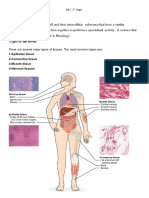
Organs consist of multiple tissues. An organ system is a group of organs that function together.
Different Tissues make up an organ
Example: The stomach wall is arranged in layers: Epithelial cells Connective tissue Smooth muscle Neurons Connective tissue
Figure 40.7 Tissues Form Organs
Fig 40.7 whole figure except stomach
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Animal Tissues: Structures and Functions in 40 CharactersDocumento41 pagineAnimal Tissues: Structures and Functions in 40 Charactersenkidani100% (1)
- Animal Cells, Tissues, and Organs - Exercise 12Documento53 pagineAnimal Cells, Tissues, and Organs - Exercise 12James SiazonNessuna valutazione finora
- Class Discussion On TissueDocumento2 pagineClass Discussion On TissueKristhine Abegail Manangan-GamiaoNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesDocumento11 pagineCH 6 Tissues Animal TissuesRishabh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissues: TissueDocumento4 pagineAnimal Tissues: TissuePrasad SwaminathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento13 pagineAnimal TissuesYudatami TiaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento23 pagineAnatomy and Physiologyapi-464344582100% (1)
- TissuesDocumento46 pagineTissuesericaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissueDocumento32 pagineAnimal TissueIan Kerby Sollano100% (1)
- Human Tissues - 1Documento43 pagineHuman Tissues - 1Angel Diadem ViloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissueDocumento3 pagineAnimal TissueAkmal MusyaffaNessuna valutazione finora
- HAP Question Paper Solution D. PharmaDocumento9 pagineHAP Question Paper Solution D. PharmaSinger Rahul Sharma100% (1)
- Jaringan Hewan (Animal Tissue)Documento28 pagineJaringan Hewan (Animal Tissue)Adi GunawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lab.2Documento8 pagineAnatomy Lab.2aminqasm111Nessuna valutazione finora
- محاضرات أنسجة 2017Documento20 pagineمحاضرات أنسجة 2017Salam H Alhelali100% (2)
- GEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDocumento4 pagineGEN BIO Q1M1subtopic WK 4 LectureDonnalyn Mae EscrupoloNessuna valutazione finora
- AnaphyDocumento2 pagineAnaphyFlorence Nichole RoganNessuna valutazione finora
- Simple Epithelium Stratified EpitheliumDocumento2 pagineSimple Epithelium Stratified EpitheliumFlorence Nichole RoganNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Documento10 pagine11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- Exercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreDocumento9 pagineExercises 1 Tissues: 1. Define What Tissues AreMaria MarmitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1Documento60 pagineLesson 1 Plant and Animal Tissue Presentation1abdullahfahdelm.adiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento6 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyDelixae Phoinix80% (5)
- Histology Notes: Epithelial TissueDocumento4 pagineHistology Notes: Epithelial TissueSteph AsideNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Tissues (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Documento53 pagineLesson 2 Tissues (Human Anatomy and Physiology)Dump Acc 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocumento19 pagineStructural Organisation in AnimalsBiju Mylachal100% (1)
- TissuesDocumento70 pagineTissuesayssNessuna valutazione finora
- HistologyDocumento11 pagineHistologyKeith OmwoyoNessuna valutazione finora
- CELLDocumento18 pagineCELLshivanshkansal099Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Tissue GKDocumento6 pagineAnimal Tissue GKlakshya GandhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells & Tissues (LS1151 & SM0030) Notes On Histology LecturesDocumento7 pagineCells & Tissues (LS1151 & SM0030) Notes On Histology LecturesArezo TanhaNessuna valutazione finora
- TISSUESDocumento12 pagineTISSUESMaria Stephanie LabutapNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Documento37 pagineWhy Human Beings Are Considered Complex Organisms Group 5Nuraini Zul100% (3)
- التشريح والفسلجة نظريDocumento16 pagineالتشريح والفسلجة نظريem2200139Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocumento7 pagineChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- Types of Cells in the Human Body ExplainedDocumento34 pagineTypes of Cells in the Human Body ExplainedJiezel CastorNessuna valutazione finora
- The Tissue Level of OrganizationDocumento31 pagineThe Tissue Level of OrganizationYunandhika RizkiNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology 25: Human Biology: Prof. Gonsalves Los Angeles City College Loosely Based On Mader's Human Biology, 7 EditionDocumento42 pagineBiology 25: Human Biology: Prof. Gonsalves Los Angeles City College Loosely Based On Mader's Human Biology, 7 EditionRhaine EstebanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissue SystemDocumento41 pagineTissue Systemrahul royNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology - 4th SemDocumento76 paginePhysiology - 4th SemSandeep AdapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy Lab Quizlet Flashcards Converted For AnkiDocumento6 pagineAnaphy Lab Quizlet Flashcards Converted For AnkiAldrin LimcuandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissueDocumento6 pagineAnimal TissueAhmad NadeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Body Tissues Power PointDocumento60 pagineHuman Body Tissues Power PointMaxwell C Jay KafwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento33 pagineTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1 - Tissues. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve, Blood, ReproductiveDocumento4 pagine1.1 - Tissues. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve, Blood, ReproductiveAris PaparisNessuna valutazione finora
- BIOL223-Lab 9Documento53 pagineBIOL223-Lab 9chicken fries100% (1)
- Connective tissue properDocumento26 pagineConnective tissue properPuspita SariNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento92 pagineAnatomy and Physiologyzaneta.szuckaNessuna valutazione finora
- ANIMAL CELLS AND TISSUES Lecture Notes PDFDocumento17 pagineANIMAL CELLS AND TISSUES Lecture Notes PDFAnonymous HXLczq380% (5)
- Chapter 11: Human Organization: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocumento3 pagineChapter 11: Human Organization: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Editionjadusingh000Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento44 pagineAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology LabDocumento12 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Labشهد إياد0% (1)
- Cellular Histology GuideDocumento27 pagineCellular Histology GuideJonaya AmpasoNessuna valutazione finora
- TissuesDocumento4 pagineTissuesJaveria ZaidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Tissues, Organs and Organ SystemsDocumento17 pagineTissues, Organs and Organ SystemsDestinee Sullivan100% (1)
- Tissues PPT SummaryDocumento16 pagineTissues PPT SummarySamarjeet BaliyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective Tissue 4nursing@2024Documento67 pagineConnective Tissue 4nursing@2024abdurezakayano724Nessuna valutazione finora
- Animal TissuesDocumento3 pagineAnimal TissuesSalman HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiDocumento22 pagineBiology Lect1. Type of Tissue DR - Aida AlobaidiYaqeen AlaidyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Documento33 pagineThe Four Primary Tissue Types:: Epithelial (Covering) Connective Tissue (Support) Muscle (Movement) Nervous (Control)Maira Garcia C.100% (2)
- A2 Biology Notes For EdexcelDocumento150 pagineA2 Biology Notes For EdexcelAbdulrahman Jijawi83% (6)
- Rehabilitation Will Increase The Capacity of Your Insert Musculoskeletal Tissue Here Defining Tissue Capacity A Core Concept For CliniciansDocumento3 pagineRehabilitation Will Increase The Capacity of Your Insert Musculoskeletal Tissue Here Defining Tissue Capacity A Core Concept For CliniciansChristhoper HermosillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of The Target-Capture PCR Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Quantitative Assay and Comparison With Commercial HBV DNA Quantitative AssaysDocumento6 pagineAssessment of The Target-Capture PCR Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) DNA Quantitative Assay and Comparison With Commercial HBV DNA Quantitative AssaysdwimarufNessuna valutazione finora
- Booklet - Consious Water v09Documento35 pagineBooklet - Consious Water v09martinscodellerNessuna valutazione finora
- Mothership Character SheetDocumento2 pagineMothership Character SheetAlexander Dalton0% (1)
- 8.5 Power Notes PDFDocumento1 pagina8.5 Power Notes PDFMaria Jose SantamariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Erwin-Sheppard Autopsy Report - Redacted by Medical ExaminerDocumento17 pagineErwin-Sheppard Autopsy Report - Redacted by Medical ExaminerCheryl Sullenger100% (1)
- Pharmacological AntagonismDocumento4 paginePharmacological AntagonismMuhammad MasroorNessuna valutazione finora
- Mendel and The Principles of HeredityDocumento61 pagineMendel and The Principles of Heredityfae-ar_raziNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomechanics of BoneDocumento27 pagineBiomechanics of BoneJimmy ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- WasteDocumento49 pagineWasteMirza ShahrezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Olympiad Mock Test 1Documento8 pagineScience Olympiad Mock Test 1vidhan tiwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Fertilization to Birth: A Guide to Pregnancy DevelopmentDocumento7 pagineFertilization to Birth: A Guide to Pregnancy DevelopmentSamson BongsiwNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress 2Documento4 pagineStress 2le thi lan anhNessuna valutazione finora
- Excretory System of FrogDocumento3 pagineExcretory System of FrogSree Lekshmi V SNessuna valutazione finora
- Microbiology Ans Scheme 1-23-29!30!33 38 by g34Documento100 pagineMicrobiology Ans Scheme 1-23-29!30!33 38 by g34Arief NorddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocumento16 paginePolymerase Chain ReactionAbdulati Abu RewillaNessuna valutazione finora
- The SupernaturalistDocumento2 pagineThe SupernaturalistAlex LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment AnswersDocumento2 pagineAssignment Answersxewoj59015Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antioxidant Assays: 1. DPPH Assay (2, 2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl)Documento4 pagineAntioxidant Assays: 1. DPPH Assay (2, 2-Diphenyl-1-Picrylhydrazyl)Krishnaswamy VkdNessuna valutazione finora
- Termamyl 120LDocumento8 pagineTermamyl 120Lnothing2902Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cepheids.: No. of Systematic Area Position Variables DeviationDocumento9 pagineCepheids.: No. of Systematic Area Position Variables DeviationLefrina GusrianiiNessuna valutazione finora
- Acceptability: ©WHO/Sergey VolkovDocumento26 pagineAcceptability: ©WHO/Sergey VolkovBeatriz PatricioNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Cementum and Alveolar BoneDocumento24 pagine4 Cementum and Alveolar Boneceudmd3d100% (1)
- Anti AIDS HerbsDocumento6 pagineAnti AIDS Herbskhansa maryamNessuna valutazione finora
- SAFC Supply Solutions - Proligo® Reagents CatalogDocumento64 pagineSAFC Supply Solutions - Proligo® Reagents CatalogSAFC-Global100% (1)
- POST OP BrunnerDocumento7 paginePOST OP Brunnerjamie carpioNessuna valutazione finora
- Dwnload Full Medical Terminology For Health Professions 7th Edition Ehrlich Test Bank PDFDocumento36 pagineDwnload Full Medical Terminology For Health Professions 7th Edition Ehrlich Test Bank PDFmarchingpalmerbabg100% (9)
- Thermochemistry Heteroatomic CompoundsDocumento7 pagineThermochemistry Heteroatomic CompoundsAnisatya AmaliahNessuna valutazione finora
- OCSPP Harmonized Test Guidelines - Master List: Available Electronically atDocumento20 pagineOCSPP Harmonized Test Guidelines - Master List: Available Electronically atmelimeli106Nessuna valutazione finora