Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Model Propagasi Selular
Caricato da
Aenur RofiqTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Model Propagasi Selular
Caricato da
Aenur RofiqCopyright:
Formati disponibili
SISTEM KOMUNIKASI NIRKABEL
Jati Fallat
Pendekatan Analitik dan Empirik
Mobile Radio Channel Characterisation
Theoretical approach
Free space loss
Plane earth path loss
Diffraction loss
Empirical/prediction approach
Okumura-Hatta - Blomquist-Ladel
Lee - Alsebrook
Egli - Ibrahim Parson
Measurement of large scale and application in coverage prediction
Some examples
Karakterisasi Propagasi
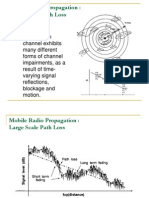
Mobile Radio Propagasi
Large-scale propagation Small-scale propagation
Mean signal
Signal Variation
Time
spreading of
signal
Time
variation of
channel
MODEL PROPAGASI SISTEM SELULAR
Model untuk memperkirakan redaman :
Model teoretis
Model empiris
Model Lee
Persamaan Umum Redaman Propagasi
Perkiraan Titik demi Titik
Model Okumura-Hatta
Faktor Koreksi Undulasi
Faktor Koreksi Kemiringan
Theoretical approach
Free space formula
Received power density at distance d when Tx antena gain G
t
is
Received power when Rx antenna gain G
t
is
Ratio of Rx/Tx power is
Free space path loss is L
p(FS)
[dB] = 32.45 + 20 log f + 20 log d
2
t t
r
d 4
G W
P
t
=
t
t
=
4
G
d 4
G W
W
r
2
2
t t
r
2
r t
2
r t
t
r
df 4
c
G G
d 4
G G
W
W
|
.
|
\
|
t
=
|
.
|
\
|
t
=
Plane earth propagation
Path loss model plane earth is L
p(PE)
= 120 + 40 log
d 20 log h
t
20 log h
r
Tx
Rx
h
t
h
r
d
Diffraction Loss
The difference of path length between direct and diffracted ray is
T
x
R
x
d
1
d
2
h (positif)
T
x
R
x
d
1
d
2
h (negatif)
2 1
2 1
2
d d
d d
2
h
d
+
~ A
Fresnel zone (path clearance)
The phase difference when h << d
1
and h << d
2
is
with v is diffraction parameter which can be expressed as
The n-th Fresnel zone is area between Tx and Rx inside the
ellipsoide with radius of its cross section of r
n
where
2
2 1
2 1
2
v
2 d d
d d
2
h 2 d 2 t
=
+
t
=
A t
= A
|
|
.
|
\
| +
=
2 1
2 1
d d
d d 2
h v
2 1
2 1
n
d d
d d n
h r
+
= =
Empirical Prediction Approach
Based on signal measurement
Okumura - Blomquist-Ladel
Lee - Alsebrook
Egli - Ibrahim-Peterson
Mathematical Formulation based on signal
measurement
Hatta (Japan)
COST-231 (Europe)
Okumura Hatta Model
L
p(open)
= L
p(urban)
4.78(logf)
2
+ 18.33 log f 40.94
For urban area:
L
pu
[dB] = 69.55 + 26.16 log f 13.82 log h
b
a(h
m
) + (44.9 6.55 log h
b
) log d
Model Okumura Hatta
KLASIFIKASI
DAERAH
PELAYANAN
RUMUS REDAMAN PERAMBATAN
Urban Area
Lu = 69,55 +26,16 log f
c
13,82 log h
b
a (h
m
) + (44,9
6,55 log h
b
) log R..(dB)
- Faktor koreksi untuk tinggi antena stasiun mobil
yang bergantung kepada tipe daerah urban yang
dibagi sebagai berikut :
Medium small city :
a (h
m
) = (1,1 log f
c
0,7) h
m
(1,56 log f
c
0,8) .(dB)
Large City
a (h
m
) = 8,29 (log f
c
1,54 h
m
)
2
1,1 , f
c
< 200 MHz
a (h
m
) = 3,2 (log f
c
11,75 h
m
)
2
4,97 , f
c
> 400 MHz
Sub Urban Area Lsu = Lu (urban area) 2 [log (f
c
/28)]
2
5,4 .(dB)
Open Area Lo = Lu (urban area) 4,78 (log f
c
)
2
+ 18,33 log f
c
40,94 .(dB)
Keterangan :
f
c
= frekuensi kerja yang berharga : 150 MHz 1500 MHz
h
b
= tinggi antena stasiun tetap (RBS) : 30 m 200 m
hm = tinggi antena stasiun mobil (MS) : 1 m 3 m
R = jarak pemancar penerima : 1 km 20 km
Lee Model
Lee formulated the path loss of being
L
p
[dB] = L
0
+ log d ; with L
0
is path loss at d = 1 km and is the
path loss slope.
Area L
0
[dB] (dB/decade]
Free space 91.2 20
Open/rural area 90.4 43.5
Suburban area 104.3 38.4
New Ark 105.5 43.1
Philadelphia 112.8 36.8
New York City 117.5 48
Tokyo 128.1 30.5
Egli Model dan Blomquist-Laded Model
EGLI MODEL
Based on Plane Earth Theoretical model with correction factors
L
p
[dB] = 120 + 40 log d 20 log h
t
20 log h
r
+ |
Blomquist-Laded Model
L
p
[dB] = L
free space
+{(L
iplane earth
L
free space
)
2
+
(L
diffraction
)
2
}
1/2
Alsebrook Model
For flat areas L
p
[dB] = L
plane earth
+L
B
+ ,
For hilly areas :
L
p
[dB] = L
free space
+{(L
iplane earth
L
free
space
)
2
+ (L
diffraction
)
2
}
1/2
+ L
B
+ ,
Ibrahim-Peterson Model
L
p
[dB] = 40 log d 20 log(h
b
h
m
) + o
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- What Is Communication ? Significance of Guided and Unguided Communication Wireless / Mobile Communication Radio Propagation EffectsDocumento61 pagineWhat Is Communication ? Significance of Guided and Unguided Communication Wireless / Mobile Communication Radio Propagation EffectsSrinath RavichandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Path-Specific Propa ModelsDocumento71 paginePath-Specific Propa ModelsOmotowa DapoNessuna valutazione finora
- Diffraction ModelsDocumento57 pagineDiffraction ModelsGürsoy PekşenNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagation Models PDFDocumento21 paginePropagation Models PDFLarissa LissinaNessuna valutazione finora
- WMC Experiment-3 PDFDocumento34 pagineWMC Experiment-3 PDFBlahNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.3 Model Propagasi Okumura HattaDocumento32 pagine8.3 Model Propagasi Okumura HattaNOAH PALWA YUWANA -Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless 03 Large ScaleDocumento14 pagineWireless 03 Large ScaleRandeel WimalagunarathneNessuna valutazione finora
- The Wireless Channel 1Documento43 pagineThe Wireless Channel 1Anil FkNessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Simulation Model of Mobile Fading Channel: Tomáš Marek, Vladimír Pšenák, Vladimír WieserDocumento6 pagineComplex Simulation Model of Mobile Fading Channel: Tomáš Marek, Vladimír Pšenák, Vladimír Wiesergzb012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hata and Hata SRD Implementation - v2 PDFDocumento5 pagineHata and Hata SRD Implementation - v2 PDFvladiforeNessuna valutazione finora
- WC 4 - Shivani - Varu - 190423116010Documento4 pagineWC 4 - Shivani - Varu - 190423116010Shivani VaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: The Wireless Channel: Ronal D. Montoya M. Ronalmontoya5310@correo - Itm.edu - CoDocumento13 pagineUnit 1: The Wireless Channel: Ronal D. Montoya M. Ronalmontoya5310@correo - Itm.edu - CoJuan GallegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Jane Musengya-Assignment 2Documento11 pagineJane Musengya-Assignment 2Jane Muli100% (1)
- Wireless Communication LAb Manual - 02-11-21Documento45 pagineWireless Communication LAb Manual - 02-11-21jayanth100% (2)
- S-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)Documento24 pagineS-72.245 Transmission Methods in Telecommunication Systems (4 CR)vamseeNessuna valutazione finora
- Questions MCDocumento20 pagineQuestions MCAndima Jeff HardyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial1 Sol 180102Documento9 pagineTutorial1 Sol 180102Punky HeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Mobile - BasicsDocumento54 pagineChapter 3 - Mobile - Basicsn2hj2nNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Propagation. Path Loss Models. Shadowing: Lecture OutlineDocumento3 pagineSignal Propagation. Path Loss Models. Shadowing: Lecture OutlineUbaidullah JoyiaNessuna valutazione finora
- WCCH2015 1 PathLoss and ShadowingDocumento42 pagineWCCH2015 1 PathLoss and ShadowingTrong NđNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture6 - Radio Propagation Models (Final)Documento77 pagineLecture6 - Radio Propagation Models (Final)Enakshi KapoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Sat Comm Sys EngineeringDocumento34 pagineSat Comm Sys EngineeringHamis RamadhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp-1: Understand The Pathloss Prediction FormulaDocumento6 pagineExp-1: Understand The Pathloss Prediction FormulaM Xubair Yousaf XaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.3 Empirical Models For Urban PropagationDocumento5 pagine7.3 Empirical Models For Urban PropagationlabviewloverNessuna valutazione finora
- ENTC 3320: Active FiltersDocumento60 pagineENTC 3320: Active FiltersAbdullah NisarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Coverage PlanningDocumento100 pagine2 Coverage PlanningDon BuetaNessuna valutazione finora
- 020 Propagation Path-Loss Model For TV White Space of KoreaDocumento6 pagine020 Propagation Path-Loss Model For TV White Space of Koreaeuler.amNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt-5 - Lab Manual - TE Lab PDFDocumento10 pagineExpt-5 - Lab Manual - TE Lab PDFAaryan Rizvan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Radio Wave Propagation PDFDocumento29 paginePrinciples of Radio Wave Propagation PDFAmir.stNessuna valutazione finora
- Link Budget Calculation Example For UMTSDocumento5 pagineLink Budget Calculation Example For UMTSexcaliburslvNessuna valutazione finora
- Evaluation For Suitable Large-Scale Propagation Models To Mobile Communications in Urban-AreaDocumento7 pagineEvaluation For Suitable Large-Scale Propagation Models To Mobile Communications in Urban-Areawww.irjes.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Propagation Theory and Models ISSUE1.0Documento39 pagineRadio Propagation Theory and Models ISSUE1.0Subhi RosdianNessuna valutazione finora
- Multirate Digital Signal ProcessingDocumento59 pagineMultirate Digital Signal ProcessingSachita Nand MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Microwave CommunicationsDocumento79 pagineMicrowave CommunicationsKatyrynne GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Path Loss Propagation ModelsDocumento5 paginePath Loss Propagation ModelsFarEast RamdzanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell RangeDocumento14 pagineCell RangeSummer MamunNessuna valutazione finora
- Path Loss CalculationsDocumento13 paginePath Loss CalculationsTheodoros TzouralasNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 5221 Personal Communication Systems: Prepared By: Dr. Ivica KostanicDocumento13 pagineECE 5221 Personal Communication Systems: Prepared By: Dr. Ivica KostanicalperusluNessuna valutazione finora
- B.1.4 Propagation ModelsDocumento3 pagineB.1.4 Propagation ModelsMohammed Amine HalbabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fading 11 ChannelsDocumento30 pagineFading 11 ChannelsVinutha AsamNessuna valutazione finora
- Filters 2Documento60 pagineFilters 2Nguyễn Hoàng KhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless ChannelsDocumento30 pagineWireless Channelsprosenjeet_singhNessuna valutazione finora
- ch4 PDFDocumento29 paginech4 PDFSridhar BolliNessuna valutazione finora
- ECS 455 Chapter 1: Introduction & ReviewDocumento37 pagineECS 455 Chapter 1: Introduction & ReviewKalolo SadathNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 2 88Documento4 pagine3 2 88vishalnimavat1834Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Radio Propagation Large Scale EffectsDocumento59 pagineChapter 3 Radio Propagation Large Scale EffectsAdisu WagawNessuna valutazione finora
- Propagation Characteristics of Wireless ChannelsDocumento33 paginePropagation Characteristics of Wireless ChannelsMichael KitNessuna valutazione finora
- (Mobile Communication) Take Home Exam Solution Ryid Al-Kahtani ID#423121512Documento16 pagine(Mobile Communication) Take Home Exam Solution Ryid Al-Kahtani ID#423121512Muqeet Khaja UddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Transmission PlanningDocumento47 pagineBasics of Transmission PlanningTushar PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Communications: Multipath FadingDocumento13 pagineWireless Communications: Multipath FadingAhmed SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- WC-Chapter 1-Path Loss and Shadowing PDFDocumento11 pagineWC-Chapter 1-Path Loss and Shadowing PDFQuoc NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey System Design and EnggDocumento123 pagineSurvey System Design and Enggvisakh21Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dagupan To Baguio Via Mt. Sto. Tomas Microwave Link DesignDocumento58 pagineDagupan To Baguio Via Mt. Sto. Tomas Microwave Link DesignMarc Lester TanNessuna valutazione finora
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignDa EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Newnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket BookDa EverandNewnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket BookNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericDa EverandRadio Propagation and Adaptive Antennas for Wireless Communication Networks: Terrestrial, Atmospheric, and IonosphericNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsDa EverandFundamentals of Electronics 3: Discrete-time Signals and Systems, and Quantized Level SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationDa EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNessuna valutazione finora
- Hatchery Practice: InternationalDocumento40 pagineHatchery Practice: Internationalabhe prasetyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Models of EIDocumento13 pagineDifferent Models of EIneena686236Nessuna valutazione finora
- Esmeril Makita PDFDocumento16 pagineEsmeril Makita PDFwjzabalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Metric Conversion WorksheetDocumento3 pagineMetric Conversion WorksheetKaiden HughesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Future of Comparative Literary StudiesDocumento14 pagineThe Future of Comparative Literary StudiesNabeesath ArifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Marketing Research Completed RevisedDocumento70 pagineMarketing Research Completed RevisedJodel DagoroNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Waves AnswersDocumento2 pagine5 Waves AnswersNoor Ulain NabeelaNessuna valutazione finora
- DBL10 - Sapporo X Schematics Document: Compal ConfidentialDocumento50 pagineDBL10 - Sapporo X Schematics Document: Compal ConfidentialEvgeniy BaranovskiyNessuna valutazione finora
- Education and Its LegitimacyDocumento4 pagineEducation and Its LegitimacySheila G. Dolipas100% (6)
- Kalbelia Dance Rajasthan - Kalbelia Rajasthani Folk Dance KalbeliaDocumento6 pagineKalbelia Dance Rajasthan - Kalbelia Rajasthani Folk Dance KalbeliarahulgabdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hunk (Aakc) - (Nov 2015)Documento68 pagineHunk (Aakc) - (Nov 2015)Russell RiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Educational Strategic Plans in Nigeria: Challenges of Implementation and Ways ForwardsDocumento7 pagineEducational Strategic Plans in Nigeria: Challenges of Implementation and Ways ForwardsresearchparksNessuna valutazione finora
- User Instructions: Installation Operation Maintenance NAF Duball DL Pocket ValveDocumento12 pagineUser Instructions: Installation Operation Maintenance NAF Duball DL Pocket ValveMauricio Contreras R.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Admission Prspectus English 2021-2022Documento9 pagineAdmission Prspectus English 2021-2022A.B. SiNessuna valutazione finora
- TM GUIDE (Basic Competencies)Documento19 pagineTM GUIDE (Basic Competencies)Emelito T. ColentumNessuna valutazione finora
- Chinese MedicineDocumento16 pagineChinese MedicineTrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 SimulationDocumento8 pagineLab 4 SimulationaziziNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca Final Compiler Paper 5 Advanced Management Accounting PDFDocumento432 pagineCa Final Compiler Paper 5 Advanced Management Accounting PDFAnn SerratoNessuna valutazione finora
- Altium Designer Training For Schematic Capture and PCB EditingDocumento248 pagineAltium Designer Training For Schematic Capture and PCB EditingAntonio Dx80% (5)
- Simon Bolivar PresentationDocumento7 pagineSimon Bolivar Presentationapi-345742212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment 3 Comparative Analysis Primary Vs Secondary SourcesDocumento5 pagineAssessment 3 Comparative Analysis Primary Vs Secondary SourcesMATOZA, YLJOE V.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Course: Consumer Behaviour: Relaunching of Mecca Cola in PakistanDocumento10 pagineCourse: Consumer Behaviour: Relaunching of Mecca Cola in PakistanAnasAhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- NCS V5 1.0 Layer Name FormatDocumento4 pagineNCS V5 1.0 Layer Name FormatGouhar NayabNessuna valutazione finora
- Motivational QuotesDocumento39 pagineMotivational QuotesNarayanan SubramanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Power Factor Improvement SystemDocumento25 paginePower Factor Improvement SystemBijoy SahaNessuna valutazione finora
- ScriptDocumento12 pagineScriptWaleed Nadeem50% (2)
- Graphs in ChemDocumento10 pagineGraphs in Chemzhaney0625Nessuna valutazione finora
- User Manual For Scanbox Ergo & Banquet Line: Ambient (Neutral), Hot and Active Cooling. Scanbox Meal Delivery CartsDocumento8 pagineUser Manual For Scanbox Ergo & Banquet Line: Ambient (Neutral), Hot and Active Cooling. Scanbox Meal Delivery CartsManunoghiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1609 Um009 - en PDocumento34 pagine1609 Um009 - en PAnonymous VKBlWeyNessuna valutazione finora
- N Mon Visualizer OverviewDocumento27 pagineN Mon Visualizer OverviewClaudioQuinterosCarreñoNessuna valutazione finora