Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Congestive Heart Failure
Caricato da
Shayne Jessemae AlmarioDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Congestive Heart Failure
Caricato da
Shayne Jessemae AlmarioCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Congestive heart failure
Dr. Walaa Nasr Lecturer of Adult Nursing Second year
Congestive heart failure
outlines
Definition Causes and pathophysiology Types of heart failure Compensatory mechanism failure Clinical manifestations Classification of heart failure Diagnostic evaluation Medical management Nursing management
of
heart
Congestive heart failure
Definition
Heart failure describes the clinical syndrome that develops when the heart cannot maintain an adequate cardiac output. The heart pumps blood inadequately, leading to reduced blood flow, back-up (congestion) of blood in the veins and lungs, and other changes that may further weaken the heart.
Causes of congestive heart failure
Coronary
artery disease Heart attack High blood pressure Heart valves disorders
Inflammation
of Heart muscle (myocarditis, cardiomyopathy)
Causes of congestive heart failure (cont)
Severe
lung disease ( pulmonary hypertension) Severe anemia Overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) Underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) Abnormal heart rhythms ( atrial fibrillation) Kidney failure
Congestive heart failure
Types
Left-sided
heart failure
There are two types of leftsided heart failure Systolic dysfunction Diastolic dysfunction Right-sided heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Compensatory Mechanisms of heart failure
Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system Sympathetic nervous system Enlargement of the muscular walls of the ventricles (ventricular hypertrophy).
Congestive heart failure
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms (back up of blood and fluid) Dyspnea Orthopnea Reduced exercise tolerance, lethargy, fatigue Nocturnal cough Wheeze Ankle swelling Anorexia
Congestive heart failure
Clinical manifestations ( cont)
Signs
Cachexia and muscle wasting Tachycardia Pulsus alternans Elevated jugular venous pressure Crepitations or wheeze Third heart sound Oedema Hepatomegaly (tender) Ascites
Congestive heart failure
Classification of heart failure
New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Classification
Class
I II III IV
% of patients
35% 35% 25% 5%
Symptoms
No symptoms or limitations in ordinary physical activity Mild symptoms and slight limitation during ordinary activity Marked limitation in activity even during minimal activity. Comfortable only at rest Severe limitation. Experiences symptoms even at rest
Congestive heart failure
Diagnostic evaluation
Patient history Physical examination Diagnostic studies 1. Electrocardiography (ejection fraction) 2. Radionuclide 3. magnetic resonance 4. computed tomography imaging 5. cardiac catheterization with angiography 6. a biopsy of heart muscle is needed
Congestive heart failure
Treatment
lifestyle change
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Salt restriction Exercises Smoking and alcoholism Body weight (daily weight) Supportive stockings
Congestive heart failure
Treatment (cont)
Drug management Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Angiotensin II receptor blockers Beta-blockers Other vasodilators ( nitroglycerin) Cardiac glycosides (digoxin) Aldosterone receptor blockers (spironolactone) Loop diuretics
Congestive heart failure
Treatment (cont)
Potassium-sparing diuretics Thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics Anticoagulants (heparine) Opioids (morphine) to relieve anxiety Positive inotropic drugs (drugs that make muscle contract more forcefully) (dopamine)
Oxygen for pulmonary edema is required
Congestive heart failure
Treatment (cont)
Non pharmacological management of heart failure (surgical intervention)
Coronary artery bypass grafting (
revascularization)
(Angioplasty)
Percutaneous coronary intervention
Valve replacement Biventricular pacemaker
Heart transplantation Left ventricular assist device (LVAD)
Nursing care of patients with congestive heart failure Maintain the patient in high fowler's position Elevate extremities except when the patient is in acute distress Frequently monitor vital signs Change position frequently Monitor intake and output and daily weight
Nursing care of patients with congestive heart failure (cont)
Restrict fluids as ordered
Teach the patient and family and provide emotional support (life style change)
Explain the side effect of diuretic medications for additional actions ( side effects of diuretics include electrolyte imbalance, symptomatic hypotension Use aseptic procedures invasive lines when caring for
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Authorization Letter To DepositDocumento1 paginaAuthorization Letter To DepositEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocumento15 pagine6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Primary Health Care: Mr. John Michael M. Pitoy, B.S.N., R.NDocumento44 paginePrimary Health Care: Mr. John Michael M. Pitoy, B.S.N., R.NJohn Michael Manlupig Pitoy100% (9)
- Football Speed TrainingDocumento6 pagineFootball Speed TrainingTBM607Nessuna valutazione finora
- Emphysema & EmpyemaDocumento26 pagineEmphysema & EmpyemaManpreet Toor80% (5)
- Congestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocumento3 pagineCongestive Heart Failure Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramJasleen KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Care Plan ON Periampullary Carcinoma: SUBMITTED TO-Ms. Tarika Sharma SUBMITTED BY-Mr. DeepakDocumento27 pagineCare Plan ON Periampullary Carcinoma: SUBMITTED TO-Ms. Tarika Sharma SUBMITTED BY-Mr. Deepakamit100% (2)
- Pulmonary Function TestDocumento9 paginePulmonary Function TestMarivic DianoNessuna valutazione finora
- On PurpuraDocumento22 pagineOn Purpurakiran kumari yadav100% (1)
- Hypovolemic Shock PPT EdDocumento17 pagineHypovolemic Shock PPT EdNoor Ali100% (1)
- Digital Rectal ExaminationDocumento17 pagineDigital Rectal Examinationyulianpatriawan100% (2)
- Diabetes Mellitus: Presented By-Deepanshi Masih 1 Year M.Sc. Nursing EconDocumento34 pagineDiabetes Mellitus: Presented By-Deepanshi Masih 1 Year M.Sc. Nursing EconAru VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- AppendicitisDocumento14 pagineAppendicitispreethijojo2003558288% (8)
- Congestive Heart Failure Nursing CareDocumento20 pagineCongestive Heart Failure Nursing Careminikompo100% (3)
- Cardiac Assessment FormatDocumento20 pagineCardiac Assessment FormatSalman Habeeb75% (4)
- Emphysema: Presented By: Mis. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorDocumento10 pagineEmphysema: Presented By: Mis. M.K.Kaku Nursing TutorKaku ManishaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Liver DiseaseDocumento12 pagineChronic Liver DiseaseamitNessuna valutazione finora
- CardiomegalyDocumento15 pagineCardiomegalysreejagopinath100% (2)
- Nursing Management: OF ArteriosclerosisDocumento6 pagineNursing Management: OF ArteriosclerosisANCHAL SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 8 BSC 3rd YearDocumento20 pagineUnit 8 BSC 3rd Yearsimonjosan100% (2)
- Heart Block: BY DR - AriyalakshmiDocumento26 pagineHeart Block: BY DR - AriyalakshmiDiksha chaudharyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cirrhosis of LiverDocumento7 pagineCirrhosis of LivermOHAN.S100% (2)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocumento13 pagineChronic Renal FailureAnusha VergheseNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure: Dr. J. SaravananDocumento31 pagineCongestive Heart Failure: Dr. J. Saravananpetervazhayil100% (1)
- Bronchial Hygiene Therapy ElectiveDocumento20 pagineBronchial Hygiene Therapy ElectiveHelen Grace Dela Cruz0% (1)
- Mitral StenosisDocumento43 pagineMitral StenosisEricka SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- 13th & 14th WK - Oxygen Therapy With VideoDocumento89 pagine13th & 14th WK - Oxygen Therapy With VideoJesus Mario Lopez100% (1)
- Sequential Compression DeviceDocumento2 pagineSequential Compression Deviceal-obinay shereen0% (1)
- Cardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentDocumento8 pagineCardiovascular Assessment: Assessment Uses of CVS AssessmentKawaljit KaurNessuna valutazione finora
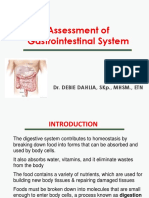
- Assessment of GI SystemDocumento40 pagineAssessment of GI SystemJeffRy SinyOe100% (1)
- Case Presentation 3 DR Oscar Laryngitis TBDocumento33 pagineCase Presentation 3 DR Oscar Laryngitis TBmarajuu50% (2)
- Aetiology Heart Diasease in Children May Be Congenital or AcquiredDocumento23 pagineAetiology Heart Diasease in Children May Be Congenital or AcquiredkasondaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Acyanotic Heart DiseaseDocumento55 pagineNursing Care Plan For Acyanotic Heart DiseaseDeepikaxena John79% (14)
- Hypertension: Unit-5 - Non-Communicable Disease Community Health Nursing - IDocumento19 pagineHypertension: Unit-5 - Non-Communicable Disease Community Health Nursing - IPrabhakaran AranganathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study TBDocumento5 pagineDrug Study TBSanvar Mal SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac AssessmentDocumento7 pagineCardiac AssessmentElle ChasenNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDocumento19 pagineCardiogenic Shock: BY Dr. M L Patel MD Associate Professor Deptt. of MedicineDurgesh PushkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Dysrhythmia PowerpointDocumento10 pagineDysrhythmia PowerpointWynton De JesusNessuna valutazione finora
- Myocardial InfarctionDocumento45 pagineMyocardial InfarctionGopal SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Reconstructive & Cosmetic SurgeryDocumento28 pagineTypes of Reconstructive & Cosmetic SurgerySimon JosanNessuna valutazione finora
- Urethritis PathophysiologyDocumento4 pagineUrethritis PathophysiologyMonica Melo HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Cardiac Failure PDFDocumento28 pagineCongestive Cardiac Failure PDFNANDHINI S100% (1)
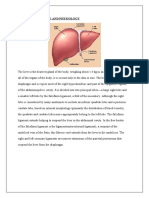
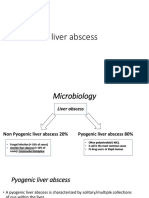
- Liver AbscessDocumento15 pagineLiver AbscessAli Aborges Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Medical 2021 Question Paper BSC NursingDocumento24 pagineMedical 2021 Question Paper BSC NursingWinter BearNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Renal FailureDocumento17 pagineAcute Renal FailureDina Rasmita100% (1)
- DCLDDocumento36 pagineDCLDAnonymous uoxEU3mkNessuna valutazione finora
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)Documento70 pagineIschemic Heart Disease (IHD)Deborah AnnNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure PDFDocumento11 pagineCongestive Heart Failure PDFpriyanka bhavsarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan On Myocardial InfarctionDocumento4 pagineLesson Plan On Myocardial Infarctionpreet kaur0% (1)
- HYPERTENSIONDocumento24 pagineHYPERTENSIONCuttie Anne GalangNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemDocumento31 paginePhysical Assessment of Cardiovascular SystemaagNessuna valutazione finora
- Tetralogy of FallotDocumento12 pagineTetralogy of Fallotneetuthakur100% (4)
- Case Presentation CardiomyopathyDocumento30 pagineCase Presentation CardiomyopathyKshayna 1234Nessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart FailureDocumento118 pagineCongestive Heart Failureunagracia100% (6)
- Case Study MijaresDocumento55 pagineCase Study Mijaresiura echinNessuna valutazione finora
- Intravenous PyelogramDocumento5 pagineIntravenous PyelogramAlbert IvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ulcerative ColitisDocumento12 pagineUlcerative ColitisSanthu SuNessuna valutazione finora
- CardiomyopathyDocumento18 pagineCardiomyopathyDimpal Choudhary100% (1)
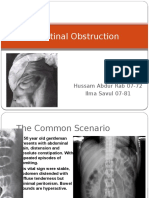
- Intestinal ObstructionDocumento120 pagineIntestinal ObstructionHussam Abdur RabNessuna valutazione finora
- CystitisDocumento24 pagineCystitisTaufik Ramadhan BiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Da EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure Nursing CareDocumento20 pagineCongestive Heart Failure Nursing Careminikompo100% (1)
- Coronary Artery DiseaseDocumento15 pagineCoronary Artery DiseaseMuhammad Daha SanusiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardaic ArrestDocumento17 pagineCardaic ArrestM Farhad KhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart FaliureDocumento59 pagineHeart FaliureMahesh RathnayakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Anna Marie T. Arteta 2419 C Tramo St. Pasay City Objective: To Make Others Dream, Come TrueDocumento1 paginaAnna Marie T. Arteta 2419 C Tramo St. Pasay City Objective: To Make Others Dream, Come TrueEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fe Eleanor MDocumento1 paginaFe Eleanor MEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Liturgical Music Ministry: Date ActivityDocumento2 pagineLiturgical Music Ministry: Date ActivityEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Clara PaloozaDocumento1 paginaClara PaloozaEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mary LogosDocumento11 pagineMary LogosEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sayawit 2018Documento1 paginaSayawit 2018Ezekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anna Marie 1Documento3 pagineAnna Marie 1Ezekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- File 1802Documento3 pagineFile 1802Ezekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- ScoliosisDocumento23 pagineScoliosisEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anna Marie 1Documento3 pagineAnna Marie 1Ezekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Airways DiseaseDocumento26 pagineAirways DiseaseEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- October 05, 2011: Attention: Pedro Lantin Iii, M.DDocumento6 pagineOctober 05, 2011: Attention: Pedro Lantin Iii, M.DEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranio Syn Ostos IsDocumento18 pagineCranio Syn Ostos IsEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mary Crowned With Living Light ChordsDocumento2 pagineMary Crowned With Living Light ChordsEzekiel Arteta33% (3)
- Lower Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocumento21 pagineLower Respiratory Tract InfectionsEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- ConjunctivitisDocumento2 pagineConjunctivitisEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Keyboard Lessons RecordDocumento15 pagineKeyboard Lessons RecordEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Week ROPA PressOnDocumento2 pagine1st Week ROPA PressOnEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- DDXDocumento4 pagineDDXEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiological Chest SignsDocumento15 pagineRadiological Chest SignsEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 712Documento9 pagineReport 712Ezekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Chest X-Ray InterpretationDocumento40 pagineBasic Chest X-Ray InterpretationEzekiel Arteta0% (1)
- EDocumento1 paginaEEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Exchage GiftsDocumento1 paginaExchage GiftsEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- GDocumento1 paginaGEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- JDocumento1 paginaJEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Music Ministers PDFDocumento6 pagineMusic Ministers PDFEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Meanne ResumaeDocumento4 pagineMeanne ResumaeEzekiel ArtetaNessuna valutazione finora
- BFPPPDocumento15 pagineBFPPPFaith JacalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Start A Quick Budget Start A Budget by MonthDocumento13 pagineStart A Quick Budget Start A Budget by MonthMichelle PadillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hindustan Coca-Cola Beverages PVT LTD B-91 Mayapuri Industrial Area Phase-I New DelhiDocumento2 pagineHindustan Coca-Cola Beverages PVT LTD B-91 Mayapuri Industrial Area Phase-I New DelhiUtkarsh KadamNessuna valutazione finora
- Cleaning Disinfecting School ClassroomsDocumento2 pagineCleaning Disinfecting School ClassroomsFitz JaminitNessuna valutazione finora
- Xtra ReportDocumento8 pagineXtra ReportTahfeem AsadNessuna valutazione finora
- Diesel Engine Lab ReportDocumento27 pagineDiesel Engine Lab ReportParadoodleNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 F 957375 B 361250 FB 704Documento15 pagine9 F 957375 B 361250 FB 704api-498018677Nessuna valutazione finora
- MR Afnan CVDocumento3 pagineMR Afnan CVShazada Dauod Khan100% (1)
- 2015 English Grade 7Documento16 pagine2015 English Grade 7AyushNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Installation - AfbcDocumento2 pagineBoiler Installation - AfbcSarah FrazierNessuna valutazione finora
- Guía Oficial de La Delegación Argentina de Los Juegos Olímpicos Tokio 2020Documento330 pagineGuía Oficial de La Delegación Argentina de Los Juegos Olímpicos Tokio 2020Leandro BonavidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Black and Decker Vaporera Electrica RecetarioDocumento17 pagineBlack and Decker Vaporera Electrica RecetarioFabio AtenógenesNessuna valutazione finora
- Daftar Pustaka ProposalDocumento4 pagineDaftar Pustaka ProposalraniNessuna valutazione finora
- HC SB 61 227Documento22 pagineHC SB 61 227Hamed BarjestehNessuna valutazione finora
- Roadshow Advanced 7.2 V3.2 221004 FinalDocumento347 pagineRoadshow Advanced 7.2 V3.2 221004 FinalEddy StoicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Shekhar Challa Joins Bioscience Americas Board of AdvisorsDocumento2 pagineDr. Shekhar Challa Joins Bioscience Americas Board of AdvisorsPR.comNessuna valutazione finora
- SinusitisDocumento402 pagineSinusitisIsidro Roberto Santana Gonzalez100% (1)
- Curriculum Guide: Exploratory Course On Household ServicesDocumento5 pagineCurriculum Guide: Exploratory Course On Household ServicesJovanni Mancao PodadorNessuna valutazione finora
- Australian TaxationDocumento45 pagineAustralian TaxationEhtesham HaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Fuel EnergizerDocumento17 pagineFuel Energizerrakshak25100% (1)
- Personal Loan For JoiningDocumento3 paginePersonal Loan For JoiningAzim SengalNessuna valutazione finora
- Strip Seal Expansion JointDocumento13 pagineStrip Seal Expansion JointsmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation On Dysuria 1Documento25 paginePresentation On Dysuria 1ankur acharyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Easy Exercises For Hip Flexor PainDocumento1 paginaEasy Exercises For Hip Flexor PainJackieNessuna valutazione finora
- Icu2 Vol22 Sepsisincriticalcare 29marchDocumento52 pagineIcu2 Vol22 Sepsisincriticalcare 29marchricardoatejassNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 RevlonDocumento13 pagine20 RevlonmskrierNessuna valutazione finora
- Leon County Sheriff'S Office Daily Booking Report 18-Oct-2020 Page 1 of 3Documento3 pagineLeon County Sheriff'S Office Daily Booking Report 18-Oct-2020 Page 1 of 3WCTV Digital TeamNessuna valutazione finora