Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2
Caricato da
gautamckumarTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2
Caricato da
gautamckumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2
From the movie
Warriors of the Net
Fibers from the view of Geometrical
Optics
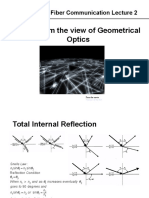
Total Internal Reflection
u u
u u
u u
u u
u
u u
=
=
>
= =
>
1 1 2 2
1 3
1 2 1 2
2
1 2
1
1
:
sin sin
Re
90 deg
sin sin
c c
c
c
Snells Law
n n
flection Condition
When n n and as increases eventually
goes to rees and
n
n n or
n
is called the Critical angle
For there is no pro pagating refracted ray
Reflection as a function of angle
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
This additional Phase
Shift is not accounted for
in geometrical wave
approach
The reflectivities of waves polarized
parallel and perpendicular to the plane of
incidence as given by the Fresnel equations
Principal Types of Optical Fiber
Understanding Fiber Optics-Hecht
Types of Fibers
Single mode/Multi-mode
Step Index/Graded Index
Dispersion Shifted/Non-dispersion shifted
Silica/fluoride/Other materials
Major Performance Concerns for Fibers
Wavelength range
Maximum Propagation Distance
Maximum bitrate
Crosstalk
Fabrication of Optical Fiber
Fabrication of fiber preform:
macroscopic version with correct index
profile
Drawing of preform down into thin fiber
Jacketing and cabling
Step-Index Fiber
Cladding typically pure silica
Core doped with germanium to increase
index
Index difference referred to as delta in
units of percent (typically 0.3-1.0%)
Tradeoff between coupling and bending
losses
Index discontinuity at core-clad
boundary
Basic Step index Fiber Structure
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
Ray Trajectories in Step Index
fiber
Meridional Rays
Skew Rays
Coupling Light into an Optical
Fiber
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
Acceptance Angle
Optics-Hecht & Zajac
The acceptance angle (u
i
) is the largest incident
angle ray that can be coupled into a guided ray
within the fiber
The Numerical Aperature (NA) is the sin(u
i
) this
is defined analagously to that for a lens
#
tan
1
2
f f
f
D FullAccep ceAngle
NA
=
=
1 1 1
2 2 2
2 2 2
1 2
1 2 1 2
( ) (2 ) (2 )
and
2
NA n n n n
n n n n
Where n
n
= - = D = D
- +
D
2
n
CO
n
CL
For Corning SMF-28 optical fiber
n
co
=1.4504, n
CL
=1.4447 at 1550 nm
NA = 0.13
Acceptance angle = 7.35 degrees
Geometrical View of Modes
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
Ray approximation valid in the
limit that goes to zero
Geometrical Optics does not
predict the existance of discrete
modes
Maxwells Equations and
dielectric boundary conditions
give rise to the requirement that
the fields and phase reproduce
themselves each cycle
Rays and Their E-field Distribution
Origin of Modal Dispersion
Straight path along fiber axis has distance L and velocity c/n
CO
for
transit time of Ln
CO
/c
Path at maximum acceptance angle
c
has distance L/cos
2
where
2
=90-
c
and thus a longer transit time.
Transit time difference equal to
Dispersion limits rate of signals that fiber can handle
If spread can be up to 70% of bit period, then maximum bit rate is
1.4cn
CO
/(NA)
2
2
2
2
2
1 sin 1 cos
|
|
.
|
\
|
= =
CO
n
NA
|
|
.
|
\
|
= 1
1 2
CL
CO CO
n
n
c
Ln
t t
Intermodal Dispersion
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
1
SI
2
1 2 SI
2
SI
L
t
c
L
t for
c
( ) L
t
c
2
n
n
n
n n n
NA
n
D = D
D @ D @
D @
Bandwidth for Various Fiber Types
Fiber Optics Communication Technology-Mynbaev & Scheiner
2
1
2
1
8
4
1
Bit Rate BR<
4
1
4 4
2
2
SI
SI
SI
GI
GI
c
BR
Ln
t
c
BR
t Ln
c
BR
n L
c
BR n L
= =
D
D
D
= =
D D
=
D
D
No intermodal time shift for single
Mode Fiber
Graded Index Fiber
Fiber Optic Communication Systems-Agarwal
| |
( )
1
1 2
2
1
2
1
2
1
( ) 1 for <a
( ) 1 =n for >a
for 2 a "parabolic profile"
NA=n 2 1 which varies with
8
GI
n n
a
n n
a
Ln
t
c
o
(
| |
= A
(
|
\ .
(
= A
=
| |
A
|
\ .
A
A =
Fiber Optic Communications-Palais
Ray Propagation in Graded-Index
Fiber
Graded Index Slab Uniform in X and Z
Fundamentals of Photonics - Saleh and Teich
Ray spreading comparison
( )
3
4
8
CO
GI
cn
NA L
t = A
( )
CO
SI
cn
NA L
t
2
2
= A
Comparison, continued
If NA=0.13 and n
CO
=1.45,
t
SI
/L=19 ps/m
t
GI
/L=0.039 ps/m
Graded-index fiber has substantially less
modal dispersion
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Fibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2Documento21 pagineFibers From The View of Geometrical Optics: EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 2mofiwNessuna valutazione finora
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignDa EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Communication Unit VDocumento10 pagineOptical Communication Unit VSambashiva SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksDa EverandOptical and Microwave Technologies for Telecommunication NetworksNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 2 - Features of Fibre OpticDocumento21 pagineLec 2 - Features of Fibre OpticMtende MosesNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 3 Waveguide/Fiber ModesDocumento27 pagineEE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 3 Waveguide/Fiber Modeshema_swizNessuna valutazione finora
- OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsDocumento36 pagineOPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION Basic and CharactersticsabidNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optic Communication: OutlineDocumento16 pagineFiber Optic Communication: Outlineshankar_smvNessuna valutazione finora
- OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMDocumento64 pagineOPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMAmit Samrat MauryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect5-Optical Fibers 2Documento134 pagineLect5-Optical Fibers 2trlp1712100% (1)
- Fiber Optics1Documento29 pagineFiber Optics1Biswajith MohapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Advance Communication Lab Report - Fiber Optics Experiments and ConceptsTITLE Advance Comm Lab Report - Fiber Optics Code, Analog & Digital Link MeasureDocumento37 pagineAdvance Communication Lab Report - Fiber Optics Experiments and ConceptsTITLE Advance Comm Lab Report - Fiber Optics Code, Analog & Digital Link MeasurePPPPPNessuna valutazione finora
- OC Expt 6 PDFDocumento5 pagineOC Expt 6 PDFPrasad RaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Photonics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocumento41 pagineIntroduction to Photonics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsLauren Stevenson100% (1)
- Turowicz 1Documento62 pagineTurowicz 1Saurav KauraNessuna valutazione finora
- Step-Index Fiber Bend SimulationDocumento24 pagineStep-Index Fiber Bend SimulationMoti Ben LaishNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber CommunicationDocumento48 pagineOptical Fiber CommunicationPrateekMittalNessuna valutazione finora
- TC-315 Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 6aDocumento28 pagineTC-315 Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 6aTahreem FatimaNessuna valutazione finora
- HFC ManualDocumento71 pagineHFC ManualSushmitha ThulasimaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece Dept: Sri Mittapalli College of EngineeringDocumento44 pagineEce Dept: Sri Mittapalli College of EngineeringbrsreddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Optical FibersDocumento60 pagineChapter 2 - Optical Fiberseyohamehari235Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 3 1 Optical Applications With CST MICROWAVE STUDIODocumento36 pagine3 3 1 Optical Applications With CST MICROWAVE STUDIOmsajjad_68Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Communication and NetworksDocumento37 pagineOptical Communication and NetworksChandra MathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dispersion Management Techniques and Their Limitations in Optical Communication SystemsDocumento84 pagineDispersion Management Techniques and Their Limitations in Optical Communication SystemsAbhinav ChoukseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Communication and Networking FundamentalsDocumento26 pagineOptical Communication and Networking FundamentalsEkambaramMuniyandiNessuna valutazione finora
- Atmospheric Aberrations in Coherent Laser Systems: Snowmass, July 12, 2007 Aniceto BelmonteDocumento40 pagineAtmospheric Aberrations in Coherent Laser Systems: Snowmass, July 12, 2007 Aniceto BelmonteImad Ha AliNessuna valutazione finora
- EC2402 Optical Communication and Networks 12Documento21 pagineEC2402 Optical Communication and Networks 12vinothiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics Communications SystemDocumento73 pagineFiber Optics Communications SystemKim Brian CarboNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Linear Effects in FiberDocumento25 pagineNon Linear Effects in Fiberthanhtam3819Nessuna valutazione finora
- Figure 3.1 The Structure of The Step-Index Optical FiberDocumento12 pagineFigure 3.1 The Structure of The Step-Index Optical FiberMalakonda ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- ON Expt4Documento10 pagineON Expt4Shubh ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- OFC TechnologyDocumento52 pagineOFC TechnologyBattinapati ShivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical FiberDocumento16 pagineOptical FiberRinju DuttNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 PropagationDocumento29 pagine2 PropagationrazifhamzahNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber Communication: Dept of Electronics & Communication Engineering, JbietDocumento66 pagineOptical Fiber Communication: Dept of Electronics & Communication Engineering, Jbietraj_bhureNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical CommunicationDocumento154 pagineOptical CommunicationNavaRatnamNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 1Documento57 pagineOptical Fiber Communication Lecture 1Achala DeshmukhNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optic Gyroscopes ExplainedDocumento40 pagineFiber Optic Gyroscopes ExplainedFrancisco100% (1)
- OCN Unit 1,2Documento23 pagineOCN Unit 1,2M Madhu MaliniNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical With AnswerDocumento19 pagineNumerical With AnswerRahul KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Gyroscope Technologies For Space Applications: Armenise@poliba - ItDocumento26 pagineGyroscope Technologies For Space Applications: Armenise@poliba - ItAhmed HamoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- All-Optical AND Logic Gate Based On 2-D Photonic Crystal: Kajal BhadelDocumento10 pagineAll-Optical AND Logic Gate Based On 2-D Photonic Crystal: Kajal BhadelalgwaalNessuna valutazione finora
- EE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021Documento78 pagineEE493 - Second Set of Lecture Slides-Spring 2021احمد الديريNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Optical FibreDocumento195 pagineFundamentals of Optical Fibrebinarystars100% (1)
- Optical Communication: EC8751 - OC 11Documento30 pagineOptical Communication: EC8751 - OC 11BinoStephenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec.1 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsDocumento45 pagineLec.1 - COMM 554 Optical Communication SystemsMahmoud Sayed100% (1)
- QDT - CH 05 - Soi QuangDocumento162 pagineQDT - CH 05 - Soi QuangFlo NghẾchNessuna valutazione finora
- OFC Module 1Documento85 pagineOFC Module 1VargheseMartinNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optic Cable Course (Summarised)Documento36 pagineFiber Optic Cable Course (Summarised)yousuf dawwinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics Module 1Documento63 pagineFiber Optics Module 1Ravi Teja AJNessuna valutazione finora
- Fiber Optics: by Vikas KaduskarDocumento81 pagineFiber Optics: by Vikas Kaduskarvpkvikas100% (1)
- SS12 PhysEngII 1 PDFDocumento81 pagineSS12 PhysEngII 1 PDFMuhammad FarooqNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Lecture 1Documento119 pagineOptical Lecture 1Tharun RagavNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Networks Lecture 1: Introduction Part 1 ReviewDocumento59 pagineOptical Networks Lecture 1: Introduction Part 1 Reviewjeddo2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 12 - Transmission Characterisrtics of Optical Fiber-Bending (OFC)Documento10 pagineLecture 12 - Transmission Characterisrtics of Optical Fiber-Bending (OFC)samarthNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonlinear Optics Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocumento23 pagineNonlinear Optics Fundamentals and ApplicationsPriya NeelakandanNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Communication Question BankDocumento24 pagineOptical Communication Question BankdhivyakrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 02 - TTQ 2022ADocumento73 pagineChapter 02 - TTQ 2022Ahai NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject:-Reply To Pre-Bid Queries in Respect To Tender For Supply, InstallationDocumento1 paginaSubject:-Reply To Pre-Bid Queries in Respect To Tender For Supply, InstallationgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- OMLT For Dummies 9517Documento51 pagineOMLT For Dummies 9517gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PostponementT510 MNG PAN DTD 280715Documento1 paginaPostponementT510 MNG PAN DTD 280715gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mbit Report - 2014Documento6 pagineMbit Report - 2014gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- NGMN Whitepaper LTE Back Hauling Deployment ScenariosDocumento34 pagineNGMN Whitepaper LTE Back Hauling Deployment ScenariosSam LokeNessuna valutazione finora
- Wi-Fi Blurs: The Broadband LinesDocumento9 pagineWi-Fi Blurs: The Broadband LinesgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Light Wave Aug Sep 2012Documento26 pagineLight Wave Aug Sep 2012gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Usda Training MplsDocumento181 pagineUsda Training MplsgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ac PPTDocumento62 pagineAc PPTgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Backhaul Sync Requirements and ViewpointsDocumento13 pagineMobile Backhaul Sync Requirements and ViewpointsgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Hierarchical QoSDocumento4 pagineHierarchical QoSYooseop KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Built For Speed: Differentiating The Ethernet Service ExperienceDocumento4 pagineBuilt For Speed: Differentiating The Ethernet Service ExperiencegautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 15: From The MovieDocumento24 pagineEE 230: Optical Fiber Communication Lecture 15: From The MoviegautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Reliance Industries Bracing For The Broadband HungamaDocumento5 pagineReliance Industries Bracing For The Broadband HungamagautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- NGN - Techno Economic InsiteDocumento22 pagineNGN - Techno Economic InsitegautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis Buffer SizingDocumento112 pagineThesis Buffer SizinggautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- LLD Template 7april05Documento170 pagineLLD Template 7april05gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Martinotti Mpls TP Interworking 02Documento35 pagineDraft Martinotti Mpls TP Interworking 02gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Saisree Video DistributionDocumento25 pagineSaisree Video DistributiongautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Fang Mpls TP Use Cases and Design 04Documento19 pagineDraft Fang Mpls TP Use Cases and Design 04gautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Google FiberDocumento18 pagineGoogle Fibergautamckumar100% (1)
- Business World - Print - Why Huawei Is Betting On India For Its FutureDocumento6 pagineBusiness World - Print - Why Huawei Is Betting On India For Its FuturegautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Multicast Support in MPLS-TPDocumento3 pagineMulticast Support in MPLS-TPgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- STM SFP Interface DetailsDocumento3 pagineSTM SFP Interface DetailsgautamckumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Empowerment Technologies Learning ActivitiesDocumento7 pagineEmpowerment Technologies Learning ActivitiesedzNessuna valutazione finora
- Geneva IntrotoBankDebt172Documento66 pagineGeneva IntrotoBankDebt172satishlad1288Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 5 HExDocumento16 pagineTutorial 5 HExishita.brahmbhattNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparing Time Series Models to Predict Future COVID-19 CasesDocumento31 pagineComparing Time Series Models to Predict Future COVID-19 CasesManoj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Salary Slip Oct PacificDocumento1 paginaSalary Slip Oct PacificBHARAT SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- Social EnterpriseDocumento9 pagineSocial EnterpriseCarloNessuna valutazione finora
- Corruption in PakistanDocumento15 pagineCorruption in PakistanklutzymeNessuna valutazione finora
- Dinsmore - Gantt ChartDocumento1 paginaDinsmore - Gantt Chartapi-592162739Nessuna valutazione finora
- CFEExam Prep CourseDocumento28 pagineCFEExam Prep CourseM50% (4)
- SyllabusDocumento4 pagineSyllabusapi-105955784Nessuna valutazione finora
- (SIRI Assessor Training) AM Guide Book - v2Documento19 pagine(SIRI Assessor Training) AM Guide Book - v2hadeelNessuna valutazione finora
- Mba Assignment SampleDocumento5 pagineMba Assignment Sampleabdallah abdNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflatable Packers enDocumento51 pagineInflatable Packers enDavid LuhetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Econometrics Chapter 1 7 2d AgEc 1Documento89 pagineEconometrics Chapter 1 7 2d AgEc 1Neway AlemNessuna valutazione finora
- 28 Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) vs. Velasco, 834 SCRA 409, G.R. No. 196564 August 7, 2017Documento26 pagine28 Government Service Insurance System (GSIS) vs. Velasco, 834 SCRA 409, G.R. No. 196564 August 7, 2017ekangNessuna valutazione finora
- Oop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Documento14 pagineOop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Hashir KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample Property Management AgreementDocumento13 pagineSample Property Management AgreementSarah TNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentos de Medición y Herramientas de Precisión Starrett DIAl TEST INDICATOR 196 A1ZDocumento24 pagineInstrumentos de Medición y Herramientas de Precisión Starrett DIAl TEST INDICATOR 196 A1Zmicmarley2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- ITSCM Mindmap v4Documento1 paginaITSCM Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNessuna valutazione finora
- ABS Rules for Steel Vessels Under 90mDocumento91 pagineABS Rules for Steel Vessels Under 90mGean Antonny Gamarra DamianNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Case - Uganda Maize Export To South SudanDocumento44 pagineBusiness Case - Uganda Maize Export To South SudanInfiniteKnowledge33% (3)
- Theme Meal ReportDocumento10 pagineTheme Meal Reportapi-434982019Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook The Managers Guide To Effective Feedback by ImpraiseDocumento30 pagineEbook The Managers Guide To Effective Feedback by ImpraiseDebarkaChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- 9780702072987-Book ChapterDocumento2 pagine9780702072987-Book ChaptervisiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding CTS Log MessagesDocumento63 pagineUnderstanding CTS Log MessagesStudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Tyron Butson (Order #37627400)Documento74 pagineTyron Butson (Order #37627400)tyron100% (2)
- Expert Business Analyst Darryl Cropper Seeks New OpportunityDocumento8 pagineExpert Business Analyst Darryl Cropper Seeks New OpportunityRajan GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Software EngineeringDocumento3 pagineSoftware EngineeringImtiyaz BashaNessuna valutazione finora
- RAP Submission Form, OBIDocumento3 pagineRAP Submission Form, OBIAhmed MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Palmetto Bay's Ordinance On Bird RefugeDocumento4 paginePalmetto Bay's Ordinance On Bird RefugeAndreaTorresNessuna valutazione finora