Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
M21_nethistory jjlldjlas;ldas;ldl;asldas;ld;ls;lda;lskd;laskd;lksl;dklksd;lkas;lkd;las;ldklas;kelaks;lekas;ldlks;alkd;laskl;dk;laskd;la;ldk;akd;ask;ldk;laskd;laks;kd;laskd;lks;ld;laskd;las;ldas;lkdkas;ldkas;lkdsak;dka;ld;alkd;lak;dla;kd;alask;dk;akd;lskd;askd;las;ldkas;lkd;lak;dlkasd;lkas;ldkas;lkd;lask;ldas;kd;lask;dlkas;ldas;ldk;lkd;lsd;lask;dlaks;lkd;lkd;lask;dka;lkd;ald;l;ldk;aslkd;aslk;dlka;ld;aslkds;lakd;lask;dl;dsa;lkd;laskd;lask;dlkas;ldkas;lkd;lk;
Caricato da
Vikas RockCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
M21_nethistory jjlldjlas;ldas;ldl;asldas;ld;ls;lda;lskd;laskd;lksl;dklksd;lkas;lkd;las;ldklas;kelaks;lekas;ldlks;alkd;laskl;dk;laskd;la;ldk;akd;ask;ldk;laskd;laks;kd;laskd;lks;ld;laskd;las;ldas;lkdkas;ldkas;lkdsak;dka;ld;alkd;lak;dla;kd;alask;dk;akd;lskd;askd;las;ldkas;lkd;lak;dlkasd;lkas;ldkas;lkd;lask;ldas;kd;lask;dlkas;ldas;ldk;lkd;lsd;lask;dlaks;lkd;lkd;lask;dka;lkd;ald;l;ldk;aslkd;aslk;dlka;ld;aslkds;lakd;lask;dl;dsa;lkd;laskd;lask;dlkas;ldkas;lkd;lk;
Caricato da
Vikas RockCopyright:
Formati disponibili
13-Sep-13 nethistory.
ppt
HISTORY OF THE INTERNET PRESENTED BY ;-HARDEEP SAINI
1
WHO CREATED THE INTERNET?
13-Sep-13
when did it start? why? how did it evolve? why do we care?
nethistory.ppt
how does it work?
what does it take to get access to it?
2
WHO STARTED IT, AND WHY?
the U. S. Department of Defense
13-Sep-13
Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) began ~1962 in reaction to the Soviet Union's launch of Sputnik in 1957 DARPA was told to find ways to utilize the nations investment in computers funding for projects that might provide dramatic advances for military timeframe of research could be 5 years or longer formed with an emphasis towards basic computing research
nethistory.ppt
was not oriented only to military products
eventually, DARPA settled on computer networking as a main goal
3
IT DIDNT HAPPEN ALL AT ONCE
1969 ARPANET commissioned by DoD for research into networking
13-Sep-13
1971 15 nodes (23 hosts) networked for the first time used NCP (network control protocol) to allow computers to communicate UCLA, SRI, UCSB, Univ of Utah, BBN, MIT, RAND, SDC, Harvard, Lincoln Lab, Stanford, UIU(C), CWRU, CMU, NASA/Ames 1972 the first e-mail program was created by Ray Tomlinson of BBN 1973 first international connections to the ARPANET
nethistory.ppt
University College of London (England) via NORSAR (Norway) (collaboration between Stanford and DARPA)
development began on the protocol later to be called TCP/IP
1974 first use of term internet in a paper on Transmission Control Protocol 1976 Elizabeth II, Queen of the United Kingdom, sends her first email 4
HOW DID THE NETWORK EVOLVE?
13-Sep-13
ARPAs created the first network ARPA did not act as an enforcer on standards, but instead, invited public participation in improving the network
nethistory.ppt
the founding philosophy:
to be resilient, the network was not supposed to rely on a centralized control this was revolutionary
the network relied on a growing number of standard specification documents
only standards-compliant computers could communicate
ARPA retained control but exercised it judiciously (little)
WHO WROTE THE NETWORK STANDARDS?
13-Sep-13
university researchers participated in standards work private industry research contributed personnel
nethistory.ppt
AT&T, IBM, and many others funded their employees to work on network improvements
some people did it for free as a sideline to their work
standards were created by the public and developers everywhere
via the RFC process (public proposals) if many in industry and research institutions implemented the proposals, they eventually became standard
6
13-Sep-13 nethistory.ppt
INTERNET IN
1977
NETWORKING TIMELINE
1978 TCP protocol (Stanford research since 1976) split into TCP and IP protocols 1980 ARPANET grinds to a complete halt on 27 October
- EIGHTIES
13-Sep-13
because of an accidentally-propagated status-message virus so users would not have to know the exact path to other systems TCP/IP became the core internet protocol, replacing NCP entirely
name server developed at University of Wisconsin
on January 1st, every machine connected to ARPANET had to use TCP/IP
nethistory.ppt
1983 first IBM personal computers sold 1984
Domain Name System (DNS) introduced on ARPANET
1986
Mail Exchanger (MX) records developed
to allow non-IP network hosts to have email domain addresses to coordinate contractors for DARPA Coordinated work on ARPANET, US Defense Data Network (DDN), and the Internet core gateway system
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) created
1987 email link established between Germany and China
1989 number of hosts breaks 100,000
NETWORKING TIMELINE
ADVENT OF WWW
1990 ARPANET ceases to exist
Tim Berners-Lee and CERN in Geneva implement HTTP for members of the international high-energy physics community independent internet service provicers begin to spring up everywhere
13-Sep-13
nethistory.ppt
1991 PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) released by Philip Zimmerman 1992 number of internet hosts breaks 1,000,000
no web yet; email and newsnet only (mostly at command line) world-wide web (WWW) HTTP protocol released by CERN
Tim Berners-Lee, developer
9
THANK YOU
10
13-Sep-13 nethistory.ppt
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Arpanet: Arpanet Transitions To Tcp/IpDocumento2 pagineArpanet: Arpanet Transitions To Tcp/IpMelody BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- How Does The Internet Work?: FromDocumento7 pagineHow Does The Internet Work?: FromRyan SanitaNessuna valutazione finora
- History of InternetDocumento4 pagineHistory of InternetTimothy Roger ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- GEC9 History of Internet ReportDocumento30 pagineGEC9 History of Internet ReportCrisjoan BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- History of The InternetDocumento6 pagineHistory of The Internetshani9976614Nessuna valutazione finora
- ARPANET - WikipediaDocumento24 pagineARPANET - WikipediaJim RansoNessuna valutazione finora
- STS InternetDocumento2 pagineSTS InternetToni Francesca MarquezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Origin of Internet and Its EvolutionDocumento18 pagineThe Origin of Internet and Its EvolutionLailanie Macalos100% (1)
- History of The InternetDocumento13 pagineHistory of The InternetFlorencio CoquillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arpanet: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento7 pagineArpanet: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRAHUL SONINessuna valutazione finora
- ParallelDocumento9 pagineParallelPashiv GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Birth of Packet-Switched Networks: Internet HistoryDocumento2 pagineBirth of Packet-Switched Networks: Internet HistoryJyo ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- A Short History of The Internet by Bruce Sterling: F&SF Science Column #5 "Internet"Documento6 pagineA Short History of The Internet by Bruce Sterling: F&SF Science Column #5 "Internet"SaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- InternetDocumento2 pagineInternetRiadh HadefNessuna valutazione finora
- History of InternetDocumento9 pagineHistory of InternetMathew Santiago AdolfoNessuna valutazione finora
- The Internet Is A Global Network of Networks WhileDocumento2 pagineThe Internet Is A Global Network of Networks WhileMelody BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet: This Article Is About The Public Worldwide Computer Network System. For Other Uses, SeeDocumento8 pagineInternet: This Article Is About The Public Worldwide Computer Network System. For Other Uses, SeeSWAPNILJUMALENessuna valutazione finora
- CIR 209 (Lecture 4d) - OSI and TCP-IP ModelDocumento22 pagineCIR 209 (Lecture 4d) - OSI and TCP-IP Modeldancanongori9Nessuna valutazione finora
- 19ce013 Aman CN Practical FileDocumento87 pagine19ce013 Aman CN Practical FileAman SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Script For STSDocumento4 pagineScript For STSSkirk FallenNessuna valutazione finora
- Brief History of ISPDocumento10 pagineBrief History of ISPKIRTI SAININessuna valutazione finora
- Bruce Sterling - Short History of The InternetDocumento6 pagineBruce Sterling - Short History of The InternetMaria Eugenia Perez CalixtoNessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Maps That Will Explain InternetDocumento42 pagine40 Maps That Will Explain InternetNathan NathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution of InternetDocumento11 pagineEvolution of Internetrameesarashid09Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Internet: History of Internet and WWWDocumento15 pagineIntroduction To Internet: History of Internet and WWWswathi_mahadevanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief History of The InternetDocumento1 paginaA Brief History of The InternetIgara OliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Breif History of InternetDocumento3 pagineBreif History of InternetNi CkNessuna valutazione finora
- Sandro Yosapat Saragih - 122400091 - 38Documento3 pagineSandro Yosapat Saragih - 122400091 - 38Paulus SiahaanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 3 Computer Networks 3Documento1 paginaUnit 3 Computer Networks 3Tejendra PachhaiNessuna valutazione finora
- History of InternetDocumento2 pagineHistory of InternetMerline Cole RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- MIS 105 Chapter Reference - Chapter 1: Lecture Topic The InternetDocumento3 pagineMIS 105 Chapter Reference - Chapter 1: Lecture Topic The InternetmziabdNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The InternetDocumento8 pagineWhat Is The Internetdritus81Nessuna valutazione finora
- History of The InternetDocumento8 pagineHistory of The InternetVishnu VardhanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Brief History of The Internet That Connects Us Wherever We AreDocumento10 pagineA Brief History of The Internet That Connects Us Wherever We AreJoseph OngNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 7 - Researched ContentDocumento3 pagineGroup 7 - Researched ContentMa'arifa HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet TechnologyDocumento15 pagineInternet TechnologychandrasekaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One. Introduction To Internet and Cyber-Crime.Documento14 pagineChapter One. Introduction To Internet and Cyber-Crime.Femi ErinleNessuna valutazione finora
- Arpa Arpanet InternetDocumento20 pagineArpa Arpanet Internetarvinziba963Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 HistoryDocumento22 pagine02 HistoryPriyanka GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Internet Part TwoDocumento21 pagineThe Internet Part Twosouhasou2003.08Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Impact of The Internet On The Social and Economic Life in NigeriaDocumento48 pagineThe Impact of The Internet On The Social and Economic Life in NigeriaAwani Kester50% (2)
- Internet Timeline: Arsheil Lavein R. Mendoza 10 - MartinelliDocumento12 pagineInternet Timeline: Arsheil Lavein R. Mendoza 10 - MartinelliArsheil Lavein R. MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- The History of The InternetDocumento9 pagineThe History of The InternetMark M. MijaresNessuna valutazione finora
- The Internet How Did The Internet Develop?Documento8 pagineThe Internet How Did The Internet Develop?Rizwan Basha LalahmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Module 3 Lec - Data Security AwarenessDocumento29 pagineLesson 2 Module 3 Lec - Data Security AwarenessJenica Mae SaludesNessuna valutazione finora
- History of The InternetDocumento20 pagineHistory of The InternetRishaana SaranganNessuna valutazione finora
- Module (GRPDocumento32 pagineModule (GRPapi-3750482Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is The InternetDocumento7 pagineWhat Is The InternetAartiNessuna valutazione finora
- History of InternetDocumento25 pagineHistory of InternetMohamed Tayeb SELT100% (4)
- 37 Internet HistoryDocumento18 pagine37 Internet HistoryAmit SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture-1 History of Networking (11 Files Merged) (1) (1) (3 Files Merged) (1) (9 Files Merged) (12 Files Merged) (5 Files Merged) (7 Files Merged)Documento1.146 pagineLecture-1 History of Networking (11 Files Merged) (1) (1) (3 Files Merged) (1) (9 Files Merged) (12 Files Merged) (5 Files Merged) (7 Files Merged)Nikhil GaddamNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Internet and EmailsDocumento32 pagineIntro To Internet and Emailszakayo nyakungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Internet Web DesigningDocumento86 pagineInternet Web DesigningAjithNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey and Research Web DesignDocumento30 pagineSurvey and Research Web DesignAmir SyakirNessuna valutazione finora
- RomanSuwal 10279533 190405Documento3 pagineRomanSuwal 10279533 190405Roman SuwalNessuna valutazione finora
- History of The InternetDocumento23 pagineHistory of The InternetЭдуард СтаневичNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating A Worldwide NetworkDocumento9 pagineCreating A Worldwide NetworkWillFisherNessuna valutazione finora
- Sputnik 1957 IntDocumento9 pagineSputnik 1957 IntWillFisherNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IDocumento15 pagineComputer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Elasticity of Demand Class JLD LSK LDK Ask DK Asd As DK Las Dkas KLD As DK Ask Ldkals KDL SKL Dkal SK LDDocumento24 pagineElasticity of Demand Class JLD LSK LDK Ask DK Asd As DK Las Dkas KLD As DK Ask Ldkals KDL SKL Dkal SK LDVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash Flow StatementDocumento10 pagineCash Flow StatementVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- M21_nethistory jjlldjlas;ldas;ldl;asldas;ld;ls;lda;lskd;laskd;lksl;dklksd;lkas;lkd;las;ldklas;kelaks;lekas;ldlks;alkd;laskl;dk;laskd;la;ldk;akd;ask;ldk;laskd;laks;kd;laskd;lks;ld;laskd;las;ldas;lkdkas;ldkas;lkdsak;dka;ld;alkd;lak;dla;kd;alask;dk;akd;lskd;askd;las;ldkas;lkd;lak;dlkasd;lkas;ldkas;lkd;lask;ldas;kd;lask;dlkas;ldas;ldk;lkd;lsd;lask;dlaks;lkd;lkd;lask;dka;lkd;ald;l;ldk;aslkd;aslk;dlka;ld;aslkds;lakd;lask;dl;dsa;lkd;laskd;lask;dlkas;ldkas;lkd;lk;Documento10 pagineM21_nethistory jjlldjlas;ldas;ldl;asldas;ld;ls;lda;lskd;laskd;lksl;dklksd;lkas;lkd;las;ldklas;kelaks;lekas;ldlks;alkd;laskl;dk;laskd;la;ldk;akd;ask;ldk;laskd;laks;kd;laskd;lks;ld;laskd;las;ldas;lkdkas;ldkas;lkdsak;dka;ld;alkd;lak;dla;kd;alask;dk;akd;lskd;askd;las;ldkas;lkd;lak;dlkasd;lkas;ldkas;lkd;lask;ldas;kd;lask;dlkas;ldas;ldk;lkd;lsd;lask;dlaks;lkd;lkd;lask;dka;lkd;ald;l;ldk;aslkd;aslk;dlka;ld;aslkds;lakd;lask;dl;dsa;lkd;laskd;lask;dlkas;ldkas;lkd;lk;Vikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Pricing Methods HHHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJDocumento8 paginePricing Methods HHHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJGHJVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Demand and Supply Analysis-1 SdsakldjlasjldjlasldlasjldjklasdjasljdljasldjlaskldasljdlasjlklDocumento30 pagineDemand and Supply Analysis-1 SdsakldjlasjldjlasldlasjldjklasdjasljdljasldjlaskldasljdlasjlklVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Dka LK LSKD LSK LDKDocumento10 pagineDka LK LSKD LSK LDKVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- AsjldjlasdjsjdksdjskljdklasdlsaDocumento17 pagineAsjldjlasdjsjdksdjskljdklasdlsaVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Human in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkDocumento31 pagineHuman in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Merchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixDocumento87 pagineMerchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- PPM - Planning of Vinit RaidfdsfsdfdsdfdsfdsfDocumento11 paginePPM - Planning of Vinit RaidfdsfsdfdsdfdsfdsfVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networks ,llsldlasldk;lask;lds;lad;las;ldkl;askd;las;ldk;laskd;lklas;kdlaskldklaskdlkasl;dlakldklaskdlkasldklaskldkaslkd;laskldkas;lkd;laskd;lkaslkdlaskldk;laskdas;lkd;lsakldkasl;d;laskld;kas;lkd;lask;dkas;kd;lask;dlask;l fgkdgsjkgkldfklgdklflgkdfkljgdfklgkljdfklgjkldfklgjkldfjklgjdfkljgkljdfkgjdfjkgjkldfjglfkjgldfjgkljlkgjdfkljgkljdfkljgkldfjklgjdflkjgkldfljglkdfjglkdfjklgjdfkljgdljgkldfjgkldfjgkldjfklgjdfkljgkldfjkjgkljkDocumento14 pagineComputer Networks ,llsldlasldk;lask;lds;lad;las;ldkl;askd;las;ldk;laskd;lklas;kdlaskldklaskdlkasl;dlakldklaskdlkasldklaskldkaslkd;laskldkas;lkd;laskd;lkaslkdlaskldk;laskdas;lkd;lsakldkasl;d;laskld;kas;lkd;lask;dkas;kd;lask;dlask;l fgkdgsjkgkldfklgdklflgkdfkljgdfklgkljdfklgjkldfklgjkldfjklgjdfkljgkljdfkgjdfjkgjkldfjglfkjgldfjgkljlkgjdfkljgkljdfkljgkldfjklgjdflkjgkldfljglkdfjglkdfjklgjdfkljgdljgkldfjgkldfjgkldjfklgjdfkljgkldfjkjgkljkVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- OB Leadership GFDSFDSLFKL DSLFK Llfkds LKFLKDSL KFL DKF LDK Lfklds KLFDSJFLDKLFKLDKFKFKF Lkds LKFL DK LFK LLDocumento8 pagineOB Leadership GFDSFDSLFKL DSLFK Llfkds LKFLKDSL KFL DKF LDK Lfklds KLFDSJFLDKLFKLDKFKFKF Lkds LKFL DK LFK LLVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IDocumento15 pagineComputer Languages: Presented By: Kimmy Arora M.B.A-IVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Daimlerchryslermerger-120117024935-Phpapp02 K Kdlkas LD Laslkdlsldk Lasklkas Lkdlskldklas D Lsa LDK LLDocumento15 pagineDaimlerchryslermerger-120117024935-Phpapp02 K Kdlkas LD Laslkdlsldk Lasklkas Lkdlskldklas D Lsa LDK LLVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- SHRISTIDocumento18 pagineSHRISTIVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- RewardshhkllklklkkjljkljkljkljkljljDocumento1 paginaRewardshhkllklklkkjljkljkljkljkljljVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Human in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkDocumento31 pagineHuman in Retaili KsdklasjkldakskdasjdkllasdlasklkldkaskdlsaklldkaskljdklklkVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Merchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixDocumento87 pagineMerchandise Management: Buying and Handling The Merchandise MixVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- V KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJDocumento12 pagineV KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented by Nitesh SabharwalDocumento6 paginePresented by Nitesh SabharwalVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- 25 Lessons Jack Wesdaskdaskdk Asld As DL Asl 'Dlad La Lda SL DL' Asl' Dlasldasl DL Asl DL LCH Ten3 Minicourse2Documento21 pagine25 Lessons Jack Wesdaskdaskdk Asld As DL Asl 'Dlad La Lda SL DL' Asl' Dlasldasl DL Asl DL LCH Ten3 Minicourse2Vikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Growing Prominance of Credit and Debit CardsDocumento10 pagineGrowing Prominance of Credit and Debit CardsVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Output DevicesDocumento16 pagineOutput DevicesVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- V KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJDocumento12 pagineV KJHHKJKJJKHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJJKHKKKJKJHKJHKKJHJKHKJKJHKJHKJJKJKHKHKKJJKHKKHKHJKHKHKJHKJHJHKJHKJHKJHKJHKJVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Cash Flow StatementDocumento10 pagineCash Flow StatementVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Diagram of ComputerkjkkkkjkljlkjkDocumento10 pagineBlock Diagram of ComputerkjkkkkjkljlkjkVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Value, Norm, Chara& Affec On Consum BehaviouDocumento30 pagineValue, Norm, Chara& Affec On Consum BehaviouVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Aeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLDocumento41 pagineAeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
- Aeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLDocumento41 pagineAeb41-Week4 KKJKJKJLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLJKLVikas RockNessuna valutazione finora
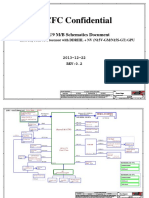
- Compal Nm-A311p r0.2 SchematicsDocumento60 pagineCompal Nm-A311p r0.2 SchematicsTitel Andrei TimocNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Waterfall Model:: Mid Questions and Answers - 4sets PDF By: Venu GopalDocumento22 pagineClassical Waterfall Model:: Mid Questions and Answers - 4sets PDF By: Venu Gopalspider dogNessuna valutazione finora
- Scantron INSIGHT 30 Datasheet From AXIS IT BangladeshDocumento4 pagineScantron INSIGHT 30 Datasheet From AXIS IT BangladeshkmmhasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Arm Linux Ts72xxDocumento49 pagineArm Linux Ts72xxNiraj KapaseNessuna valutazione finora
- Exercise 28 AnswerDocumento5 pagineExercise 28 AnswerSenan AlkaabyNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP SuccessFactors Foundation PDFDocumento466 pagineSAP SuccessFactors Foundation PDFDiogo Palermo ToblerNessuna valutazione finora
- ATC-820B User's ManualDocumento2 pagineATC-820B User's ManualMaitry ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ctai - Fexam PDFDocumento126 pagineCtai - Fexam PDFmoncarla lagonNessuna valutazione finora
- DSP ProcessorsDocumento114 pagineDSP ProcessorsArunNessuna valutazione finora
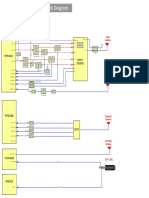
- L3 Block Diagram XT1063-XT1064-XT1068-XT1069 V1.0Documento4 pagineL3 Block Diagram XT1063-XT1064-XT1068-XT1069 V1.0Renato AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- HUAWEI HiSecEngine USG6500E Series Firewalls (Fixed-Configuration) DatasheetDocumento9 pagineHUAWEI HiSecEngine USG6500E Series Firewalls (Fixed-Configuration) DatasheethugobiarNessuna valutazione finora
- BRKIPM-2265 - Deploying BGP Fast Convergence - BGP PIC (2013 London) - 2 HoursDocumento80 pagineBRKIPM-2265 - Deploying BGP Fast Convergence - BGP PIC (2013 London) - 2 Hourskds208500% (1)
- Communication Interfaces PDFDocumento2 pagineCommunication Interfaces PDFBrittanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Wali - MP3 Full AlbumDocumento15 pagineWali - MP3 Full AlbumramziNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction of Server-Sent EventsDocumento18 pagineIntroduction of Server-Sent EventsOscarNessuna valutazione finora
- APO BW Planning SNPDocumento11 pagineAPO BW Planning SNPash4u2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scada ManualDocumento104 pagineScada Manualaaronfoley74100% (1)
- Statement:: Pdf 文件使用 "Pdffactory" 试用版本创建Documento29 pagineStatement:: Pdf 文件使用 "Pdffactory" 试用版本创建Emilio David Brito RodríguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless N150 Adsl2+ 4-Port Router: DSL-2730EDocumento75 pagineWireless N150 Adsl2+ 4-Port Router: DSL-2730EdcastelobNessuna valutazione finora
- Mem ManDocumento25 pagineMem ManRude MaverickNessuna valutazione finora
- Digitalcrafts Immersive Bootcamp Course Packet V4.originalDocumento11 pagineDigitalcrafts Immersive Bootcamp Course Packet V4.originalDe VoNessuna valutazione finora
- AdvizeX Oracle12c PosterDocumento1 paginaAdvizeX Oracle12c Posterpush5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fortinet Nse 2 - Lesson 3Documento2 pagineFortinet Nse 2 - Lesson 3Tony Celli0% (1)
- TLA7Bxx Logic Analyzer Series Product Specifications & Performance Verification Technical ReferenceDocumento30 pagineTLA7Bxx Logic Analyzer Series Product Specifications & Performance Verification Technical Referenceapi-19827677Nessuna valutazione finora
- School of Electrical, Electronic & Computer Engineering Course: Code: Practical No.: TitleDocumento5 pagineSchool of Electrical, Electronic & Computer Engineering Course: Code: Practical No.: TitleNdumiso MtshaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrating IBM Content Navigator With IBM Content Analytics With Enterprise Search Using PluginDocumento22 pagineIntegrating IBM Content Navigator With IBM Content Analytics With Enterprise Search Using PluginSofiane HamidNessuna valutazione finora
- Microstar Company Profile PDFDocumento6 pagineMicrostar Company Profile PDFDell GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- FactoryTalk AssetCentre - BrochureDocumento4 pagineFactoryTalk AssetCentre - BrochureJosé Santiago Miranda BernaolaNessuna valutazione finora
- CCIE Data Center Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocumento4 pagineCCIE Data Center Cheat Sheet: by ViaNapster KingNessuna valutazione finora
- Bca Project On Courier Management SystemDocumento245 pagineBca Project On Courier Management Systemnhnavneet85% (52)