Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basic-Laws of Chemcombi
Caricato da
Melvin CabonegroTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basic-Laws of Chemcombi
Caricato da
Melvin CabonegroCopyright:
Formati disponibili
In the study of matter, we observe certain phenomena which can be reproduced at will.
These observed phenomena are called scientific facts. Often, a large number of scientific facts can be summarized into broad or sweeping statements called laws.
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS
-which states that when an ordinary chemical reaction occurs, there is no detectable change in the masses of the substances involved before and after the reaction.
masses of the reactants = masses of the products before the reaction after the reaction
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS
However, Albert Einstein, a Nobel laureate physicist and one of the most creative intellects in human history, recognized the quantitative interconversion of mass and energy in reactions, as shown by his famous equation.
E = mc2
Where: E = energy m = mass c = velocity of light
LAW OF CONSERVATION OF MASS
The interconvertibility of mass and energy holds true in energetic processes like radioactivity and atomic explosions. Strictly speaking, the interconversion of energy and mass cannot possibly allow a constancy of one or the other. However, the amount of energy and mass change are too small to be detected in the laboratory. Therefore, we can still count on the law of conservation of mass for practical use.
LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTION
-states that a pure compound always contains the same elements combined in the same proportions by mass. -when two elements combine to form a given compound, they always do so in a fixed proportion.
LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTION
To illustrate the law of definite composition, refer to the table
Trial 1 2 3 Mass of C (g) 2.00 15.00 5.00 Mass of O2 (g) 5.34 40.05 13.36 Mass of CO2 (g) 7.34 55.05 18.36
These are the mass data for the amounts of C, O2, and CO2 in the reaction. C + O2 CO2
LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTION
Trial 1 2 3 Mass of C (g) 2.00 15.00 5.00 Mass of O2 (g) 5.34 40.05 13.36 Mass of CO2 (g) 7.34 55.05 18.36
Find the percentages of carbon and oxygen.
% of C =
x 100
% of O =
x 100
LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTION
Trial 1 2 3 Mass of C (g) 2.00 15.00 5.00 Mass of O2 (g) 5.34 40.05 13.36 Mass of CO2 (g) 7.34 55.05 18.36
Trial 1
Trial 2
Trial 3
2.0 C= x 100 7.34
= 27.2%
15.0 C= x 100 55.05
= 27.2%
5.0 C= x 100 18.36
= 27.2%
5.34 O= x 100 7.34
= 72.8%
40.05 O= x 100 55.05
= 72.8%
13.36 O= x 100 18.36
= 72.8%
LAW OF DEFINITE PROPORTION
Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3
2.0 C= x 100 7.34
= 27.2%
15.0 C= x 100 55.05
= 27.2%
5.0 C= x 100 18.36
= 27.2%
5.34 O= x 100 7.34
= 72.8%
40.05 O= x 100 55.05
= 72.8%
13.36 O= x 100 18.36
= 72.8%
These show that the percentage of carbon in CO2 which is 27.2% and the percentage of oxygen in CO2 which is 72.8% are definite. The experimental data in the example also verify and confirm the law of conservation of mass.
LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS
-this states that when two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of one element which combine with a fixed mass of the other element are in a ratio of small whole numbers such as 2:1, 1:1, 2:3, etc.
LAW OF MULTIPLE PROPORTIONS
Sample Exercise: Two different compounds elements C and D were found to have the following compositions: C D First compound 2.276 g 0.792 g Second compound 1.422 g 0.948 g Find the formulas of the two compound.
Solution: Mass may be fixed at C. C First compound 2.276 g/2.276g = 1 Second compound 1.422 g/1.422 g = 1
D 0.792 g/2.276 g = 0.348 0.948 g/1.422 g = 0.667
Therefor, the formulas of the two compounds are: Ratio C D Formula First 1 0.348/0.348 =1 CD compound Second 1 0.667/0.348 = 2 CD2 compound
Practice exercises Find the formula of the compounds having the following composition: X Y First compound 50 g 56 g Second compound 35 g 82 g
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PDF - Chemical-Arithmatic StoichiometryDocumento25 paginePDF - Chemical-Arithmatic StoichiometrySushrut GhimireNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Chemical CombinationsDocumento6 pagineLaws of Chemical CombinationsUma Shankar100% (2)
- Vidya StoichiometryDocumento34 pagineVidya StoichiometryNarendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometry March 29Documento33 pagineStoichiometry March 29Jessica PokhrelNessuna valutazione finora
- Law of Definite Proportions or Constant Composition: StatementDocumento9 pagineLaw of Definite Proportions or Constant Composition: StatementPriyanshu PalNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Equations2Documento43 pagineGas Equations2api-280572108Nessuna valutazione finora
- (L2) - Mole Concept JEEDocumento19 pagine(L2) - Mole Concept JEEHYDRA CLAN100% (1)
- 6095 - ss1 ChemistryDocumento5 pagine6095 - ss1 Chemistrypalmer okiemuteNessuna valutazione finora
- DAA660412 C 0919019103 Session73912 220929024726Documento92 pagineDAA660412 C 0919019103 Session73912 220929024726Gio SyahfutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical ArithmeticDocumento18 pagineChemical Arithmeticshivakafle039Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of MatterDocumento6 pagineClassification of MatterTyo ReynaldyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaseous StateDocumento39 pagineGaseous Statesourabhmaths100% (1)
- Physico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentDa EverandPhysico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XI - 1.1 - Matter - Laws of Chemical Combination To Formula MassDocumento50 pagineClass XI - 1.1 - Matter - Laws of Chemical Combination To Formula MassNaman SardanaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Azomethine Ylides Generated From Aziridines in Supercritical Carbon DioxideDocumento5 pagine1,3-Dipolar Cycloaddition of Azomethine Ylides Generated From Aziridines in Supercritical Carbon DioxideLineth OyolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Units 3 and 4 Practice QuestionsDocumento51 pagineChemistry Units 3 and 4 Practice QuestionsElmo Bluey100% (1)
- Lecture 10 ChemDocumento3 pagineLecture 10 Chemlldgee33Nessuna valutazione finora
- CHEMARITHMOLEFMFDocumento43 pagineCHEMARITHMOLEFMFPaul Jeremiah Serrano NarvaezNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoicchiomentry and Redox Reactiions TheoryDocumento22 pagineStoicchiomentry and Redox Reactiions TheoryVenkycommercial 23Nessuna valutazione finora
- X Mat Che 3 L.o.che - CombiDocumento29 pagineX Mat Che 3 L.o.che - CombiShorya KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd EditionDocumento36 pagineSolution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Editionsaturantbruniontvg0100% (43)
- Full Download Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Edition PDF Full ChapterDocumento36 pagineFull Download Solution Manual For Chemistry An Atoms First Approach 2nd Edition PDF Full Chapterloudly.nereisnai6100% (15)
- DPP 9 Chem XiDocumento2 pagineDPP 9 Chem XiamansheelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 11Documento12 pagineChapter 11JeromeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometry: CH + 2 O Co + 2 H ODocumento11 pagineStoichiometry: CH + 2 O Co + 2 H OAlberto GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole: 1 Mole of A Substance Contains Avogadro's Number (N 6.02E23)Documento53 pagineMole: 1 Mole of A Substance Contains Avogadro's Number (N 6.02E23)Juan Carlos Gonzalez LNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry General: Chapter 2: Atoms and The Atomic TheoryDocumento34 pagineChemistry General: Chapter 2: Atoms and The Atomic Theoryblackdevil169Nessuna valutazione finora
- Selected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionDa EverandSelected Constants: Oxidation–Reduction Potentials of Inorganic Substances in Aqueous SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- CH06Documento81 pagineCH06黃偉荏Nessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Chemistry1702951908Documento62 pagine40 Chemistry1702951908ilegbedionkNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Booklet Science and Fun Part 1Documento102 pagineChemistry Booklet Science and Fun Part 1ext.xd6948Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometry PDFDocumento80 pagineStoichiometry PDFGadde Gopala KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermodynamics and Kinetics ReviewDocumento15 pagineThermodynamics and Kinetics Reviewhahaha7777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Laws: University of Perpetual Help System Laguna - JONELTADocumento12 pagineGas Laws: University of Perpetual Help System Laguna - JONELTANeale NayveNessuna valutazione finora
- Estequiometría Del Crecimiento Microbiano y Formación de ProductoDocumento9 pagineEstequiometría Del Crecimiento Microbiano y Formación de ProductoDaniela NavasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 16Documento8 pagineChem 16Adi SoNessuna valutazione finora
- GC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and IonsDocumento45 pagineGC1 Lesson 3 Atoms Molecules and IonsYeri KimNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermochemistry: What Is The Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?Documento7 pagineThermochemistry: What Is The Difference Between Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions?riza amoresNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Principles 8th Edition Zumdahl Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineChemical Principles 8th Edition Zumdahl Solutions Manualdement.disturnlklpvp95% (22)
- Mole ConceptDocumento52 pagineMole ConceptRekha Purohit60% (5)
- Chemical Exergy Calculation CharpterDocumento10 pagineChemical Exergy Calculation CharpterFernanda PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Stoichiometry - WikipediaDocumento58 pagineStoichiometry - WikipediaInam KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- ChE 505 Chapter 2NDocumento27 pagineChE 505 Chapter 2NAkshay GopanNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws 2Documento13 pagineLaws 2Michelle Sollano RemediosNessuna valutazione finora
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Documento8 pagineLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Jhude JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mole Concept: Prepared By: Pooran Appadu (Type The Company Name) 9/1/2009Documento44 pagineThe Mole Concept: Prepared By: Pooran Appadu (Type The Company Name) 9/1/2009aldemairaNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution Manual For Principles of General Chemistry 3rd Edition Silberberg 0073402699 9780073402697Documento36 pagineSolution Manual For Principles of General Chemistry 3rd Edition Silberberg 0073402699 9780073402697susanbradygajkznydrf100% (23)
- Basic Concept of Chemistry (1-24)Documento24 pagineBasic Concept of Chemistry (1-24)deepakkr08080% (5)
- Chemistry Module For Remidial ClassDocumento52 pagineChemistry Module For Remidial ClassMuktaar HassenNessuna valutazione finora
- (Chemical Laws) Yr 10intl Wk1Documento23 pagine(Chemical Laws) Yr 10intl Wk1Victor OkosunNessuna valutazione finora
- Ponderal Laws and StoichiometryDocumento17 paginePonderal Laws and StoichiometryLeonardoFloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole Concept PDFDocumento26 pagineMole Concept PDFPrashant Kumar67% (3)
- CHM 101 Complete - LNDocumento80 pagineCHM 101 Complete - LNSimon Adediran100% (1)
- General Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsDocumento23 pagineGeneral Physics1 Q2 W8 Module8 ThermodynamicsRegine Ann ViloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Essential Chemical Concepts Session IIDocumento26 pagineEssential Chemical Concepts Session IIHamza QureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 06 Chemical KineticsDocumento108 pagineChapter 06 Chemical KineticsJishen ZhuNessuna valutazione finora
- StoichiometryDocumento10 pagineStoichiometryIjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Deped Order No. 42, S. 2016 Taligaman National High School Melvin C. CabonegroDocumento6 pagineDeped Order No. 42, S. 2016 Taligaman National High School Melvin C. CabonegroMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Taligaman National High School Taligaman, Butuan CityDocumento1 paginaTaligaman National High School Taligaman, Butuan CityMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- School Base Management Dimensions A. Leadership and Governance B. Curriculum and LearningDocumento2 pagineSchool Base Management Dimensions A. Leadership and Governance B. Curriculum and LearningMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- G8 DLL Arts Q3Documento16 pagineG8 DLL Arts Q3Crys Alvin MaticNessuna valutazione finora
- Daily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterDocumento16 pagineDaily Lesson LOG: School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Dates and Time QuarterShemae Obni89% (9)
- Daily Lesson LogDocumento4 pagineDaily Lesson LogMelvin Cabonegro100% (2)
- Travel Authority: Taligaman National High SchoolDocumento2 pagineTravel Authority: Taligaman National High SchoolMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
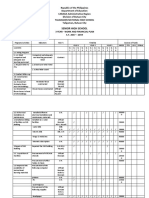
- SHS 3 Years Work and Financial Plan WFPDocumento8 pagineSHS 3 Years Work and Financial Plan WFPMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- School Form 7 (SF7) School Personnel Assignment List and Basic ProfileDocumento6 pagineSchool Form 7 (SF7) School Personnel Assignment List and Basic ProfileMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Bi OmegaDocumento7 pagineBi OmegaMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9: Name of Student School Last Attended Residence Address Contact Number RemarksDocumento2 pagineGrade 9: Name of Student School Last Attended Residence Address Contact Number RemarksMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Objective TabbingDocumento8 pagineObjective TabbingMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9: Name of Student School Last Attended Residence Address Contact Number RemarksDocumento2 pagineGrade 9: Name of Student School Last Attended Residence Address Contact Number RemarksMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Sf5 - 2017 - Grade 7 (Year I) - FrondaDocumento3 pagineSf5 - 2017 - Grade 7 (Year I) - FrondaMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Assignment Mam RuthDocumento21 pagineFinal Assignment Mam RuthMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- BE Form 5 - RECORD OF DONATIONS RECEIVEDDocumento1 paginaBE Form 5 - RECORD OF DONATIONS RECEIVEDMelvin Cabonegro0% (1)
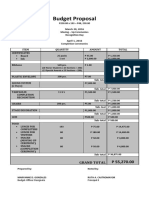
- Budget Proposal: March 29, 2016Documento2 pagineBudget Proposal: March 29, 2016Melvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Conduct of Meetings Policy 2015Documento6 pagineConduct of Meetings Policy 2015Melvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- DEPED-Butuan City-Notice of Evaluation-SchoolsDocumento1 paginaDEPED-Butuan City-Notice of Evaluation-SchoolsMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Tnhs Annual Report Finale 1Documento44 pagineTnhs Annual Report Finale 1Melvin Cabonegro100% (1)
- Jhs Class Program BlankDocumento45 pagineJhs Class Program BlankMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Grain 2016Documento12 pagineGrain 2016Melvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Class ProgramDocumento30 pagineClass ProgramMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Substitute FormDocumento1 paginaSubstitute FormMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- 2015 SALN FormDocumento4 pagine2015 SALN Formwyclef_chin100% (6)
- Appearance 3Documento2 pagineAppearance 3Melvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Committees and AncillaryDocumento6 pagineCommittees and AncillaryMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Grain 2016Documento12 pagineGrain 2016Melvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Letterr NewDocumento1 paginaLetterr NewMelvin CabonegroNessuna valutazione finora
- Awards and RecognitionDocumento19 pagineAwards and RecognitionMelvin Cabonegro0% (1)
- Stamford Sx460 Voltage RegulatorDocumento4 pagineStamford Sx460 Voltage Regulatorthegr8t1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure MeasurementDocumento19 paginePressure Measurementdevarshikumar vaidya100% (1)
- Q.Bank Air NavDocumento14 pagineQ.Bank Air Navsakshee gojreNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4 Cross Flow Heat ExchangerDocumento19 pagineExperiment 4 Cross Flow Heat Exchangerbeasturs1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Black HolesDocumento5 pagineBlack Holesman2503Nessuna valutazione finora
- Eddy Current NDT InspectionDocumento172 pagineEddy Current NDT InspectionBrahim Letaief100% (1)
- Physics 222 Ohm's Law Lab ReportDocumento12 paginePhysics 222 Ohm's Law Lab ReportEmily Gatlin81% (27)
- Effect of Prime-Mover Speed Governor Characteristics On Power-System Frequency Variations and Tie-Line Power SwingsDocumento9 pagineEffect of Prime-Mover Speed Governor Characteristics On Power-System Frequency Variations and Tie-Line Power SwingsansarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp1 (Final) PDFDocumento15 pagineExp1 (Final) PDFZaidNessuna valutazione finora
- Janitza Manual Prophi 7 GBDocumento35 pagineJanitza Manual Prophi 7 GBJose TroscaNessuna valutazione finora
- Force & Pressure PPT-3Documento11 pagineForce & Pressure PPT-3ARNAB GHOSH CLASS V100% (1)
- A Numerical Model For Thermal-Hydraulic Design of A Shell and Single Pass Low Finned Tube Bundle Heat ExchangerDocumento27 pagineA Numerical Model For Thermal-Hydraulic Design of A Shell and Single Pass Low Finned Tube Bundle Heat ExchangerSilvio PeluffoNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Winding TransformersDocumento6 pagine3 Winding TransformersAmitabhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical Electrodynamics: Review of ElectrostaticsDocumento16 pagineClassical Electrodynamics: Review of ElectrostaticsBaby SileshiNessuna valutazione finora
- HVAC Simplified-Solution-ManualDocumento78 pagineHVAC Simplified-Solution-ManualRefrigeration Training UnitNessuna valutazione finora
- On Basic Electrical - 1Documento18 pagineOn Basic Electrical - 1Sakshi RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- General Physics 1: Grade 11 - Quarter 1 - Week 3 Kinematics: Motion in 1-Dimension and 2 DimensionsDocumento12 pagineGeneral Physics 1: Grade 11 - Quarter 1 - Week 3 Kinematics: Motion in 1-Dimension and 2 DimensionsKim CortezNessuna valutazione finora
- Pilot10 Aviaton Academy 9652045612 Insta/Youtube - Doc - Pilot10Documento1 paginaPilot10 Aviaton Academy 9652045612 Insta/Youtube - Doc - Pilot10Vamsidhar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab5 Eecs2200Documento6 pagineLab5 Eecs2200Md Aminul HaqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of Svcs To Satisfy Reactive Power Needs of Power SystemsDocumento6 pagineApplication of Svcs To Satisfy Reactive Power Needs of Power SystemsRejhan KaramanNessuna valutazione finora
- CE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Documento5 pagineCE Module 9 - Physics (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenDocumento20 pagineMechanical Properties of Fluids: Chapter TenjjNessuna valutazione finora
- Computers & Fluids: Andreas Hölzer, Martin SommerfeldDocumento18 pagineComputers & Fluids: Andreas Hölzer, Martin SommerfeldBRANDON ALBERTO QUINTERO CIFUENTESNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics Manual Notes For CSEC and CAPEDocumento114 paginePhysics Manual Notes For CSEC and CAPEConnor England100% (1)
- AI8302Documento55 pagineAI8302vikirhythmNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 3Documento10 pagineExperiment 3hellothere100% (1)
- Controlling & Switching: - Switches - Installation Contactors - Relays - Signalling Devices - TransformersDocumento88 pagineControlling & Switching: - Switches - Installation Contactors - Relays - Signalling Devices - TransformersSoos JozsefNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal QnsDocumento2 pagineThermal Qnsarul343Nessuna valutazione finora