Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
HPLC and GC by S Narwadiya
Caricato da
snarwadiya100%(2)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (2 voti)
225 visualizzazioni8 pagineIt shows in short the methods of HPLC and GC
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoIt shows in short the methods of HPLC and GC
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
100%(2)Il 100% ha trovato utile questo documento (2 voti)
225 visualizzazioni8 pagineHPLC and GC by S Narwadiya
Caricato da
snarwadiyaIt shows in short the methods of HPLC and GC
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato PPT, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 8
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
GC is useful for compounds which are
naturally volatile or can be converted into
a volatile form.
GC has been a widely used method due to
its high resolution, low detection limits,
accuracy and high resolution limits, and
short analytical time.
Retention of a compound is determined by
its vapour pressure and volatility which, in
turn, depends on its interaction with
stationary phase.
Two types of stationary phases are
commonly used in GC are solid absorbent
(Solid Gas Chromatography [GSD]), and
liquid coated on solid support (Gas-Liquid
Chromatography [GLC]).
In GSC same material (usually silica,
alumina, or activated carbon) act as both
the stationary phase and support phase.
GLC uses liquid phases such as polymers,
hydrocarbons, fluorocarbons, liquid
crystals, and molten organic salts to coat
the solid support materials.
Calcin diatomaceous earth graded into
appropriate size ranges used as a
stationary phase because it is stable
inorganic substance.
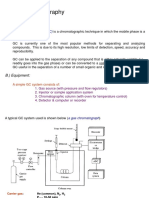
Components of a typical GC system
consists five components: a gas
cylinder as a mobile phase source, a
sample injector, a column, a detector,
and a computer for data acquisition.
The mobile phase used in GC usually
inert gas such as nitrogen, helium,
hydrogen, argon, carbon dioxide,
nitrous oxide and ammonia.
The carrier gas should be of high
purity, and the flow must be tightly
controlled to ensure optimum column
efficiency and reproducibility of test
results.
Samples are introduced in to GC using
hypodermic syringe or automated
samplers.
Each injection port is heated to very
high temperatures to derivatize it into
more volatile form by derivatization
reactions like silylation, alkylation, and
acylation.
• Silylation is most common technique
which replaces active hydrogen on
compounds with alkylsilyl group. This
substitution results in a more volatile
form that is less polar and more
thermally stable.
• Retention of compounds in a GC
column can be adjusted by changing
temperature.
• The column temperature affects
volatility of compounds and thus the
degree of their interaction with the
stationary phase.
High performance Liquid
Chromatography
HPLC uses small rigid support and special
mechanical pumps producing high pressure
to pass the mobile phase through the column.
HPLC column may be used several times
without regeneration.
The resolution achieved by HPLC is superior
than any other forms of liquid
chromatography.
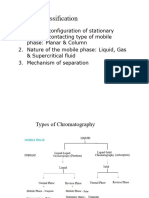
There are five commonly used separation
techniques in liquid chromatography.
They include adsorption, partition, ion
exchange, affinity and size exclusion.
Each is characterized by a unique
combination of stationary phase and mobile
phase.
______________________________________
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- PowerTech 4.5L &6.8L Diesel Engines - Level 12 Electronic Fuel System-Stanadyne DE10 Pump-CTM331Documento550 paginePowerTech 4.5L &6.8L Diesel Engines - Level 12 Electronic Fuel System-Stanadyne DE10 Pump-CTM331grand fir100% (39)
- Chromatography, Classification, Principle of Working and Selected TechniquesDocumento13 pagineChromatography, Classification, Principle of Working and Selected TechniquesS.Umair Jarwar70% (10)
- Construction Safety and Health Narrative MethodsDocumento46 pagineConstruction Safety and Health Narrative MethodsEldreen Ann Jebulan Vargas100% (1)
- IEEE Guide To The Assembly and Erection of Metal Transmission Structures PDFDocumento44 pagineIEEE Guide To The Assembly and Erection of Metal Transmission Structures PDFjuanperezpintoNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Technology Formulations Hand BookDocumento10 pagineManufacturing Technology Formulations Hand BookAhmed HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Liquid ChromotographyDocumento29 pagineGas Liquid Chromotographyscicws1133Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Chromatography FinalDocumento91 pagineGas Chromatography Finalshruti shahNessuna valutazione finora
- InstrumentalDocumento23 pagineInstrumentalSuraj KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Analytical SeparationDocumento75 pagineIntroduction To Analytical SeparationVincentius EkyNessuna valutazione finora
- InTech Stationary PhasesDocumento25 pagineInTech Stationary PhasesqncargbNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento38 pagineGas ChromatographyManoj SigdelNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento50 pagineGas ChromatographySuman GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento19 pagineGas ChromatographySeagal AsjaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento75 pagineGas Chromatographyshruti shahNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern ChromatographyDocumento23 pagineModern ChromatographySomnath Banerjee100% (1)
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento31 pagineGas ChromatographyNadia AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Theory of HPLC IntroductionDocumento16 pagine1 Theory of HPLC IntroductionaugustoxavierNessuna valutazione finora
- Theory and Instrumentation of GC IntroductionDocumento13 pagineTheory and Instrumentation of GC Introductionaugur886Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4 - Gas ChromatographyDocumento49 pagine4 - Gas Chromatographyamany mohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognosy Lab PresentationDocumento16 pagineCognosy Lab PresentationAhsham AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Food PresentationDocumento18 pagineFood PresentationEducationNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Chromatography - A Brief Review: July 2018Documento8 pagineGas Chromatography - A Brief Review: July 2018hàNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 - GC Dan HPLCDocumento33 pagine5 - GC Dan HPLCDewi AnjaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromatographic MethodsDocumento32 pagineChromatographic MethodsFawziyyah AgboolaNessuna valutazione finora
- P1W4 ChromatographyDocumento27 pagineP1W4 ChromatographyJoshua Richard Jr Tubiano PayopaninNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento11 pagineGas Chromatographysumit sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- HPLC PowerpointDocumento33 pagineHPLC PowerpointSunshine BaclaanNessuna valutazione finora
- High Performance Liquid Chromatography: Chem. 333Documento73 pagineHigh Performance Liquid Chromatography: Chem. 333Ahmed Al-syaniNessuna valutazione finora
- General Description of ChromatographyDocumento5 pagineGeneral Description of ChromatographySrima DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento22 pagineGas ChromatographyYoussef AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Chromatography: Presented by Supriyono, M.SiDocumento53 pagineGas Chromatography: Presented by Supriyono, M.SisiraitrumiNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Examination Question Solve For ChromatogrphyDocumento44 pagineFinal Examination Question Solve For ChromatogrphyMunna IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4, Instrumental Methods of Analysis, B Pharmacy 7th Sem, Carewell PharmaDocumento27 pagineUnit 4, Instrumental Methods of Analysis, B Pharmacy 7th Sem, Carewell Pharmaayush pathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 27 Gas ChromatographyDocumento37 pagineChapter 27 Gas Chromatographysenthilkumar99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gas ChromatographyDocumento8 pagineGas ChromatographyGunner StonerNessuna valutazione finora
- GC Connections: A Compendium of GC Terms and TechniquesDocumento5 pagineGC Connections: A Compendium of GC Terms and TechniquesClaudia GarcíaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Differences Between HPLC GCDocumento1 paginaThe Differences Between HPLC GCSh_PharmacyNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V-3-CromatographyDocumento39 pagineUnit V-3-CromatographyharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Original Paper Fast HPLC Method For The Determination of Glimepiride, Glibenclamide, and Related Substances Using Monolithic Column and Flow ProgramDocumento7 pagineOriginal Paper Fast HPLC Method For The Determination of Glimepiride, Glibenclamide, and Related Substances Using Monolithic Column and Flow ProgramAdelia DinayantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Zulfadli Kromatografi PDFDocumento6 pagineZulfadli Kromatografi PDFLilis TasniaNessuna valutazione finora
- HPLC Analysis FinallllllDocumento104 pagineHPLC Analysis Finallllll7204710911Nessuna valutazione finora
- How Does Gas Chromatography Work?Documento1 paginaHow Does Gas Chromatography Work?Vijay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 Theory and Instrumentation of GC IntroductionDocumento11 pagine01 Theory and Instrumentation of GC IntroductioniperettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Metoda Pengukuran Dan Analisis Proses Agroindustri: ChromatographyDocumento68 pagineMetoda Pengukuran Dan Analisis Proses Agroindustri: ChromatographyREJA PUTRA SIRINGORINGONessuna valutazione finora
- CHE 221 - Gas and Column ChromatographyDocumento10 pagineCHE 221 - Gas and Column ChromatographyCandy PearlNessuna valutazione finora
- LakshmiDocumento27 pagineLakshmiRachamalla KrishnareddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Chromatograhy (G.C) : Schematic Diagram For Gas ChromatographyDocumento10 pagineGas Chromatograhy (G.C) : Schematic Diagram For Gas ChromatographySunday IstifanusNessuna valutazione finora
- Curs HPLCDocumento130 pagineCurs HPLCPishta BmcNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromatography: by DR Nur Zazarina RamlyDocumento103 pagineChromatography: by DR Nur Zazarina RamlyBakalJenazahNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix III D. Liquid Chromatography - BP 2014Documento7 pagineAppendix III D. Liquid Chromatography - BP 2014NhonPhanThanhNessuna valutazione finora
- GC DNSDocumento23 pagineGC DNSNasima akterNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 27 Gas ChromatographyDocumento37 pagineChapter 27 Gas Chromatographyginga716Nessuna valutazione finora
- Liquid ChromatographyDocumento24 pagineLiquid ChromatographyDr. M. Prasad NaiduNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 Chromatography (GC & HPLC)Documento46 pagineL4 Chromatography (GC & HPLC)htsszetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Notes: The GC ColumnDocumento16 pagineStudy Notes: The GC ColumnLaxmi Kant PrasadNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Liquid Chromatography (GLC)Documento10 pagineGas Liquid Chromatography (GLC)Gopinathan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 12 GC and SFCDocumento38 pagineTopic 12 GC and SFCNurshuhada NordinNessuna valutazione finora
- Org Chem Hoffman 2Documento46 pagineOrg Chem Hoffman 2susantaNessuna valutazione finora
- Supercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) : by Karey O'LearyDocumento7 pagineSupercritical Fluid Chromatography (SFC) : by Karey O'LearybjpkNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas Chromatography - Chemistry LibreTextsDocumento22 pagineGas Chromatography - Chemistry LibreTextsMohammad NadimNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Gas ChromatographyDocumento17 paginePrinciples of Gas ChromatographyAtef LasheenNessuna valutazione finora
- IMA Unit 4Documento30 pagineIMA Unit 4vinushakaveripakam26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V-2-CromatographyDocumento40 pagineUnit V-2-CromatographyharshiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Well Production Performance Analysis for Shale Gas ReservoirsDa EverandWell Production Performance Analysis for Shale Gas ReservoirsNessuna valutazione finora
- For Life Science Students by Sachin Narwadiya Scientist Vigyan PrasarDocumento62 pagineFor Life Science Students by Sachin Narwadiya Scientist Vigyan PrasarsnarwadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Graphs Using Microsoft Word: Chart OptionsDocumento2 pagineCreating Graphs Using Microsoft Word: Chart OptionssnarwadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Curriculum - Vitae: Dr. Keertisheel N. SahareDocumento5 pagineCurriculum - Vitae: Dr. Keertisheel N. SaharesnarwadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Map To NimhDocumento1 paginaMap To NimhsnarwadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Surya JalDocumento1 paginaSurya JalsnarwadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholesterol-An IntroductionDocumento1 paginaCholesterol-An IntroductionsnarwadiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Yogasana and Health (A)Documento27 pagineYogasana and Health (A)snarwadiya100% (2)
- Xylazine HydrochlorideDocumento1 paginaXylazine HydrochlorideKasidit SornchaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 6 PREPARE ELECTRICAL POWER TOOLSDocumento22 pagineModule 6 PREPARE ELECTRICAL POWER TOOLSOtep CamaroteNessuna valutazione finora
- C592 13Documento9 pagineC592 13Ichwan Ciptadi100% (1)
- Método EPA 3010ADocumento5 pagineMétodo EPA 3010APaulina Armella RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Left Hand Console: Electrical System 313 and 313 GC ExcavatorDocumento6 pagineLeft Hand Console: Electrical System 313 and 313 GC ExcavatorHenry Sergio HuayhuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Distribution System Specifications: St. Charles County Public Water Supply District NO. 2Documento45 pagineWater Distribution System Specifications: St. Charles County Public Water Supply District NO. 2muhammad iqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Danfoss - Compressor Case StudiesDocumento5 pagineDanfoss - Compressor Case Studiesgpax42Nessuna valutazione finora
- Service ManUal - Error CodesDocumento13 pagineService ManUal - Error CodesStefanoViganóNessuna valutazione finora
- Paint Coverage ConsumptionDocumento2 paginePaint Coverage ConsumptionSahilNessuna valutazione finora
- Magnum Composite Plug Catalog 06-30-10Documento21 pagineMagnum Composite Plug Catalog 06-30-10Emad JamshidiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydronic Cooling - OikosDocumento5 pagineHydronic Cooling - OikosShashank JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Rigid Electrical Steel ConduitDocumento2 pagineRigid Electrical Steel ConduitBuckNessuna valutazione finora
- Zelio Time Re8ta21buDocumento2 pagineZelio Time Re8ta21buJonathan Meza FlorNessuna valutazione finora
- Iso 2528Documento8 pagineIso 2528nisa nurhidayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Cs of Dust Control InformationalDocumento5 pagine4 Cs of Dust Control Informationalabu_shofiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dream HouseDocumento14 pagineDream Housepreciousz.angel09Nessuna valutazione finora
- GlazingDocumento81 pagineGlazingAnjalySinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fan Coil Unit: TCR TCRQ TFM TC TKM TFRDocumento20 pagineFan Coil Unit: TCR TCRQ TFM TC TKM TFRydsNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm21 1510Documento18 pagineAstm21 1510Robert ChenNessuna valutazione finora
- Honeywell Sensing Px3 SeriesDocumento7 pagineHoneywell Sensing Px3 SeriesNicolas SirtakysNessuna valutazione finora
- Stress Strain ModelDocumento3 pagineStress Strain ModelKtk ZadNessuna valutazione finora
- Om The Laboratory To Ton Scale in Continuous FlowDocumento3 pagineOm The Laboratory To Ton Scale in Continuous FlowAaron Troy SmallNessuna valutazione finora
- Owner's Manual: Downloaded From Manuals Search EngineDocumento12 pagineOwner's Manual: Downloaded From Manuals Search EnginegragrNessuna valutazione finora
- Plazmax Servicio PDFDocumento109 paginePlazmax Servicio PDFLeonel Losada Cardozo0% (1)
- Precommissioning ChecklistDocumento2 paginePrecommissioning ChecklistPankaj PandeyNessuna valutazione finora
- 12d20105a Experimental Stress AnalysisDocumento1 pagina12d20105a Experimental Stress AnalysissubbuNessuna valutazione finora