Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Safety Factor
Caricato da
Anonymous mcFvPwzXTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Safety Factor
Caricato da
Anonymous mcFvPwzXCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Factor of Safety (Safety Factor)
Eg: If a component needs to withstand a load of 100 N and a FoS of 3 is selected then it is designed with strength to support 300 N.
Is used to provide a design margin over the theoretical design
capacity to allow for uncertainty in the design process. In the calculations, Material strengths, Manufacturing process
Strength of the component (Max load) FoS Load on the component (Actual load)
Factor of Safety (Safety Factor)
FoS (Based on Application Material properties known in detail Operating conditions known in detail Load and the resulting stresses and strains are known to a high degree of accuracy Low weight is important For less tried materials or Brittle materials under average conditions of environment, load and stress For untried materials under average conditions of environment, load and stress Better known materials under uncertain environment or uncertain stresses
yeild strength)
1.25 1.5
23
34
Above FoS should consider fatigue strength, Impact shock forces, Vibration, Brittle materials
Factor of Safety (Safety Factor)
Strength of the component ( Su,Sy ) FoS Stress in the component due to the actual load
Factor of Safety (Safety Factor)
How critical that component is The cost factor (cost of material, manufacture)
Whether failure could cause serious injury or death (a steam boiler or pressure vessel would use 8 10 FoS)
Unknown stresses in the manufacturing process (casting would use 10 14 FoS) Environmental conditions (used in harsh environment or not) Knowledge of the environment Knowledge of the properties of the material used Knowledge of the loads (tension, compressive, shear, bending, cyclic loads, impact loads etc) Weight factor (aerospace 1.5 3 to reduce weight but strict quality control) Quality control, maintenance
Potrebbero piacerti anche
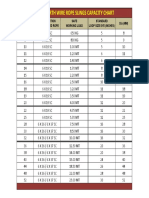
- Wellworth Wire Rope Slings CapacityDocumento1 paginaWellworth Wire Rope Slings CapacityMehul Paghdal0% (1)
- Sling AnglesDocumento1 paginaSling AnglesyogihardNessuna valutazione finora
- Rci BS 7262Documento3 pagineRci BS 7262Rizwan AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Check Soil Bearing CapacityDocumento4 pagineCheck Soil Bearing CapacityKelvin LauNessuna valutazione finora
- Defination of Rigging TermsDocumento3 pagineDefination of Rigging TermsGoliBharggavNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Plan Site InspectionDocumento4 pagineLifting Plan Site Inspectionkhaled redaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Pressure Vessel with 2 Main Cranes and 1 Tail CraneDocumento12 pagineLifting Pressure Vessel with 2 Main Cranes and 1 Tail Cranezeusvares100% (1)
- Cranes Hoisting and RiggingDocumento25 pagineCranes Hoisting and Riggingkanakarao1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Complex Lift Plan and ChecklistDocumento3 pagineComplex Lift Plan and Checklistsudeesh kumar100% (1)
- 5220 Wind Load Example Calc PDFDocumento1 pagina5220 Wind Load Example Calc PDFAhmed TrabelsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh LIfting Plan #1Documento5 pagineContoh LIfting Plan #1KevinNessuna valutazione finora
- Conveyor Belt EquationsDocumento6 pagineConveyor Belt EquationsWaris La Joi WakatobiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Supervision EssentialsDocumento28 pagineLifting Supervision EssentialsYahya YusufzayNessuna valutazione finora
- Marine LiftingDocumento17 pagineMarine LiftingMarian LazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Safety Considerations When Lifting With Two or More CranesDocumento9 pagineSafety Considerations When Lifting With Two or More CranesKyaw Kyaw AungNessuna valutazione finora
- Hoist and Jib Crane Safety InspectionDocumento3 pagineHoist and Jib Crane Safety InspectionSamsung Joseph0% (1)
- UCO Standard Crane ProceduresDocumento10 pagineUCO Standard Crane ProceduresMonica Colin100% (1)
- Dasar Dasar LOP PDFDocumento45 pagineDasar Dasar LOP PDFMuhamad Syarifudin100% (1)
- Lifting Device Used in ConstructionDocumento18 pagineLifting Device Used in ConstructionAr Deyvanai Kannan100% (1)
- Crane SafetyDocumento11 pagineCrane SafetyBill BilcarsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Crosby ShackleDocumento1 paginaCrosby ShacklevrandyNessuna valutazione finora
- February 2012 Wire Rope ExchangeDocumento80 pagineFebruary 2012 Wire Rope ExchangeWire Rope ExchangeNessuna valutazione finora
- LIFTING AND MOBILE EQUIPMENT AWARENESSDocumento100 pagineLIFTING AND MOBILE EQUIPMENT AWARENESSPhilip AdewunmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Rated Load Chart 50 Ton Tr-500xl-3Documento8 pagineRated Load Chart 50 Ton Tr-500xl-3george israelNessuna valutazione finora
- Safe Rigging PracticeDocumento81 pagineSafe Rigging PracticeAlvinSuparmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Lifting Plan ChecklistDocumento1 paginaBasic Lifting Plan ChecklistParashuram PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting PlanDocumento9 pagineLifting Plansatyabrath dhalNessuna valutazione finora
- Bagian Bagian CraneDocumento29 pagineBagian Bagian Cranerois67% (3)
- Crane Safety: Factors Reducing Lifting Capacity Below Rated ValuesDocumento1 paginaCrane Safety: Factors Reducing Lifting Capacity Below Rated ValuesvishnuNessuna valutazione finora
- GONDOLADocumento26 pagineGONDOLAMarvanNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of A Counterbalance Forklift Based On A Predictive Anti-Tip-Over ControllerDocumento16 pagineDesign of A Counterbalance Forklift Based On A Predictive Anti-Tip-Over ControllerHo Van RoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Slings SWLDocumento8 pagineSlings SWLEhsan YarmohammadiNessuna valutazione finora
- TÜV Rheinland Arabia Services CalendarDocumento1 paginaTÜV Rheinland Arabia Services Calendarshoaib2scribedNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 14 - Crane & HoistsDocumento11 paginePart 14 - Crane & HoistsrickymmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting Equipment InspectionDocumento113 pagineLifting Equipment Inspectionmac1677Nessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Safety of Lifting ProcedureDocumento83 pagineIndustrial Safety of Lifting Proceduresaravanan_c1Nessuna valutazione finora
- H Beams in Accordance With JISDocumento3 pagineH Beams in Accordance With JISaselabollegalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lifting and Rigging Training Session 1 - 2021 01 22Documento25 pagineLifting and Rigging Training Session 1 - 2021 01 22ELMLEMROZINessuna valutazione finora
- G18-2-LP-003 DG - Lifting PlanDocumento25 pagineG18-2-LP-003 DG - Lifting PlanMohammed JassimNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculation Rigging PlanDocumento1 paginaCalculation Rigging PlancahyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tower Crane Installation Spread Footing DesignDocumento1 paginaTower Crane Installation Spread Footing Designdanilolbg2903Nessuna valutazione finora
- PPL-PVS-023 - Rev1 - Barge Calculation During Transportation On SeaDocumento80 paginePPL-PVS-023 - Rev1 - Barge Calculation During Transportation On SeaThanh Anh MaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Pdfsam - JSN-20-008-LOP-WPS3-OS-001 Rev 00Documento1 pagina1 - Pdfsam - JSN-20-008-LOP-WPS3-OS-001 Rev 00ibnu rizalNessuna valutazione finora
- TaiLing by Duo CraneDocumento9 pagineTaiLing by Duo CraneHaGun Gunawan100% (1)
- Rigging Safety Training ProgramDocumento35 pagineRigging Safety Training ProgramMadhan MNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Steel Structures.1-10Documento10 pagineDesign of Steel Structures.1-10Rajeev BujjiNessuna valutazione finora
- Failure Theories Iii: Factor of Safety (Fos) Numerical Exercises (Fos + Failure Theories)Documento26 pagineFailure Theories Iii: Factor of Safety (Fos) Numerical Exercises (Fos + Failure Theories)محمد عادل خٹکNessuna valutazione finora
- Factor of SafetyDocumento3 pagineFactor of SafetykalvinnunagNessuna valutazione finora
- Factor of SafetyDocumento4 pagineFactor of SafetyAdityaraj Singh ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Nts On FOSDocumento11 pagineBasic Nts On FOSShyam Prasad K SNessuna valutazione finora
- Factor of Safety: Technological Studies Support Materials: Structures and Materials (Higher) Outcome 4Documento10 pagineFactor of Safety: Technological Studies Support Materials: Structures and Materials (Higher) Outcome 4ganeshrams88Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2E4: Solids & Structures: Dr. Bidisha Ghosh Notes: Lids & StructuresDocumento25 pagine2E4: Solids & Structures: Dr. Bidisha Ghosh Notes: Lids & StructuresMarco Ruiz CastronuevoNessuna valutazione finora
- Is There Any Difference Between Allowable Stress and Yield Strength?Documento1 paginaIs There Any Difference Between Allowable Stress and Yield Strength?christianutnNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Stress Yield Stress Ultimate Stress and Factor of SafetyDocumento1 paginaWorking Stress Yield Stress Ultimate Stress and Factor of SafetyNaveen HlNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview of Mechanical TestingDocumento39 pagineOverview of Mechanical TestingRobinson PrabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Anderson PDFDocumento7 pagineAnderson PDFChristian MavarezNessuna valutazione finora
- STEEL STRUCTURES: Safety, Economy, Aesthetics & SustainabilityDocumento78 pagineSTEEL STRUCTURES: Safety, Economy, Aesthetics & SustainabilityChowdhury PriodeepNessuna valutazione finora
- Negative Stress Margins - Are They RealDocumento31 pagineNegative Stress Margins - Are They Realchetan_thakur4278Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reliability of Engineering MaterialsDa EverandReliability of Engineering MaterialsAlrick L SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated TemperaturesDa EverandExperiment and Calculation of Reinforced Concrete at Elevated TemperaturesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Water EngineerDocumento5 pagineWater EngineerAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Work StudyDocumento21 pagineWork StudysivainamduguNessuna valutazione finora
- AmepDocumento4 pagineAmepAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical EngineeringDocumento5 pagineMechanical EngineeringAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Advanced Engineering Materials and ProcessingDocumento1 paginaAdvanced Engineering Materials and ProcessingAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Smart SensorsDocumento3 pagineSmart SensorsAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing 05 63xxDocumento97 pagineComputer Integrated Manufacturing 05 63xxAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 14: Intelligent Sensor Systems: Compensation Computation Communications IntegrationDocumento15 pagineLecture 14: Intelligent Sensor Systems: Compensation Computation Communications IntegrationAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing 05 63xxDocumento97 pagineComputer Integrated Manufacturing 05 63xxAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- SIFLDocumento42 pagineSIFLAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- BBC News - 'Smart Skin' Hope For Touch SensorDocumento2 pagineBBC News - 'Smart Skin' Hope For Touch SensorAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Perspective ProjectionDocumento10 paginePerspective ProjectionAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Dupont Smart SenSmart - SensorDocumento7 pagineDupont Smart SenSmart - SensorAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- SensorDocumento6 pagineSensorAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- SensorDocumento6 pagineSensorAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora
- Dupont Smart SenSmart - SensorDocumento7 pagineDupont Smart SenSmart - SensorAnonymous mcFvPwzXNessuna valutazione finora