Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Revision Exercise On Structures & Properties: S3 Chemistry
Caricato da
simonlee2007Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Revision Exercise On Structures & Properties: S3 Chemistry
Caricato da
simonlee2007Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Revision Exercise on Structures & Properties
S3 Chemistry
What is the bonding structure of the compound/element formed by : a) Sodium Atoms
1.
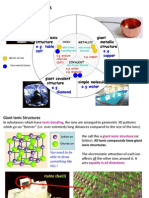
Giant Metallic Structure (Metal Metal)
b) c)
Chlorine and Potassium
Giant Ionic Structure (Metal Non-metal)
Simple Molecular Structure
(Non-metal Non-metal) Van der Waals Attraction between molecules
Carbon and Oxygen
d)
Bonding Structure
Giant Covalent Structure
Carbon (in form of diamond)
(Non-metal Non-metal)
Structure
Giant Ionic Structure Metal and Nonmetal
Giant Metallic Structure Metal and Metal
Giant Covalent Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Simple Molecular Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Attraction between
Bonding Structure Comparison
2.
Map the compound/element to their melting point & boiling point.
3550 oC /4827 oC 98oC/883oC - 78 oC / - 57 oC
Strong bond / Giant metallic structure
Strong bond / Giant ionic structure
Sodium Potassium chloride Carbon Dioxide
Weak Van Der Waals Attraction
Diamond
770 oC /1420 oC
Strong bond / Giant covalent structure
Melting point / Boiling point
Structure
Giant Ionic Structure Metal and Nonmetal
Giant Metallic Structure Metal and Metal
Giant Covalent Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Simple Molecular Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Attraction between
Attraction
Strong Metallic Bond Strong Ionic Bond between the between the ions positive ions and mobile electrons High High
Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms
Intramolecular Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms. Intermolecular Weak Van Der Waals Attraction between the molecules. Low
Melting point/ boiling point
Very High
Melting point / Boiling point Comparison
3.
What are the states of the following substances ? Sodium
(Solid) (Solid) (Gas) (Solid)
Potassium Chloride
Carbon Dioxide
Diamond
State
Structure
Giant Ionic Structure Metal and Nonmetal
Giant Metallic Structure Metal and Metal
Giant Covalent Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Simple Molecular Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Attraction between
Attraction
Strong Metallic Bond Strong Ionic Bond between the between the ions positive ions and mobile electrons High Solid High Solid
Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms
Intramolecular Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms. Intermolecular Weak Van Der Waals Attraction between the molecules. Low Gas/Liquid
Melting point/ boiling point State at room temperature and pressure
Very High Solid
State Comparison
4.
Estimate the electrical conductivity of the following substance
Sodium Potassium Chloride
Solid / Liquid
Good / Poor Good / Poor ( Molten ) Good / Poor ( Any ) Good / Poor ( Any )
Because it has mobile electrons
Because it has mobile ions
Because it is a gas
Carbon Dioxide
Diamond
Because it doesnt have mobile eletrons/ions
Electrical Conductivity
Structure
Giant Ionic Structure Metal and Nonmetal
Giant Metallic Structure Metal and Metal
Giant Covalent Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Simple Molecular Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Attraction between
Attraction
Strong Metallic Bond Strong Ionic Bond between the between the ions positive ions and mobile electrons High Solid Good in molten state Because it has mobile ions High Solid
Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms
Intramolecular Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms. Intermolecular Weak Van Der Waals Attraction between the molecules. Low Gas/Liquid Poor Because it doesnt have mobile ions/electrons
Melting point/ boiling point State at room temperature and pressure
Very High Solid
Electrical Conductivity
Good in Solid or Poor Liquid Because it doesnt Because it has have mobile mobile ions/electrons electrons Except graphite
Conductivity Comparison
5.
What are the solubility of the following substances ? Sodium
(Insoluble)
Potassium Chloride (Soluble)
Carbon Dioxide
(Insoluble) (Insoluble)
Diamond
Solubility
Structure
Giant Ionic Structure Metal and Nonmetal
Giant Metallic Structure Metal and Metal
Giant Covalent Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Simple Molecular Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Attraction between
Attraction
Strong Metallic Bond Strong Ionic Bond between the between the ions positive ions and mobile electrons
Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms
Intramolecular Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms. Intermolecular Weak Van Der Waals Attraction between the molecules.
Melting point/ boiling point State at room temperature and pressure
High
Solid Good in molten state Because it has mobile ions Soluble
High
Solid
Very High
Solid
Low
Gas/Liquid Poor Because it doesnt have mobile ions/electrons Insoluble
Electrical Conductivity
Solubility
Good in Solid or Poor Liquid Because it doesnt Because it has have mobile mobile ions/electrons electrons Except graphite Insoluble Insoluble
Solubility Comparison
Substance
Melting point (oC)
Boiling point (oC)
Electrical Conductivity Solid state Molten state
Solubility
A
B C D
a)
130
690 1470 -99
450
1790 3420 -25
Good
Poor Poor Poor
Good
Good Poor Poor
Insoluble
Soluble Insoluble Insoluble
What is the bonding structure of A ? Explain. Giant Metallic Structure. Good Electrical Conductivity in Solid/Molten b) What is the bonding structure of B ? Explain. Giant Ionic Structure. Good Conductivity in Molten & Soluble c) What is the bonding structure of C ? Explain. Giant Covalent Structure. Poor Conductivity, Insoluble & high m.p./b.p. d) What is the bonding structure of D ? Explain. Simple Molecular Structure. Low m.p./b.p., poor conductivity & insoluble
Integrated Question (Predict Structure)
Element
W
Carbon
X
Florine
Y
Neon
Z
Sodium
Atomic number
a) b)
2,4
9
2,7
10
2,8
11
2,8,1
c)
Predict the state of each elements. Two compounds, one is formed by W and X and another is formed by X and Z. Which one will soluble in water ? Explain it in details. ZX. Ionic Compound By considering all the substances above including the compounds in (b), W. Z is soft, X and Y are gases
Which Which Which Which one is the most hardness? Why? one is not reactive? Why? Y . Octet structure, noble gas one is toxic? Why? X. Group 7 are toxic. of them can conduct electricity? Why?
Integrated Question (Predict Properties)
Z, it is metal and ZX conduct in molten state
MgO, SiO2, SO2 are oxides of Period 3 elements in the Periodic Table. Discuss how the melting points of these oxides are related to their bonding and structure.
SO2 MgO SiO2 Non-metal, Non-metal Metal ,Non-metal Non-metal, Non-metal Covalent Bond Ionic Bond Covalent Bond Giant ionic structure Giant covalent structure Van der Waals Attraction Simple molecular structure
Essay Type Question
SiO2>MgO>SO2
Structure
Giant Ionic Structure Metal and Nonmetal
Giant Metallic Structure Metal and Metal
Giant Covalent Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Simple Molecular Structure Nonmetal and Nonmetal
Attraction between
Attraction
Strong Metallic Bond Strong Ionic Bond between the between the ions positive ions and mobile electrons High Solid Good in molten state Because it has mobile ions Soluble High Solid
Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms
Intramolecular Strong Covalent Bond between the atoms. Intermolecular Weak Van Der Waals Attraction between the molecules. Low Gas/Liquid Poor Because it doesnt have mobile ions/electrons Insoluble
Melting point/ boiling point State at room temperature and pressure
Very High Solid
Electrical Conductivity
Good in Solid or Poor Liquid Because it doesnt Because it has have mobile mobile ions/electrons electrons Except graphite Insoluble Insoluble
Solubility
Summary
The End
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Da EverandChemical Bonding: Understanding The Forces that Hold Molecules Together.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic and Covalent Bonds ExplainedDocumento17 pagineIonic and Covalent Bonds ExplainedMahi QuaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 10.2 The Solid StateDocumento14 pagineLesson 10.2 The Solid StatefitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesDocumento3 pagineSummary of Bonding, Structure and Properties of SubstancesAnonymous L7ZuSkR100% (1)
- Unit 3 - Chemical BondingDocumento58 pagineUnit 3 - Chemical BondingTrang Vũ Thị BằngNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic and Covalent BondingDocumento39 pagineIonic and Covalent Bondingchickuwa pawawawaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondingDocumento50 pagineChemical BondingLeila BonNessuna valutazione finora
- CSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingDocumento10 pagineCSEC Chemistry - Structure and BondingCornflakes ToastedNessuna valutazione finora
- Describe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent CompoundsDocumento6 pagineDescribe The Differences in Volatility, Solubility and Electrical Conductivity Between Ionic and Covalent Compoundsmadhuri pawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Documento11 pagineCh3 - Chemical Bonding (IGCSE Study Notes)Amal HassanNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements, Compounds and AtomsDocumento12 pagineElements, Compounds and Atomsananya.arumugarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 2unDocumento5 pagineChem 2unMerey ZiyabekNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding NotesDocumento6 pagineChemical Bonding NotesAyesha Awan100% (1)
- 4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondDocumento71 pagine4 Lewis Dot Structure and Types of BondEren Micaella100% (1)
- Giant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond NotesDocumento8 pagineGiant Covalent Bond and Metallic Bond Notesnihan.8558Nessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Thhourlab 9 BakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderDocumento5 pagine8 Thhourlab 9 Bakerbrunatikallalkaneoberlanderapi-297169088Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anglo-Chinese School Structure of MatterDocumento12 pagineAnglo-Chinese School Structure of Matterいい子Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Covalent and Metallic BondingDocumento8 pagineNotes On Covalent and Metallic Bondingselma samadNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Chem Bonding NotesDocumento9 pagineRevision Chem Bonding Notesrania samirNessuna valutazione finora
- STRUCTURE AND BONDING PowerPoint For Fourth Form.Documento54 pagineSTRUCTURE AND BONDING PowerPoint For Fourth Form.tsteadmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure: Physical Properties Ionic Comp Covalent Compound Metal Iodine Diamond GraphiteDocumento2 pagineStructure: Physical Properties Ionic Comp Covalent Compound Metal Iodine Diamond GraphiteAnonymous ATvkkrtr2yNessuna valutazione finora
- 2023 SCHB021 Notes Coordination ChemistryDocumento89 pagine2023 SCHB021 Notes Coordination ChemistryEvans EvansNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocumento6 pagineChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Chemical BondingDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To Chemical BondingMini PGNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionic BondingDocumento30 pagineIonic BondinghidhhsdfhgidsufgNessuna valutazione finora
- Atoms CombiningDocumento12 pagineAtoms Combiningshehryar khanNessuna valutazione finora
- IGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesDocumento16 pagineIGCSE Chemistry - Structure of SubstancesChemistryKlipz100% (6)
- C2: Structure, Bonding and The Properties of Matter: Key ConceptsDocumento9 pagineC2: Structure, Bonding and The Properties of Matter: Key ConceptsMrs S Baker100% (1)
- ch-3,chemDocumento6 paginech-3,chemAbdullah SalmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Che 142 Chapter1 1.2, 1.3, 1.4Documento52 pagineChe 142 Chapter1 1.2, 1.3, 1.4nur haslindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry - Chemical BondingDocumento3 pagineChemistry - Chemical BondingMegan TaylorNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment - 2Documento15 pagineAssignment - 2padhiyararpitaNessuna valutazione finora
- O Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical BondingDocumento16 pagineO Levels Cehimstry-Atomic Structure - Chemical Bondingjave_yeongNessuna valutazione finora
- Core Chem Bonding Intro PresDocumento43 pagineCore Chem Bonding Intro PresSHEILA MARIE CORTADO - UNDANNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondingDocumento11 pagineChemical BondingAsilah AsyiqinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding1Documento35 pagineChemical Bonding1drchewieNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and Bonding: Bonding: The Structure of MatterDocumento8 pagineStructure and Bonding: Bonding: The Structure of MatterAngeline NgouNessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding and Naming CompoundsDocumento10 pagineBonding and Naming CompoundsDaniel BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Ministry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDocumento3 pagineMinistry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDaniel DowdingNessuna valutazione finora
- Condensed Matter Physics Materials Science Greek Solid Long-Range Order Crystal Glass Glass Transition Gels Thin FilmsDocumento6 pagineCondensed Matter Physics Materials Science Greek Solid Long-Range Order Crystal Glass Glass Transition Gels Thin FilmsimnasNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Blocks of MatterDocumento18 pagineBuilding Blocks of MatterPaul AckermannNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsDocumento24 pagineLecture 02 Atomic Structure and Inter-Atomic Bonding BiomaterialsAbdallah ShaatNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and BondingDocumento12 pagineStructure and BondingNisha JodhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondsDocumento6 pagineChemical BondsARDIUZNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 2 Chemical Bonding PDFDocumento26 pagineCH 2 Chemical Bonding PDFTonald DrumpNessuna valutazione finora
- (L1) Carbon and Its Compounds Class10Documento22 pagine(L1) Carbon and Its Compounds Class10Rekha Mishra0% (1)
- Decreasing The Volume: Pressure IncreasesDocumento6 pagineDecreasing The Volume: Pressure IncreasesREZA FARDGHASSEMINessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bonding Board NotesDocumento19 pagineChemical Bonding Board NotesEmaan KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Formation and Types of Covalent BondsDocumento55 pagineFormation and Types of Covalent Bonds陈凯雯Nessuna valutazione finora
- MELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1Documento32 pagineMELC 7 Chemical Bonding 1A Dee YoungNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallic BondDocumento5 pagineMetallic BondDinak ConsultingNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingDocumento10 pagine02 Chem X Icse Summary Chemical BondingShreyash ThamkeNessuna valutazione finora
- Bonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Documento4 pagineBonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Mel Patricia M. CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic BondingDocumento19 pagineAtomic BondingSabir AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk and Surface Properties of BiomaterialsDocumento82 pagineBulk and Surface Properties of BiomaterialsZeynu KulizeynNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic BondingDocumento80 pagineAtomic BondingChan Chan M100% (1)
- PH 1203 NoteDocumento16 paginePH 1203 NoteTA MI MNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1.3 - BondingDocumento15 pagine3.1.3 - BondingaprildazzleNessuna valutazione finora
- C2 Knowledge PowerpointsDocumento33 pagineC2 Knowledge PowerpointsMrs S BakerNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 NotesDocumento8 pagine1 NotesillegiblecaptchaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 June C3 RWDocumento11 pagine12 June C3 RWsimonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- FP2 - June 2009 PaperDocumento28 pagineFP2 - June 2009 PaperchequillasNessuna valutazione finora
- 6666 01 Rms 20130307Documento29 pagine6666 01 Rms 20130307simonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6683 01 Rms 20050618Documento7 pagine6683 01 Rms 20050618Muneeb ArshadNessuna valutazione finora
- 6666 01 Rms 20130307Documento29 pagine6666 01 Rms 20130307simonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- S2 January 2012 Question PaperDocumento20 pagineS2 January 2012 Question PapergerikaalhuNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 June C3 RWDocumento11 pagine12 June C3 RWsimonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- D1 June 09 QPDocumento24 pagineD1 June 09 QPms94ukkNessuna valutazione finora
- FP2 - June 2009 PaperDocumento28 pagineFP2 - June 2009 PaperchequillasNessuna valutazione finora
- D1 June 09 QPDocumento24 pagineD1 June 09 QPms94ukkNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 June C3 RWDocumento11 pagine12 June C3 RWsimonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel GCE January 2010 Core Mathematics C2 QPDocumento24 pagineEdexcel GCE January 2010 Core Mathematics C2 QPgerikaalhu100% (1)
- 15 M1 June 2006Documento5 pagine15 M1 June 2006simonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 June C3 RWDocumento11 pagine12 June C3 RWsimonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- PP Bio EDocumento45 paginePP Bio E大利Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1MA0 2H Rms 20120823Documento28 pagine1MA0 2H Rms 20120823Ibrahim Eleas Sarah YaseenNessuna valutazione finora
- D1 June 09 QPDocumento24 pagineD1 June 09 QPms94ukkNessuna valutazione finora
- D1 June 09 QPDocumento24 pagineD1 June 09 QPms94ukkNessuna valutazione finora
- C4 June 2008Documento28 pagineC4 June 2008redkyungjinNessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel GCE: Core Mathematics C1Documento28 pagineEdexcel GCE: Core Mathematics C1Marianna IacovouNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 June C3 RWDocumento11 pagine12 June C3 RWsimonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- H Physics All 2011Documento24 pagineH Physics All 2011simonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2009 CIT Paper 1A With KeyDocumento12 pagine2009 CIT Paper 1A With Keysimonlee2007Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wheel Protector MSDSDocumento3 pagineWheel Protector MSDSgregorius DwijosaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramics Chap12Documento22 pagineCeramics Chap12Amar SheelwantNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry - Free Practice Exam PaperDocumento18 pagineChemistry - Free Practice Exam PaperAsia SimpsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan k13 HydrocarbonDocumento17 pagineLesson Plan k13 HydrocarbonRosyadi Minamoto IzzuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Mock Test 2Documento27 pagineMock Test 2SUBHASHRATHORENessuna valutazione finora
- Colour Identification of Gas Cylinders and Related Equipment Intended For Medical UseDocumento12 pagineColour Identification of Gas Cylinders and Related Equipment Intended For Medical UseIICT TrivandrumNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Fragrance ChemistryDocumento13 pagineBasic Fragrance ChemistryshishirchemNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Engineering Journal: Abdellah Ait El Fakir, Zakaria Anfar, Mohamed Enneiymy, Amane Jada, Noureddine El AlemDocumento12 pagineChemical Engineering Journal: Abdellah Ait El Fakir, Zakaria Anfar, Mohamed Enneiymy, Amane Jada, Noureddine El Alemsilambarasan kNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Scinece (MCQS)Documento36 pagineEnvironmental Scinece (MCQS)Fahad Areeb67% (6)
- Which Instrument Is Used To Tell DirectionDocumento12 pagineWhich Instrument Is Used To Tell DirectionLousy MoNessuna valutazione finora
- End Year 2010 Paper 1Documento18 pagineEnd Year 2010 Paper 1Ramanath RamNessuna valutazione finora
- NiFe2o4 On Carbon FibersDocumento8 pagineNiFe2o4 On Carbon Fibersmehmil kunwarNessuna valutazione finora
- WeldingDocumento4 pagineWeldingAnonymous LFgO4WbIDNessuna valutazione finora
- Tappi T413Documento4 pagineTappi T413Hansel OmarNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of Chemical Combinations: General Chemistry 1Documento59 pagineLaws of Chemical Combinations: General Chemistry 1Miaka LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocumento16 pagineCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary EducationAdam GhaliNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-2 Mineralogy: CrystallographyDocumento19 pagineUNIT-2 Mineralogy: CrystallographyKarnalPreethNessuna valutazione finora
- Biomedical Admissions Test 4500/02: Section 2 Scientific Knowledge and ApplicationsDocumento20 pagineBiomedical Admissions Test 4500/02: Section 2 Scientific Knowledge and ApplicationsPunPun Ranchana WorahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fishpond Site Evaluation and Management FactorsDocumento6 pagineFishpond Site Evaluation and Management FactorsSandy Gallego Sapong Jr.100% (1)
- IGNOU FST-01 Solved AssignmentsDocumento11 pagineIGNOU FST-01 Solved AssignmentsSUSMITA MONDALNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallography of A Common Carbon Steel Sample University of La Sabana 24/02/2020Documento4 pagineMetallography of A Common Carbon Steel Sample University of La Sabana 24/02/2020MarthaAlbaGuevaraNessuna valutazione finora
- FIITJEE ALL INDIA TEST SERIES PART TEST – I PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY AND MATHEMATICSDocumento20 pagineFIITJEE ALL INDIA TEST SERIES PART TEST – I PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY AND MATHEMATICSKratosNessuna valutazione finora
- Methanol Product SpecificationDocumento1 paginaMethanol Product SpecificationSohag MiahNessuna valutazione finora
- Skinner 2014Documento58 pagineSkinner 2014Kesya SaragihNessuna valutazione finora
- Naskah Soal Tes Persiapan Un 1 Bulan April 2016 Primagama Nagoya - Puri Kelas 9 SMP - Kode Soal: 90643 Mapel: Bahasa InggrisDocumento5 pagineNaskah Soal Tes Persiapan Un 1 Bulan April 2016 Primagama Nagoya - Puri Kelas 9 SMP - Kode Soal: 90643 Mapel: Bahasa InggrisHarum Dwi WahyuniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationDocumento20 pagineChemistry: Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary EducationVarun PanickerNessuna valutazione finora
- ADM and LG Chem To Develop Sustainable Technology For Superabsorbent PolymersDocumento2 pagineADM and LG Chem To Develop Sustainable Technology For Superabsorbent PolymersEng Hau QuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Designation of The Types of SteelsDocumento6 pagineDesignation of The Types of SteelsDavid FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- PrepASH ASTM D5142 Proximate AnalysisDocumento4 paginePrepASH ASTM D5142 Proximate AnalysisCH PurnimaRajeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Aa STPM Chemistry T1 2012Documento5 pagineAa STPM Chemistry T1 2012Chan KarlokNessuna valutazione finora