Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MBR Presentation
Caricato da
Thanneeru Naga RajuDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MBR Presentation
Caricato da
Thanneeru Naga RajuCopyright:
Formati disponibili
What is MBR ?
Combined Technology of Activated Sludge Process and Membrane Separation Process
Comparison with Conventional System
<Conventional System>
Influent
Screen GC
What is MBR?
Recycle
Primary Clarifier
Effluent Sedimentation SF UV
Deni
Nitri
RAS
Excess Sludge Effluent
<MBR System>
Influent Screen GC Fine Screen
Recycle
MLSS: 10000-15000ppm
Deni Excess Sludge
Nitri
MBR Enables High Quality Treated Water, 2 Smaller Footprint & Simple system
What is MBR?
Schematic Diagram of MBR
Coarse Screen Feed Pump Fine Screen
Membrane Unit
Blower
Grit Chamber Balancing Tank Denitrification Tank Nitrification Tank Disinfection Tank Sludge Storage Tank
What is MBR?
Comparison of Footprint
Attractive for limited land projects: Retrofits (increased capacity and/or stricter consent) Decentralised or Industrial
MBR
Conventional
5,600 m3/d, 0.7 ha
6,000 m3/d, 4.5 ha
4
Introduction of typical SMU
Membrane Cartridge
Chlorinated polyethylene Nozzle Micro Filtration Membrane Panel Pore size : 0.4m Spacer Membrane Sheet 0.5m1.0m 0.8m2/Cartridge
Micro scope
Introduction of typical SMU
Structure of typical SMU
Manifold Tube Membrane case Membrane cartridge Diffuser case
Diffuser
6
Features of Typical MBR
Simple system Less equipment Energy saving Easy operation Long Lifetime Worlds market leader
7
Features of typical MBR
Simple System Less Equipment Sodium Hypochlorite Dosing Tank
No backwash pump
No permeate pump
Membrane Unit
M
No chemical cleaning tank Simple piping design
Membrane tank
Blower
Permeate tank
Features of typical MBR
Simple System Gravity Filtration Filtration at low pressure is possible. (Typical pressure: 5 10 kPa)
Water Head
Small water head is applicable to collect permeate.
Suction pump is not required.
Typical gravity filtration
Features of typical MBR
Simple System In Situ Cleaning Cleaning Timing
Periodically36 month Increase of Trans-membrane Pressure (TMP)
Clean membranes in aeration tanks !
Chemical Dosing Tank
Chemical
for organic fouling Oxalic acid1.0% for inorganic fouling
Sodium hypochlorite0.5%
M
Chemical Volume : 3L/cartridge Cleaning Duration
Pouring 5min.cleaning 60120min.
MBR Tank
Permeate Tank
10
Features of typical MBR
Energy Saving Membrane Aeration Aeration plays two roles for energy conservation !
1. Membrane Scouring Coarse bubble aeration under the membrane enables the membrane surface clean
2. Oxygen supply for biomass This air is also used to transfer the oxygen into the biomass
11
Upward airflow among membranes
Features of typical MBR
Long Lifetime
4% failure in 10 years!
% of Membranes Replaced
Age Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 # of Panel Used in Study 175796 152696 112221 79386 64486 35636 15386 4286 686 386 Failures Excluding Repairs 0 394 530 669 1388 33 55 20 0 0 Annual % Excluding Repairs 0 0.26 0.47 0.84 2.15 0.09 0.36 0.47 0 0 Cumulative % Excluding Repairs 0.00 0.26 0.73 1.57 3.73 3.82 4.18 4.64 4.64 4.64 Annual % Including Repairs 0.00 0.27 0.58 0.91 2.34 0.32 0.36 0.47 0.00 0.00 Cumulative % Including Repairs 0.00 0.27 0.85 1.76 4.10 4.42 4.78 5.25 5.25 5.25
12
Reference Plants
Design Parameters of
<Design flow rate> Peak 78,000m3/dFlux=0.80m3/m2/d
Ave. 55,000m3/dFlux=0.56m3/m2/d <Design water quality>
Influent BOD SS NH4-N NO3-N T-N F.colifoms Turbidity 312 228 35 50 Effluent 10 10 1 8 10 2.2 c/100mL 2NTU
13
Reference Plants
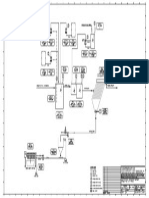
System Flow of STP
Fine Screen (1mm bar)
Coagulant Blower Sodium Hypochlorite
Permeate Reuse
RAS (2Q) Pump Station Equalizatio n Tank (4.6hrs) Anoxic Tank (3.0hrs) Aerobic Tank (3.0hrs)
Excess Sludge Membrane Unit
14
15
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Flat Plate Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) System TrainingDocumento56 pagineFlat Plate Membrane Bioreactor (MBR) System TrainingmarvilouNessuna valutazione finora
- Syngineering Water MBR Vs SBR PDFDocumento5 pagineSyngineering Water MBR Vs SBR PDFjaianit89Nessuna valutazione finora
- MBR Vs SBRDocumento2 pagineMBR Vs SBRSanjeev Kachhara100% (1)
- Membrane Bio ReactorsDocumento16 pagineMembrane Bio Reactorsvvrckumar100% (1)
- MBR Technologies: East Valley Water DistrictDocumento17 pagineMBR Technologies: East Valley Water Districtkaran198524Nessuna valutazione finora
- HeadworksBio (2) - Latest - Eg - Ro - 047543 PDFDocumento40 pagineHeadworksBio (2) - Latest - Eg - Ro - 047543 PDFrjohnson277100% (1)
- MBR-STP Design Features PDFDocumento7 pagineMBR-STP Design Features PDFManjunath HrmNessuna valutazione finora
- MBR Presentation LatestDocumento12 pagineMBR Presentation LatestRuchi GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBR Vs Othe STPsDocumento22 pagineMBBR Vs Othe STPsNeelam Sharma67% (3)
- MBRDocumento9 pagineMBRAuspicious MuthuNessuna valutazione finora
- MBR Design ConsiderationsDocumento16 pagineMBR Design ConsiderationsDhanraj BnNessuna valutazione finora
- Pptonfab MBBR 130616081952 Phpapp01Documento18 paginePptonfab MBBR 130616081952 Phpapp01TAREK ALMAHDY100% (3)
- Membrane BioreactorsDocumento20 pagineMembrane BioreactorsSharathBanakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 6 MBRDocumento37 pagineLec 6 MBRMohammad ShafiNessuna valutazione finora
- MBR-STP Design FeaturesDocumento7 pagineMBR-STP Design FeaturesManjunath Hrm0% (1)
- Next Generation of MBBR TechnologyDocumento48 pagineNext Generation of MBBR TechnologyLouay Mansour100% (1)
- Report of Membrane Bioreactor System (MBR) For Wastewater TreatmentDocumento10 pagineReport of Membrane Bioreactor System (MBR) For Wastewater TreatmentJulie MahadiNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBR MediaDocumento2 pagineMBBR MediaAseem Vivek Masih100% (2)
- Enviraj MBBR CalculatorDocumento3 pagineEnviraj MBBR Calculatorankur100% (2)
- Tech City-STP 100 KLD Price Comparison (03092016)Documento10 pagineTech City-STP 100 KLD Price Comparison (03092016)Preston VargheseNessuna valutazione finora
- ASP - Process Design CalculationDocumento21 pagineASP - Process Design Calculationvishu100% (1)
- MBBR Wastewater Treatment Basin Sizing and Aeration Calculations - S.I. UnitsDocumento30 pagineMBBR Wastewater Treatment Basin Sizing and Aeration Calculations - S.I. Unitsdiego83% (6)
- Tubular Sidestream (Cross Flow) MBR Applications For Industrial EffluentsDocumento6 pagineTubular Sidestream (Cross Flow) MBR Applications For Industrial EffluentsDileep C DileepNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBR Technical BreifDocumento12 pagineMBBR Technical Breifraghu kiran100% (1)
- Efficiency Comparison of Various Sewage Treatment Plants in BangaloreDocumento36 pagineEfficiency Comparison of Various Sewage Treatment Plants in BangalorePRETTY MARY100% (1)
- Hollow Fibre MBR - 30 MLDDocumento8 pagineHollow Fibre MBR - 30 MLDakshay salviNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Biological WWTP III - Membrane BioreactorDocumento26 pagine02 - Biological WWTP III - Membrane BioreactorAhmed100% (1)
- Biological Wastewater Treatment III - MBR Processes R1Documento26 pagineBiological Wastewater Treatment III - MBR Processes R1NUR ASYIQIN BINTI AZAHARNessuna valutazione finora
- STP AdequacyDocumento5 pagineSTP AdequacyenvsandyNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBRDocumento37 pagineMBBRLye Yp100% (2)
- Techno-Commercial Offer For 150 KLD STP, Based Upon MBBR.Documento9 pagineTechno-Commercial Offer For 150 KLD STP, Based Upon MBBR.Anshika RaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Techno-Commercial Offer 100 KLD TM Shiv Shakti Developers, Betul SiteDocumento9 pagineTechno-Commercial Offer 100 KLD TM Shiv Shakti Developers, Betul SiteTech MongerNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment of Seafood Processing Wastewater Using A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)Documento4 pagineTreatment of Seafood Processing Wastewater Using A Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)Dương Ánh100% (1)
- MBBR OM Manual-250Documento42 pagineMBBR OM Manual-250senthil2002100% (3)
- Chapter 1 Basic Design ConsiderationDocumento38 pagineChapter 1 Basic Design ConsiderationAce ThunderNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Sewage Treatment Plants CourseDocumento56 pagineDesign of Sewage Treatment Plants CourseChanel100% (1)
- Pratik's Final Report On MBRDocumento25 paginePratik's Final Report On MBRpratik100% (1)
- Operator - Book-StpDocumento113 pagineOperator - Book-StpAce Dynamics India100% (1)
- SEKO Solenoid Dosing Pumps Kompact SeriesDocumento3 pagineSEKO Solenoid Dosing Pumps Kompact SeriesmauiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Activated Sludge Calculations With Excel QuizDocumento2 pagineActivated Sludge Calculations With Excel Quiztrantrunghoa290784Nessuna valutazione finora
- SBR DesignDocumento14 pagineSBR DesignRanjan RahiNessuna valutazione finora
- Aqua Engineers-250 KLD MBR Membrane System Design Summary: Influent FlowsDocumento2 pagineAqua Engineers-250 KLD MBR Membrane System Design Summary: Influent FlowsNithin BharathiNessuna valutazione finora
- UASB-Process Design For Various Types of WastewatersDocumento21 pagineUASB-Process Design For Various Types of WastewatersapitbhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Techno-Commercial Offer 100 KLD TM Shiv Shakti Developers, Betul SiteDocumento9 pagineTechno-Commercial Offer 100 KLD TM Shiv Shakti Developers, Betul SiteTech MongerNessuna valutazione finora
- Effluent Treatment PlantDocumento16 pagineEffluent Treatment PlantVishal guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Role of Microorganisms in Waste Water Treatment FinalDocumento12 pagineRole of Microorganisms in Waste Water Treatment FinalAhmad AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBR TechnologyDocumento5 pagineMBBR Technologymsajidfcc100% (2)
- Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)Documento13 pagineMembrane Bioreactor (MBR)Hasriyani HafidNessuna valutazione finora
- SBR DesignDocumento7 pagineSBR DesignRANJINI02V88% (8)
- Membrane Filtration: Water and Wastewater Engineering (ECE4453) Group 1Documento30 pagineMembrane Filtration: Water and Wastewater Engineering (ECE4453) Group 1Asfand Yar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 KLD STP Upgreation PROPOSAL-GMCPLDocumento7 pagine20 KLD STP Upgreation PROPOSAL-GMCPLTech Monger100% (1)
- Grit RemovalDocumento42 pagineGrit RemovalChanel100% (1)
- Etp Manual STDDocumento49 pagineEtp Manual STDapi-2759629991% (33)
- Construction of STP - 350 KLD For CPMF - Part 1Documento9 pagineConstruction of STP - 350 KLD For CPMF - Part 1Praveen100% (2)
- Bi Water Membrane BrochureDocumento8 pagineBi Water Membrane BrochurebazediNessuna valutazione finora
- SBR DesignDocumento10 pagineSBR DesignQuốc TuyênNessuna valutazione finora
- 5m3d MBR Packaged STP 2017.3.28Documento13 pagine5m3d MBR Packaged STP 2017.3.28DevNessuna valutazione finora
- WASTEH20 MBR Process Design PDFDocumento23 pagineWASTEH20 MBR Process Design PDFDavid LambertNessuna valutazione finora
- Sewage Treatment WorksheetDocumento18 pagineSewage Treatment WorksheetRemedanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Handbook For Indian BusinessDocumento108 pagineA Handbook For Indian BusinessThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- MBBR SystemDocumento7 pagineMBBR SystemThanneeru Naga Raju100% (1)
- Good Cip SystemDocumento7 pagineGood Cip SystemThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For Assessment of Huygenic ConditionsDocumento13 pagineGuidelines For Assessment of Huygenic ConditionslanikhilNessuna valutazione finora
- Make Some OzoneDocumento7 pagineMake Some OzoneThanneru SakethNessuna valutazione finora
- How Does Ozone Technology WorkDocumento4 pagineHow Does Ozone Technology WorkThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Benefits of Ozone VsDocumento2 pagineBenefits of Ozone VsThanneeru Naga Raju100% (1)
- Electroplating Wastewater PDFDocumento1 paginaElectroplating Wastewater PDFThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lamella Clarifier / Lamella SeparatorDocumento1 paginaLamella Clarifier / Lamella SeparatorThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Calcaulation of ResinDocumento1 paginaCalcaulation of ResinThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Industry Document On Electroplating IndustriesDocumento92 pagineComprehensive Industry Document On Electroplating Industrieskaranahuja18Nessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Audit PDFDocumento8 pagineEnvironmental Audit PDFThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Sara Water & Waste Treatment BrochureDocumento2 pagineSara Water & Waste Treatment BrochureThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Electroplating IndustryDocumento5 pagineElectroplating IndustryRangasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ozone in Sea Food ProcessDocumento20 pagineOzone in Sea Food ProcessThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Inclined Plate Clarifier (Parallel Plate Clarifier, Lamella Clarifier) Basic Theory of OperationDocumento2 pagineInclined Plate Clarifier (Parallel Plate Clarifier, Lamella Clarifier) Basic Theory of OperationThanneeru Naga Raju100% (2)
- Flow Charts For PipesDocumento5 pagineFlow Charts For PipesThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Department OF Drinking Water SupplyDocumento11 pagineDepartment OF Drinking Water SupplyThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- BiomedicalDocumento28 pagineBiomedicalThanneeru Naga RajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Laminar Flow in ChannelsDocumento15 pagineLaminar Flow in ChannelsNeybilNessuna valutazione finora
- Boiler Internal & External TreatmentDocumento62 pagineBoiler Internal & External Treatmentmdnor100% (1)
- Welding Guides Lincoln ElectricDocumento49 pagineWelding Guides Lincoln Electricpkn_pnt9950Nessuna valutazione finora
- Exploring Liquids Unit TestDocumento6 pagineExploring Liquids Unit Testapi-265908930100% (1)
- Compressible Flow 12batchDocumento74 pagineCompressible Flow 12batchSirajul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER 2 - Pipe FlowDocumento45 pagineCHAPTER 2 - Pipe FlowLugisaniMushavhanamadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 4 - TurbomachineryDocumento77 pagineTopic 4 - TurbomachinerySati Ullah MaikashNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Treatment Plant: Case StudiesDocumento16 pagineWater Treatment Plant: Case Studieskesavaganesan58100% (2)
- PHL 500Documento4 paginePHL 500dharwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Tubing Performance Relation CurveDocumento1 paginaTubing Performance Relation CurveLeon ZidaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Matters Ch01 Textbk ANSDocumento3 pagineChemistry Matters Ch01 Textbk ANSZeneon85% (26)
- Data Sheet Filter Drier With Interchangeable Solid Core Type DCRDocumento8 pagineData Sheet Filter Drier With Interchangeable Solid Core Type DCRDima ArfNessuna valutazione finora
- Big Science Competition Practise Questions Years 7-12 Part 2Documento5 pagineBig Science Competition Practise Questions Years 7-12 Part 2Happy4314100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2-Water and Wastewater Analysis (Part 1)Documento50 pagineCHAPTER 2-Water and Wastewater Analysis (Part 1)محمد أمير لقمانNessuna valutazione finora
- Wikipedia Air CompositionDocumento11 pagineWikipedia Air CompositionAzrul NizamNessuna valutazione finora
- Schematic of A Wastewater Treatment PlantDocumento1 paginaSchematic of A Wastewater Treatment PlantAnindyolarasNessuna valutazione finora
- Orifice Plate For Flow MeasurementDocumento3 pagineOrifice Plate For Flow Measurementcinema bizarreNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitsubishi Service ManualDocumento220 pagineMitsubishi Service ManualJeff ChatreauNessuna valutazione finora
- 250lph RO QuoteDocumento9 pagine250lph RO QuotekarthikeyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecw331 Chapter 01 Final PDFDocumento31 pagineEcw331 Chapter 01 Final PDFMuhd MuqhreyNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics I CE-407: Basic Concepts, Properties of Fluid and Fluid StaticsDocumento26 pagineFluid Mechanics I CE-407: Basic Concepts, Properties of Fluid and Fluid Staticstaha zafarNessuna valutazione finora
- Report On Urea Production and Process AnalysisDocumento102 pagineReport On Urea Production and Process AnalysisSameer SaxenaNessuna valutazione finora
- P45-11041 Curve (Rev1) 20220325Documento2 pagineP45-11041 Curve (Rev1) 20220325Raksha KMNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Course - Process Gas DehydrationDocumento3 pagineMechanical Course - Process Gas DehydrationmahdicmmNessuna valutazione finora
- Reynolds NumberDocumento21 pagineReynolds NumberShiela SorinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Equilibrium Study of K2CO3, KHCO3, CO2 and WaterDocumento27 pagineEquilibrium Study of K2CO3, KHCO3, CO2 and Waterbmeghani100% (5)
- Finding The Source: The Coming Freshwater Crisis Is Already HereDocumento26 pagineFinding The Source: The Coming Freshwater Crisis Is Already HereThe Wilson CenterNessuna valutazione finora
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 1Documento2 pagineCE Board Nov 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 1Asif UsmanNessuna valutazione finora
- EvaporationDocumento11 pagineEvaporationMary Rose MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- JCT College of Engineering and Technology: Pichanur, Coimbatore-641105Documento2 pagineJCT College of Engineering and Technology: Pichanur, Coimbatore-641105Muzz ZamilNessuna valutazione finora