Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Statistical Methodology (TQM Report)
Caricato da
Cherilyn ZerochiiDomoCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Statistical Methodology (TQM Report)
Caricato da
Cherilyn ZerochiiDomoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
STATISTICAL METHODOLOGY
Statistical
Methodology
Data
Collection
Organization
&
Presentation
Descriptive
Measures
Statistical
Inference
Predictive
Statistics
Descriptive Statistics
It is the first major component of statistical
methodology. It is also the efficient collection,
organization, and description of data. Results
are useful in identifying quality problems and
as a means of measuring improvement.
Descriptive Statistics
Measures of Central Tendency Mean is the
average score. The mode is the most
frequently occurring score. The median is the
middle most score.
N
X
N
i
i
=
=
1
n
X
X
N
i
i
=
=
1
MEAN PROPORTION
Population:
Sample:
n
q
p =
N
Q
= t
MEDIAN
Descriptive Statistics
Measures of Dispersion Range is the
difference between the highest and lowest
score. We usually use two other measures of
dispersion: Variance which is the average
squared distance between each score and the
mean and Standard Deviation which is the
average distance between each score and the
mean.
Range
LS HS R =
Standard Deviation Variance
Population:
Sample:
( )
N
x
N
i
i
=
=
1
2
o
( )
n
x x
s
n
i
i
=
=
1
2
( )
N
x
N
i
i
=
=
1
2
2
o
( )
n
x x
s
n
i
i
=
=
1
2
2
Measures of Central Tendency and
Dispersion by Level of Measurement
Statistical Analysis with Microsoft
Excel
Microsoft Excel provides data analysis tools,
called the Analysis ToolPack. To view a list of
available analysis tools, click on Data Analysis
group under the Data Tab in the menu. A
second useful tool is the Histogram tool.
A histogram is a representation of a frequency
distribution by means of rectangles whose
widths represent class intervals and whose
areas are proportional to the corresponding
frequencies.
Statistical Inference
It is the process of drawing conclusions about
unknown characteristics of a population from
which the data were taken.
Sampling Distributions It is a distribution of
all possible statistics calculated from all
possible samples of size n drawn from a
population. Samples are drawn to infer
something about the population.
Statistical Inference
For Simple Random Sampling
The expected value of the sample mean is the
population mean.
The standard deviation of the sample mean
(often called standard error of the mean):
Infinite: Finite:
( ) = x E
n
x
o
o =
n
N
n N
x
o
o
1
=
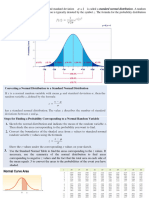
Central Limit Theorem
As the variance decreases, the sample size
increases. Normal distribution is
approximately 30 in its sample size.
If the population is known to be normal, the
distribution of the sample mean is normal for
any sample size.
Sampling distribution n = 3
5 4 3 2 1
Sampling distribution n = 4
5 4 3 2 1
Means (n=30)
4 3 2
Means (n=60)
4 3 2
Means (n=120)
4
3
2
For Sampling Distribution of
p
:
The expected value of the sample mean is the
population mean.
The standard deviation of the sample mean
(often called standard error of the mean):
Infinite: Finite:
( ) t = p E
( )
n
s
p
t t
=
1
( )
n N
n N
s
p
t t
=
1
1
Statistical Inference
Confidence of Intervals It is an estimate of
population parameter that specifies the
likelihood that the interval contains the true
population parameter. Commonly used
confidence levels are 90, 95 and 99. The higher
the cf, the more assurance we have that the
interval contains the true population parameter.
expressed as a percentage.
o =1 cf
Statistical Inference
Hypothesis Testing It involves drawing
inferences about two contrasting propositions
(hypotheses) relating to the value of a population
parameter, one of which is assumed to be true in
the absence of contradictory data.
The null hypothesis is the proposition that
implies no effect or no relationship.
The alternative hypothesis is the proposition that
implies with effect or has a relationship.
The level of significance is denoted by and
determines the size of the rejection region.
Steps:
Formulate the hypotheses to test.
Select a level of significance.
Determine a decision rule.
Collect data and calculate a test statistic.
Apply the decision rule to the test statistic and
draw a conclusion.
Decision Making:
Critical Value Method one of the methods that
leads to a decision about rejection or non-rejection
of the null hypothesis, wherein critical values are
the tabular values of the test statistic that divides
the rejection and non-rejection region.
1. If the computed value is within the non-
rejection region, the null hypothesis is
accepted.
2. If the computed value lies or falls on the
rejection region, the null hypothesis is rejected.
Decision Making:
P-Value Method P stands for PROBABILITY, it
is referred to as the observed level.
1. If P-value is less than or equal to alpha ,
then is rejected.
2. If P-value is greater than alpha ,
then is not rejected.
( ) o s P
0
H
( ) o > P
0
H
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Statistics: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideDa EverandStatistics: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- CH04 - Wooldridge - 7e PPT - 2ppDocumento38 pagineCH04 - Wooldridge - 7e PPT - 2ppMahlatse Mabeba100% (2)
- Basic - Statistics 30 Sep 2013 PDFDocumento20 pagineBasic - Statistics 30 Sep 2013 PDFImam Zulkifli S100% (1)
- Investigating Habituation To A StimulusDocumento10 pagineInvestigating Habituation To A Stimulussandali636100% (5)
- Lecture 7.descriptive and Inferential StatisticsDocumento44 pagineLecture 7.descriptive and Inferential StatisticsKhurram SherazNessuna valutazione finora
- 14-Statisticsandprobability q4 Mod14 ProblemsolvingDocumento27 pagine14-Statisticsandprobability q4 Mod14 ProblemsolvingLerwin Garinga100% (1)
- CFA Level 1 Review - Quantitative MethodsDocumento10 pagineCFA Level 1 Review - Quantitative MethodsAamirx6450% (2)
- Practical-Research-2-Module (Part 2)Documento21 paginePractical-Research-2-Module (Part 2)Julius MacaballugNessuna valutazione finora
- IMS 504-Week 4&5 NewDocumento40 pagineIMS 504-Week 4&5 NewAhmad ShahirNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-Iv 1. Testing of HypothesisDocumento28 pagineUnit-Iv 1. Testing of Hypothesismalleda haneeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Inferential StatisticsDocumento38 pagineInferential Statisticszephers2002100% (1)
- UntitledDocumento43 pagineUntitledMuhammad AreebNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11Documento113 pagineStatistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11statistics Modules 8-11Karl Wilson GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareDa EverandOverview Of Bayesian Approach To Statistical Methods: SoftwareNessuna valutazione finora
- Stat 115 - Basic Statistical MethodsDocumento6 pagineStat 115 - Basic Statistical MethodsaramafeNessuna valutazione finora
- ECN 416 - Applied Statistics Week 5Documento46 pagineECN 416 - Applied Statistics Week 5OREJESU EUNICE OJUTIKUNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical InferenceDocumento56 pagineStatistical InferenceRuchika MotwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Biostatistics 140127003954 Phpapp02Documento47 pagineBiostatistics 140127003954 Phpapp02Nitya KrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Descriptive Statistics Summary (Session 1-5) : Types of Data - Two TypesDocumento4 pagineDescriptive Statistics Summary (Session 1-5) : Types of Data - Two TypesDipak Kumar PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical InferenceDocumento33 pagineStatistical Inferencedeneke100% (1)
- Unit II: Basic Data Analytic MethodsDocumento38 pagineUnit II: Basic Data Analytic MethodsvaibhavbdxNessuna valutazione finora
- Probability Distributions-Sarin BDocumento20 pagineProbability Distributions-Sarin BsarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Treatment of DataDocumento26 pagineStatistical Treatment of DataPaunavNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 .Documento6 pagineLab 4 .w.balawi30Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocumento93 pagineStatistics For Data ScienceCesar LobatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dsbda Unit 2Documento155 pagineDsbda Unit 2king makerNessuna valutazione finora
- RSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUDocumento34 pagineRSU - Statistics - Lecture 3 - Final - myRSUirina.mozajevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter-Summary of BacalDocumento11 pagineChapter-Summary of BacalTammy OgoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics For Data ScienceDocumento27 pagineStatistics For Data ScienceDr. Sanjay GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- StatisticsDocumento49 pagineStatisticshazalulger5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical and Probability Tools For Cost EngineeringDocumento16 pagineStatistical and Probability Tools For Cost EngineeringAhmed AbdulshafiNessuna valutazione finora
- Agenda: Review Homework Lecture/discussion Week 9 AssignmentDocumento30 pagineAgenda: Review Homework Lecture/discussion Week 9 Assignmentsourplum34Nessuna valutazione finora
- Forms of Test StatisticDocumento31 pagineForms of Test StatisticJackielou TrongcosoNessuna valutazione finora
- 05 Lecture4 - EstimationDocumento37 pagine05 Lecture4 - EstimationLakshmi Priya BNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 5 StatisticsDocumento52 pagineLecture 5 Statisticsbedasie23850% (1)
- 3 - Data Analysis - Tests of DifferencesDocumento50 pagine3 - Data Analysis - Tests of Differencesmnrk 1997Nessuna valutazione finora
- Estimation NewDocumento37 pagineEstimation Newmubasher akramNessuna valutazione finora
- Confidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests For MeansDocumento40 pagineConfidence Intervals and Hypothesis Tests For MeansJosh PotashNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 BiostatisticsDocumento16 pagine1 BiostatisticsireneNessuna valutazione finora
- QMB Final NTCRD PDFDocumento17 pagineQMB Final NTCRD PDFJUN0Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH Ii Business StatDocumento27 pagineCH Ii Business StatWudneh AmareNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm Research: Statistical Treatment Research: de La Salle University - DasmariñasDocumento7 pagineMidterm Research: Statistical Treatment Research: de La Salle University - DasmariñasJheaneClaireArevaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit IVDocumento132 pagineUnit IVShay ShayNessuna valutazione finora
- Distribution of Sample MeansDocumento32 pagineDistribution of Sample MeansEva Elžbieta SventickaitėNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Inference: Prepared By: Antonio E. Chan, M.DDocumento227 pagineStatistical Inference: Prepared By: Antonio E. Chan, M.Dश्रीकांत शरमाNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Techniques 1Documento37 pagineQuantitative Techniques 1nprash123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Statistical Evaluation of Analytical Data: Quality Assurance ProgrammeDocumento80 pagineStatistical Evaluation of Analytical Data: Quality Assurance ProgrammeNasir KasimNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 3 Normal Probabaility Curve and Hypothesis TestingDocumento7 pagineMODULE 3 Normal Probabaility Curve and Hypothesis TestingShijiThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics: - MACHINE LEARNING - Exciting!Documento18 pagineStatistics: - MACHINE LEARNING - Exciting!pranav sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Descriptive StatisticsDocumento4 pagineDescriptive StatisticsRaghad Al QweeflNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Statistics CH 2Documento49 pagineBusiness Statistics CH 2assenmiftahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 and 9Documento7 pagineChapter 8 and 9Ellii YouTube channelNessuna valutazione finora
- MATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFDocumento31 pagineMATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFAldrien S. AllanigueNessuna valutazione finora
- Formalizing The Concepts: Simple Random Sampling: Juan Muñoz Kristen Himelein March 2013Documento25 pagineFormalizing The Concepts: Simple Random Sampling: Juan Muñoz Kristen Himelein March 2013Lester JohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Top 50 Interview Questions & Answers: Statistics For Data ScienceDocumento21 pagineTop 50 Interview Questions & Answers: Statistics For Data SciencemythrimNessuna valutazione finora
- BS - CH II EstimationDocumento10 pagineBS - CH II Estimationnewaybeyene5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit I BbbbbbbbbbbbbbaDocumento8 pagineUnit I Bbbbbbbbbbbbbbacarryminati238Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The T-Statistic: PSY295 Spring 2003 SummerfeltDocumento19 pagineIntroduction To The T-Statistic: PSY295 Spring 2003 SummerfeltEddy MwachenjeNessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling Distributions of Sample Means and Proportions PDFDocumento14 pagineSampling Distributions of Sample Means and Proportions PDFsound05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sampling DistDocumento40 pagineSampling DistSanket SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stats NotesDocumento4 pagineStats NotesLUISA CARESSE FLAVIANO BRITANICONessuna valutazione finora
- Statistics Ready ReckonerDocumento4 pagineStatistics Ready ReckonerAdarsh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MGMT 222 Ch. IVDocumento30 pagineMGMT 222 Ch. IVzedingel50% (2)
- Mba Final ProjectDocumento62 pagineMba Final ProjectNaveen kumar5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Effects of Depression On Students Academ PDFDocumento6 pagineEffects of Depression On Students Academ PDFKristine Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Stat and Probability TestDocumento22 pagineStat and Probability TestMartina GuisadoNessuna valutazione finora
- What I Can Do Hypothesis Testing InfographicDocumento1 paginaWhat I Can Do Hypothesis Testing InfographicRheanna Marie DoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tucker Et AlDocumento16 pagineTucker Et AlEno RLNessuna valutazione finora
- Writing STS ReportDocumento4 pagineWriting STS ReportS ArtNessuna valutazione finora
- FN GRP 4.2 Assignment No 5Documento7 pagineFN GRP 4.2 Assignment No 5Darshan sakleNessuna valutazione finora
- HypothesisDocumento11 pagineHypothesisAbegail Song BaliloNessuna valutazione finora
- AP 2015 StatisticsDocumento65 pagineAP 2015 Statisticssam sunNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Governance and Its Effects On Financial Performance of Banks Evidence From Selected Private Commercial Banks in EthiopiaDocumento12 pagineCorporate Governance and Its Effects On Financial Performance of Banks Evidence From Selected Private Commercial Banks in EthiopiaHenock GetachewNessuna valutazione finora
- Test For One Sample CaseDocumento43 pagineTest For One Sample CaseMiqz ZenNessuna valutazione finora
- StatisticsDocumento4 pagineStatisticsKim B. ManilaNessuna valutazione finora
- PR2 Q2 Week4 7Documento9 paginePR2 Q2 Week4 7NinarjahNessuna valutazione finora
- Difficulties Faced by Teachers in Using ICT in Teaching-Learning at Technical and Higher Educational Institutions of UgandaDocumento11 pagineDifficulties Faced by Teachers in Using ICT in Teaching-Learning at Technical and Higher Educational Institutions of UgandaAdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Statistics: Module 4. Z-Test Page 1 of 7Documento7 pagineBusiness Statistics: Module 4. Z-Test Page 1 of 7ArahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ding D 2019 PHD ThesisDocumento235 pagineDing D 2019 PHD ThesisGag PafNessuna valutazione finora
- Ready For Final Paper February 22 2023Documento29 pagineReady For Final Paper February 22 2023Dave RatunilNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Work-Life Balance On Employees' Turnover and Turnover Intentions: An Empirical Study On Multinational Corporations in BangladeshDocumento19 pagineImpact of Work-Life Balance On Employees' Turnover and Turnover Intentions: An Empirical Study On Multinational Corporations in BangladeshEmira AdrinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jun18l1-Ep05 QaDocumento26 pagineJun18l1-Ep05 QajuanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bellack A.s., Hersen M. Eds. Comprehensive Clinical Psychology Volume 3 2000Documento367 pagineBellack A.s., Hersen M. Eds. Comprehensive Clinical Psychology Volume 3 2000ontzy26Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sta301 Solved Mcqs Final Term by JunaidDocumento55 pagineSta301 Solved Mcqs Final Term by Junaidmalik rehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Virtual Learning Packet in Pattern Drafting and Designing For Garments, Fashion and Design StudentsDocumento8 pagineVirtual Learning Packet in Pattern Drafting and Designing For Garments, Fashion and Design StudentsPsychology and Education: A Multidisciplinary JournalNessuna valutazione finora
- StatisticsDocumento20 pagineStatisticsEconomic TruthNessuna valutazione finora
- TM Xime PGDM QT IDocumento40 pagineTM Xime PGDM QT IRiya SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT-702 Unit # 1Documento84 pagineSTAT-702 Unit # 1Hannah NazirNessuna valutazione finora