Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Block
Caricato da
Elisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base Balance Block
Caricato da
Elisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-base Balance Block
ACID-BASE BALANCE By Harliansyah, PhD 2012
HYDROGEN IONS, ACIDS, AND BASES
HYDROGEN IONS (H+)
ACIDS BASES PH Normal arterial pH is 7.35 7.45
ACID-BASE BALANCES
Acidosis pH < 7.35 Alkalosis pH > 7.45 Buffers
PRIMARY BUFFER SYSTEMS IN EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
REGULATION OF ACIDS AND BASES
THE BIG THREE ACID-BASE REGULATORS
Chemical regulation Biological regulation Physiological regulation
PHYSIOLOGICAL REGULATION
Alkalosis
Acidosis
ACID BASE IMBALANCES
RESPIRATORY ACIDOSIS RESPIRATORY ALKALOSIS METABOLIC ACIDOSIS METABOLIC ALKALOSIS
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES
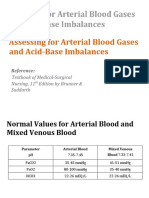
NORMAL BLOOD GAS VALUES pH 7.35-7.45 PCO2 35-45 mmHg HCO3 22-27 mEq/L PO2 80-100 mmHg
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES
RESPIRATORY IMBALANCES Respiratory function indicator is PCO2 Opposite response between the pH and PCO2 pH is down in an acidotic condition and is elevated in an alkalotic condition pH and PCO determines if the condition is a respiratory problem
ARTERIAL BLOOD GASES
METABOLIC IMBALANCES HCO3 is indicator for metabolic function A corresponding response between the pH and the HCO3 pH is down in an acidotic condition and is elevated in an alkalotic condition The pH and the HCO3 determines if the condition is a metabolic problem
ANALYZING ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS RESULTS
PYRAMID STEPS
Look at the blood gas report Look at the pH. Is it up or down? If it is up, it reflects alkalosis. If it is down, it reflects acidosis. Look at the PCO2. Is it up or down? If it reflects an opposite response as the pH then you know that the condition is a respiratory imbalance. If it does not reflect an opposite response as the pH, then move on to Pyramid Step 3.
PYRAMID STEP 1
PYRAMID STEP 2
ANALYZING ARTERIAL BLOOD GAS RESULTS
PYRAMID STEP 3
Look at the HCO3. Does the HCO3 reflect a corresponding response with the pH? If it does, then the condition is a metabolic imbalance. Remember, compensation has occurred if the pH is in a normal range of 7.35-7.45. If the pH is not within normal range, look at the respiratory or metabolic function indicators.
PYRAMID STEP 4
FLUID, ELECTROLYTE & ACID -BASE
REMEMBER~~~~
NORMAL CHEMISTRY LABORATORY VALUES
Serum electrolyte levels CBC (changes in Hct related to FVD & FVE) BUN & Blood Creatinine Levels (kidney functions) Urine Specific gravity (normal 1.003 1.023) ABGs
LUID, ELECTROLYTE & ACID BASE
OVERALL GOALS/EVALUATION
NORMAL FLUID, ELECTROLYTE AND ACID BASE BALANCE CAUSES OF IMBALANCES IDENTIFIED OR CORRECTED
NO COMPLICATIONS FROM THERAPIES NEEDED TO RESTORE BALANCE
INCLUDE FAMILY IN PROCESS
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- FightReady 4D M 1Documento16 pagineFightReady 4D M 1Jeffrey Xie100% (10)
- Kegel Exercises 4 Pelvic Floor MusclesDocumento10 pagineKegel Exercises 4 Pelvic Floor MusclesSHAIK SHABEENA100% (1)
- Abg InterpretationDocumento14 pagineAbg Interpretationmara5140100% (7)
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyDa EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- HyperthyroidismDocumento73 pagineHyperthyroidismZNEROL100% (1)
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento43 pagineArterial Blood Gas AnalysisLoribel Coma100% (1)
- Mnemonics Anatomy 1st SemDocumento4 pagineMnemonics Anatomy 1st SemNastassja Callmedoctor Douse67% (3)
- Acid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNDocumento36 pagineAcid Base Balance: Carol Johns, MSN, RNkatrinasdNessuna valutazione finora
- Back To Basics Critical Care Transport Review Course Simple Rules For Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocumento12 pagineBack To Basics Critical Care Transport Review Course Simple Rules For Arterial Blood Gas Interpretationedderj2585Nessuna valutazione finora
- G-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR)Documento43 pagineG-Protein Coupled Receptors (GPCR)Avin GupthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of The EyeDocumento32 pagineHistology of The EyehendriNessuna valutazione finora
- By Sandhya KumarDocumento20 pagineBy Sandhya KumarKhalid ShafiqNessuna valutazione finora
- ABGDocumento14 pagineABGPhillip MartinezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Alkaline Diet Made Easy: Reclaim Your Health, Lose Weight & Heal NaturallyDa EverandThe Alkaline Diet Made Easy: Reclaim Your Health, Lose Weight & Heal NaturallyNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base Balancing ActDocumento6 pagineAcid Base Balancing ActjohnkuysNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base Balance and ImbalanceDocumento72 pagineAcid Base Balance and ImbalanceAnusha Verghese100% (2)
- Care of Client in Mechanical VentilatorDocumento11 pagineCare of Client in Mechanical VentilatorVignesh Viggy100% (4)
- Arterial Blood Gases Analysis: Adult Health IiDocumento16 pagineArterial Blood Gases Analysis: Adult Health IiTkNessuna valutazione finora
- ABG AnalysisDocumento39 pagineABG AnalysisDocRN100% (2)
- Arterial Blood GasDocumento55 pagineArterial Blood GasRathis Dasan100% (1)
- ABG InterpretationDocumento10 pagineABG InterpretationNisha MathewNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento28 pagineArterial Blood Gas Analysishendra_darmawan_4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) AnalysisDocumento18 pagineArterial Blood Gas (ABG) AnalysisAnandhu GNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical-Surgical Nursing Lecture NotesDocumento90 pagineMedical-Surgical Nursing Lecture NotesJessica AnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Solutions (Cellullar Biophysics - Vol 1 - Trasport) WeissDocumento173 pagineSolutions (Cellullar Biophysics - Vol 1 - Trasport) WeissErick100% (1)
- Abg AnalysisDocumento43 pagineAbg AnalysisHakuna MatataNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas (Abg) Analysis: Submitted ToDocumento5 pagineArterial Blood Gas (Abg) Analysis: Submitted ToRumela ChakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base Lecture 2012Documento34 pagineAcid Base Lecture 2012IrfanArifZulfikarNessuna valutazione finora
- NSG 201 - Acid Base Lecture NOTESDocumento14 pagineNSG 201 - Acid Base Lecture NOTESdlneisha61Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABG AnalysisDocumento57 pagineABG AnalysisHardik RathodNessuna valutazione finora
- Clarifying The Confusion of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Is It Compensation or Combination?Documento5 pagineClarifying The Confusion of Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Is It Compensation or Combination?Andi Tiara S. AdamNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis and InterpretationDocumento23 pagineArterial Blood Gas Analysis and InterpretationKrutthivaasa PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Echilibrul Acido-Bazic: Respiratory If The Change Is Primarily Due To A Change in PcoDocumento3 pagineEchilibrul Acido-Bazic: Respiratory If The Change Is Primarily Due To A Change in PcoIoana CNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect 04Documento4 pagineLect 04الحاج كاملNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Acid-Base Balance: When It Comes To Acids and Bases, The Difference Between Life and Death IsDocumento5 pagineBasics of Acid-Base Balance: When It Comes To Acids and Bases, The Difference Between Life and Death IsAyaz Ahmed BrohiNessuna valutazione finora
- GasometriaDocumento8 pagineGasometriaEslândia SampaioNessuna valutazione finora
- ABG InterpretationDocumento23 pagineABG Interpretationprateekbatra0% (1)
- Interpretation of Blood GasesDocumento22 pagineInterpretation of Blood GasesdjokerNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: BY-Shivam Sachan (JR Ii) Moderator - Dr. R.K YADAV (M.D)Documento52 pagineArterial Blood Gas Analysis: BY-Shivam Sachan (JR Ii) Moderator - Dr. R.K YADAV (M.D)imranqazi11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento20 pagineArterial Blood Gas AnalysisAdiantoNessuna valutazione finora
- D MystifiedDocumento10 pagineD MystifiedWalaa YousefNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial-Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento49 pagineArterial-Blood Gas AnalysisGovernance Book100% (1)
- 3 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Seminar 4 yDocumento18 pagine3 Interpretation of Arterial Blood Gases Seminar 4 yPrasenjit SarkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Paco2: Abg: Definition: Blood Gas Analysis, Also Called Arterial Blood Gas Hco3 (Bicarbonate)Documento7 paginePaco2: Abg: Definition: Blood Gas Analysis, Also Called Arterial Blood Gas Hco3 (Bicarbonate)Amoroso, Marian Corneth D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fisio 2Documento6 pagineFisio 2anaNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Learning Objectives:: Introduction/ OverviewDocumento5 pagineArterial Blood Gas Analysis Learning Objectives:: Introduction/ OverviewjanorberteNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid BaseDocumento6 pagineAcid BaseCarol Solanyi Gacha QuinteroNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 Acid Base DisordersDocumento48 pagine2016 Acid Base DisordersbellabelbonNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Gases (Abgs) Interpretation Dr/Baha Eldin Hassan Ahmed Fellow Paediatric Critical CareDocumento48 pagineBlood Gases (Abgs) Interpretation Dr/Baha Eldin Hassan Ahmed Fellow Paediatric Critical Carehagir alhajNessuna valutazione finora
- Stepwise Approach To Acid-Base AnalysisDocumento16 pagineStepwise Approach To Acid-Base AnalysisTryanto Amrisal MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Acid Base Balance: Faculty of Medicine Anesthesia and Intensive Care DepartmentDocumento36 pagineThe Acid Base Balance: Faculty of Medicine Anesthesia and Intensive Care DepartmentCamelia A. ParuschiNessuna valutazione finora
- So What Does The Blood Gas Analysis Actually Measure?Documento12 pagineSo What Does The Blood Gas Analysis Actually Measure?Veterinarska Bolnica Zavetišče BrežiceNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gases Easyas: InterpretingDocumento5 pagineArterial Blood Gases Easyas: Interpretingoccam1132Nessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento24 pagineArterial Blood Gas AnalysisDeepika PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base DisordersDocumento33 pagineAcid Base DisordersShre RanjithamNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis Workshop: Key Teaching ObjectivesDocumento8 pagineArterial Blood Gas Analysis Workshop: Key Teaching ObjectivesBayan Abu AlrubNessuna valutazione finora
- ABG Made EasyDocumento42 pagineABG Made EasyMahima LakhanpalNessuna valutazione finora
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) : Nancy NG (SCM-027308)Documento22 pagineArterial Blood Gas (ABG) : Nancy NG (SCM-027308)Christine Nancy NgNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhonda Lucas Sicu, Rashid Hospital JUNE, 2011Documento11 pagineRhonda Lucas Sicu, Rashid Hospital JUNE, 2011gliftanNessuna valutazione finora
- "Blood Gas Analysis in A Nutshell: DR Anshuman MishraDocumento28 pagine"Blood Gas Analysis in A Nutshell: DR Anshuman MishraMinaz PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 C&PacidbaseDocumento4 pagine6 C&PacidbaseZaidan Failasufa100% (1)
- Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Normal ValuesDocumento3 pagineArterial Blood Gas (ABG) Analysis: Normal ValuesNayem Hossain HemuNessuna valutazione finora
- ABG InterpretationDocumento8 pagineABG InterpretationMaria Angelika BughaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Interpretation: Compensated and Uncompensated Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento30 pagineInterpretation: Compensated and Uncompensated Blood Gas AnalysisJadie Barringer IIINessuna valutazione finora
- WEB ORIENTATION Interpretation Comp and Uncomp Blood Gas AnalysisDocumento30 pagineWEB ORIENTATION Interpretation Comp and Uncomp Blood Gas Analysiskwame100% (1)
- How To Interpret Arterial Blood Gas ResultsDocumento9 pagineHow To Interpret Arterial Blood Gas ResultsteleasadgramNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid-Base Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and ManagementDa EverandAcid-Base Disorders: Clinical Evaluation and ManagementNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsDa EverandRespiratory Monitoring in Mechanical Ventilation: Techniques and ApplicationsJian-Xin ZhouNessuna valutazione finora
- Alkaline Diet for Beginners: Understand pH, Eat Well and Reclaim Your Health with Easy Alkaline Diet Recipes.Da EverandAlkaline Diet for Beginners: Understand pH, Eat Well and Reclaim Your Health with Easy Alkaline Diet Recipes.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hipertensi PortalDocumento8 pagineHipertensi PortalElisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Isna Git B Coli 13Documento12 pagineDr. Isna Git B Coli 13Elisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Trematodes: Isna Indrawati Department of ParasitologyDocumento30 pagineBlood Trematodes: Isna Indrawati Department of ParasitologyElisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaNessuna valutazione finora
- DR - Wan Nedra Sp.A: Child Health Dept. School of Medicine University of YARSIDocumento18 pagineDR - Wan Nedra Sp.A: Child Health Dept. School of Medicine University of YARSIElisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anemia Megaloblastik: Elsye SouvriyantiDocumento9 pagineAnemia Megaloblastik: Elsye SouvriyantiElisa Fata Marokeh TedadEspochachaNessuna valutazione finora
- Section A: Select Any 60 Consecutive Multiple Choice Questions. For Each Question Circle One Best AlternativeDocumento17 pagineSection A: Select Any 60 Consecutive Multiple Choice Questions. For Each Question Circle One Best AlternativeJeshuah JehopioNessuna valutazione finora
- Section1: General English: DIRECTION For Questions 1 To 3: Read The Passage Carefully and Choose The Best Answer For TheDocumento4 pagineSection1: General English: DIRECTION For Questions 1 To 3: Read The Passage Carefully and Choose The Best Answer For TheSaksham BejwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiologi SinusitisDocumento42 pagineRadiologi SinusitisMonic GultomNessuna valutazione finora
- Uptodate-Causes and Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in AdultsDocumento50 pagineUptodate-Causes and Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency and Iron Deficiency Anemia in AdultsYohanes Handoko0% (1)
- Zum BarangayDocumento16 pagineZum BarangayMary Jane Jaramillo TubonNessuna valutazione finora
- Exo-Glove: A Soft Wearable Robot For The Hand With A Soft Tendon Routing SystemDocumento9 pagineExo-Glove: A Soft Wearable Robot For The Hand With A Soft Tendon Routing SystemAtm MarinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Persian Shallot, Allium Hirtifolium Boiss, Induced Apoptosis PDFDocumento14 paginePersian Shallot, Allium Hirtifolium Boiss, Induced Apoptosis PDFมนัชชนก ศรีสุวรรณ์Nessuna valutazione finora
- Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103) Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103)Documento12 paginePrincipals of General Zoology (Zoo-103) Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103)shahidmahboob60Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocumento5 pagineAnkylosing SpondylitisHarry IsraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 08 10 Sanjay Pandarbale Yogesh Nerkar Sufala MalnekarDocumento4 pagine2020 08 10 Sanjay Pandarbale Yogesh Nerkar Sufala MalnekarYogesh NerkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pancreatic Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDocumento29 paginePancreatic Cancer Early Detection, Diagnosis, and StagingDokter LinggauNessuna valutazione finora
- SwooshDocumento4 pagineSwooshAnabela Torres MendesNessuna valutazione finora
- Test P1 Topic 1 Visible Light and The Solar System and P1 Topic 22 The Electromagnetic Spectrum (And A Little Bit of B1 Topic 13 - 14Documento14 pagineTest P1 Topic 1 Visible Light and The Solar System and P1 Topic 22 The Electromagnetic Spectrum (And A Little Bit of B1 Topic 13 - 14Paul BurgessNessuna valutazione finora
- Bone McqsDocumento4 pagineBone McqsAwan1994100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan - MergedDocumento13 pagineNursing Care Plan - MergedJuls Flares SycaycoNessuna valutazione finora
- Create Database QLKHDocumento35 pagineCreate Database QLKHLinh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- TreinsDocumento23 pagineTreinsKosygin LeishangthemNessuna valutazione finora
- Infant 20care 202020 PDFDocumento226 pagineInfant 20care 202020 PDFRusaneanu Robert-CatalinNessuna valutazione finora
- TransportDocumento22 pagineTransportTri Romini100% (1)
- For Grade 9 Regular: Science Instructional PacketsDocumento107 pagineFor Grade 9 Regular: Science Instructional PacketsFhranscea KimNessuna valutazione finora
- COVID-19 MRNA Pfizer - BioNTech Vaccine Analysis Print 2Documento59 pagineCOVID-19 MRNA Pfizer - BioNTech Vaccine Analysis Print 2Maldita.esNessuna valutazione finora